


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (21): 2599-2604.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.21.006
• Specialist Nursing Practice and Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
NI Xiumei, HU Shaohua, FU Hong, SHEN Xiaoxia, ZHAO Lican, ZHANG Yu, HAN Jiangying
Received:2025-06-20
Online:2025-11-10
Published:2025-11-05
倪秀梅, 胡少华, 付红, 申小侠, 赵利灿, 张玉, 韩江英
作者简介:倪秀梅:女,硕士,副主任护师,护士长,E-mail:marynxm@163.com
基金资助:NI Xiumei, HU Shaohua, FU Hong, SHEN Xiaoxia, ZHAO Lican, ZHANG Yu, HAN Jiangying. A study on the application of bedside ultrasound-based precise intervention strategies in ICU patients with constipation[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(21): 2599-2604.
倪秀梅, 胡少华, 付红, 申小侠, 赵利灿, 张玉, 韩江英. 基于床旁超声的精准干预策略在ICU便秘患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(21): 2599-2604.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.21.006
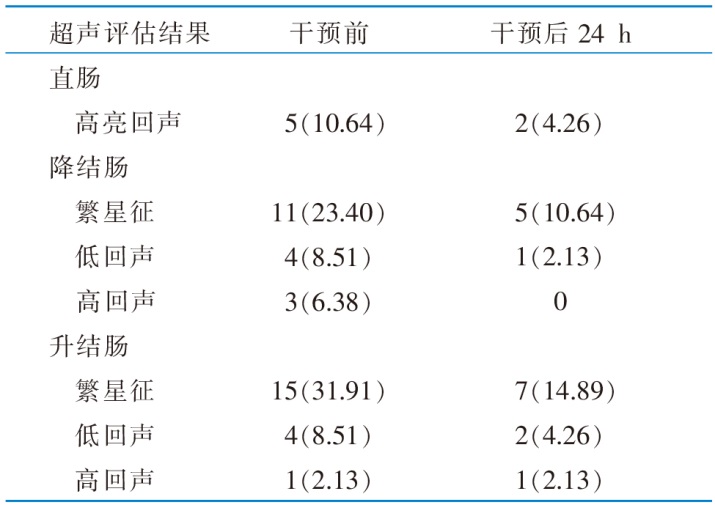 |
Table 2 Ultrasound examination results in intervention group of patients before intervention and 24 hours after intervention[n=47,cases(percentage,%)]
 |
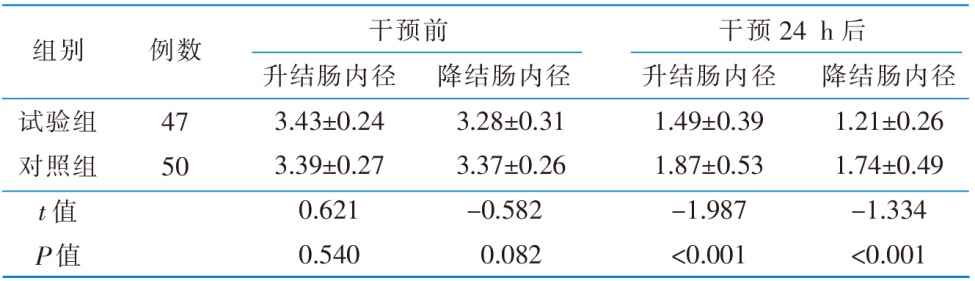 |
Table 3 Comparison of the diameters of the ascending colon and descending colon in the 2 groups before the intervention and 24 hours after intervention(cm,$\bar{x} \pm s$)
 |
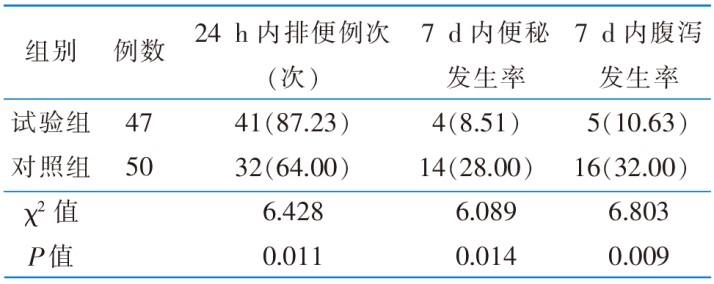 |
Table 4 Comparison of the number of defecation cases and the incidence of constipation and diarrhea in the 2 groups after intervention[cases(percentage,%)]
 |
| [1] | 功能性胃肠病协作组, 中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠动力学组. 中国慢性便秘专家共识意见(2019,广州)[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2019, 39(9):577-598. |
| Neurogastroenterology and Motility Committee, Chinese Society of Gastroenterolog. Chinese Society of Gastroenterolog. Chinese expert consensus on chronic con-stipation(2019,Guangzhou)[J]. Chin J Dig, 2019, 39(9):577-598. | |
| [2] | Mostafa SM, Bhandari S, Ritchie G, et al. Constipation and its implications in the critically ill patient[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2003, 91(6):815-819. |
| [3] | 孙仁华, 刘景全, 邵自强. 重症患者胃肠功能障碍:当前聚焦点[J]. 浙江医学, 2021, 43(23):2501-2504,2516. |
| Sun RH, Liu JQ, Shao ZQ. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in critically ill patients:current focus[J]. Zhejiang Med J, 2021, 43(23):2501-2504,2516. | |
| [4] | Asai T. Constipation:does it increase morbidity and mortality in critically ill patients?[J]. Crit Care Med, 2007, 35(12):2861-2862. |
| [5] |
Masri Y, Abubaker J, Ahmed R. Prophylactic use of laxative for constipation in critically ill patients[J]. Ann Thorac Med, 2010, 5(4):228-231.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Dionne JC, Johnstone J, Smith O, et al. Content analysis of bowel protocols for the management of constipation in adult critically ill patients[J]. J Crit Care, 2020, 58:98-104.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Manabe N, Kamada T, Kusunoki H, et al. Usefulness of ultrasonographic evaluation of stool and/or gas distribution for the treatment strategy of chronic constipation[J]. JGH Open, 2019, 3(4):310-315.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Klijn AJ, Asselman M, Vijverberg MAW, et al. The diameter of the rectum on ultrasonography as a diagnostic tool for constipation in children with dysfunctional voiding[J]. J Urol, 2004, 172(5 Pt 1):1986-1988. |
