


中华护理杂志 ›› 2026, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (1): 113-120.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.01.016
李奎1( ), 潘爱红2,*(
), 潘爱红2,*( ), 徐佩丽3, 许采颉3, 任汝南1, 王春1
), 徐佩丽3, 许采颉3, 任汝南1, 王春1
收稿日期:2025-05-26
出版日期:2026-01-10
发布日期:2026-01-04
*通讯作者:
潘爱红,E-mail:281851862@qq.com作者简介:李奎:男,本科(硕士在读),主管护师,E-mail:likui6425897@163.com
基金资助:
LI Kui1( ), PAN Aihong2,*(
), PAN Aihong2,*( ), XU Peili3, XU Caijie3, REN Runan1, WANG Chun1
), XU Peili3, XU Caijie3, REN Runan1, WANG Chun1
Received:2025-05-26
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2026-01-04
* Corresponding author:
PAN Aihong,E-mail:281851862@qq.comFunding program:摘要:
目的 运用潜在剖面分析法对维持性血液透析(maintenance hemodialysis,MHD)患者容量管理行为的群体特征进行分类,并探讨各潜在类别的影响因素。 方法 便利选取2024年3月—2025年3月在安徽省某三级甲等医院接受治疗的304例门诊规律血液透析患者作为调查对象,采用一般资料调查表、维持性血液透析患者容量管理行为量表、医院焦虑抑郁量表、家庭关怀度指数问卷以及一般自我效能感量表对其进行问卷调查。采用潜在剖面分析和多元Logistic回归分析MHD患者容量管理行为的潜在剖面及其影响因素。 结果 本研究共回收有效问卷278份,有效问卷回收率为91.45%。MHD患者容量管理行为可分为低管理行为组(23.74%)、中等管理行为组(56.48%)、高管理行为组(19.78%) 3个潜在类别。透析前血压、透析间期体重增长、文化程度、透析龄、家庭关怀度、一般自我效能是维持性血液透析患者容量管理行为潜在剖面的影响因素(均P<0.05)。 结论 MHD患者在容量管理方面的行为存在群体差异性。医护人员可以根据MHD患者容量管理行为不同剖面的类别特征及影响因素,制订针对性的护理干预策略,提高患者的生存质量。
李奎, 潘爱红, 徐佩丽, 许采颉, 任汝南, 王春. 维持性血液透析患者容量管理行为潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 113-120.
LI Kui, PAN Aihong, XU Peili, XU Caijie, REN Runan, WANG Chun. Latent profile analysis and influencing factors of volume management behaviors in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 113-120.
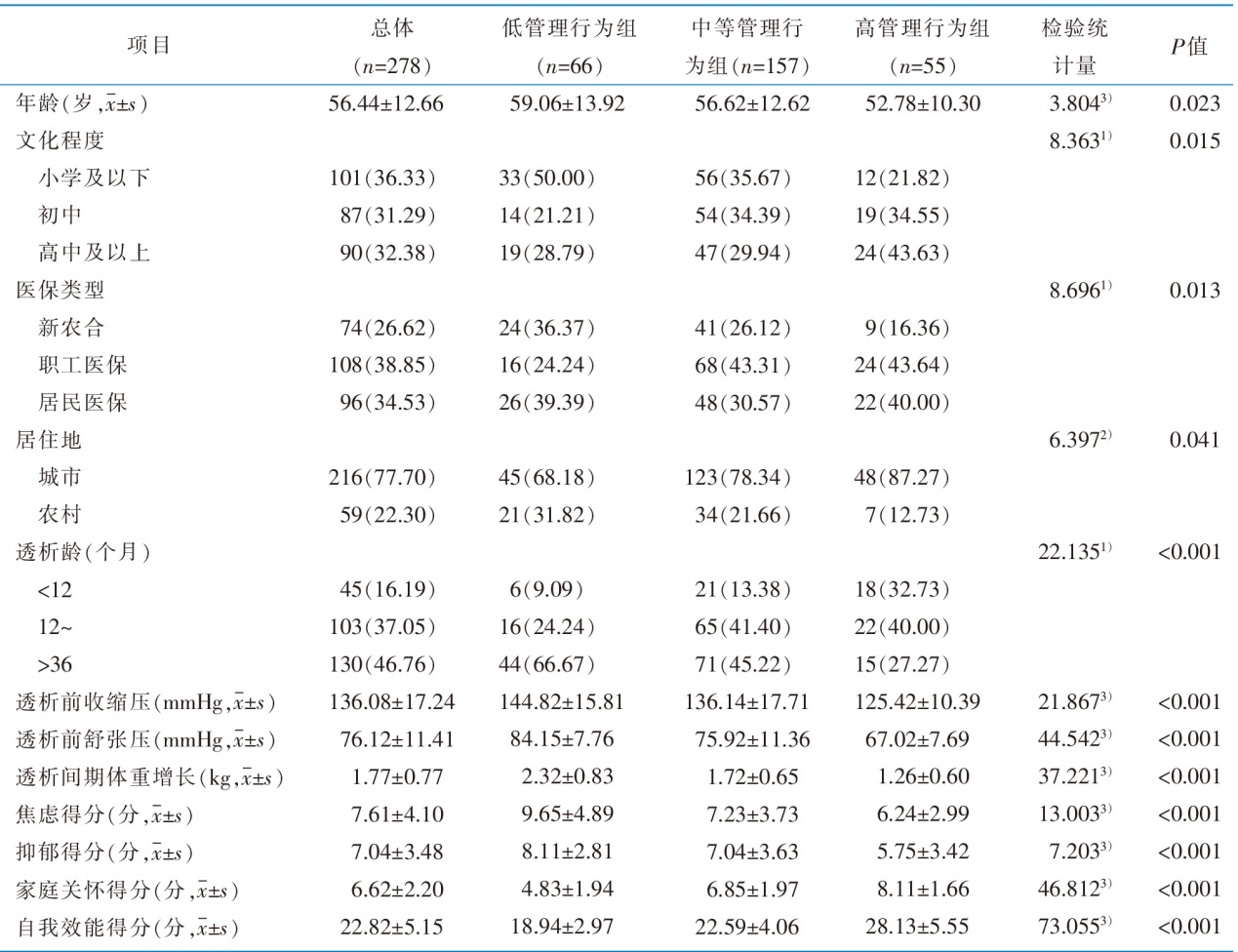 |
表1 维持性血液透析患者的一般资料及容量管理行为潜在剖面的单因素分析
