


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (21): 2572-2578.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.21.002
• Special Planning—Liver Transplant Nursing • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Yile( ), YANG Yan(
), YANG Yan( ), CHEN Guoli
), CHEN Guoli
Received:2025-03-11
Online:2025-11-10
Published:2025-11-05
Contact:
YANG Yan
通讯作者:
杨艳
作者简介:黄一乐:男,本科(硕士在读),副主任护师,护士长,E-mail:huang_yile@163.com
HUANG Yile, YANG Yan, CHEN Guoli. Trend of the temperature variation for hypothermia during pediatric living-donor liver transplantation and nursing implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(21): 2572-2578.
黄一乐, 杨艳, 陈国立. 婴幼儿活体肝移植术中体温变化趋势及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(21): 2572-2578.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.21.002
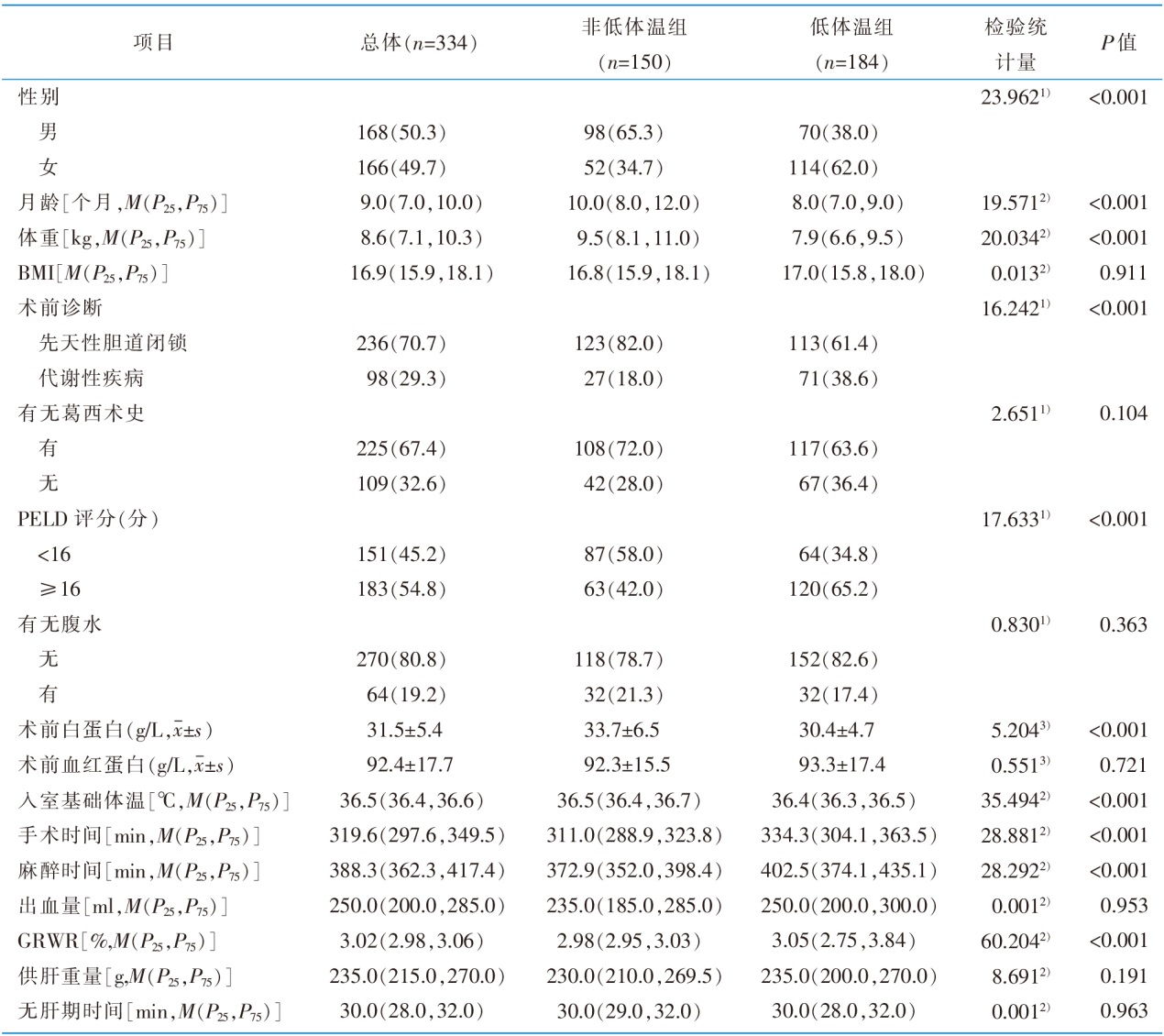 |
Table 1 Univariate analysis of the general information of the subjects and the influencing factors of hypothermia during living donor liver transplantation
 |
| [1] | 夏强, 朱欣烨. 儿童肝移植发展现状及展望[J]. 临床小儿外科杂志, 2022, 21(5):401-404. |
| Xia Q, Zhu XY. Current development and future outlook of pediatric liver transplantation[J]. J Clin Pediatr Surg, 2022, 21(5):401-404. | |
| [2] | Kehar M, Parekh RS, Stunguris J, et al. Superior outcomes and reduced wait times in pediatric recipients of living donor liver transplantation[J]. Transplant Direct, 2019, 5(3):e430. |
| [3] | 曹义, 彭玉娜, 王曼, 等. 肝移植患儿术中低体温发生现状及影响因素分析[J]. 天津护理, 2023, 31(2):146-149. |
| Cao Y, Peng YN, Wang M, et al. Analysis of the status and influencing factors of intraoperative hypothermia in pediatric patients undergoing liver transplantation[J]. Tianjin J Nurs, 2023, 31(2):146-149. | |
| [4] |
Beedle SE, Phillips A, Wiggins S, et al. Preventing unplanned perioperative hypothermia in children[J]. AORN J, 2017, 105(2):170-183.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
李丽, 颜艳, 房馨, 等. 腹腔镜手术患者术中低体温风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(4):463-468.
