


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (22): 2700-2709.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.22.002
• Research Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Qi( ), GU Ying(
), GU Ying( ), WANG Huimei, SUN Yu, ZHANG Xueping, REN Yuehong, ZHU Mengxin, XING Lan
), WANG Huimei, SUN Yu, ZHANG Xueping, REN Yuehong, ZHU Mengxin, XING Lan
Received:2023-12-26
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
GU Ying
章琪( ), 顾莺(
), 顾莺( ), 王慧美, 孙瑜, 张雪萍, 任玥宏, 朱孟欣, 邢岚
), 王慧美, 孙瑜, 张雪萍, 任玥宏, 朱孟欣, 邢岚
通讯作者:
顾莺
作者简介:章琪:女,本科(硕士在读),E-mail:3036591698@qq.com
ZHANG Qi, GU Ying, WANG Huimei, SUN Yu, ZHANG Xueping, REN Yuehong, ZHU Mengxin, XING Lan. Construction and initial application of a intervention programme for breastfeeding in infants with congenital heart disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(22): 2700-2709.
章琪, 顾莺, 王慧美, 孙瑜, 张雪萍, 任玥宏, 朱孟欣, 邢岚. 先天性心脏病患儿母乳喂养干预方案的构建及初步应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(22): 2700-2709.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.22.002
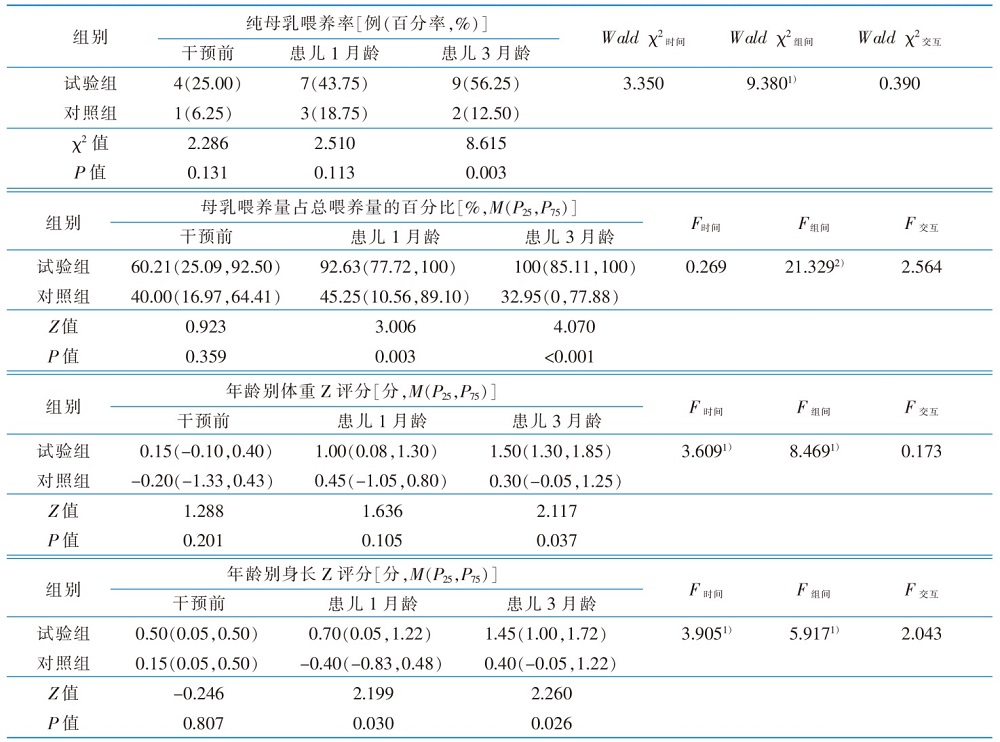 |
Table 3 Comparison of exclusive breastfeeding rate, daily human milk as a percentage of total feeds, weight for age Z-score and height for age Z-score at different time points between the 2 groups
 |
| [1] | Zhao QM, Liu F, Wu L, et al. Prevalence of congenital heart disease at live birth in China[J]. J Pediatr, 2019, 204:53-58. |
| [2] | Harrison TM. Trajectories of parasympathetic nervous system function before,during,and after feeding in infants with transposition of the great arteries[J]. Nurs Res, 2011, 60(3 Suppl):S15-S27. |
| [3] | Elgersma KM, McKechnie AC, Sommerness SA, et al. Wayfinding through the “ocean of the great unknown”:how lactating parents establish a direct breastfeeding relationship with an infant with critical CHD[J]. Cardiol Young, 2023, 33(10):2000-2011. |
| [4] | Davis JA, Spatz DL. Human milk and infants with congenital heart disease:a summary of current literature supporting the provision of human milk and breastfeeding[J]. Adv Neonatal Care, 2019, 19(3):212-218. |
| [5] |
Elgersma KM, McKechnie AC, Schorr EN, et al. The impact of human milk on outcomes for infants with congenital heart disease:a systematic review[J]. Breastfeed Med, 2022, 17(5):393-411.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Marino BL, O’Brien P, LoRe H. Oxygen saturations during breast and bottle feedings in infants with congenital heart disease[J]. J Pediatr Nurs, 1995, 10(6):360-364.
