


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (24): 2986-2992.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.24.006
史广玲( ), 张燕红(
), 张燕红( ), 王筱筱, 刘娟, 蒋学娟, 余天浩, 施伟
), 王筱筱, 刘娟, 蒋学娟, 余天浩, 施伟
收稿日期:2025-03-27
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
张燕红,E-mail:1002820216@qq.com作者简介:史广玲:女,本科,主任护师,护士长,E-mail:shigl1978@163.com
SHI Guangling( ), ZHANG Yanhong(
), ZHANG Yanhong( ), WANG Xiaoxiao, LIU Juan, JIANG Xuejuan, YU Tianhao, SHI Wei
), WANG Xiaoxiao, LIU Juan, JIANG Xuejuan, YU Tianhao, SHI Wei
Received:2025-03-27
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-19
摘要:
目的 将重症动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血患者术后目标血压管理最佳证据应用于临床实践,评价其实施效果。方法 采用循证护理学方法,系统检索建库至2024年3月国内外有关重症动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血患者术后目标血压管理的临床决策、指南、系统评价、证据总结、专家共识等。以研究者-管理者-实践者理论模型为指导,筛选最佳证据,制订循证实践方案,并于2024年8—9月在南京市某三级甲等医院ICU实施。比较循证实践前后患者血压在目标范围内时间、医护人员对最佳证据的认知水平及审查条目执行率的差异。 结果 共纳入15篇文献,遴选出13条适合临床的最佳证据,构建了12条审查条目。循证实践后,患者收缩压和平均动脉压在目标范围内时间由(69.74±5.09)%和(70.50±5.09)%提高至(80.50±3.07)%和(80.85±3.24)%;医护人员对最佳证据的认知水平由(59.69±8.67)分提高至(76.06±10.03)分;各审查条目执行率由58.22%~95.77%提高至89.87%~100%,差异具有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。 结论 开展重症动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血患者术后目标血压管理的循证实践,提高了患者血压在目标范围内时间、医护人员对最佳证据的认知水平以及审查条目的执行率。
史广玲, 张燕红, 王筱筱, 刘娟, 蒋学娟, 余天浩, 施伟. 重症动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血患者术后目标血压管理的循证实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(24): 2986-2992.
SHI Guangling, ZHANG Yanhong, WANG Xiaoxiao, LIU Juan, JIANG Xuejuan, YU Tianhao, SHI Wei. Evidence-based practice for targeted blood pressure management in postoperative patients with critical aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(24): 2986-2992.
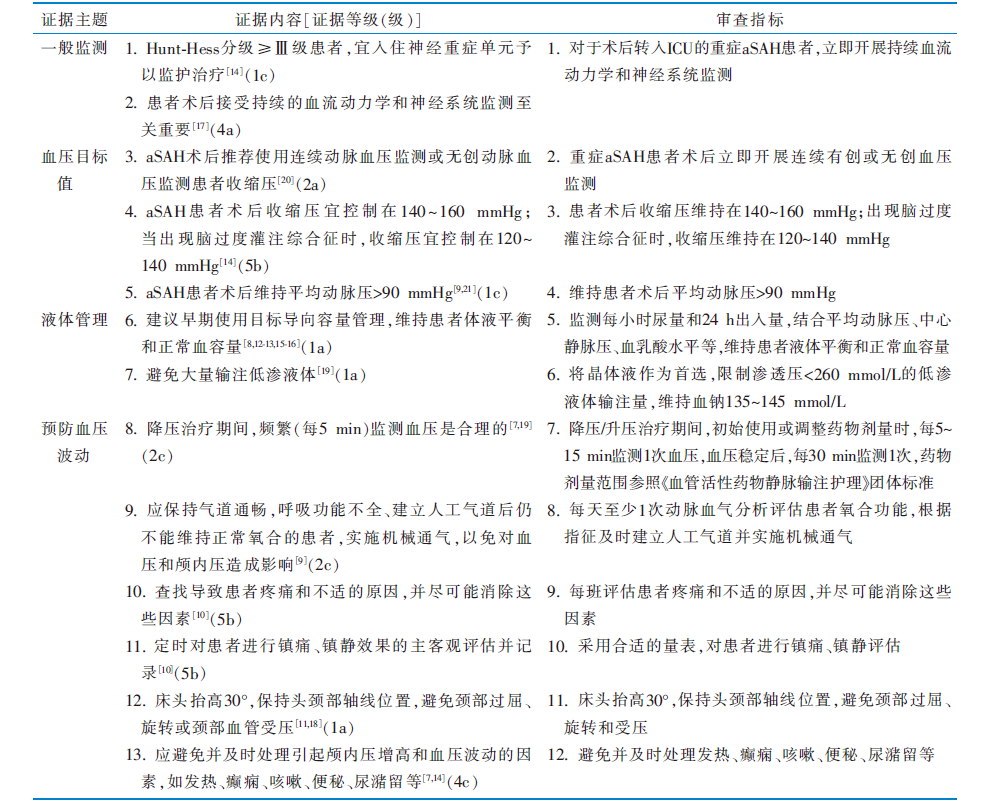 |
表1 重症动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血患者术后目标血压管理的证据内容及审查指标
Table 1 Evidence content and review indicators for postoperative target blood pressure management after severe aSAH
 |
| [1] |
Ran KR, Wang AC, Nair SK, et al. Acute multidisciplinary management of aneurysmal subarach noid hemorrhage(aSAH)[J]. Balkan Med J, 2023, 40(2):74-81.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 国家卫生健康. 脑血管病防治指南(2024年版)[EB/OL]. (2024-12-30)[2025-04-10]. https://www.nhc.gov.cn/ylyjs/zcwj/202412/ba037e931fff4870930f65ff667ea9ed/files/1736390751587_80714. |
| National Health Commission. Chinese cerebrovascular disease guidelines 2024[EB/OL]. (2024-12-30)[2025-04-10]. https://www.nhc.gov.cn/ylyjs/zcwj/202412/ba037e931fff4870930f65ff667ea9ed/files/1736390751587_80714. | |
| [3] | Sakata H, Endo H. Postoperative management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. No Shinkei Geka, 2024, 52(5):906-913. |
| [4] | 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组, 中国重症卒中管理指南2024[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2024, 57(7):698-714. |
| Chinese Society of Neurology,Chinese Stroke Society. Chinese guidelines for the management of severe stroke 2024[J]. Chin J Neurol, 2024, 57(7):698-714. | |
| [5] |
