


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (3): 347-354.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.03.013
收稿日期:2024-04-08
出版日期:2025-02-10
发布日期:2025-01-22
通讯作者:
葛莉娜,E-mail:geln@sj-hospital.org作者简介:赵蕊:女,硕士,护师,E-mail:Zrui651394@163.com
基金资助:
ZHAO Rui( ), FAN Wenqi, LIU Xiaoxia, GE Lina(
), FAN Wenqi, LIU Xiaoxia, GE Lina( )
)
Received:2024-04-08
Online:2025-02-10
Published:2025-01-22
摘要:
目的 基于机器学习构建3种妇产科护士共情疲劳的风险预测模型,比较不同模型的预测性能。方法 采用便利抽样法,于2022年12月—2023年3月选取9个城市11所三级甲等医院的1 323名妇产科护士作为调查对象,按照7∶3的比例随机分为训练集和测试集,采用同情疲劳量表、五因素正念度量表及情绪智力量表进行调查。基于机器学习构建妇产科护士共情疲劳的Logistic回归模型、决策树模型和随机森林模型3种风险预测模型,比较各模型的准确率、精确率、灵敏度、F1指数和受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线下面积(area under the curve,AUC),评价模型的预测性能。结果 最终1 276名妇产科护士完成调查。3种模型均显示,正念水平、情绪智力、用工性质和工作年限是妇产科护士共情疲劳的影响因素(P<0.05)。Logistic回归模型、决策树模型和随机森林模型的准确率分别为0.804、0.806、0.796,精确率分别为0.821、0.827、0.823,灵敏度分别为0.956、0.949、0.939,F1指数分别为0.883、0.884、0.877,AUC分别为0.704(95%CI为0.701~0.713)、0.760(95%CI为0.751~0.771)、0.742(95%CI为0.723~0.762)。结论 通过决策树构建的妇产科护士共情疲劳风险预测模型性能优于随机森林模型和Logistic回归模型,多模型有效结合预测妇产科护士共情疲劳的发生风险、多维度探索影响因素交互作用,可为共情疲劳的早期识别和预防、相关干预措施的制订提供参考。
赵蕊, 范文琪, 刘晓夏, 葛莉娜. 基于机器学习的3种妇产科护士共情疲劳风险预测模型的构建与比较[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 347-354.
ZHAO Rui, FAN Wenqi, LIU Xiaoxia, GE Lina. Establishment and comparison of 3 compassion fatigue risk prediction models for obstetrics and gynaecology nurses based on machine learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(3): 347-354.
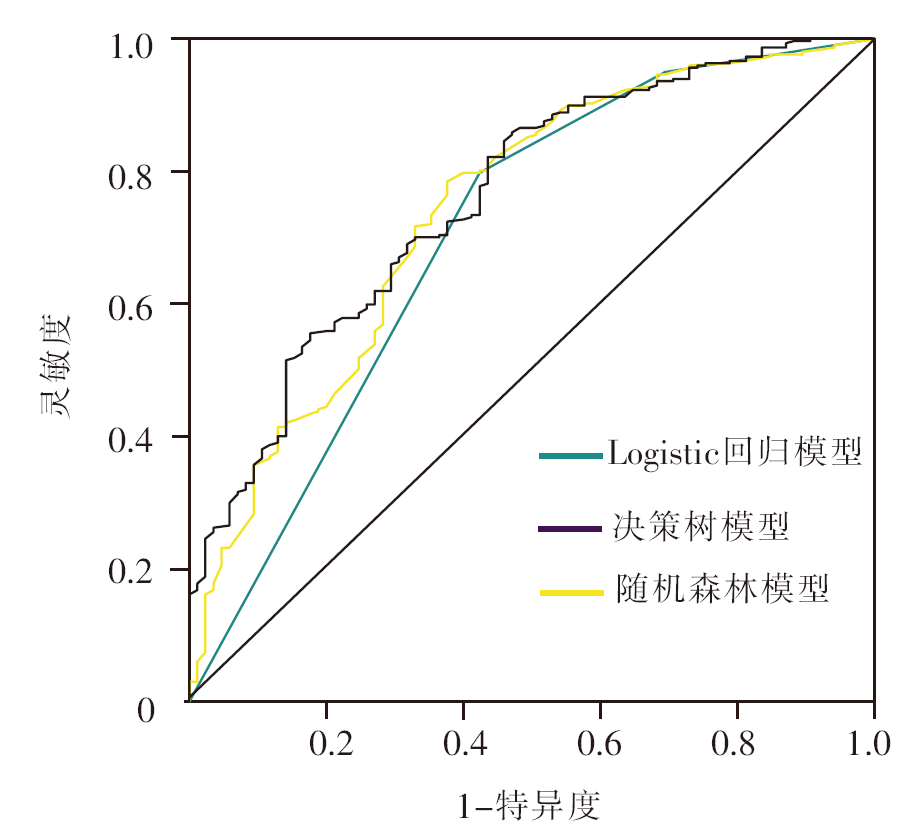
图1 3种风险预测模型预测妇产科护士共情疲劳的受试者工作特征曲线
Figure 1 Receiver operating characteristic curve of 3 risk assessment models predicting compassion fatigue in obstetrics and gynecology nurses
