


中华护理杂志 ›› 2026, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (1): 23-29.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.01.003
收稿日期:2025-08-01
出版日期:2026-01-10
发布日期:2026-01-04
*通讯作者:
金学勤,E-mail:653993023@qq.com作者简介:陆沁怡:女,本科(硕士在读),护士,E-mail:2283566726@qq.com
基金资助:
LU Qinyi1( ), LU Chengqian2, ZHAO Yafen2, JIN Xueqin2,*(
), LU Chengqian2, ZHAO Yafen2, JIN Xueqin2,*( )
)
Received:2025-08-01
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2026-01-04
* Corresponding author:
JIN Xueqin,E-mail:653993023@qq.comFunding program:摘要:
目的 探讨跌倒恐惧对社区老年2型糖尿病患者跌倒警觉度的影响及阈值效应,为预防老年人跌倒提供依据。 方法 便利选取2025年3—7月昆山市某社区卫生服务中心250例老年2型糖尿病患者作为调查对象。采用一般资料调查表、老年人跌倒警觉度量表、修订版跌倒恐惧量表进行调查,通过分层线性回归探究跌倒恐惧对社区老年2型糖尿病患者跌倒警觉度的影响,并进行阈值效应分析。 结果 回收有效问卷245份,有效问卷回收率为98.00%。社区老年2型糖尿病患者跌倒恐惧得分为(36.34±11.46)分,跌倒警觉度得分为(56.87±15.47)分。分层线性回归分析结果显示,跌倒恐惧可独立解释社区老年2型糖尿病患者跌倒警觉度9.7%的变异度。拟合曲线结果提示,跌倒恐惧和跌倒警觉度呈非线性关系(P<0.001),跌倒恐惧得分<32分时,跌倒警觉度随跌倒恐惧得分的增加而降低(P<0.05)。 结论 社区老年2型糖尿病患者跌倒警觉度处于较高水平,跌倒恐惧呈中等程度,且跌倒恐惧与跌倒警觉度存在非线性关联,当跌倒恐惧<32分时,可将其作为心理干预切入点,通过缓解跌倒恐惧提升患者的跌倒警觉度。
陆沁怡, 陆程倩, 赵亚芬, 金学勤. 跌倒恐惧对社区老年2型糖尿病患者跌倒警觉度的影响研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 23-29.
