


中华护理杂志 ›› 2026, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (1): 85-92.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.01.012
蒋向玲1,*( ), 陆慧芬2, 虞幼军1, 林晓丽1, 黄佩铃1
), 陆慧芬2, 虞幼军1, 林晓丽1, 黄佩铃1
收稿日期:2025-07-17
出版日期:2026-01-10
发布日期:2026-01-04
*通讯作者:
蒋向玲:女,E-mail:825891160@qq.com基金资助:
JIANG Xiangling1,*( ), LU Huifen2, YU Youjun1, LIN Xiaoli1, HUANG Peiling1
), LU Huifen2, YU Youjun1, LIN Xiaoli1, HUANG Peiling1
Received:2025-07-17
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2026-01-04
* Corresponding author:
JIANG Xiangling,E-mail:825891160@qq.comFunding program:摘要:
目的 探讨鼻咽癌放疗后听力损伤的发生现状及其影响因素,为听力损伤的防控提供参考。 方法 采用分层随机抽样法,于2023年10月—2025年3月选取佛山市某三级甲等医院的431例鼻咽癌放疗后患者进行调查,收集患者的疾病资料、放疗后耳部护理行为及并发症等随访资料,并评估听力损伤情况。采用随机森林算法与弹性网络回归,分析并确定影响放疗后听力损伤的主要影响因素。 结果 鼻咽癌放疗后1~12年内,患者平均听阈为(47.37±21.90)dB,听力损伤总体发生率为73.78%(318/431)。经单因素分析、随机森林算法及弹性网络回归分析结果显示,放疗后年限、顺铂剂量、年龄、放疗后中耳炎首次出现时间、耳部并发症数量及前2年内咽鼓管功能锻炼情况是鼻咽癌放疗后听力损伤的主要影响因素。 结论 鼻咽癌放疗后听力损伤发生率较高,临床医护人员应在优化治疗方案减少听力损伤的同时,重视放疗后耳部并发症的预防与处理,以延缓听力损伤的发生进程并减轻其严重程度。
蒋向玲, 陆慧芬, 虞幼军, 林晓丽, 黄佩铃. 鼻咽癌患者放疗后听力损伤影响因素研究及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 85-92.
JIANG Xiangling, LU Huifen, YU Youjun, LIN Xiaoli, HUANG Peiling. Influencing factors and nursing implications of hearing impairment in patients with post-radiotherapy nasopharyngeal cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 85-92.
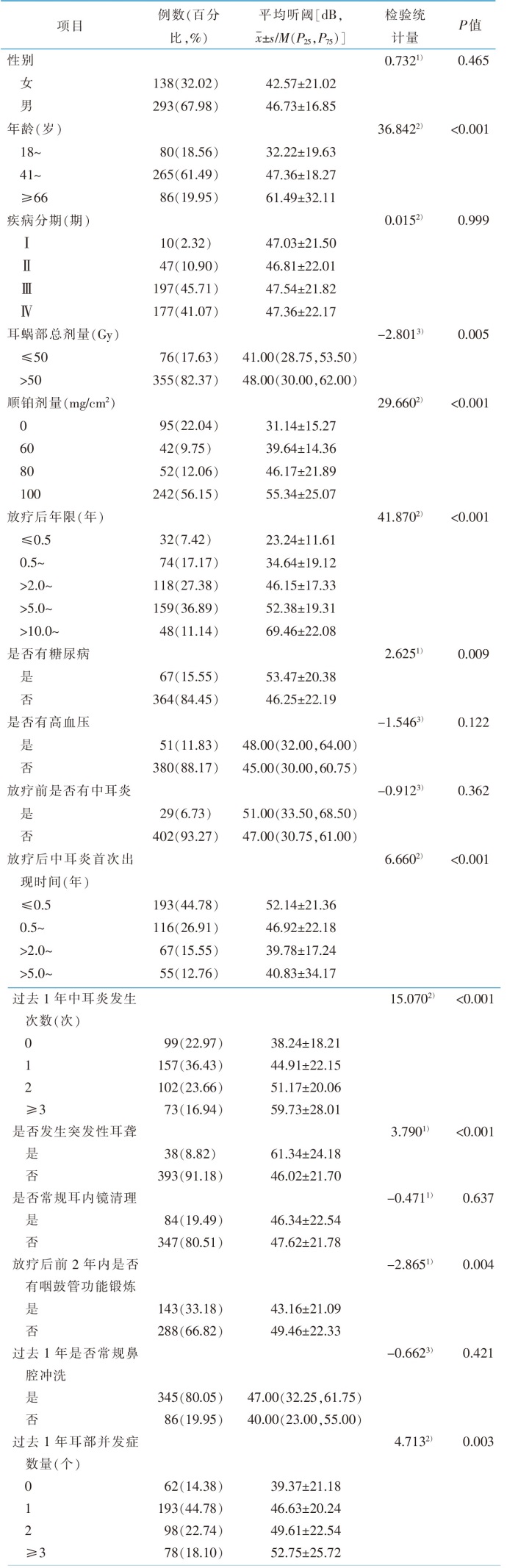 |
表1 调查对象的一般资料及平均听阈的相关因素分析(n=431)
Table 1 Univariate analysis of general data and mean hearing threshold in patients after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma(n=431)
 |
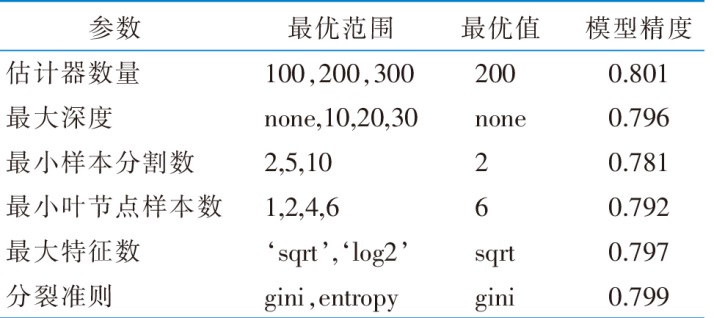 |
表4 鼻咽癌放疗后患者听力损伤随机森林模型参数调优最优范围及最优值
Table 4 Optimal ranges and optimal values of hyperparameter tuning for the random forest model of hearing impairment after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
 |
| [12] | Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology(CSCO). CSCO Guide-lines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Car-cinoma 2020[M/OL]. Beijing: Chinese Society of Clinical Onco-logy(CSCO), 2020[2025-07-16]. https://www.csco.org.cn/cn/nlist.aspx?cids=645. |
| [13] | Harrell FE. Regression modeling strategies[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Springer,2015:97. |
| [14] | Scornet E, Biau G, Vert JP. Consistency of random forests[J]. Ann Statist, 2015, 43(4):1716-1741.. |
