


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (24): 3000-3006.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.24.008
平凌( ), 罗彩凤(
), 罗彩凤( ), 孙炜怡, 李倩, Natsuko K.Wood, 周洁玉, 许俊, 卢红艳
), 孙炜怡, 李倩, Natsuko K.Wood, 周洁玉, 许俊, 卢红艳
收稿日期:2025-03-25
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
罗彩凤,E-mail:lcf0105@163.com作者简介:平凌:女,本科(硕士在读),主管护师,E-mail:pinglingapple@qq.com
基金资助:
PING Ling( ), LUO Caifeng(
), LUO Caifeng( ), SUN Weiyi, LI Qian, Natsuko K.Wood, ZHOU Jieyu, XU Jun, LU Hongyan
), SUN Weiyi, LI Qian, Natsuko K.Wood, ZHOU Jieyu, XU Jun, LU Hongyan
Received:2025-03-25
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-19
摘要:
目的 探讨产后6个月内母婴喂养互动现状及潜在剖面,分析不同类别母婴喂养互动水平的影响因素,为制订针对性干预措施促进纯母乳喂养提供参考。 方法 采用便利抽样法,于2024年11—12月,选取江苏省7所三级甲等医院542名产后6个月内的产妇为调查对象,使用一般资料调查表、母乳喂养关系量表、母乳喂养自我效能简式量表进行调查。对产后6个月内母婴喂养互动水平进行潜在剖面分析,并通过单因素分析和Logistic回归分析探究不同剖面的影响因素。 结果 最终纳入468名产妇,其母乳喂养关系量表条目均分为(4.13±0.54)分。产后6个月内母婴喂养互动关系可分为“联结薄弱型”(55.13%)、“同步失调型”(11.32%)、“高效协同型”(33.55%)3个潜在剖面。Logistic回归分析结果显示,居住地、产后照顾者、母乳喂养方式、喂养类型、母乳喂养自我效能是产后6个月内母婴喂养互动水平的影响因素(均P<0.05)。 结论 产后6个月内母婴喂养互动处于中等偏上水平且存在异质性,可分为3个潜在剖面。医护人员应重点关注“联结薄弱型”和“同步失调型”母婴,根据不同潜在剖面的影响因素对母婴进行干预,以提高其母乳喂养水平。
平凌, 罗彩凤, 孙炜怡, 李倩, Natsuko K.Wood, 周洁玉, 许俊, 卢红艳. 产后6个月内母婴喂养互动现状及潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(24): 3000-3006.
PING Ling, LUO Caifeng, SUN Weiyi, LI Qian, Natsuko K.Wood, ZHOU Jieyu, XU Jun, LU Hongyan. Current status and latent profile analysis of mother-infant feeding interaction within 6 months postpartum[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(24): 3000-3006.
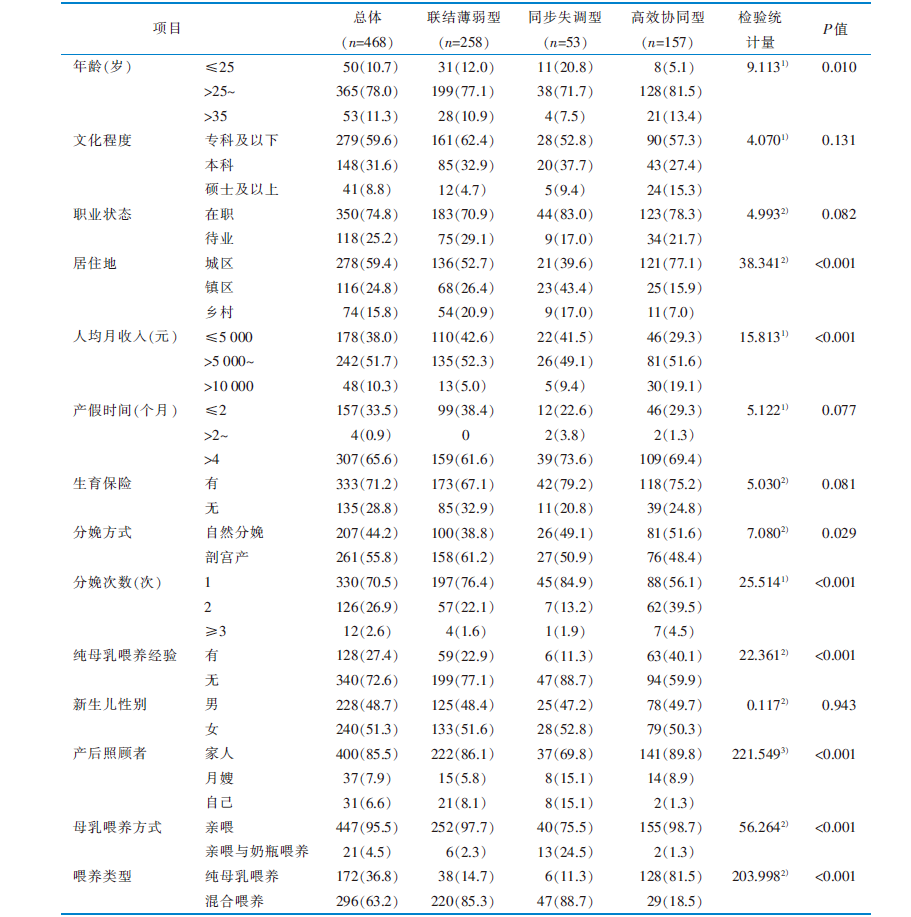 |
表1 调查对象的一般资料及母婴喂养互动水平3个潜在剖面的单因素分析结果[名(百分比,%)]
Table 1 Univariate analysis of 3 potential profiles of survey participants, general information and the feeding interaction[cases(percentage,%)]
 |
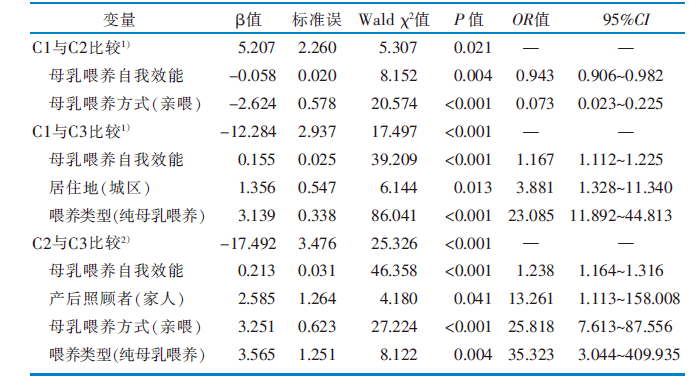 |
表4 产后6个月内母婴喂养互动水平潜在剖面的多元Logistic回归分析结果(n=468)
Table 4 Multivariate logistic regression analyses of potential profiles of the mother-infant feeding interaction in the first 6 months postpartum(n=468)
 |
| [1] | 国务院办公厅. 关于印发母乳喂养促进行动计划(2021-2025年)的通知[EB/OL].(2021-11-15)[2025-02-03]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-11/24/content_5653169.htm. |
| General Office of the State Council. Circular on the issuance of the breastfeeding promotion action plan(2021-2025)[EB/OL].(2021-11-15)[2025-02-03]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zheng-ceku/2021-11/24/content_5653169.htm. | |