| [9] | 王小亭, 刘大为, 于凯江, 等. 中国重症超声专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2016, 55(11):900-912. |
|
Wang XT, Liu DW, Yu KJ, et al. China expert consensus on critical ultrasound[J]. Chin J Intern Med, 2016, 55(11):900-912.
DOI PMID |
|
| [10] | 中华医学会外科学分会结直肠肛门外科学组, 中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠动力学组. 中国慢性便秘诊治指南(2013,武汉)[J]. 胃肠病学, 2013, 18(10):605-612. |
| Colorectal and Anorectal Surgery Group of Surgical Branch of the Chinese Medical Association,Gastrointestinal Dynamics Group of Digestive Disease Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of chronic constipation in China(2013,Wuhan)[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol, 2013, 18(10):605-612. | |
| [11] |
Association AG, Bharucha AE, Dorn SD, et al. American Gas-troenterological Association medical position statement on constipation[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(1):211-217.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Nguyen T, Frenette AJ, Johanson C, et al. Impaired gastrointestinal transit and its associated morbidity in the intensive care unit[J]. J Crit Care, 2013, 28(4):537.e11-537.e17. |
| [13] | 代明营, 王慧敏, 李堃, 等. ICU长期机械通气患者发生便秘的相关因素分析:一项前瞻性观察性队列研究[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2017, 29(1):75-80. |
| Dai MY, Wang HM, Li K, et al. Correlation factor analysis on constipation in long-term ventilated patients in intensive care unit:a prospective observational cohort study[J]. Chin Crit Care Med, 2017, 29(1):75-80. | |
| [14] | de Azevedo RP, Freitas FGR, Ferreira EM, et al. Daily laxative therapy reduces organ dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients:a phase Ⅱ randomized controlled trial[J]. Crit Care, 2015, 19(1):329. |
| [15] | Hay T, Bellomo R, Rechnitzer T, et al. Constipation,diarrhea,and prophylactic laxative bowel regimens in the critically ill:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Crit Care, 2019,(52):242-250. |
| [16] | 刘宝华, 刘沂. 国内外便秘诊治指南比较分析[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2019, 41(19):1846-1851. |
| Liu BH, Liu Y. Comparison analysis between domestic and foreign guidelines on constipation diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Third Mil Med Univ, 2019, 41(19):1846-1851. | |
| [17] |
Doniger SJ, Dessie A, Latronica C. Measuring the transrectal diameter on point-of-care ultrasound to diagnose constipation in children[J]. Pediatr Emerg Care, 2018, 34(3):154-159.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Matsumoto M, Yabunaka K, Yoshida M, et al. Improvement of constipation symptoms in an older adult patient by defecation care based on using a handheld ultrasound device in home care settings:a case report[J]. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs, 2020, 47(1):75-78.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Joensson IM, Siggaard C, Rittig S, et al. Transabdominal ultrasound of rectum as a diagnostic tool in childhood constipation[J]. J Urol, 2008, 179(5):1997-2002.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | 柳亚南. 床旁超声监测胃窦动力对重症患者胃肠功能的评估价值[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2021. |
| Liu YN. Evaluation value of bedside ultrasound monitoring gastric antrum motility on gastrointestinal function in critically ill patients[D]. Tangshan: North China University of Science and Technology, 2021. | |
| [21] |
王壮英, 王元凤, 梁苗苗, 等. 重型颅脑损伤患者便秘风险评分量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(5):582-587.
