


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (23): 2835-2842.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.23.003
黄婵( ), 张海燕(
), 张海燕( ), 徐银环, 池艳宇, 王琳楠, 刘岩, 闵玉娣
), 徐银环, 池艳宇, 王琳楠, 刘岩, 闵玉娣
收稿日期:2025-07-31
出版日期:2025-12-10
发布日期:2025-12-15
通讯作者:
张海燕:E-mail:zhanghaiyan@pkuph.edu.cn作者简介:黄婵:女,硕士,副主任护师,护理部副主任,E-mail:huangchan_0@163.com
基金资助:
HUANG Chan( ), ZHANG Haiyan(
), ZHANG Haiyan( ), XU Yinhuan, CHI Yanyu, WANG Linnan, LIU Yan, MIN Yudi
), XU Yinhuan, CHI Yanyu, WANG Linnan, LIU Yan, MIN Yudi
Received:2025-07-31
Online:2025-12-10
Published:2025-12-15
摘要:
目的 通过质量改进行动提升住院患者静脉采血质量,评价质量改进行动的成本与效果,为高频护理操作流程的质量改进提供参考。方法 2023年1月18日—2024年10月13日,在北京市某三级甲等综合医院74个住院护理单元中,采用计划-实施-分析与研究-处理循环开展静脉采血质量改进行动。应用成本效果分析法,将静脉采血相关差错发生率、每千出院患者因重复采血延长的诊疗时长作为效果指标,将因重复采血增加的年化医疗成本、质量改进行动实施成本作为成本指标,评价静脉采血质量改进行动的成本与效果。结果 通过质量改进,全院住院患者静脉采血相关差错发生率从0.18%降低至0.03%(P<0.001);每千出院患者因重复采血延长的诊疗时长由1 853.89 min缩短至377.04 min;因重复采血增加的年化医疗成本由26 433.89元降低至4 160.30元;质量改进行动实施成本总计18.36万元。结论 通过质量改进行动能够降低静脉采血相关差错发生率,缩短因重复采血延长的诊疗时长,减少因重复采血增加的医疗成本,总体可提高护理质量、提升诊疗效率、减少医疗资源浪费。
黄婵, 张海燕, 徐银环, 池艳宇, 王琳楠, 刘岩, 闵玉娣. 静脉采血质量改进行动的成本效果分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(23): 2835-2842.
HUANG Chan, ZHANG Haiyan, XU Yinhuan, CHI Yanyu, WANG Linnan, LIU Yan, MIN Yudi. Cost-effectiveness analysis of quality improvement action for venous blood sampling[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(23): 2835-2842.
