


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (24): 3003-3008.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.24.009
• Specialist Nursing Practice and Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Li( ), SHEN Yawen, LI Delong, CHENG Fangfang, YU Xifeng, PAN Linlin, ZHUANG Shuyuan, DONG Sihong, WU Jiao, LIANG Yan, ZANG Yuantong(
), SHEN Yawen, LI Delong, CHENG Fangfang, YU Xifeng, PAN Linlin, ZHUANG Shuyuan, DONG Sihong, WU Jiao, LIANG Yan, ZANG Yuantong( )
)
Received:2024-04-24
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-12-20
Contact:
ZANG Yuantong
李莉( ), 申雅文, 李德龙, 程芳芳, 于喜凤, 潘琳琳, 庄淑渊, 董思鸿, 吴娇, 梁艳, 臧苑彤(
), 申雅文, 李德龙, 程芳芳, 于喜凤, 潘琳琳, 庄淑渊, 董思鸿, 吴娇, 梁艳, 臧苑彤( )
)
通讯作者:
臧苑彤
作者简介:李莉:女,硕士,副主任护师,护理部副主任,E-mail:408375918@qq.com
基金资助:LI Li, SHEN Yawen, LI Delong, CHENG Fangfang, YU Xifeng, PAN Linlin, ZHUANG Shuyuan, DONG Sihong, WU Jiao, LIANG Yan, ZANG Yuantong. Analysis of influencing factors and pathways of postoperative self-efficacy in patients with fragility fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(24): 3003-3008.
李莉, 申雅文, 李德龙, 程芳芳, 于喜凤, 潘琳琳, 庄淑渊, 董思鸿, 吴娇, 梁艳, 臧苑彤. 脆性骨折术后患者康复自我效能感的影响因素及路径分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(24): 3003-3008.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.24.009
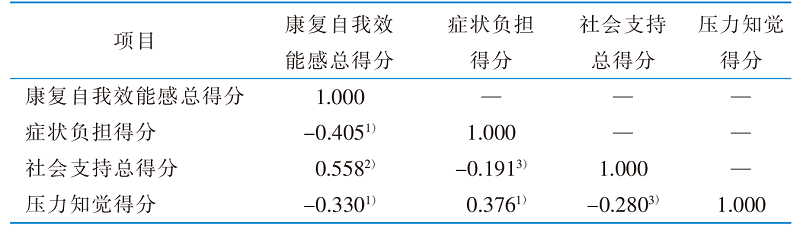 |
Table 2 Results of correlation analysis among symptom burden,rehabilita-tion self-efficacy,social support and perceived stress of patients with fragility fracture(r value)
 |
| [1] | 李宁, 李新萍, 杨明辉, 等. 老年髋部骨折的骨质疏松症诊疗专家共识[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2021, 14(8):657-663. |
| Li N, Li XP, Yang MH, et al. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis in elderly patients with hip fractures[J]. Chin J Bone Joint Surg, 2021, 14(8):657-663. | |
| [2] | Jia DM, Zhang K, Xu YM. The relationship between social support and relapse tendency among those who struggle with drug addiction:multiple mediators of exercise self-efficacy and health-related quality of life[J]. J Drug News, 2024, 54(1):120-133. |
| [3] | 刘珊, 张先庚, 郭勤, 等. 康复锻炼自我效能在老年骨质疏松性髋部骨折患者心理弹性与生存质量间的中介效应分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2022, 49(19):3547-3552. |
| Liu S, Zhang XG, Guo Q, et al. The mediating effect of rehabilitation exercise self-efficacy on mental resilience and quality of life in elderly patients with osteoporotic hip fracture[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2022, 49(19):3547-3552. | |
| [4] | 王慧, 严妍, 汪纯. 健康管理对骨质疏松症患者和高危人群知识认知和自我效能的影响[J]. 上海医药, 2019, 40(24):34-37. |
| Wang H, Yan Y, Wang C. Effect of health management on knowledge cognition and self-efficacy of patients with osteoporosis and high risk populations[J]. Shanghai Med Pharm J, 2019, 40(24):34-37. | |
| [5] |
Sheehan KJ, Fitzgerald L, Lambe K, et al. Effectiveness of community-based rehabilitation interventions incorporating outdoor mobility on ambulatory ability and falls-related self-efficacy after hip fracture:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Arch Osteoporos, 2021, 16(1):99.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | 任晓冉, 史瑞洁, 彭晶, 等. 骨科康复期患者自我效能感的研究进展[J]. 上海护理, 2015, 15(5):70-73. |
| Ren XR, Shi RJ, Peng J, et al. Research progress on self-efficacy of patients in orthopedic rehabilitation period[J]. Shanghai Nurs, 2015, 15(5):70-73. | |
| [7] |
Rashid AA, Zuhra H, Tan CE. Social support,self-efficacy and their correlation among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus:a primary care perspective[J]. Med J Malaysia, 2018, 73(4):197-201.