Dong R, Li JW, Chen QM, et al. Variations in the clinical practice of blood pressure and sedo-analgesia management for intracerebral hemorrhage:a case-based survey of Chinese healthcare workers[J]. BMC Neurol, 2025, 25(1):279.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | 葛向煜, 胡雁, 徐建鸣, 等. 研究者管理者实践者协作性循证实践工作模式解析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2017, 32(4):23-25. |
| Ge XY, Hu Y, Xu JM, et al. A researcher-manager-practitioner collaborative working model of evidence-based practice[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2017, 32(4):23-25. | |
| [7] |
Hemphill JC, Greenberg SM, Anderson CS, et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage:a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association[J]. Stroke, 2015, 46(7):2032-2060.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Cho WS, Kim JE, Park SQ, et al. Korean clinical practice guidelines for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. J Korean Neurosurg Soc, 2018, 61(2):127-166.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组, 中华医学会神经病学分会神经血管介入协作组. 中国蛛网膜下腔出血诊治指南2019[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2019, 52(12):1006-1021. |
| Chinese Society of Neurology, Chinese Stroke Society, Neurovascular Intervention Group of Chinese Society of Neurology. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of subarachnoid hemorrhage 2019[J]. Chin J Neurol, 2019, 52(12):1006-1021. | |
| [10] | 中华医学会神经外科学分会, 中国神经外科重症管理协作组. 中国神经外科重症管理专家共识(2020版)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2020, 100(19):1443-1458. |
| Chinese Society of Neurology,China Neurocritical Care Collaborative Group. China expert consensus on neurocritical care(2020)[J]. Chin Med J, 2020, 100(19):1443-1458. | |
| [11] |
Shoamanesh A, Patrice Lindsay M, Castellucci LA, et al. Canadian stroke best practice recommendations:management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage,7th edition update 2020[J]. Int J Stroke, 2021, 16(3):321-341.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 中国医师协会神经介入专业委员会, 中国颅内动脉瘤计划研究组. 中国颅内破裂动脉瘤诊疗指南2021[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2021, 18(8):546-574. |
| Chinese Federation of Interventional Clinical Neurosciences,China Intracranial Aneurysm Project Study Group. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysm 2021[J]. Chin J Cerebrovasc Dis, 2021, 18(8):546-574. | |
| [13] | National Institute for Health and Care Excellence(NICE). Subarachnoid haemorrhage caused by a ruptured aneurysm:diagnosis and management[EB/OL]. (2022-11-23)[2024-04-10]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng228. |
| [14] | 中国医师协会神经外科医师分会神经重症专家委员会, 中华医学会神经外科学分会脑血管病学组, 中国医师协会神经介入专业委员会, 等. 重症动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血管理专家共识(2023)[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2023, 20(2):126-144,封3. |
| Neurointensive Care Expert Committee of Chinese Neurosurgeons Association,Cerebrovascular Group, Chinese Neurosurgical Society, Chinese Federation of Interventional Clinical Neurosciences, et al. Expert consensus on the management of severe aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage 2023[J]. Chin J Cere-brovasc Dis, 2023, 20(2):126-144,Feng 3[inside back cover]. | |
| [15] | Hoh BL, Ko NU, Amin-Hanjani S, et al. 2023 guideline for the management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage:a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association[J]. Stroke, 2023, 54(7):e314-e370. |