| [2] | UNICEF,WHO. Global breastfeeding scorecard 2024:meeting the global target for breastfeeding requires bold commitments and accelerated action by governments and donors[EB/OL].(2024)[2025-06-20]. https://www.globalbreastfeedingcollective.org/media/2856/file. |
| [3] |
Farwell AL. Integrative review of breastfeeding duration and influencing factors among women serving active duty in the U.S. military[J]. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs, 2017, 46(2):171-181.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 欧阳婧, 周维敏, 汪柏云. 杭州市二胎产妇纯母乳喂养状况及影响因素分析[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2025, 40(2):318-321. |
| Ouyang J, Zhou WM, Wang BY. Analysis of exclusive breast-feeding status and influencing factors of second-born women in Hangzhou[J]. Matern Child Health Care China, 2025, 40(2):318-321. | |
| [5] | 汪维, 王欲晓, 屠蕾. 0-9月龄婴儿母乳喂养现状及母乳中断影响因素分析[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2021, 36(9):2117-2119. |
| Wang W, Wang YX, Tu L. Analysis on the current situation of breast-feeding and the influencing factors of breast-feeding interruption in infants aged 0-9 months[J]. Matern Child Health Care China, 2021, 36(9):2117-2119. | |
| [6] |
Newby RM, Davies PW. Why do women stop breast-feeding? Results from a contemporary prospective study in a cohort of Australian women[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2016, 70(12):1428-1432.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Safon C, Keene D, Guevara WJU, et al. Determinants of percei-ved insufficient milk among new mothers in León,Nicaragua[J]. Matern Child Nutr, 2017, 13(3):e12369.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Horta BL, Loret de Mola C, Victora CG. Long-term consequen-ces of breastfeeding on cholesterol,obesity,systolic blood pre-ssure and type 2 diabetes:a systematic review and meta-analy-sis[J]. Acta Paediatr, 2015, 104(467):30-37.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Chowdhury R, Sinha B, Sankar MJ, et al. Breastfeeding and ma-ternal health outcomes:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Acta Paediatr, 2015, 104(467):96-113.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Wood NK, Barbosa-Leiker C, Odom-Maryon T, et al. Instrument development and psychometric validation using confirmatory factor analysis of the Breastfeeding Relationship Scale[J]. J Nurs Meas, 2022, 30(3):449-463.