| [15] | World Health Organization. World report on hearing[EB/OL].(2021-03-03)[2025-07-16]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240020481. |
| [16] | Shi WX, Hou X, Bao XY, et al. Mechanism and protection of radiotherapy induced sensorineural hearing loss for head and neck cancer[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021,2021:3548706. |
| [17] |
Chan SL, Ng LS, Goh X, et al. Time course and clinical char-acterization of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity after treatment for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a South East Asian population[J]. Head Neck, 2018, 40(7):1425-1433.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Wungcharoen P, Prayongrat A, Tangjaturonrasme N. Hearing loss and middle ear effusion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma follow-ing radiotherapy:dose-response relationship and normal tissue complication probability modeling[J]. Int Arch Otorhinolaryn-gol, 2025, 29(2):1-9. |
| [19] |
Kalyanam B, Sarala N, Azeem Mohiyuddin SM, et al. Auditory function and quality of life in patients receiving cisplatin chemotherapy in head and neck cancer:a case series follow-up study[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2018, 14(5):1099-1104.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Ohkoshi A, Ishii R, Higashi K, et al. Sensorineural hearing loss after concurrent chemoradiotherapy with high-dose cisplatin in head and neck cancer patients:roles of nutrition and trace elements[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2025, 52(2):141-145.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Kessler L, Koo C, Richter CP, et al. Hearing loss during che-motherapy:prevalence,mechanisms,and protection[J]. Am J Can-cer Res, 2024, 14(9):4597-4632. |
| [22] |
Shankar V, Seethapathy J, Srinivas S, et al. Oncologists’ views on ototoxicity monitoring in head and neck cancer patients:a South Indian qualitative study[J]. PLoS One, 2025, 20(1):e0312847.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality world-wide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3):209-249. |
| [2] |
Wong KCW, Hui EP, Lo KW, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma:an evolving paradigm[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2021, 18(11):679-695.