LU Qinyi, LU Chengqian, ZHAO Yafen, JIN Xueqin. The impact of fear of falling on self-awareness of falls in community-dwelling older adults with type 2 diabetes[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 23-29.
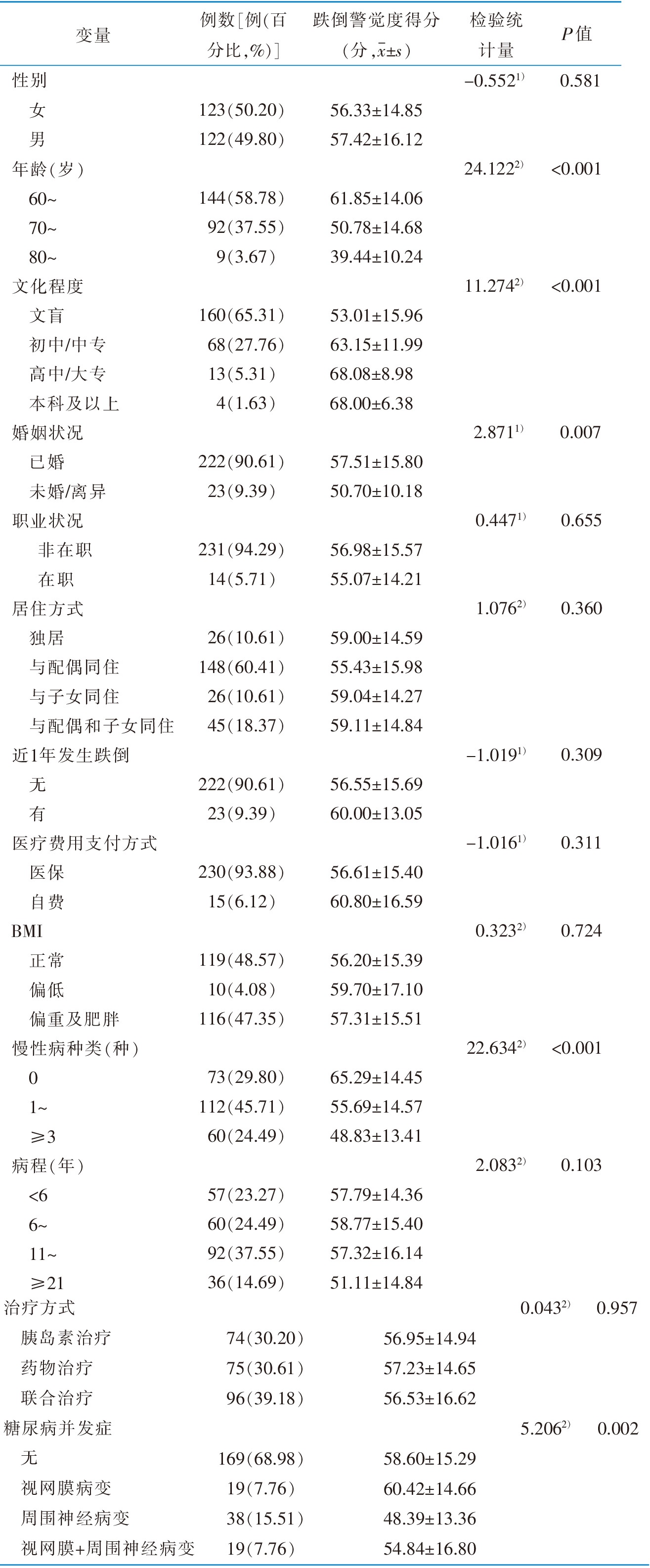 |
表1 社区老年2型糖尿病患者的一般资料及跌倒警觉度的单因素分析(n=245)
Table 1 Univariate analysis of general data and self-awareness of falls in elderly community-dwelling patients with type 2 diabetes(n=245)
 |
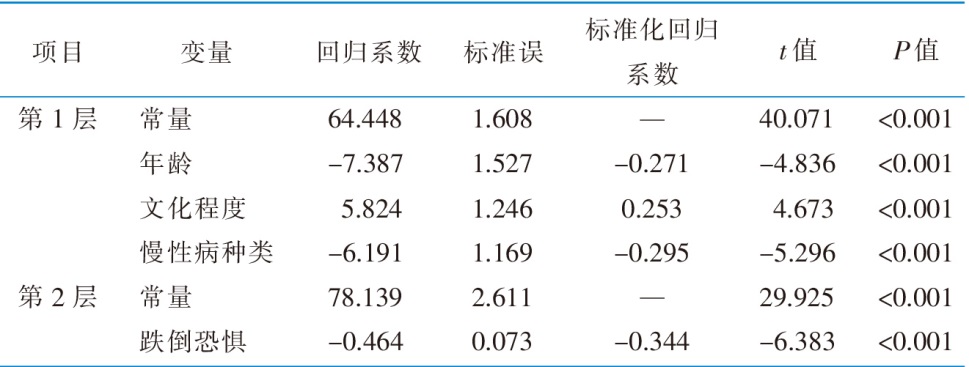 |
表3 社区老年2型糖尿病患者跌倒警觉度的线性回归分析(n=245)
Table 3 Linear regression analysis of self-awareness of falls in elderly community-dwelling patients with type 2 diabetes(n=245)
 |
| [1] |
蔡佩萱, 梁怡青, 王晶晶, 等. 中青年2型糖尿病患者饮食行为依从性变化轨迹及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(13):1592-1599.
DOI |
|
Cai PX, Liang YQ, Wang JJ, et al. Analysis of the trajectory of changes in dietary behavioral adherence in young and middle-aged patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and the influencing factors[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(13):1592-1599.