DOI |
|
Wang ZY, Wang YF, Liang MM, et al. Development and reliability and validity test of constipation risk scale for patients with severe craniocerebral injury[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(5):582-587.
DOI |
|
| [22] |
倪秀梅, 胡少华, 韩江英, 等. 护士主导的床旁超声在ICU肠内营养患者腹胀管理中的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(17):2123-2129.
DOI |
|
Ni XM, Hu SH, Han JY, et al. The application of nurse-performed point-of-care ultrasound in the management of abdominal distension in patients with enteral nutrition in ICU[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(17):2123-2129.
DOI |
| [1] | HUANG Panpan, LI Liling, HU Xiaojing. Research progress of early exercise rehabilitation in infants with congenital heart disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [2] | CHEN Liou, ZHANG Wenting, LIU Junqi, WANG Yuncong, WANG Zhenlin, QI Sai, YANG Na. Study on the effect of pulmonary lobes surface projection localization combined with pulmonary segment drainage and sputum expectoration technique on airway clearance in patients with aspiration pneumonia [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [3] | YANG Nana, CHENG Chuanli, ZENG Hui, FU Dandan, WANG Yan, CHEN Yue, RAN Hongmin, FAN Hongjing, LONG Xia. Evaluation of the effect of graded exercise rehabilitation on patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [4] | CAO Yun, SUN Guozhen, CHEN Feng, JI Xueli, YAN Mengwan, JING Lei, QIAN Kun. A study of modified ankle pump exercise in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [5] | XIE Min, QI Wenkai, YIN Ling, ZHANG Xuan, ZHAO Ruqin. Potential profile analysis and influencing factors of kinesiophobia in patients with peritoneal dialysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [6] | CHEN Bingqian, ZHAO Bin, SUN Jiarong, HAO Sifang, HOU Xiaoli. Oral health management dilemmas of chronic periodontitis patients with implant dentures:a qualitative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [7] | QIN Chunlan, WU Zhenyun, QIAN Hongying, ZHAO Qian, SUN Jinting. Experiences of disease self-control among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:a qualitative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [8] | LI Ziwei, FENG Lijuan, CHEN Xusheng, HUANG Yi, YANG Jie. Development and application of a Fear of Movement Assessment Scale for patients with peripherally inserted central catheters [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [9] | CHENG Zhiqiang, ZHANG Baozhen, TANG Liping, LI Jing, XIA Jiaoyun, WEI Xueyan, GONG Zhixian, ZHANG Meizhen, LI Lusi. Reliability and validity test of the Chinese version of the Urinary Incontinence Awareness and Attitude Scale [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [10] | SHI Meiqin, WU Jianfang, ZHANG Duo, WU Chunping, CHEN Ling, TAO Lei. Nursing care for postoperative laryngeal function rehabilitation in a patient undergoing primary voice prosthesis implantation after total laryngectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [11] | GU Qian, HUANG Xi, SHI Weixiong, WU Jing, TAN Ruoming, WANG Feng. Nursing care for a patient with cytokine release syndrome following T-cell immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| [12] | ZHOU Miao, CHEN Xing, PENG Fei, SUN Shangxue, LI Yangyang. Systematic review of risk prediction instruments for central line associated bloodstream infections in ICU patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1132-1139. |
| [13] | PENG Yingjie, LIU Aihong, ZHU Wenli, MEI Yuxin, ZHOU Meng, GUAN Wenjing. Systematic review of readiness assessment tools for advance care planning in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1146-1153. |
| [14] | RAN Lingxiao, WANG Dongmin, XU Ke, WANG Cong, CAO Hua, CUN Wei, JIANG Yan. Application of biomechanical simulation based on three-dimensional human body model in preventing pressure ulcers:a scoping review [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 1012-1018. |
| [15] | JIN Yujia, JIANG Hu, WANG Xiaoxuan, YI Jingna, MEI Yongxia, GUO Zhiting, ZHANG Zhenxiang, LIN Beilei. Application of information-based risk communication in primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases:a scoping review [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 1019-1025. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||