| [1] | Ondrejková N, Halamová J. Prevalence of compassion fatigue among helping professions and relationship to compassion for others,self-compassion and self-criticism[J]. Health Soc Care Com-munity, 2022, 30(5):1680-1694. |
| [2] | 田梅梅, 范霖, 施雁, 等. 临床护士共情疲劳的现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(1):76-82. |
| Tian MM, Fan L, Shi Y, et al. The current status and influencing factors of compassion fatigue in clinical nurses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(1):76-82. | |
| [3] | Favrod C, Jan du Chêne L, Martin Soelch C, et al. Mental health symptoms and work-related stressors in hospital midwives and NICU nurses:a mixed methods study[J]. Front Psychiatry, 2018, 9:364. |
| [4] | Wang J, Su M, Chang WZ, et al. Factors associated with com-passion fatigue and compassion satisfaction in obstetrics and gynaecology nurses:a cross-sectional study[J]. Nurs Open, 2023, 10(8):5509-5520. |
| [5] | Labrague LJ, de Los Santos JAA. Resilience as a mediator bet-ween compassion fatigue,nurses’ work outcomes,and quality of care during the COVID-19 pandemic[J]. Appl Nurs Res, 2021, 61:151476. |
| [6] |
丛胜楠, 张爱霞, 刘颖, 等. 江苏省妇产专科医院护士共情疲劳的影响因素及路径分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(8):977-984.
DOI URL |
|
Cong SN, Zhang AX, Liu Y, et al. Analysis of influencing factors and impact path of compassion fatigue in nurses from maternity hospitals in Jiangsu[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(8):977-984.
DOI URL |
|
| [7] |
曲超然, 王青, 韩琳, 等. 机器学习算法在压力性损伤管理中的应用进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(2):212-217.
DOI URL |
|
Qu CR, Wang Q, Han L, et al. A literature review on the application of machine learning algorithms in pressure injury management[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(2):212-217.