PMID |
| [8] | Pedersen HS, Christensen KS, Prior A, et al. The dimensionality of the Perceived Stress Scale:the presence of opposing items is a source of measurement error[J]. J Affect Disord, 2024, 344:485-494. |
| [9] | 王永炫, 李梅, 章振林, 等. 《原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)》要点解读[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2023, 14(6):1203-1207. |
| Wang YX, Li M, Zhang ZL, et al. Interpretation on the guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of primary osteoporosis(2022)[J]. Med J Peking Union Med Coll Hosp, 2023, 14(6):1203-1207. | |
| [10] |
Cleeland CS, Mendoza TR, Wang XS, et al. Assessing symptom distress in cancer patients:the M.D. Anderson Symptom Inven-tory[J]. Cancer, 2000, 89(7):1634-1646.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Freund T, Gensichen J, Goetz K, et al. Evaluating self-efficacy for managing chronic disease:psychometric properties of the six-item Self-Efficacy Scale in Germany[J]. J Eval Clin Pract, 2013, 19(1):39-43. |
| [12] | 刘继文, 李富业, 连玉龙. 社会支持评定量表的信度效度研究[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2008, 31(1):1-3. |
| Liu JW, Li FY, Lian YL. Research on reliability and validity of Social Support Rating Scale[J]. J Xinjiang Med Univ, 2008, 31(1):1-3. | |
| [13] | 杨廷忠, 黄汉腾. 社会转型中城市居民心理压力的流行病学研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2003, 24(9):760-764. |
| Yang TZ, Huang HD. An epidemiological study on stress among urban residents in social transition period[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2003, 24(9):760-764. | |
| [14] | Lavoie JAA, Douglas KS. The Perceived Stress Scale:evaluating configural,metric and scalar invariance across mental health status and gender[J]. J Psychopathol Behav Assess, 2012, 34(1):48-57. |
| [15] | 黄慧敏. 股骨颈骨折患者关节置换术后社会疏离水平及其相关危险因素分析[J]. 慢性病学杂志, 2023, 24(9):1400-1403. |
| Huang HM. Analysis of social distancing level and related risk factors in patients with femoral neck fracture after joint replacement[J]. Chron Pathol J, 2019, 24(9):1400-1403. | |
| [16] |
McArthur C, Gibbs JC, Ashe MC, et al. The association between trunk muscle endurance,balance and falls self-efficacy in women with osteoporotic vertebral fractures:an exploratory analysis from a pilot randomized controlled trial[J]. Disabil Rehabil, 2021, 43(16):2268-2274.
DOI |
| [17] |
Ma XX, Xue CH, Wang X, et al. Effect of multi-platform extended care on postoperative self-efficacy and quality of life in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compressive fracture[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13(6):6945-6951.
PMID |
| [18] |
邓雁, 余琼, 武福姣, 等. 基于自我效能理论的护理干预对食管癌根治术后患者的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9):1042- 1048.
DOI URL |
| Deng Y, Yu Q, Wu FJ, et al. Effect of nursing intervention based on self-efficacy theory on patients with esophageal cancer after radical surgery[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(9):1042-1048. | |
| [19] |
Morse L, Cooper BA, Ritchie CS, et al. Stability and consistency of symptom clusters in younger versus older patients receiving chemotherapy[J]. BMC Geriatr, 2024, 24(1):164.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Endrighi R, Dimond AJ, Waters AJ, et al. Associations of perceived stress and state anger with symptom burden and functional status in patients with heart failure[J]. Psychol Health, 2019, 34(10):1250-1266.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | 杨露, 罗娟, 姚佳伟. 社会支持对老年人健康的影响机制研究[J]. 经济研究导刊, 2022(4):53-55. |
| Yang L, Luo J, Yao JW. Study on the impact mechanism of social support on the health status of the elderly[J]. Econ Res Guide, 2022(4):53-55. | |
| [22] |
Erdemsoy Karahan B, Izgu N. Impact of symptom burden and self-efficacy on functional status in advanced breast cancer patients:a path analysis[J]. Nurs Health Sci, 2023, 25(3):354-364.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
郦杭婷, 沈娇妮, 万昕瑞, 等. 髋膝关节置换术患者康复自我效能感在正念与恐动症间的中介效应研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(10):1177-1183.