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Wood NK, Barbosa-Leiker C, Odom-Maryon T. Determinants of exclusive direct breastfeeding using constructs from the Breast-feeding Relationship Scale[J]. J Reprod Infant Psychol, 2024, 42(5):949-963.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Little TD. The Oxford Handbook of quantitative methods in psychology:vol 2:statistical analysis[M]. Oxford: Oxford Univer-sity Press, 2013. |
| [13] | 倪平, 陈京立, 刘娜. 护理研究中量性研究的样本量估计[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010, 45(4):378-380. |
| Ni P, Chen JL, Liu N. The sample size estimation in quantita-tive nursing research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010, 45(4):378-380. | |
| [14] | 蒲江锋, 王婉儿, 李格格, 等. 护士组织支持感现状及潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3):340-347. |
| Pu JF, Wang WE, Li GG, et al. Study on the current situation and latent profile analysis of nurses’ perceived organizational support[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(3):340-347. | |
| [15] |
Dennis CL. The breastfeeding self-efficacy scale:psychometric assessment of the short form[J]. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs, 2003, 32(6):734-744.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 刘延锦, 王敏, 董小方. 中文版母乳喂养自我效能简式量表的信效度研究[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2016, 32 (18):1361-1364. |
| Liu YJ, Wang M, Dong XF. Reliability and validity of Chinese version of the Breastfeeding Self-efficacy Scale short form[J]. Chin J Pract Nurs, 2016, 32 (18):1361-1364. | |
| [17] | 江苏省委办公厅. 江苏省关于优化生育政策促进人口长期均衡发展实施方案[EB/OL].(2022-03-01)[2025-02-12]. https://www.zgjssw.gov.cn/fabuting/shengweiwenjian/202203/t20-220301_7446842.sht. |
| General Office of CPC Jiangsu Provincial Committee. Jiangsu Province issued the implementation plan of Jiangsu Province on optimizing birth policy and promoting long-term balanced development of population[EB/OL].(2022-03-01)[2025-02-12]. https://www.zgjssw.gov.cn/fabuting/shengweiwenjian/202203/t20-220301_7446842.sht. | |
| [18] | Kelly JF, Barnard KE. Assessment of parent-child interaction:implications for early intervention[M]//Handbook of Early Childhood Intervention. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000:258-289. |
| [19] |
钟娜, 胡琼燕, 梁旭霞, 等. 医院-社区母乳喂养链式管理模式的应用及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(14):1669-1675.
