


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2026, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (4): 549-556.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.04.016
• Occupational Protection and Humanistic Care for Nurses • Previous Articles Next Articles
LU Fengjuan1( ), XIE Zihui1, GUAN Yinyin2, PEI Xiaoli1, FANG Yuxia2,*(
), XIE Zihui1, GUAN Yinyin2, PEI Xiaoli1, FANG Yuxia2,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-30
Online:2026-02-20
Published:2026-02-06
* Corresponding author:
FANG Yuxia,E-mail:fyx0119@163.com
芦凤娟1( ), 解子惠1, 关银银2, 裴晓莉1, 房玉霞2,*(
), 解子惠1, 关银银2, 裴晓莉1, 房玉霞2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
房玉霞,E-mail:fyx0119@163.com作者简介:芦凤娟:女,硕士,副主任护师,护士长,E-mail:66884786@qq.com
LU Fengjuan, XIE Zihui, GUAN Yinyin, PEI Xiaoli, FANG Yuxia. Latent profile analysis of empathy for pain and its associated factors among orthopedic nurses[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 549-556.
芦凤娟, 解子惠, 关银银, 裴晓莉, 房玉霞. 骨科护士疼痛共情的现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(4): 549-556.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.04.016
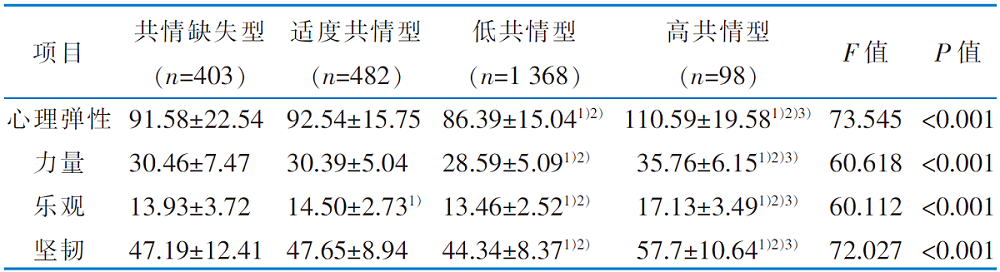 |
Table 4 Univariate analysis of the latent profiles of empathy for pain and psychological resilience among orthopedic nurses(n=2 351,scores,$\bar{x}\pm s$)
 |
| [1] | Baig KS, Hayat MK, Khan MAA, et al. Empathy levels in me-dical students:a single center study[J]. Cureus, 2023, 15(5):e38487. |
| [2] |
Jeffrey D. Clarifying empathy:the first step to more humane clinical care[J]. Br J Gen Pract, 2016, 66(643):e143-e145.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Naor N, Rohr C, Schaare LH, et al. The neural networks under-lying reappraisal of empathy for pain[J]. Soc Cogn Affect Neuro-sci, 2020, 15(7):733-744. |
| [4] | Xiong RC, Fu X, Wu LZ, et al. Brain pathways of pain em-pathy activated by pained facial expressions:a meta-analysis of fMRI using the activation likelihood estimation method[J]. Neu-ral Regen Res, 2019, 14(1):172-178. |
| [5] |
伍冬冬, 尹志勤, 袁旭晶. 疼痛共情的研究进展[J]. 护理学报, 2022, 29(10):43-46.
DOI |
| Wu DD, Yin ZQ, Yuan XJ. Research progress of pain empathy[J]. J Nurs(China), 2022, 29(10):43-46. | |
| [6] | 高云飞, 代凤玲, 陈杰, 等. 临床护士疼痛共情现状及影响因素分析[J]. 军事护理, 2022, 39(11):62-64,100. |
| Gao YF, Dai FL, Chen J, et al. Status quo of pain empathy among clinical nurses and its influencing factors[J]. Mil Nurs, 2022, 39(11):62-64,100. | |
| [7] | 颜志强, 苏金龙, 苏彦捷. 共情与同情:词源、概念和测量[J]. 心理与行为研究, 2018, 16(4):433-440. |
| Yan ZQ, Su JL, Su YJ. Empathy and sympathy or compassion:source,conception and measurement[J]. Stud Psychol Behav, 2018, 16(4):433-440. | |
| [8] | Jin R, Li XY, Huang HQ. Empathy and mental health of pres-chool teachers:a latent profile analysis[J]. Psychol Res Behav Manag, 2025,18:255-269. |
| [9] | 任春霞, 王家动, 江明媚, 等. 安徽省临床护士疼痛共情现状及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国护理管理, 2023, 23(10):1471-1475. |
| Ren CX, Wang JD, Jiang MM, et al. Status quo and influencing factors of pain empathy among nurses in Anhui province[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2023, 23(10):1471-1475. | |
| [10] | 伍冬冬, 袁旭晶, 尹志勤. 临床护士疼痛共情能力现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国现代医生, 2022, 60(26):102-105. |
| Wu DD, Yuan XJ, Yin ZQ. Occurrence of pain empathy of clinical nurses and its influencing factors[J]. China Mod Dr, 2022, 60(26):102-105. | |
| [11] | 董勇, 关琼瑶, 蔡帅中, 等. 肿瘤专科医院临床护士疼痛共情现状及影响因素[J]. 护理研究, 2024, 38(2):344-348. |
| Dong Y, Guan QY, Cai SZ, et al. Statues quo and influencing factors of empathy for pain among clinical nurses in tumor specialized hospitals[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2024, 38(2):344-348. | |
| [12] | 刘斌, 邱贵兴, 裴福兴, 等. 骨科加速康复围手术期疼痛管理专家共识[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2022, 15(10):739-745. |