DOI URL |
|
| [8] | Stamm BH. The Concise ProQOL Manual:the concise manual for the Professional Quality of Life Scale[M]. 2nd ed. East-woods, 2010. |
| [9] | 陈华英, 王卫红. 中文版同情疲劳量表的信度、效度研究[J]. 中国护理管理, 2013, 13(4):39-41. |
| Chen HY, Wang WH. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Compassion Fatigue Scale[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2013, 13(1):39-41 | |
| [10] | Baer RA, Smith GT, Hopkins J, et al. Using self-report assess-ment methods to explore facets of mindfulness[J]. Assessment, 2006, 13(1):27-45. |
| [11] | Deng YQ, Liu XH, Rodriguez MA, et al. The Five Facet Mind-fulness Questionnaire:psychometric properties of the Chinese version[J]. Mindfulness, 2011, 2(2):123-128. |
| [12] | Salovey P, Mayer JD. Emotional intelligence[J]. Imagin Cogn Pers, 1990, 9(3):185-211. |
| [13] | Wong CS, Law KS, Wong PM. Development and validation of a forced choice emotional intelligence measure for Chinese respondents in Hong Kong[J]. Asia Pac J Manag, 2004, 21(4):535-559. |
| [14] | Xie WQ, Liu ML, Okoli CTC, et al. Construction and evalua-tion of a predictive model for compassion fatigue among emergency department nurses:a cross-sectional study[J]. Int J Nurs Stud, 2023, 148:104613. |
| [15] | Algamdi M. Prevalence of oncology nurses’ compassion sati-sfaction and compassion fatigue:systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Nurs Open, 2022, 9(1):44-56. |
| [16] | Guo SJ, Chang YL, Chang HW, et al. Patient satisfaction with nurses’ care is positively related to the nurse-patient relation-ship in Chinese hospitals:a multicentre study[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10:1109313. |
| [17] | Kartsonaki MG, Georgopoulos D, Kondili E, et al. Prevalence and factors associated with compassion fatigue,compassion satisfaction,burnout in health professionals[J]. Nurs Crit Care, 2023, 28(2):225-235. |
| [18] | 张宇婷, 刘瑞云, 焦雪萍. 肿瘤科护士关怀能力、职业倦怠与护理缺失的相关性[J]. 护理研究, 2021, 35(11):2046-2049. |
| Zhang YT, Liu RY, Jiao XP. Correlation among caring ability,job burnout and missed nursing care in oncology nurses[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2021, 35(11):2046-2049. | |
| [19] | İlter SM, Ovayolu Ö, Serçe S, et al. An investigation of the relationship between compassion fatigue and moral sensitivity of intensive care nurses[J]. Omega, 2022:302228221107976. |
| [20] |
廖俪雯, 王琳. 护士心理弹性干预的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(8):942-949.
DOI URL |
| Liao LW, Wang L. Research progress on resilience interven-tion for nurses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(8):942-949. | |
| [21] | 陈莉莉, 寇红艳, 李霜, 等. 川东北地区手术室护士共情疲劳现状及主客观影响因素分析[J]. 卫生职业教育, 2023, 41(6):135-139. |
| Chen LL, Kou HY, Li S, et al. Analysis of compassion fatigue status and subjective and objective influencing factors of operating room nurses in northeast Sichuan[J]. Health Vocat Educ, 2023, 41(6):135-139. | |
| [22] | 姚雪, 谢仙萍, 张晓红, 等. 某新建三甲医院护士离职状况研究[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2019, 19(21):3701-3703. |
| Yao X, Xie XP, Zhang XH, et al. A study on the resignation of nurses in a newly built tertiary hospital[J]. Chin Remedies Clin, 2019, 19(21):3701-3703. | |
| [23] |
Shahar I, Asher I, Ben Natan M. Compassion fatigue among nurses working in a long-term care facility:the Israeli expe-rience[J]. Nurs Health Sci, 2019, 21(3):291-296.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | O’Mahony S, Ziadni M, Hoerger M, et al. Compassion fatigue among palliative care clinicians:findings on personality factors and years of service[J]. Am J Hosp Palliat Care, 2018, 35(2):343-347. |
| [25] | Green AA, Kinchen EV. The effects of mindfulness meditation on stress and burnout in nurses[J]. J Holist Nurs, 2021, 39(4):356-368. |