DOI |
|
Li L, Yan Y, Fang X, et al. Establishment and validation of a risk prediction model for intraoperative hypothermia in patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(4):463-468.
DOI |
|
| [6] |
刘婷, 王林, 郝艳丽, 等. 不停跳冠状动脉旁路移植患者术中低体温风险预测模型的构建[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(20):2481-2487.
DOI |
|
Liu T, Wang L, Hao YL, et al. Construction of a preoperative risk prediction nomogram model for hypothermia during off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(20):2481-2487.
DOI |
|
| [7] | 中华护理学会手术室护理专业委员会. 手术室护理实践指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010. |
| Operating Room Nursing Committee of Chinese Nursing Association. Practice guidelines for operating room nursing[M]. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2010. | |
| [8] | 李大伟, 陆天飞, 华相伟, 等. 儿童终末期肝病模型评分用于预测婴幼儿活体肝移植预后的作用[J]. 器官移植, 2014, 5(4):213-216. |
| Li DW, Lu TF, Hua XW, et al. Value of pediatric end-stage liver disease score in predicting prognosis after pediatric living donor liver transplantation[J]. Organ Transplant, 2014, 5(4):213-216. | |
| [9] |
Rhu J, Jung SM, Choe YH, et al. PELD score and age as a prognostic index of biliary atresia patients undergoing Kasai portoenterostomy[J]. Pediatr Surg Int, 2012, 28(4):385-391.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | 国家麻醉专业质量控制中心. 围术期患者低体温防治专家共识(2023版)[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2023, 14(4):734-743. |
| National Center for Quality Assurance of Anesthesia. 2023 Chinese expert consensus statement for prevention and management of perioperative hypothermia[J]. Med J Peking Union Med Coll Hosp,2023, 14(4):734-743. | |
| [11] | 于冬男, 李鹏, 吴群林, 等. 原位肝移植围术期核心体温变化趋势及应对策略[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2015, 31(12):1974-1977. |
| Yu DN, Li P, Wu QL, et al. Changes of core body temperature during perioperative period of orthotopic liver transplantation and its coping strategies[J]. J Pract Med, 2015, 31(12):1974-1977. | |
| [12] | 国家麻醉专业质量控制中心,中华医学会麻醉学分会. 围手术期患者低体温防治专家共识(2017)[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2017, 8(6):352-358. |
| National Center for Quality Control of Anesthesiology,Chinese Society of Anesthesiology. Expert consensus on prevention and treatment of hypothermia in perioperative patients(2017)[J]. Med J Peking Union Med Coll Hosp, 2017, 8(6):352-358. | |
| [13] | 季彬, 徐维虹, 陈航, 等. 儿童术中低体温列线图预测模型构建[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(1):39-41. |
| Ji B, Xu WH, Chen H, et al. A nomogram model to predict intraoperative hypothermia in children[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(1):39-41. | |
| [14] | Nemeth M, Miller C, Bräuer A. Perioperative hypothermia in children[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18(14):7541. |
| [15] | Lai L, See MH, Rampal S, et al. Significant factors influencing inadvertent hypothermia in pediatric anesthesia[J]. J Clin Monit Comput, 2019, 33(6):1105-1112. |
| [16] | Gao Y, Fan JB, Zhao JL, et al. Risk factors for intraoperative hypothermia in infants during general anesthesia:a retrospective study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2023, 102(34):e34935. |
| [17] | Hooper VD, Chard R, Clifford T, et al. ASPAN’s evidence-based clinical practice guideline for the promotion of perioperative normothermia:second edition[J]. J Perianesth Nurs, 2010, 25(6):346-365. |
| [18] | AORN. Guideline for prevention of hypothermia[M]. Denver, CO: 2020. |
| [19] | Han SB, Gwak MS, Choi SJ, et al. Risk factors for inadvertent hypothermia during adult living-donor liver transplantation[J]. Transplant Proc, 2014, 46(3):705-708. |
| [20] | 黄一乐, 胡文娟. 手术患者术中低体温危险因素评价指标体系的构建[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2016(35):2727-2730. |
| Huang YL, Hu WJ. Development of risk factors evaluation index system for perioperative hypothermia[J]. Chin J Pract Nurs, 2016(35):2727-2730. | |
| [21] |
Sessler DI. Perioperative thermoregulation and heat balance[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10038):2655-2664.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
余文静, 肖瑶, 胡娟娟, 等. 预防围手术期患者低体温的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(4):589-594.