| Liu B, Qiu GX, Pei FX, et al. Expert consensus on periopera-tive pain management in orthopaedics in enhanced recovery after surgery program[J]. Chin J Bone Jt Surg, 2022, 15(10):739-745. | |
| [13] | 陈杰, 徐红. 抽样调查中样本量的设计和计算[J]. 武汉职业技术学院学报, 2006, 5(1):118-120. |
| Chen J, Xu H. Designing and calculating of quantities in sa-mple investigation[J]. J Wuhan Inst Technol, 2006, 5(1):118-120. | |
| [14] |
Giummarra MJ, Fitzgibbon BM, Georgiou-Karistianis N, et al. Affective,sensory and empathic sharing of another’s pain:the Empathy for Pain Scale[J]. Eur J Pain, 2015, 19(6):807-816.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | 尚静, 叶旭春, 王怡, 等. 疼痛共情量表的汉化及其在医学生中的信效度检验[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2020, 26(9):1140-1145. |
| Shang J, Ye XC, Wang Y, et al. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Empathy for Pain Scale in medical students[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2020, 26(9):1140-1145. | |
| [16] |
Yu XN, Zhang JX. Factor analysis and psychometric evalua-tion of the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale(CD-RISC) with Chinese people[J]. Soc Behav Pers, 2007, 35(1):19-30.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 王孟成, 毕向阳. 潜变量建模与Mplus应用-进阶篇[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2018. |
| Wang MC, Bi XY. Latent variable modeling and Mplus appli-cation-advanced chapter[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 2018. | |
| [18] |
周丹, 蒋小平, 陈澜, 等. 恶性肿瘤患儿家庭管理特征的潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(20):2493-2501.
DOI URL |
|
Zhou D, Jiang XP, Chen L, et al. Latent profile analysis of family management characteristics in children with malignant tumor[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(20):2493-2501.
DOI URL |
|
| [19] |
尹奎, 彭坚, 张君. 潜在剖面分析在组织行为领域中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7):1056-1070.
DOI |
|
Yin K, Peng J, Zhang J. The application of latent profile ana-lysis in organizational behavior research[J]. Adv Psychol Sci, 2020, 28(7):1056-1070.
DOI URL |
|
| [20] | Huang YL, Li B, Feng SB, et al. Mediating and suppressing effects of coping styles between resilience and empathy for pain in clinical nurses:a cross-sectional study[J]. J Multidis-cip Healthc, 2024,17:4653-4667. |
| [21] | 张碧馨. 石家庄市省级三甲医院临床医生共情能力现状及影响因素研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020. |
| Zhang BX. Study on the current situation and influencing factors of clinicians’ empathy ability in provincial 3A hospi-tals in Shijiazhuang City[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020. | |
| [22] |
Cheng L, Yang J, Li MY, et al. Mediating effect of coping style between empathy and burnout among Chinese nurses working in medical and surgical wards[J]. Nurs Open, 2020, 7(6):1936-1944.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Shoji K, Noguchi N, Waki F, et al. Empathy and coping stra-tegies predict quality of life in Japanese healthcare profes-sionals[J]. Behav Sci, 2024, 14(5):400.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
韩冰, 李春敏, 郭晨明, 等. 骨科护士共情疲劳症状的影响因素及路径分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(12):1479-1485.
DOI URL |
|
Han B, Li CM, Guo CM, et al. Influencing factors and path analysis of compassion fatigue symptoms in orthopedic nurses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(12):1479-1485.
DOI URL |
|
| [25] |
Preston SD, de Waal FBM. Empathy:its ultimate and proxi-mate bases[J]. Behav Brain Sci, 2002, 25(1):1-71.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
de Vignemont F, Singer T. The empathic brain:how,when and why?[J]. Trends Cogn Sci, 2006, 10(10):435-441.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
李雄, 李祚山, 向滨洋, 等. 注意线索对自闭特质个体疼痛共情的影响:来自事件相关电位的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(3):294-306.
DOI |
|
Li X, Li ZS, Xiang BY, et al. Empathy for pain in individuals with autistic traits influenced by attention cues:evidence from an ERP study[J]. Acta Psychol Sin, 2020, 52(3):294-306.