 |
表2 维持阶段静脉采血操作流程查检发现的质量问题(n=842)
Table 2 Inspection results of quality issues in venous blood sampling procedures during the sustainability phase(n=842)
 |
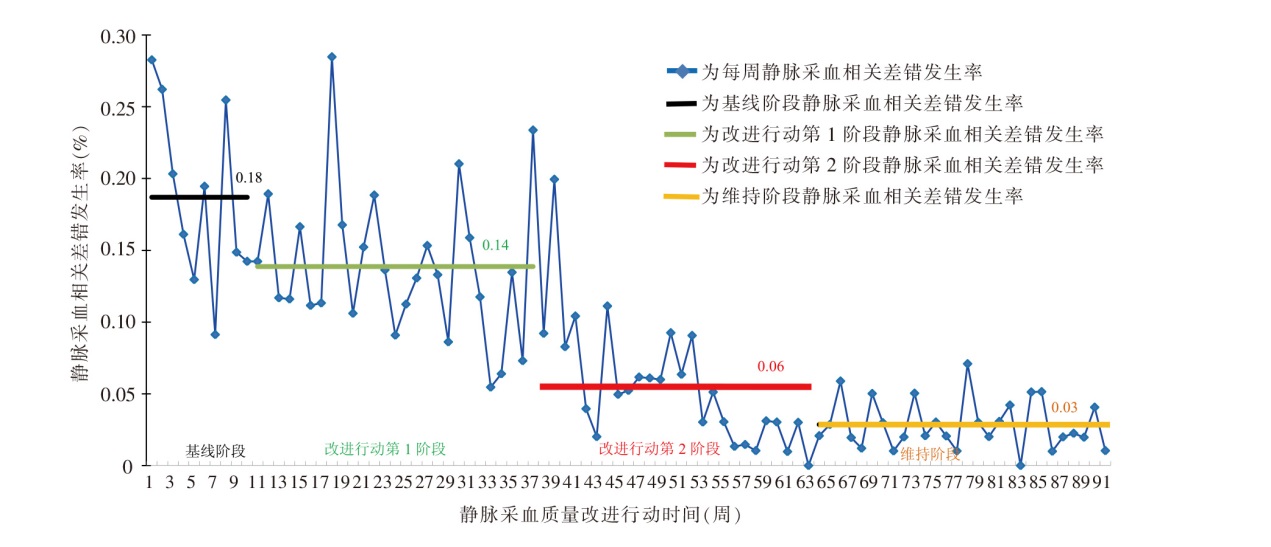
图1 静脉采血质量改进行动各阶段静脉采血相关差错发生率变化趋势
Figure 1 Trends in the incidence of venous blood sampling-related errors across different phases of quality improvement action
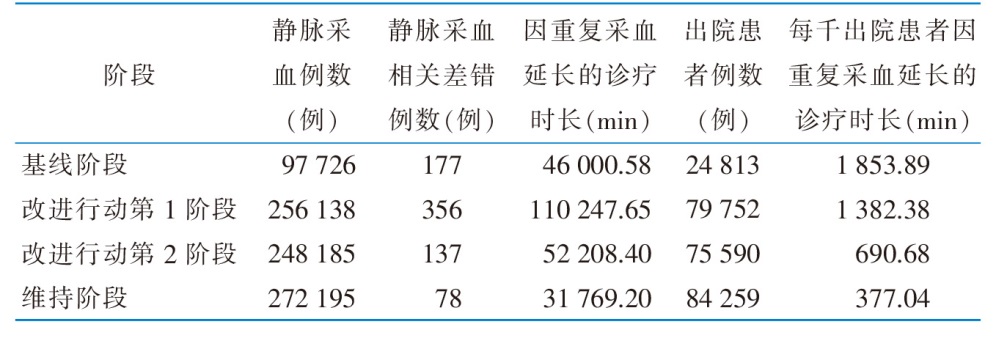 |
表5 静脉采血质量改进行动各阶段每千出院患者因重复采血延长的诊疗时长
Table 5 Prolonged diagnostic and treatment duration per 1 000 discharged patients due to repeated venous blood sampling at each phase of the quality improvement action
 |
| [1] | 中华医学会检验医学分会. 不合格静脉血标本管理中国专家共识[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2020, 43(10):956-963. |
| Chinese Society of Laboratory Medicine,Chinese Medical Asso-ciation. Chinese expert consensus on the management of un-qualified venous blood specimens[J]. Chin J Lab Med, 2020, 43(10):956-963. | |
| [2] |
Cheng XL, Yu HM, Zhang L, et al. Evaluation of pre-analytical specimen rejection using Six Sigma metrics:a retrospective single-center study[J]. PLoS One, 2025, 20(6):e0324840.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Mesganaw B, Misganaw K, Belayneh M. Trends and determi-nants of laboratory specimen rejection rates at Debre Markos comprehensive specialized hospital in Ethiopia[J]. Sci Rep, 2025, 15:25823.