DOI |
|
| [2] |
姬春晖, 李月, 董正惠, 等. 远程饮食与运动干预在老年2型糖尿病合并肌少症患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(21):2565-2571.
DOI |
|
Ji CH, Li Y, Dong ZH, et al. A study of a tele-diet combined exercise intervention program in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus combined with sarcopenia[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(21):2565-2571.
DOI |
|
| [3] | Sun LN, Fu JL, Mu ZJ, et al. Association between body fat and sarcopenia in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus:a cross-sectional study[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2023,14:1094075. |
| [4] |
章毅, 王欣格, 黎春常, 等. 7种运动训练对糖尿病周围神经病变患者平衡功能影响的网状Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1):89-97.
DOI |
| Zhang Y, Wang XG, Li CC, et al. The effect of 7 different exercise training in balance function of patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy:a network meta-analysis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(1):89-97. | |
| [5] |
Freire LB, Brasil-Neto JP, da Silva ML, et al. Risk factors for falls in older adults with diabetes mellitus:systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Geriatr, 2024, 24(1):201.
DOI |
| [6] | 鲍冠君, 罗烨, 刘苑菲, 等. 社区老年人跌倒风险感知量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(24):9-13. |
| Bao GJ, Luo Y, Liu YF, et al. Development of Fall Risk Perception Scale for Community-Dwelling Older Adults:reliability and validity testing[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(24):9-13. | |
| [7] |
Shyu ML, Huang HC, Wu MJ, et al. Development and validation of the Self-Awareness of Falls in Elderly Scale among elderly inpatients[J]. Clin Nurs Res, 2018, 27(1):105-120.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 赵宏霞, 王衍富, 吕学瑞, 等. 老年2型糖尿病住院患者衰弱、认知功能与跌倒恐惧的相关性[J]. 中华老年多器官疾病杂志, 2022, 21(2):125-129. |
| Zhao HX, Wang YF, Lü XR, et al. Correlation of frailty and cognitive function with fear of falling in the elderly inpatients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin J Mult Organ Dis Elder, 2022, 21(2):125-129. | |
| [9] |
Xiong WH, Wang D, Ren W, et al. The global prevalence of and risk factors for fear of falling among older adults:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Geriatr, 2024, 24(1):321.
DOI |
| [10] | 姚晶, 刘伟, 李娜, 等. 老年人跌倒警觉度研究进展[J]. 护理学杂志, 2023, 38(24):109-112. |
| Yao J, Liu W, Li N, et al. Self-awareness of falls in the elderly:a literature review[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2023, 38(24):109-112. | |
| [11] | 《中国老年型糖尿病防治临床指南》编写组. 中国老年2型糖尿病防治临床指南(2022年版)[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2022, 30(1):2-51. |
| The Writing Group of the Clinical Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetes in the Elderly in China. Clinical guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes in the elderly in China(2022 edition)[J]. Chin J Diabetes, 2022, 30(1):2-51. | |
| [12] | 倪平, 陈京立, 刘娜. 护理研究中量性研究的样本量估计[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010, 45(4):378-380. |
| Ni P, Chen JL, Liu N. The sample size estimation in quantitative nursing research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010, 45(4):378-380. | |
| [13] |
Bower ES, Wetherell JL, Merz CC, et al. A new measure of fear of falling:psychometric properties of the Fear of Falling Ques-tionnaire Revised(FFQ-R)[J]. Int Psychogeriatr, 2015, 27(7):1121-1133.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 王蕾, 王颖, 鲁志卉, 等. 修订版跌倒恐惧问卷的汉化及信效度研究[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(7):1134-1138. |
| Wang L, Wang Y, Lu ZH, et al. Study on the chinesination and its reliability and validity of the Fear of Falling Question-naire-Reversed(FFQ.R)[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2022, 36(7):1134-1138. | |
| [15] |
谭铮可可, 杨丽, 唐雯桢, 等. 腹部大手术患者首次下床跌倒恐惧的潜在剖面分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(20):2479-2486.