Table 1 General information and univariate analysis of potential profiles of volume management behavior among maintenance hemodialysis patients
 |
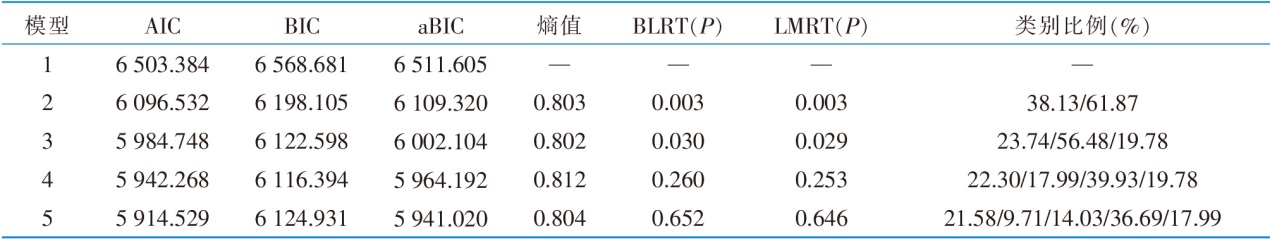 |
表3 维持性血液透析患者容量管理行为潜在剖面模型的拟合指标(n=278)
Table 3 Model fitting results of potential profile analysis model for volume management behavior among maintenance hemodialysis patients(n=278)
 |
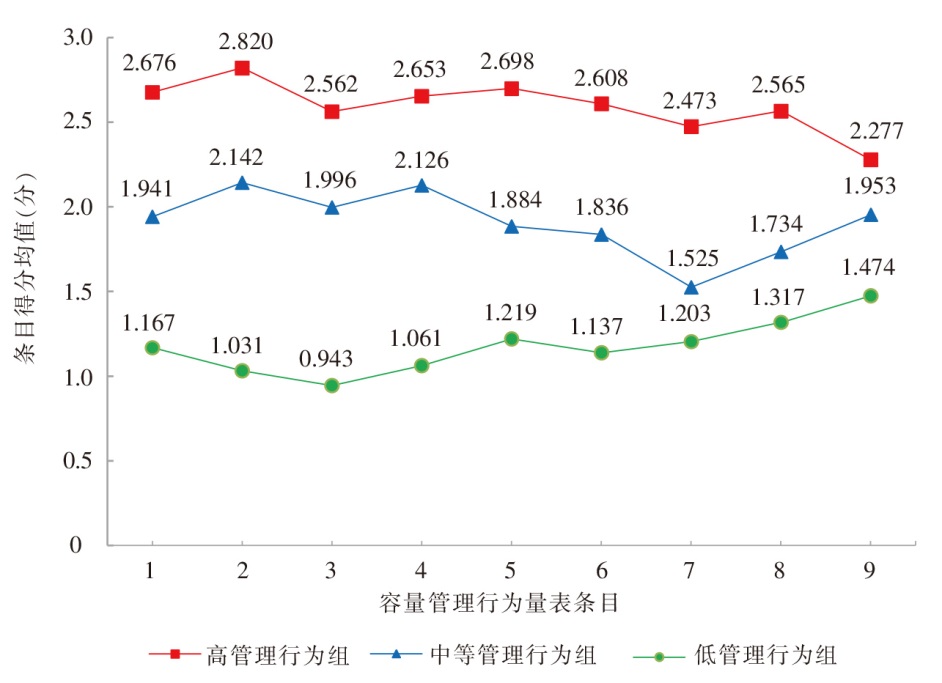
图1 维持性血液透析患者容量管理行为3个潜在剖面的特征分布
Figure 1 The characteristic distribution of 3 potential profiles of volume management behavior among maintenance hemodialysis patients
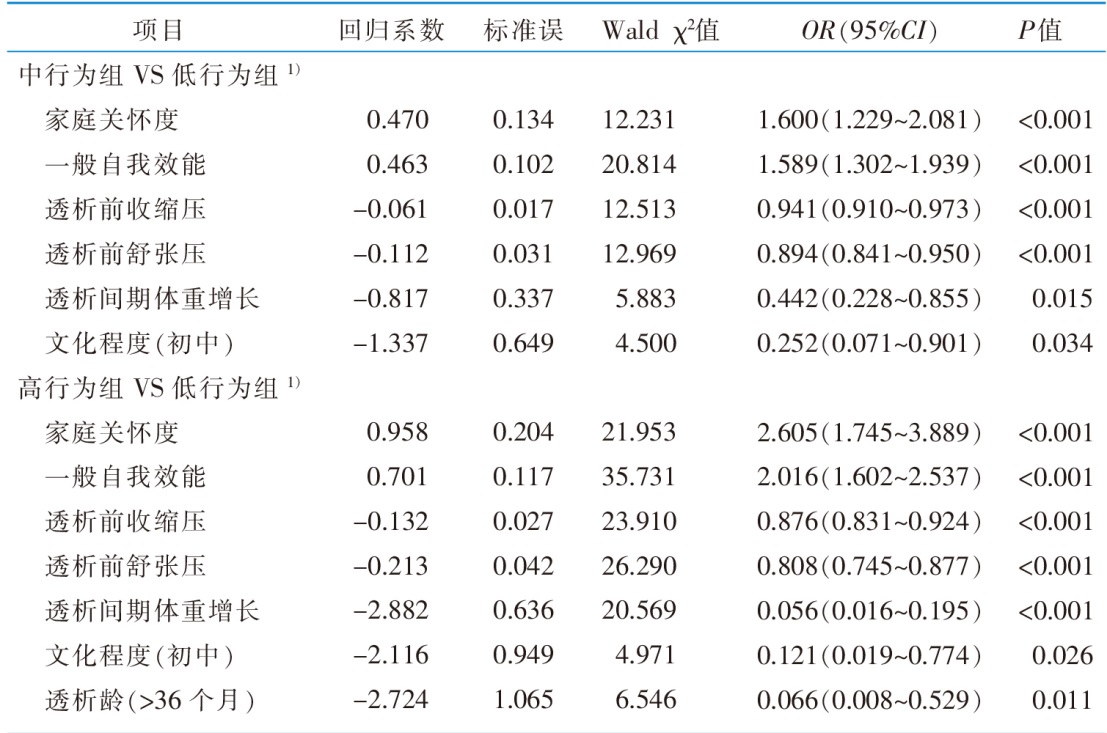 |
表5 维持性血液透析患者容量管理行为潜在剖面的多因素分析(n=278)
Table 5 Multifactor analysis of potential profiles of volume management behavior among maintenance hemodialysis patients(n=278)
 |
| [1] | 梁耀先, 赵新菊, 韦洮. 中国血液透析行业发展调研报告[J]. 中国血液净化, 2024, 23(5):321-329. |
| Liang YX, Zhao XJ, Wei T. Research report on the develop-ment of China’s hemodialysis[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2024, 23(5):321-329. | |
| [2] |
Mayne KJ, Shemilt R, Keane DF, et al. Bioimpedance indices of fluid overload and cardiorenal outcomes in heart failure and chronic kidney disease:a systematic review[J]. J Card Fail, 2022, 28(11):1628-1641.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 范孟杰, 田凤美, 王赟, 等. 腹膜透析患者容量管理行为的异质性及影响因素分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2024, 39(10):35-40. |
| Fan MJ, Tian FM, Wang Y, et al. Analysis of heterogeneity and influencing factors of volume management behavior in perito-neal dialysis patients[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2024, 39(10):35-40. | |