PMID |
| [7] | Al-Shehri SS, Knox CL, Liley HG, et al. Breastmilk-saliva interactions boost innate immunity by regulating the oral microbiome in early infancy[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(9):e0135047. |
| [8] | Spatz DL. Ten steps for promoting and protecting breastfeeding for vulnerable infants[J]. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs, 2004, 18(4):385-396. |
| [9] | 顾莺, 倪玉丹, 曹育玲. 先天性心脏病患儿营养问题与母亲喂养行为的相关性研究[J]. 护理研究, 2010, 24(28):2570-2571. |
| Gu Y, Ni YD, Cao YL. Study on the relativity between nutrition problem of infants with congenital heart disease and mother’s feeding behavior[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2010, 24(28):2570-2571. | |
| [10] | Tandberg BS, Ystrom E, Vollrath ME, et al. Feeding infants with CHD with breast milk:Norwegian mother and child cohort study[J]. Acta Paediatr, 2010, 99(3):373-378. |
| [11] | 柯淞淋, 冷虹瑶, 唐语蔓, 等. 出院新生儿母乳喂养随访清单的构建[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(16):1962-1969. |
| Ke SL, Leng HY, Tang YM, et al. Construction of a breastfeeding follow-up checklist for discharged newborns[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(16):1962-1969. | |
| [12] |
杭琳, 张洁苹, 项丹玉, 等. 基于共同养育理论的母乳喂养支持方案在NICU早产儿医院-家庭过渡期中的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(12):1435-1441.
DOI URL |
|
Hang L, Zhang JP, Xiang DY, et al. Application of an intervention based on co-parenting theory on hospital-home transitional breastfeeding of NICU preterm infants[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(12):1435-1441.
DOI URL |
|
| [13] |
Michie S, van Stralen MM, West R. The behaviour change wheel:a new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions[J]. Implement Sci, 2011, 6:42.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
朱虹宣, 庞建美, 孙盛楠, 等. 老年肺癌患者术后过渡期肺康复行为影响因素的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(1):15-21.
DOI URL |
|
Zhu HX, Pang JM, Sun SN, et al. A qualitative study of the factors of pulmonary rehabilitation behavior of elderly patients with lung cancer in the post-operative transitional period[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(1):15-21.
DOI URL |
|
| [15] | 孙佳蓉, 董丽媛, 王娇, 等. 基于COM-B模型的孕期保健方案在分娩恐惧初产妇中的应用研究[J]. 护理管理杂志, 2023, 23(4):234-238. |
| Sun JR, Dong LY, Wang J, et al. Application of COM-B model-based pregnancy care program in primiparae with fear of childbirth[J]. J Nurs Adm, 2023, 23(4):234-238. | |
| [16] |
Barbas KH, Kelleher DK. Breastfeeding success among infants with congenital heart disease[J]. Pediatr Nurs, 2004, 30(4):285-289.
PMID |
| [17] |
周芸, 杨丽, 凌静, 等. 基于互联网+全程母乳喂养支持的护理干预在剖宫产产妇中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(16):1933-1941.
DOI URL |
|
Zhou Y, Yang L, Ling J, et al. Research on the application of nursing intervention of Internet + whole course breastfeeding support in cesarean section women[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(16):1933-1941.
DOI URL |
|
| [18] |
杭琳, 张洁苹, 项丹玉, 等. 基于共同养育理论的母乳喂养支持方案在NICU早产儿医院-家庭过渡期中的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(12):1435-1441.
DOI URL |
|
Hang L, Zhang JP, Xiang DY, et al. Application of an intervention based on co-parenting theory on hospital-home transitional breastfeeding of NICU preterm infants[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(12):1435-1441.