DOI |
|
Yu WJ, Xiao Y, Hu JJ, et al. Evidence summary for prevention of perioperative hypothermia in patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(4):589-594.
DOI |
| [1] | ZENG Fei, LAN Meijuan, GU Peipei, LIANG Jiangshuyuan, WANG Yandie, CAI Lingyun. Construction and preliminary verification of a postoperative pulmonary rehabilitation nursing program for children with double lung transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | YAN Yinzhi, WEN Fang, WANG Min, ZHOU Xuemei, MA Jinling, WU Huifang, YAO Wenying. Construction and application of a graded nursing program for exercise rehabilitation in children with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | LIU Xixuan, LIU Yulin, LIU Sha, YANG Fan, XIE Xiaohong, WANG Zijuan, LIU Lifang, WEI Hongyu. Construction and effect evaluation of the respiratory rehabilitation calisthenics for school-age children with bronchial asthma [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | YANG Jing, WANG Huafen, LU Fangyan, BAO Ruijie, ZHU Li. Analysis influencing factors of nutritional status changes in pediatric liver transplant patients and nursing revelation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [5] | HAN Shanshan, QIN Yongping, QU Hong, ZHENG Xianlan. Construction and validation of a risk prediction model for intraoperative acquired pressure injury in neurosurgical children [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 928-933. |
| [6] | LIU Fang, LIU Yunfang, DE Zong, PI Rong, HE Zihan, LI Suyun. Analysis of thirst sensation in patients with cirrhosis and its influencing factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 934-939. |
| [7] | LIANG Jiangshuyuan, WANG Yandie, ZENG Fei, LAN Meijuan, GU Peipei. Nursing care of 14 children after double lung transplantation for secondary bronchiolitis obliterans after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 972-976. |
| [8] | ZHOU Kebing, HUANG Xiaojiao, YAN Fengxia. Network analysis of symptom burden and its influencing factors in first-ever subacute stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(7): 792-798. |
| [9] | CHEN Lihua, HUANG Yao, SHENG Qingqing, TAN Yufeng, ZHANG Shuqin, HUANG Xiaoqun, XU Mengmeng. Status and influencing factors of feeding intolerance in patients with enteral nutrition after lung transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(7): 849-855. |
| [10] | ZHANG Ju, WEI Lili, XIN Chen, WANG Jing, HAN Yan, YANG Yanyan, SUN Mengzhu. Application research of immersive virtual reality technology in pediatric patients undergoing elective surgery under general anesthesia [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(6): 671-676. |
| [11] | HAN Wenwen, HU Chunxia, ZHANG Kai, SUI Weijing, HUANG Meili, PAN Hongying, GONG Xiaoyan, ZHUANG Yiyu. Remote nursing care for a pediatric patient with severe burns based on augmented reality technology:a case report [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(6): 677-679. |
| [12] | YANG Tongling, CHEN Yuying, WAN Fan, DOU Yalan, HU Xiaojing. Development and initial implementation of a neonatal home skin care guidance scheme [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(6): 680-687. |
| [13] | WANG Yandie, ZENG Fei, LIANG Jiangshuyuan, GU Peipei. Influencing factors and nursing enlightenment of bone metabolism abnormalities in lung transplant reci-pients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(6): 703-709. |
| [14] | TANG Nan, GAO Yuan, SU Qingqing, SONG Mi, QIU Chen, SHAO Mengqi. An analysis influencing factors of subsequent fracture among elderly osteoporotic patients and nursing countermeasures [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(6): 710-716. |
| [15] | CHEN Qianhe, CHEN Jun, JIANG Kaiyao, WU Xiaonan, HONG Wanting, ZHANG Chunmei. Qualitative study on the facilitating and obstacle factors of the pediatric medical fear intervention by pediatric nurses [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 575-580. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||