| [4] |
管婷婷, 戴莉敏, 徐敏, 等. 老年糖尿病伴营养不良患者饮食管理能力的潜在剖面及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(12):1454-1460.
DOI URL |
|
Guan TT, Dai LM, Xu M, et al. Analysis of potential profile and influencing factors in elderly diabetic patients with malnutrition risk[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(12):1454-1460.
DOI URL |
|
| [5] | 段文静, 谢煜相, 羊姝, 等. 潜在剖面分析在自杀或自伤研究中的应用进展[J]. 实用临床医学, 2024, 25(5):120-124. |
| Duan WJ, Xie YX, Yang S, et al. Latent profile analysis in suicide or self-injury:a review[J]. Pract Clin Med, 2024, 25(5):120-124. | |
| [6] |
上海慢性肾脏病早发现及规范化诊治与示范项目专家组,高翔,梅长林. 慢性肾脏病筛查诊断及防治指南[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2017, 37(1):28-34.
DOI |
| Shanghai Expert Group on Early Detection and Standardized Diagnosis of CKD,Gao X,Mei CL. Guideline for screening,diagnosis,prevention and treatment of chronic kidney disease[J]. Chin J Pract Intern Med, 2017, 37(1):28-34. | |
| [7] | 倪平, 陈京立, 刘娜. 护理研究中量性研究的样本量估计[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010, 45(4):378-380. |
| Ni P, Chen JL, Liu N. The sample size estimation in quanti-tative nursing research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010, 45(4):378-380. | |
| [8] | 董丽, 石彬, 王海芳, 等. 维持性血液透析患者容量管理行为量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 护理学杂志, 2017, 32(21):22-25. |
| Dong L, Shi B, Wang HF, et al. Capacity Management Behavior Scale for Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients:development and validation[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2017, 32(21):22-25. | |