DOI |
| [3] |
McDowell LJ, Rock K, Xu W, et al. Long-term late toxicity,quality of life,and emotional distress in patients with naso-pharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity modulated radiation therapy[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2018, 102(2):340-352.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 孙映凤, 杨海弟, 郑亿庆. 鼻咽癌放疗后听力损失特征分析[J]. 中国听力语言康复科学杂志, 2017, 15(2):115-118. |
| Sun YF, Yang HD, Zheng YQ. The characteristics of nasopha-ryngeal carcinoma radiotherapy after hearing loss[J]. Chin Sci J Hear Speech Rehabil, 2017, 15(2):115-118. | |
| [5] |
Jiang MJ, Li HF, Chen C, et al. Postirradiation otitis media with effusion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma:a comprehensive review of pathogenesis,management,and prevention[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2025, 123(4):1018-1034.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
张纤, 马秋平, 曹汝汝, 等. 社区老年人主观认知下降危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(3):342-348.
DOI |
| Zhang X, Ma QP, Cao RR, et al. Risk factors of subjective cognitive decline of the elder adults in communities:a Meta-analysis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(3):342-348. | |
| [7] |
Phillips OR, Baguley DM, Pearson SE, et al. The long-term im-pacts of hearing loss,tinnitus and poor balance on the quality of life of people living with and beyond cancer after plati-num-based chemotherapy:a literature review[J]. J Cancer Surviv, 2023, 17(1):40-58.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Mittal R, Lisi CV, Gerring R, et al. Current concepts in the pathogenesis and treatment of chronic suppurative otitis media[J]. J Med Microbiol, 2015, 64(10):1103-1116.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Burger AM, Duinkerken CW, van Sluis KE, et al. Treatment-related hearing loss in weekly versus triweekly cisplatin chemoradiation for head and neck cancer[J]. Eur Arch Otorhi-nolaryngol, 2024, 281(12):6627-6635. |
| [10] | Yip PL, Mok KJ, Ho HS, et al. Sensorineural hearing loss in nasopharyngeal carcinoma survivors in the modern treatment era:the early and late effects of radiation and cisplatin[J]. Clin Oncol, 2022, 34(4):e160-e167. |
| [11] |
乔丽敏, 赵雅宁, 刘瑶, 等. 老年轻型缺血性脑卒中患者社会衰弱的影响因素及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(10):1251-1256.
DOI |
|
Qiao LM, Zhao YN, Liu Y, et al. Study on influencing factors of social frailty in elderly patients with mild ischemic stroke[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(10):1251-1256.
DOI |
|
| [12] | 中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO). CSCO鼻咽癌诊疗指南2020[M/OL]. 北京: 中国临床肿瘤学会, 2020[2025-07-16]. https://www.csco.org.cn/cn/nlist.aspx?cids=645. |
| [23] |
Yücel B, Erdiş ED, Bahar S, et al. Factors affecting permanent sensorineural hearing loss and bone conduction in patients after receiving radiotherapy to the head and neck region[J]. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2022, 60(4):212-219.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Alshehri S, Musleh A. The role of eustachian tube dysfunction in recurrent chronic otitis media:a cross-sectional study of anatomical and functional variations[J]. Healthcare, 2025, 13(1):77.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
廖婷婷, 杨丽, 王仁生, 等. 鼻咽癌患者家庭延续性护理平台的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(9):1399-1405.