DOI URL |
|
| [28] | Xie JD, Yang HB, Xia XK, et al. The influence of medical professional knowledge on empathy for pain:evidence from fNIRS[J]. Front Psychol, 2018,9:1089. |
| [29] |
Huang YL, Li B, Jiang SF, et al. Latent profile analysis of re-silience and its relationship with empathy for pain among Chinese clinical nurses[J]. Asian Nurs Res, 2025, 19(3):264-273.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
骆婉容, 鲁才红, 陈秋云. 临床护士心理弹性与共情疲劳相关性的Meta分析[J]. 中国临床护理, 2022, 14(12):765-768.
DOI |
|
Luo WR, Lu CH, Chen QY. Meta analysis of the correlation between resilience and empathy fatigue among clinical nurses[J]. Chin Clin Nurs, 2022, 14(12):765-768.
DOI |
|
| [31] | 田梅梅, 范霖, 施雁, 等. 临床护士共情疲劳的现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(1):76-82. |
| Tian MM, Fan L, Shi Y, et al. The current status and influen-cing factors of compassion fatigue in clinical nurses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(1):76-82. |
| [1] | DU Shushu, CAO Yaqin, MIN Jikang, FENG Yue, WU Qi, JIANG Fengxian. Construction and application of a postoperative self-management program for patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 442-451. |
| [2] | ZHANG Ying, LÜ Shuoyang, ZHAO Guichun, JIANG Yingqing, HUANG Liqun, ZHANG Hongbing, YANG Huilin, NI Li, SUI Wenjie. A quantitative study on the dilemma of exercise in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures after surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 452-459. |
| [3] | WANG Xin, XU Huiping, HUANG Qian, SUN Yifang, GUO Zixin, ZHANG Xinyu. Analysis of latent classes and influencing factors for physical function trajectories in hip arthroplasty patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 460-466. |
| [4] | PAN Yuanyuan, WANG Donghui, FU Huilin. Applied research on an intervention program based on the information framing effect for self-management behaviors in pituitary adenoma patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 475-482. |
| [5] | WANG Fangying, CHEN Xuefeng, JIA Yan, WU Wanying. Subgroups and transition patterns of symptom burden among nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients during the peri-radiotherapy period:a latent transition analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 490-497. |
| [6] | JING Feng, JIANG Lingyun, CAO Yuling, TIAN Maoting, QIU Jiajia, TANG Lichen, HU Yan. Development and preliminary validation of a risk prediction model for musculoskeletal symptoms among breast cancer patients with endocrine therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 498-505. |
| [7] | JIN Guanzhen, LIU Yanjin, JIN Bo, WANG Yanyan, ZHANG Ling, LIU Fangfang. Current situation and influencing factors of self-awareness of falls in elderly patients with primary glaucoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 506-512. |
| [8] | KONG Juan, LIU Xueyan, YUAN Xiaodong, CAO Yingjuan. A study on the symptom management journey map of adult patients with generalized myasthenia gravis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 513-520. |
| [9] | SHI Ziyue, JIANG Enshe, QU Jiayuan, YU Yaqian, ZHANG Daxue, FU Mingzhu, DENG Xiaomei. Norm construction of a Negative Emotion Screening Scale for Inpatients in General Hospitals:a Guangdong provincial norm [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 521-529. |
| [10] | QIN Yushuang, YU Lili, CHENG Lili, HUANG Juan, XI Xin, WANG Liyan, TIAN En, LIN Lirong, FAN Yao, YANG Jurong, ZHOU Mingfang. Experience of pregnant women with end-stage renal disease under multidisciplinary management:a qualitative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 530-535. |
| [11] | LIU Chunli, TENG Xue, ZHANG Liuliu, YANG Bo, ZHANG Maomao, LI Xiaoxu, YU Rong, SHI Ruchun. Research progress on identification and management of malpositioned central venous access device tip into the azygos vein [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 566-570. |
| [12] | ZHOU Xinying, XU Yihong, ZHOU Liping, GONG Xiaoyan, YE Huan, LIU Xiaona, ZHUANG Yiyu. A scoping review on the relationship between gender differences and health related quality of life among stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(4): 571-577. |
| [13] | XUE Jing, WANG Zhe, CHENG Fangqun, CHEN Siyu, HE Cong, XU Qiang, PENG Peng, CHENG Peiyu. Resilience developmental trajectories and influencing factors in infertile women undergoing in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(3): 302-309. |
| [14] | HUANG Huihong, LIU Jinlian, WANG Zirui, LI Jinlu, SHI Li, YANG Rui. Analysis of the influencing factors and pathways of pain levels in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer after oocyte retrieval surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(3): 310-317. |
| [15] | WU Meiliyang, YANG Liu, YANG Juan, QU Jia, MIN Min. Mapping the assisted reproductive treatment journey for infertility patients and implications for care [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(3): 318-325. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||