DOI |
| Tan ZKK, Yang L, Tang WZ, et al. Fear of falling in the initial ambulation day among patients undergoing major abdominal surgery:latent profile analysis and nursing implications[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(20):2479-2486. | |
| [16] | 赵宏霞. 老年2型糖尿病患者衰弱、认知功能与跌倒恐惧的相关性研究[D]. 大连: 大连医科大学, 2021. |
| Zhao HX. Correlation between weakness,cognitive function and fear of falling in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[D]. Dalian: Dalian Medical University, 2021. | |
| [17] | 吕磊, 车腾雨, 成杰, 等. 老年脑卒中住院病人跌倒警觉度现状及影响因素[J]. 护理研究, 2025, 39(11):1917-1923. |
| Lü L, Che TY, Cheng J, et al. Status quo and influencing factors of fall awareness in hospitalized elderly patients with stroke[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2025, 39(11):1917-1923. | |
| [18] | 孙海超, 路丰源, 张熙雅, 等. 老年人跌倒警觉度的概念分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2025, 40(13):66-70,114. |
| Sun HC, Lu FY, Zhang XY, et al. Conceptual analysis of fall alertness in the elderly[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2025, 40(13):66-70, 114. | |
| [19] | 邓潇, 李德威, 伍祯, 等. 农村老年高血压患者跌倒警觉度现状及影响因素研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2024, 39(22):103-106,111. |
| Deng X, Li DW, Wu Z, et al. Current status and influencing factors of fall alertness in older hypertensive patients in rural areas[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2024, 39(22):103-106,111. | |
| [20] |
Jung J, Kim MG, Kang YJ, et al. Vibration perception threshold and related factors for balance assessment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18(11):6046.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
张海燕, 于卫华, 张利, 等. 2型糖尿病老年患者生活空间移动性受限风险预测模型研究[J]. 护理学报, 2023, 30(22):13-19.
DOI |
| Zhang HY, Yu WH, Zhang L, et al. Research on a risk prediction model for life-space mobility restriction in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. J Nurs (China), 2023, 30(22):13-19. | |
| [22] | 蒯春玲, 王晓宇, 舒宁波, 等. 老年糖尿病视网膜病变患者跌倒风险感知现状及影响因素分析[J]. 生命科学仪器, 2024, 22(4):164-166. |
| Kuai CL, Wang XY, Shu NB, et al. Analysis of Perception of Fall Risk And Its Influencing Factors in Elderly Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy[J]. Life Sci Instrum, 2024, 22(4): 164-166. | |
| [23] | 张海燕, 于卫华, 张利, 等. 老年糖尿病患者心理痛苦与跌倒恐惧的相关性研究[J]. 军事护理, 2023, 40(10):5-8. |
| Zhang HY, Yu WH, Zhang L, et al. Correlation between diabetes distress and fear of falling in elderly diabetes mellitus patients[J]. Mil Nurs, 2023, 40(10):5-8. | |
| [24] | 亓倩倩, 辛红菊, 周洲薇, 等. 老年综合征对老年2型糖尿病患者的躯体功能和跌倒风险的影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2022, 20(3):424-427,502. |
| Qi QQ, Xin HJ, Zhou ZW, et al. Effect of geriatric syndrome on physical function and fall risk in elderly patients with type-2 diabetes[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2022, 20(3):424-427,502. | |
| [25] |
Bayrak M, Kaşali K, Güner M, et al. Risk factors influencing fall risk in geriatric patients with type 2 diabetes:a comprehensive analysis[J]. Aging Male, 2025, 28(1):2469614.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 周白云, 马睿婕, 陆敏, 等. 社区老年糖尿病共病患者内在能力的潜在类别分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2025, 40(3):6-11. |
| Zhou BY, Ma RJ, Lu M, et al. Latent class analysis of intrinsic capacity among community-dwelling elderly diabetes mellitus patients with multimorbidity[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2025, 40(3):6-11. | |
| [27] | 张海燕, 于卫华, 张利, 等. 社区老年人跌倒风险感知潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 军事护理, 2024, 41(10):52-56. |
| Zhang HY, Yu WH, Zhang L, et al. Potential profile analysis and influencing factors of falls risk perception among elder adults in community[J]. Mil Nurs, 2024, 41(10):52-56. | |
| [28] | de Oliveira Lima RA, Piemonte GA, Nogueira CR, et al. Efficacy of exercise on balance,fear of falling,and risk of falls in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Arch Endocrinol Metab, 2021, 65(2):198-211. |
| [29] |
聂作婷, 陈龙, 曾凯, 等. 老年人跌倒风险感知研究现状及其对老年人主动跌倒预防的启示[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(19):2395-2400.