DOI |
| Liao TT, Yang L, Wang RS, et al. Construction and application of home-based continuous care platform for patients with na-sopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(9):1399-1405. | |
| [26] | Taneja V, Taneja MK, Singh VP. Role of mahendra maneuver in sinusitis and eustachian tube dysfunction[J]. Indian J Oto-laryngol Head Neck Surg, 2025, 77(1):392-395. |
| [27] | Casale J, Shumway KR, Hatcher JD. Physiology, Eustachian Tube Function[M/OL].[2025-9-13]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532284/. |
| [28] |
Apoorva KV, Vijendra Shenoy S, Athiyamaan MS, et al. Radia-tion dose to the cochlea and its association with sensorineu-ral hearing loss in head and neck cancer:a prospective study[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2023, 44(4):103914.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 祝海香, 李艳, 许启锦, 陈瑾萱, 韩小雪, 吴缘. 慢性心力衰竭患者分级分类症状识别工具的研制及应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 149-156. |
| [2] | 王蔚云, 顾则娟, 汤一帆, 苏子雯, 刘长红. 心力衰竭患者的液体平衡阈值研究及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 157-165. |
| [3] | 吴晓敏, 谷艳荣, 柴依依, 马心蕊, 朱豆, 张政, 林平, 李玲. 急性心肌梗死介入术后患者恐惧体验及应对需求的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 166-173. |
| [4] | 章盈盈, 马燕, 吴黎莉, 张丽, 孙莹, 刘璐, 庄一渝. 心血管疾病患者症状感知困境量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 174-181. |
| [5] | 陶娟, 尹永田, 秦玉婷, 王诗源, 韩榕, 张瀚丹. 左心室辅助装置植入患者照顾者居家照护体验的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 182-189. |
| [6] | 李昉, 徐翠荣, 姜琳, 张李霞, 肖艳华, 原晓, 黄朝阳, 包佳威. 早产儿经下肢置入PICC并发静脉炎风险预测模型的构建与验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 190-197. |
| [7] | 曾晗月, 彭寅森, 陈腾霞, 李韵, 朱守淋, 黄乐娇, 王彩莲, 毛世芳. 《成人有创机械通气气道内吸引技术操作》团体标准临床实践现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 198-204. |
| [8] | 丁佳蓉, 陈慧, 王雪瑞, 孙小玲, 张银. 原位新膀胱术后尿失禁患者自我管理体验及需求的纵向质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 205-212. |
| [9] | 杜雪莲, 陈华健, 黄少娟, 李灿辉, 董佩文, 廖江波, 区博伟. 骨盆骨折患者风险评估系统的开发与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 213-219. |
| [10] | 李雪梅, 李永琦, 刘颖, 李俊英, 时瑾瑾, 张兰, 江会. 母婴分离产妇母乳喂养集束化护理干预方案的构建及应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 220-228. |
| [11] | 吴萍, 于宛辰, 柳嘉怡, 尹思文, 王汕珊. 养老护理员死亡认知及应对能力的潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 229-236. |
| [12] | 兰星, 刘婷, 李勍, 柯稳, 李鑫, 张转运, 翟洁, 刘佳佳. 700所医疗机构麻醉科专科护士工作及管理现状的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 237-243. |
| [13] | 周帅帅, 王飒, 刘亚洁, 柴晶晶, 闫丹萍, 王钰炜. 1例胃内镜黏膜下剥离术后迟发性出血并发腹腔间隔室综合征患者的急救护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 244-248. |
| [14] | 蒋伟红, 唐晓敏, 周军, 朱佳佳, 金泓丞, 陈梦怡, 诸纪华. 4例心脏移植患儿的运动康复护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 249-253. |
| [15] | 徐晓佩, 李秋芳, 谈小雪, 吴玉洁. 1例妊娠合并李斯特菌感染致脓毒症休克并发噬血细胞综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 254-257. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||