| [9] |
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale[J]. Acta Psychiatr Scand, 1983, 67(6):361-370.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 叶维菲, 徐俊冕. “综合性医院焦虑抑郁量表”在综合性医院患者中的应用与评价[J]. 中国行为医学杂志, 1993, 2(3):17-19. |
| Ye WF, Xu JM. Application and evaluation of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale in general hospital patients[J]. Chin J Behav Med Sci, 1993, 2(3):17-19. | |
| [11] | Smilkstein G, Ashworth C, Montano D. Validity and reliability of the family APGAR as a test of family function[J]. J Fam Pract, 1982, 15(2):303-311. |
| [12] | 吕繁, 顾湲. 家庭APGAR问卷及其临床应用[J]. 国外医学(医院管理分册), 1995, 12(2):56-59. |
| Lü F, Gu Y. Family APGAR questionnaire and its clinical application[J]. Hosp Manag Forum, 1995, 12(2):56-59. | |
| [13] |
Schwarzer R. Self-regulatory processes in the adoption and maintenance of health behaviors[J]. J Health Psychol, 1999, 4(2):115-127.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | 王才康, 胡中锋, 刘勇. 一般自我效能感量表的信度和效度研究[J]. 应用心理学, 2001, 7(1):37-40. |
| Wang CK, Hu ZF, Liu Y. Evidences for reliability and vali-dity of the Chinese version of General Self-efficacy Scale[J]. Chin J Appl Psychol, 2001, 7(1):37-40. | |
| [15] | 王孟成, 邓俏文, 毕向阳, 等. 分类精确性指数Entropy在潜剖面分析中的表现:一项蒙特卡罗模拟研究[J]. 心理学报, 2017, 49(11):1473-1482. |
|
Wang MC, Deng QW, Bi XY, et al. Performance of the Entro-py as an index of classification accuracy in latent profile analysis:a Monte Carlo simulation study[J]. Acta Psychol Sin, 2017, 49(11):1473-1482.