DOI URL |
|
| [19] |
van der Kuip M, Hoos MB, Forget PP, et al. Energy expenditure in infants with congenital heart disease,including a meta-analysis[J]. Acta Paediatr, 2003, 92(8):921-927.
PMID |
| [20] |
Varan B, Tokel K, Yilmaz G. Malnutrition and growth failure in cyanotic and acyanotic congenital heart disease with and without pulmonary hypertension[J]. Arch Dis Child, 1999, 81(1):49-52.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | 邵文燊. 不同喂养方式下先天性心脏病患儿体格和智力发育状况的研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018. |
| Shao WS. Physical and mental development in children with congenital heart disease under different feeding patterns[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2018. |
| [1] | ZENG Fei, LAN Meijuan, GU Peipei, LIANG Jiangshuyuan, WANG Yandie, CAI Lingyun. Construction and preliminary verification of a postoperative pulmonary rehabilitation nursing program for children with double lung transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | YAN Yinzhi, WEN Fang, WANG Min, ZHOU Xuemei, MA Jinling, WU Huifang, YAO Wenying. Construction and application of a graded nursing program for exercise rehabilitation in children with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | LIU Xixuan, LIU Yulin, LIU Sha, YANG Fan, XIE Xiaohong, WANG Zijuan, LIU Lifang, WEI Hongyu. Construction and effect evaluation of the respiratory rehabilitation calisthenics for school-age children with bronchial asthma [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | HUANG Panpan, LI Liling, HU Xiaojing. Research progress of early exercise rehabilitation in infants with congenital heart disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | YANG Jing, WANG Huafen, LU Fangyan, BAO Ruijie, ZHU Li. Analysis influencing factors of nutritional status changes in pediatric liver transplant patients and nursing revelation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [6] | HAN Shanshan, QIN Yongping, QU Hong, ZHENG Xianlan. Construction and validation of a risk prediction model for intraoperative acquired pressure injury in neurosurgical children [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 928-933. |
| [7] | LIANG Jiangshuyuan, WANG Yandie, ZENG Fei, LAN Meijuan, GU Peipei. Nursing care of 14 children after double lung transplantation for secondary bronchiolitis obliterans after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 972-976. |
| [8] | ZHANG Ju, WEI Lili, XIN Chen, WANG Jing, HAN Yan, YANG Yanyan, SUN Mengzhu. Application research of immersive virtual reality technology in pediatric patients undergoing elective surgery under general anesthesia [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(6): 671-676. |
| [9] | HAN Wenwen, HU Chunxia, ZHANG Kai, SUI Weijing, HUANG Meili, PAN Hongying, GONG Xiaoyan, ZHUANG Yiyu. Remote nursing care for a pediatric patient with severe burns based on augmented reality technology:a case report [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(6): 677-679. |
| [10] | YANG Tongling, CHEN Yuying, WAN Fan, DOU Yalan, HU Xiaojing. Development and initial implementation of a neonatal home skin care guidance scheme [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(6): 680-687. |
| [11] | Writing Committee:ZHANG Qian, LIU Yafei, LI Mengran, WANG Na, WANG Yanjiao, WANG Shiyu, LI Qingyin. Expert consensus on perinatal care management of infants with congenital heart disease/National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases,Cardiovascular Professional Committee of Chinese Nursing Association [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 552-557. |
| [12] | CHEN Qianhe, CHEN Jun, JIANG Kaiyao, WU Xiaonan, HONG Wanting, ZHANG Chunmei. Qualitative study on the facilitating and obstacle factors of the pediatric medical fear intervention by pediatric nurses [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 575-580. |
| [13] | JIANG Sishan, CHENG Qinqin, LUO Tingwei, ZHANG Na, GUO Junchen, LI Dongya, LI Dandan, ZHU Lihui. A systematic review of quality assessment tools for pediatric palliative care based on COSMlN guidelines [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 611-618. |
| [14] | YANG Funa, YANG Rui, QIN Yan, CHEN Junhan, GUO Lanwei, WANG Yongqi, HO Kayan, LIU Qi, MAO Ting, MEI Xiaoxiao, WANG Wenying, XU Xiaoxia, SHI Hongying. Current situation and influencing factors of family resilience of children with cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(4): 446-452. |
| [15] | WANG Sa, MIAO Huali, LI Yuwei, WANG Hongwei, QIAO Caicai, SONG Weiting. A systematic review of tools for assessing the readiness of patients with chronic diseases aged 10-19 to transition to adulthood [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(4): 469-477. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||