DOI |
| Nie ZT, Chen L, Zeng K, et al. Current status of research on fall risk perception and its implications for active fall prevention in older adults[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2024, 27(19):2395-2400. |
| [1] | 祝海香, 李艳, 许启锦, 陈瑾萱, 韩小雪, 吴缘. 慢性心力衰竭患者分级分类症状识别工具的研制及应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 149-156. |
| [2] | 王蔚云, 顾则娟, 汤一帆, 苏子雯, 刘长红. 心力衰竭患者的液体平衡阈值研究及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 157-165. |
| [3] | 吴晓敏, 谷艳荣, 柴依依, 马心蕊, 朱豆, 张政, 林平, 李玲. 急性心肌梗死介入术后患者恐惧体验及应对需求的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 166-173. |
| [4] | 章盈盈, 马燕, 吴黎莉, 张丽, 孙莹, 刘璐, 庄一渝. 心血管疾病患者症状感知困境量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 174-181. |
| [5] | 陶娟, 尹永田, 秦玉婷, 王诗源, 韩榕, 张瀚丹. 左心室辅助装置植入患者照顾者居家照护体验的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 182-189. |
| [6] | 李昉, 徐翠荣, 姜琳, 张李霞, 肖艳华, 原晓, 黄朝阳, 包佳威. 早产儿经下肢置入PICC并发静脉炎风险预测模型的构建与验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 190-197. |
| [7] | 曾晗月, 彭寅森, 陈腾霞, 李韵, 朱守淋, 黄乐娇, 王彩莲, 毛世芳. 《成人有创机械通气气道内吸引技术操作》团体标准临床实践现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 198-204. |
| [8] | 丁佳蓉, 陈慧, 王雪瑞, 孙小玲, 张银. 原位新膀胱术后尿失禁患者自我管理体验及需求的纵向质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 205-212. |
| [9] | 杜雪莲, 陈华健, 黄少娟, 李灿辉, 董佩文, 廖江波, 区博伟. 骨盆骨折患者风险评估系统的开发与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 213-219. |
| [10] | 李雪梅, 李永琦, 刘颖, 李俊英, 时瑾瑾, 张兰, 江会. 母婴分离产妇母乳喂养集束化护理干预方案的构建及应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 220-228. |
| [11] | 吴萍, 于宛辰, 柳嘉怡, 尹思文, 王汕珊. 养老护理员死亡认知及应对能力的潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 229-236. |
| [12] | 兰星, 刘婷, 李勍, 柯稳, 李鑫, 张转运, 翟洁, 刘佳佳. 700所医疗机构麻醉科专科护士工作及管理现状的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 237-243. |
| [13] | 周帅帅, 王飒, 刘亚洁, 柴晶晶, 闫丹萍, 王钰炜. 1例胃内镜黏膜下剥离术后迟发性出血并发腹腔间隔室综合征患者的急救护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 244-248. |
| [14] | 蒋伟红, 唐晓敏, 周军, 朱佳佳, 金泓丞, 陈梦怡, 诸纪华. 4例心脏移植患儿的运动康复护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 249-253. |
| [15] | 徐晓佩, 李秋芳, 谈小雪, 吴玉洁. 1例妊娠合并李斯特菌感染致脓毒症休克并发噬血细胞综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 254-257. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||