DOI URL |
|
Li HT, Shen JN, Wan XR, et al. The mediating effect of rehabilitation self-efficacy between mindfulness and kinesiophobia in patients undergoing hip or knee arthroplasty[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(10):1177-1183.
DOI URL |
|
| [24] | Lin Q, Fu MX, Sun K, et al. The mediating role of perceived social support on the relationship between lack of occupational coping self-efficacy and implicit absenteeism among intensive care unit nurses:a multicenter cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Health Serv Res, 2024, 24(1):653. |
| [1] | HUANG Panpan, LI Liling, HU Xiaojing. Research progress of early exercise rehabilitation in infants with congenital heart disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [2] | CHEN Liou, ZHANG Wenting, LIU Junqi, WANG Yuncong, WANG Zhenlin, QI Sai, YANG Na. Study on the effect of pulmonary lobes surface projection localization combined with pulmonary segment drainage and sputum expectoration technique on airway clearance in patients with aspiration pneumonia [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [3] | YANG Nana, CHENG Chuanli, ZENG Hui, FU Dandan, WANG Yan, CHEN Yue, RAN Hongmin, FAN Hongjing, LONG Xia. Evaluation of the effect of graded exercise rehabilitation on patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [4] | CAO Yun, SUN Guozhen, CHEN Feng, JI Xueli, YAN Mengwan, JING Lei, QIAN Kun. A study of modified ankle pump exercise in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [5] | XIE Min, QI Wenkai, YIN Ling, ZHANG Xuan, ZHAO Ruqin. Potential profile analysis and influencing factors of kinesiophobia in patients with peritoneal dialysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [6] | CHEN Bingqian, ZHAO Bin, SUN Jiarong, HAO Sifang, HOU Xiaoli. Oral health management dilemmas of chronic periodontitis patients with implant dentures:a qualitative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [7] | QIN Chunlan, WU Zhenyun, QIAN Hongying, ZHAO Qian, SUN Jinting. Experiences of disease self-control among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:a qualitative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [8] | LI Ziwei, FENG Lijuan, CHEN Xusheng, HUANG Yi, YANG Jie. Development and application of a Fear of Movement Assessment Scale for patients with peripherally inserted central catheters [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [9] | CHENG Zhiqiang, ZHANG Baozhen, TANG Liping, LI Jing, XIA Jiaoyun, WEI Xueyan, GONG Zhixian, ZHANG Meizhen, LI Lusi. Reliability and validity test of the Chinese version of the Urinary Incontinence Awareness and Attitude Scale [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [10] | SHI Meiqin, WU Jianfang, ZHANG Duo, WU Chunping, CHEN Ling, TAO Lei. Nursing care for postoperative laryngeal function rehabilitation in a patient undergoing primary voice prosthesis implantation after total laryngectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [11] | GU Qian, HUANG Xi, SHI Weixiong, WU Jing, TAN Ruoming, WANG Feng. Nursing care for a patient with cytokine release syndrome following T-cell immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| [12] | ZHOU Miao, CHEN Xing, PENG Fei, SUN Shangxue, LI Yangyang. Systematic review of risk prediction instruments for central line associated bloodstream infections in ICU patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1132-1139. |
| [13] | PENG Yingjie, LIU Aihong, ZHU Wenli, MEI Yuxin, ZHOU Meng, GUAN Wenjing. Systematic review of readiness assessment tools for advance care planning in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1146-1153. |
| [14] | RAN Lingxiao, WANG Dongmin, XU Ke, WANG Cong, CAO Hua, CUN Wei, JIANG Yan. Application of biomechanical simulation based on three-dimensional human body model in preventing pressure ulcers:a scoping review [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 1012-1018. |
| [15] | JIN Yujia, JIANG Hu, WANG Xiaoxuan, YI Jingna, MEI Yongxia, GUO Zhiting, ZHANG Zhenxiang, LIN Beilei. Application of information-based risk communication in primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases:a scoping review [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 1019-1025. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||