DOI |
| [4] | Atay A, Demir L, Cuhadar S, et al. Clinical biochemistry labora-tory rejection rates due to various types of preanalytical errors[J]. Biochem Med(Zagreb), 2014, 24(3):376-382. |
| [5] |
Lippi G, von Meyer A, Cadamuro J, et al. Blood sample quality[J]. Diagnosis (Berl), 2019, 6(1):25-31.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 临床实验室质量指标:WS/T 496-2017[EB/OL].(2017-02-09)[2025-07-20]. https://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/s9492/201702/93f8eb60e0f34fc896af74f13ac53562.shtml. |
| National Health and Family Planning Commission. Clinical labo-ratory quality indicators:WS/T 496-2017[EB/OL].(2017-02-09)[2025-07-20]. https://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/s9492/201702/93f8eb60e0f34fc896af74f13ac53562.shtml. | |
| [7] | 北京市卫生健康委员会. 关于印发北京市各医疗质量控制和改进中心2020年度工作要点的通知[EB/OL].(2020-05-27)[2025-07-20]. https://wjw.beijing.gov.cn/zwgk_20040/ghjh1/202005/t2020-0527_1909725.html. |
| Beijing Municipal Health Commission. Notice on printing and distributing the 2020 annual work priorities of Beijing medical quality control and improvement centers[EB/OL].(2020-05-27)[2025-07-20]. https://wjw.beijing.gov.cn/zwgk_20040/ghjh1/202005/t2020-0527_1909725.html. | |
| [8] | 秦薇, 王文超, 姚文杰, 等. 多学科多阶段预防ICU患者呼吸机相关性肺炎的质量改进策略[J]. 中华急危重症护理杂志, 2024, 5(7):649-655. |
| Qin W, Wang WC, Yao WJ, et al. Quality improvement strate-gies for the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia in ICU patients[J]. Chin J Emerg Crit Care Nurs, 2024, 5(7):649-655. | |
| [9] |
Zacherl KM, Sterrett EC, Hughes BL, et al. Ensuring safe and equitable discharge:a quality improvement initiative for indivi-duals with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy[J]. BMJ Qual Saf, 2024, 33(6):396-405.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 柴剑丽, 吴春燕, 王文娟, 等. 糖尿病肾病患者血液透析中低血糖管理的持续质量改进[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2015, 50(2):170-174. |
| Chai JL, Wu CY, Wang WJ, et al. Continuous quality improve-ment of hypoglycemia management during hemodialysis in patients with diabetic kidney disease[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2015, 50(2):170-174. | |
| [11] | International Council of Nurses. International Nurses Day 2024 theme announced:our nurses. our future. The economic power of care[EB/OL].(2024-01-16)[2025-06-30]. https://www.icn.ch/news/international-nurses-day-2024-theme-announced-our-nur-ses-our-future-economic-power-care. |
| [12] | 孟庆悦, 刘国祥. 卫生经济学[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2023. |
| Meng QY, Liu GX. Health economics[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2023. | |
| [13] | Christoff P. Running PDSA cycles[J]. Curr Probl Pediatr Ado-lesc Health Care, 2018, 48(8):198-201. |
| [14] |
Yuzeng S, Hui L. Improving the wait time to triage at the emergency department[J]. BMJ Open Qual, 2020, 9(1):e000708.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Sondh RS, Mankotia R. Reducing prolonged fasting for abdo-minal ultrasound scans[J]. BMJ Open Qual, 2023, 12(3):e002396.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Jaekel C, Becker DP, Voss Y. Use of PDSA cycles to increase aspiration risk and swallow screening documentation in the hospitalized general medical patient care population[J]. J Nurs Care Qual, 2023, 38(1):89-95.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | 国家卫生健康委员会. 静脉血液标本采集指南:WS/T661—2020[EB/OL].(2020-04-15)[2025-07-20]. https://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/s9492/202004/c09a4128e8194e40baad2498fd8a1f26.shtml. |
| National Health Commission. Guide for venous blood speci-men collection:WS/T 661—2020[EB/OL].(2020-04-15)[2025-07-20]. https://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/s9492/202004/c09a4128e8194e40baad2498fd8a1f26.shtml. | |
| [18] | Kaplan RS, Anderson SR. Time-driven activity-based costing[J]. Harv Bus Rev, 2004, 82(11):131-138,150. |
| [19] |
Gupta P, Thomas M, Sbetan N, et al. A quality improvement initiative to reduce rejected laboratory samples and enhance specimen acceptability[J]. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf, 2021, 47(8):519-525.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | 张杰, 骆金铠, 毛文平, 等. 基于患者全息视图的静脉血标本检验前质量管理路径的构建与应用[J]. 中国护理管理, 2023, 23(12):1894-1898. |
| Zhang J, Luo JK, Mao WP, et al. Construction and application of a quality management pathway for venous blood specimens before the test based on the holographic view system of patients[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2023, 23(12):1894-1898. | |
| [21] |
朱力, 史冬雷, 王军, 等. 信息化采血登记平台的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(3):383-386.
DOI |
|
Zhu L, Shi DL, Wang J, et al. Construction and application of an informationized platform of blood collection[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(3):383-386.