DOI URL |
|
| [16] | 林翠云, 吴君桃, 邱娟娟. 维持性血透患者容量管理行为水平现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国医学创新, 2022, 19(16):101-104. |
| Lin CY, Wu JT, Qiu JJ. Analysis of current status and influe-ncing factors of volume management behavior in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Med Innov China, 2022, 19(16):101-104. | |
| [17] | Zoccali C, Tripepi G, Carioni P, et al. Fluid overload trajecto-ries and mortality in hemodialysis patients[J]. J Intern Med, 2025, 297(2):201-212. |
| [18] |
车旭, 乔东鸽, 王红霞, 等. 维持性血液透析患者治疗依从性影响因素结构方程模型构建与验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(5):562-569.
DOI URL |
|
Che X, Qiao DG, Wang HX, et al. Construction and validation of structural equation modeling of factors influencing treatment adherence in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(5):562-569.
DOI URL |
|
| [19] |
Keivan S, Shariati A, Miladinia M, et al. Role of self-mana-gement program based on 5A nursing model in quality of life among patients undergoing hemodialysis:a randomized clinical trial[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2023, 24(1):58.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | 邹转芳, 白李平, 杨玉金, 等. 维持性血液透析患者容量管理方案的构建及应用[J]. 中国护理管理, 2024, 24(1):39-45. |
| Zou ZF, Bai LP, Yang YJ, et al. Development and application of a volume management scheme for patients with mainte-nance hemodialysis[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2024, 24(1):39-45. | |
| [21] | 林萍, 高鹰, 庄建红. 维持性血液透析患者容量管理行为水平调查及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国血液净化, 2023, 22(5):389-391,400. |
| Lin P, Gao Y, Zhuang JH. Investigation and influencing factor analyses on volume management behavior in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2023, 22(5):389-391,400. | |
| [22] | 尹金红. 维持性血液透析患者容量管理行为和症状困扰的现状分析[J]. 中西医结合护理(中英文), 2021, 7(3):179-181. |
| Yin JH. A situation analysis of volume management behavior and symptom distress among maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Nurs Integr Tradit Chin West Med, 2021, 7(3):179-181. | |
| [23] |
陈辰, 郑晶, 刘旭, 等. 基于健康信念模式的血液透析患者液体管理影响因素的关系模型研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(24):2996-3003.
DOI URL |
|
Chen C, Zheng J, Liu X, et al. Relational model of factors influencing fluid management in hemodialysis patients based on the health belief model[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(24):2996-3003.
DOI URL |
|
| [24] | 李芸芸, 吴仲华, 王秀云, 等. 维持性血液透析病人容量管理行为影响因素及预测模型[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2024, 49(8):1091-1094,1101. |
| Li YY, Wu ZH, Wang XY, et al. Prediction model and influencing factors of capacity management behavior in main-tenance hemodialysis patients[J]. J Bengbu Med Coll, 2024, 49(8):1091-1094,1101. | |
| [25] |
Santos DGMD, Pallone JM, Manzini CSS, et al. Relationship between frailty,social support and family functionality of he-modialysis patients:a cross-sectional study[J]. Sao Paulo Med J, 2021, 139(6):570-575.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
张程, 王霄一, 杨文娟, 等. 双向社会支持在老年维持性血液透析患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7):813-818.