| [26] | Wu XX, Hayter M, Lee AJ, et al. Nurses’ experiences of the effects of mindfulness training:a narrative review and qualita-tive meta-synthesis[J]. Nurse Educ Today, 2021, 100:104830. |
| [27] | Watts KJ, O’Connor M, Johnson CE, et al. Mindfulness-based compassion training for health professionals providing end-of-life care:impact,feasibility,and acceptability[J]. J Palliat Med, 2021, 24(9):1364-1374. |
| [28] | Maillet S, Read E. Work environment characteristics and emo-tional intelligence as correlates of nurses’ compassion satisfa-ction and compassion fatigue:a cross-sectional survey study[J]. Nurs Rep, 2021, 11(4):847-858. |
| [29] | Dugué M, Sirost O, Dosseville F. A literature review of emo-tional intelligence and nursing education[J]. Nurse Educ Pract, 2021, 54:103124. |
| [30] | Amir K, Betty A, Kenneth AM. Emotional intelligence as pre-dictor of compassion fatigue among mental health practitio-ners[J]. OALib, 2019, 6(5):1-10. |
| [31] | 刘晓玲, 赵华, 鲁闻燕, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者30天再入院风险预测模型的研究进展[J]. 中华急危重症护理杂志, 2023, 4(12):1142-1146. |
| Liu XL, Zhao H, Lu WY, et al. Research progress on risk prediction models for 30-day readmission of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chin J Emerg Crit Care Nurs, 2023, 4(12):1142-1146. | |
| [32] | Christodoulou E, Ma J, Collins GS, et al. A systematic review shows no performance benefit of machine learning over logis-tic regression for clinical prediction models[J]. J Clin Epide-miol, 2019, 110:12-22. |
| [33] | Wallace ML, Mentch L, Wheeler BJ, et al. Use and misuse of random forest variable importance metrics in medicine:demonstrations through incident stroke prediction[J]. BMC Med Res Methodol, 2023, 23(1):144. |
| [34] | Yun K, Lee YJ. Factors influencing depression in older adults according to family structure(older adults living with adult children,a spouse,or alone):data from the 2020 national older Koreans data[J]. J Korean Gerontol Nurs, 2022, 24(1):1-12. |
| [1] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [2] | 姜珊, 郭彩霞, 郭立华, 赵媛媛, 肖蒙, 杨依玲, 魏春艳, 李硕, 刘殿媛, 尚志丽. 外周静脉留置针并发症风险管理系统的开发与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 908-913. |
| [3] | 刘方, 刘云访, 德宗, 皮蓉, 何子涵, 李素云. 肝硬化患者口渴感现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 934-939. |
| [4] | 明爱红, 龙秀红, 梁志金, 李砺, 黎凤民, 林思慧, 杨云帆, 王智慧, 冯甜. 国内医疗护理员培训和管理省级政策的文本分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 960-967. |
| [5] | 周柯冰, 黄晓娇, 闫凤侠. 首发脑卒中恢复期患者症状负担及其影响因素的网络分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 792-798. |
| [6] | 陈丽花, 黄瑶, 盛青青, 谭玉凤, 张书琴, 黄小群, 徐蒙蒙. 肺移植术后肠内营养患者喂养不耐受的现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 849-855. |
| [7] | 黄婵, 池艳宇, 闵玉娣, 曹培叶, 刘君, 郑镕昕, 张海燕. 基于信息交互需求的护理会诊信息系统的开发及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 645-651. |
| [8] | 田君叶, 张霞, 苏莉, 孙路路, 赵瑾, 丁炎明. 专科护士培训信息管理平台的建设与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 652-658. |
| [9] | 江燕, 谭莉, 邹明君, 冉懋君, 李文苑, 马佳钦. 护士主导的智能化医疗废物暂存设备的研发及实用性评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 659-665. |
| [10] | 王衍蝶, 曾妃, 梁江淑渊, 顾培培. 肺移植患者骨代谢异常影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 703-709. |
| [11] | 唐楠, 高远, 苏清清, 宋咪, 邱晨, 邵梦琪. 老年骨质疏松患者再骨折影响因素分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 710-716. |
| [12] | 朱雨涵, 李文佳, 祝雪花. 国内长期照护护理队伍建设现行政策分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 729-735. |
| [13] | 魏永婷, 田书梅, 杨娇, 余良欢, 倪福, 范雨晴, 肖瑶, 席祖洋, 沙菊艳, 刘聪. 护士循证决策能力量表的汉化及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 736-742. |
| [14] | 李燕, 吴雪, 庞建美, 强万敏, 杨川川, 孙盛楠, 李静. 24个省份胸外科护士围手术期肺康复知信行的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 569-574. |
| [15] | 施金丽, 莫军军, 鲁玲玲, 陈叶. 442所消毒供应中心应对新发突发传染病应急处置管理现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 589-595. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||