DOI |
|
| [22] | 李有, 周芸, 尉志刚, 等. 基于多学科协作的PDSA循环在静脉血栓栓塞症防治中的应用[J]. 护理研究, 2024, 38(11):2063-2068. |
| Li Y, Zhou Y, Wei ZG, et al. Application of PDSA circulation based on multidisciplinary collaboration in the prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolism[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2024, 38(11):2063-2068. | |
| [23] | Bugnitz C, Sandberg KC. Creating effective PDSA cycles[J]. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care, 2025, 55(4):101759. |
| [24] |
王凯蓉, 周英凤, 张晓菊, 等. 两种中心静脉输液技术的成本效果分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(4):574-581.
DOI |
|
Wang KR, Zhou YF, Zhang XJ, et al. A cost-effectiveness analysis of peripherally inserted central catheter versus totally implanted venous port[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(4):574-581.
DOI |
|
| [25] | 国家中医药局, 国家卫生健康委. 关于开展全面提升医疗质量行动(2023-2025年)的通知[EB/OL].(2023-05-26)[2025-07-20]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202305/content_688-3704.htm. |
| National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Na-tional Health Commission. Notice on launching the action for comprehensive improvement of medical quality(2023-2025)[EB/OL].(2023-05-26)[2025-07-20]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202305/content_688-3704.htm. |
| [1] | 姜珊, 郭彩霞, 郭立华, 赵媛媛, 肖蒙, 杨依玲, 魏春艳, 李硕, 刘殿媛, 尚志丽. 外周静脉留置针并发症风险管理系统的开发与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 908-913. |
| [2] | 明爱红, 龙秀红, 梁志金, 李砺, 黎凤民, 林思慧, 杨云帆, 王智慧, 冯甜. 国内医疗护理员培训和管理省级政策的文本分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 960-967. |
| [3] | 黄婵, 池艳宇, 闵玉娣, 曹培叶, 刘君, 郑镕昕, 张海燕. 基于信息交互需求的护理会诊信息系统的开发及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 645-651. |
| [4] | 田君叶, 张霞, 苏莉, 孙路路, 赵瑾, 丁炎明. 专科护士培训信息管理平台的建设与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 652-658. |
| [5] | 江燕, 谭莉, 邹明君, 冉懋君, 李文苑, 马佳钦. 护士主导的智能化医疗废物暂存设备的研发及实用性评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 659-665. |
| [6] | 朱雨涵, 李文佳, 祝雪花. 国内长期照护护理队伍建设现行政策分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 729-735. |
| [7] | 魏永婷, 田书梅, 杨娇, 余良欢, 倪福, 范雨晴, 肖瑶, 席祖洋, 沙菊艳, 刘聪. 护士循证决策能力量表的汉化及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 736-742. |
| [8] | 李燕, 吴雪, 庞建美, 强万敏, 杨川川, 孙盛楠, 李静. 24个省份胸外科护士围手术期肺康复知信行的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 569-574. |
| [9] | 施金丽, 莫军军, 鲁玲玲, 陈叶. 442所消毒供应中心应对新发突发传染病应急处置管理现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 589-595. |
| [10] | 崔钰震, 姚卓娅, 耿军辉, 李漫春, 詹朦, 丁丽娜, 蒋恩社. 河南省348所医疗机构口腔器械清洗消毒灭菌管理现状及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 596-602. |
| [11] | 杜洁, 余强, 李亚敏. 轮班制护士睡眠质量非药物干预的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 629-634. |
| [12] | 徐娉, 王华芬, 封亚萍, 徐婷, 许涛, 陶月仙. 安宁疗护中护士的死亡态度对悲伤情绪影响的路径分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 319-324. |
| [13] | 蒲江锋, 王婉儿, 李格格, 谢章浩, 许怡璇, 詹宁静, 黄惠根. 护士组织支持感现状及潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 340-346. |
| [14] | 赵蕊, 范文琪, 刘晓夏, 葛莉娜. 基于机器学习的3种妇产科护士共情疲劳风险预测模型的构建与比较[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 347-354. |
| [15] | 柏新蕊, 张红燕, 安宁, 韩琳. 价值共创视角下数字赋能护理质量管理的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 379-384. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||