DOI URL |
| Zhang C, Wang XY, Yang WJ, et al. Application of bidirectio-nal social support in elderly patients with maintenance hemo-dialysis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(7):813-818. | |
| [27] |
陆沁怡, 金学勤. 社会支持对老年维持性血液透析患者抑郁症状影响的研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(19):2333-2339.
DOI URL |
|
Lu QY, Jin XQ. The influence of social support on depressive symptoms among elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(19):2333-2339.
DOI URL |
|
| [28] | 查夏琴, 李文龙, 李馨蕾, 等. 基于IKAP理论在改善血液透析患者容量自我管理能力中的效果分析[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2024, 21(2):270-273. |
| Zha XQ, Li WL, Li XL, et al. Effect analysis of improving capacity self-management ability of hemodialysis patients based on IKAP theory[J]. Lab Med Clin, 2024, 21(2):270-273. |
| [1] | 陶彬彬, 阴倩羽, 柴召午, 敖春燕, 刘萍, 张黔, 杨冰. 口腔健康教育方案的构建及在社区老年人中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 9-16. |
| [2] | 茹秀丽, 韩梦丹, 纪莉莉, 周丽娜, 李雪雯, 张亦爽. 药物自我管理行为对社区老年慢性共病患者衰弱的影响研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 17-22. |
| [3] | 陆沁怡, 陆程倩, 赵亚芬, 金学勤. 跌倒恐惧对社区老年2型糖尿病患者跌倒警觉度的影响研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 23-29. |
| [4] | 高维杰, 孙玉梅. 失智老年人及其照顾者使用喘息服务障碍因素的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 30-37. |
| [5] | 汪婧颖, 罗雅婷, 贾思培, 甘港, 刘敏, 张秋香, 谢建飞. 数字健康干预在农村老年人抑郁管理中应用的范围综述[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 38-45. |
| [6] | 中华护理学会呼吸护理专业委员会(执笔:曾妃, 兰美娟, 蔡凌云, 顾培培, 朱岩, 王衍蝶, 梁江淑渊). 儿童肺移植术后肺康复护理专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 46-52. |
| [7] | 中华护理学会安宁疗护专业委员会(执笔:郭俊晨, 谌永毅, 应文娟, 吕茵茵, 赵云, 强万敏, 徐晓霞, 胡永红. 成人安宁疗护患者多学科共同照护管理专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 53-56. |
| [8] | 郑焠燕, 封亚萍, 刘志梅, 胡慧群. 双手及单手握球锻炼在PICC置管患者中应用效果的比较研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 57-62. |
| [9] | 郭恩慧, 朗秋燕, 温汉春, 甘衍梅, 王书林, 李高叶. 静脉-动脉体外膜肺氧合护理标准化方案在复杂高危冠心病患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 63-69. |
| [10] | 高丹, 姚丽伟, 黄金鹏, 刘晓霞, 张玥, 毛潇潇. 增强现实体感运动在结核性脓胸清除术患者早期活动中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 70-77. |
| [11] | 彭媛, 杨正伟, 何川, 陈玉琴. 下肢加压疗法预防乳腺癌患者化疗致周围神经病变的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 78-84. |
| [12] | 蒋向玲, 陆慧芬, 虞幼军, 林晓丽, 黄佩铃. 鼻咽癌患者放疗后听力损伤影响因素研究及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 85-92. |
| [13] | 郑文静, 张文倩, 蒋秋焕, 候琳琳, 张蒙蒙. 2型糖尿病患者自我管理行为维持困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 93-98. |
| [14] | 王红艳, 刘静, 汪红英, 夏宁宁, 肖磊娟, 苑影影. 术前量化加压束臂运动对血液透析患者自体动静脉内瘘成熟的影响研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 99-105. |
| [15] | 王阳阳, 尹娜, 李佳麒, 张菊, 龚婷婷, 杨旻斐. 老年创伤性脑损伤患者衰弱风险预测模型的构建和验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(1): 106-112. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||