DOI URL |
| Zhong N, Hu QY, Liang XX, et al. Application and effect evaluation of a hospital-community breastfeeding chain mana-gement model[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(14):1669-1675. | |
| [20] | 刘维, 温燕. 产后早期家庭照顾者认知与行为干预对初产妇母乳喂养的影响[J]. 中国计划生育学杂志, 2022, 30(11):2522-2525. |
| Liu W, Wen Y. Effects of cognitive and behavioral interven-tion of family caregivers for early postpartum primiparas on the breastfeeding[J]. Chin J Fam Plan, 2022, 30(11):2522-2525. | |
| [21] | 邢翠, 舒晓芬, 刘莉. 家庭赋权护理对初产妇母乳喂养的影响[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(4):1-4. |
| Xing C, Shu XF, Liu L. Effect of family empowerment based nursing intervention on breastfeeding behavior of primiparous women[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(4):1-4. | |
| [22] | 裘梦凡, 胡晓静. 母乳亲喂婴儿吸吮-吞咽-呼吸机制的研究进展[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2023, 54(6):1306-1311. |
| Qiu MF, Hu XJ. Latest findings on the suck-swallow-breathe mechanism of direct breastfeeding from the breast to an infant[J]. J Sichuan Univ Med Sci, 2023, 54(6):1306-1311. | |
| [23] |
Higley E, Dozier M. Nighttime maternal responsiveness and infant attachment at one year[J]. Attach Hum Dev, 2009, 11(4):347-363.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Smith JM. Breastfeeding and language outcomes:a review of the literature[J]. J Commun Disord, 2015, 57:29-40.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Sinha B, Chowdhury R, Sankar MJ, et al. Interventions to im-prove breastfeeding outcomes:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Acta Paediatr, 2015, 104(467):114-134. |
| [26] | 赖雅君, 黄娟, 黄菲菲, 等. 母乳喂养自我效能感的研究进展[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2016, 33(22):33-36. |
| Lai YJ, Huang J, Huang FF, et al. Research progress on breast-feeding self-efficacy[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2016, 33(22):33-36. | |
| [27] |
Bandura A. Human agency in social cognitive theory[J]. Am Psychol, 1989, 44(9):1175-1184.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [2] | 李红颐, 李雪, 范宇莹, 赵一莎, 李京淑. ICU患者创伤心理反应的潜在剖面及影响因素的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 842-848. |
| [3] | 刘博文, 王珊珊, 孙倩倩, 梅永霞, 林蓓蕾, 刘腊梅, 张振香. 脑卒中患者及其配偶二元心理资本的潜在剖面分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 332-339. |
| [4] | 蒲江锋, 王婉儿, 李格格, 谢章浩, 许怡璇, 詹宁静, 黄惠根. 护士组织支持感现状及潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 340-346. |
| [5] | 徐雅萍, 贾云洋, 易祖玲, 许蕊凤, 佟冰度, 鲁雪梅. 老年髋部骨折患者出院准备度的潜在剖面分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(24): 2956-2963. |
| [6] | 陆沁怡, 陆程倩, 聂奕轩, 金学勤. 老年维持性血液透析患者习得性无助感潜在剖面及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(23): 2872-2879. |
| [7] | 杨晓霞, 于子夫, 王芳, 侯亚丽, 朱礼敬, 吕利明. 结直肠癌患者社会疏离的潜在剖面分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(20): 2499-2506. |
| [8] | 铁万琴, 张曦, 王永琦, 许洋, 陈雪丰, 潘璐, 陈思羽. 乳腺癌患者化疗前后症状特征的潜在转变分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(2): 193-200. |
| [9] | 徐萍, 闫荣, 张淼淼, 柳文慧, 姜凯. 头颈部肿瘤患者身体意象潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(2): 215-222. |
| [10] | 谢倩明, 廖春燕, 陈国伟, 彭艳红, 蒋桂香, 唐慧华. 老年髋关节置换术患者运动感知的分型预测及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(19): 2364-2370. |
| [11] | 张世晴, 徐雪君, 邓曼, 杨玥, 李敏, 杨秀木. 脑卒中患者症状负担潜在剖面及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(17): 2110-2117. |
| [12] | 陶秀, 高敏, 吴凡, 孙姝怡, 卢静, 温高芹, 王琴, 孙国珍. 心力衰竭患者自我损耗潜在类别及其对自我管理行为的影响研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(16): 1933-1940. |
| [13] | 沈向捷, 尹卫, 刘巧艳, 曹松梅, 祖后娟, 沙慧颖, 王晶晶. 中青年2型糖尿病合并超重或肥胖患者营养素养潜在类别与饮食动机的关系研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(16): 1974-1980. |
| [14] | 段睫, 李传昊, 唐志红. 青少年重度意外创伤患者对社交互动错失的焦虑现状及潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(16): 1981-1988. |
| [15] | 吴敏, 刘芮, 许采颉, 赵云凤, 张莹, 潘爱红. 老年慢性病共病患者口腔衰弱的潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(15): 1804-1810. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||