| [16] | Treggiari MM, Rabinstein AA, Busl KM, et al. Guidelines for the neurocritical care management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Neurocrit Care, 2023, 39(1):1-28. |
| [17] | Singer RJ, Ogilvy CS, Rordorf G. Treatment of cerebral aneurysms[J/OL]. (2023-07-10)[2025-04-10]. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-cerebral-aneurysms?search=Rordorf%20G.Treatment%20of%20cerebral%20aneurysms&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1%7E150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1. |
| [18] | Smith ER, Amin-Hanjani. Evaluation and management of elevated intracranial pressure in adults[J/OL]. (2023-05-29)[2025-04-10]. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/zh-Hans/evaluation-and-management-of-elevated-intracranial-pressure-in-adults?search=Evaluation%20and%20management%20of%20elevated%20intracranial%20pressure%20in%20adults&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1%7E150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1. |
| [19] | Rordorf G, McDonald C. Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage:treatment and prognosis[J/OL]. (2023-10-03)[2025-04-10]. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/zh-Hans/spontaneous-intracere-bral-hemorrhage-acute-treatment-and-prognosis?search=Spontaneous%20intracerebral%20hemorrhage%3A%20Treatment%20and%20prognosis&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1%7E150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1. |
| [20] | 中华医学会神经外科学分会, 中国卒中学会脑血管外科学分会, 国家神经系统疾病医学中心, 等. 中国破裂颅内动脉瘤临床管理指南(2024版)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2024, 104(21):1940-1971. |
| Society of Neurosurgery of Chinese Medical Association, Society of Cerebrovascular Surgery of Chinese Stroke Associa-tion, National Center for Neurological Disorders, et al. Chinese guideline for the clinical management of patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms(2024)[J]. Natl Med J China, 2024, 104(21):1940-1971. | |
| [21] | 张丽华, 田丹英, 欧阳燕, 等. 颅内动脉瘤破裂出血患者血压管理策略的证据总结[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2022, 38(16):1255-1261. |
| Zhang LH, Tian DY, Ouyang Y, et al. Evidence summary of blood pressure management strategies in patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysm bleeding[J]. Chin J Prac Nurs, 2022, 38(16):1255-1261. | |
| [22] |
唐佳怡, 唐桂清, 张娜, 等. 慢加急性肝衰竭患者营养管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5):581-589.
DOI URL |
|
Tang JY, Tang GQ, Zhang N, et al. Best evidence summary of nutritional management in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(5):581-589.
DOI URL |
|
| [23] |
Oddo M, Poole D, Helbok R, et al. Fluid therapy in neurointensive care patients:ESICM consensus and clinical practice recommendations[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2018, 44(4):449-463.
DOI |
| [24] | 中华护理学会. 血管活性药物静脉输注护理[EB/OL]. (2021-12-31)[2025-04-10]. hltb.kxj.org.cn/uploads/admin/202403/65e1719a65f94.pdf. |
| Chinese Nursing Association. Nursing management of intravenous vasoactive drug infusion[EB/OL]. (2021-12-31)[2025-04-10]. hltb.kxj.org.cn/uploads/admin/202403/65e1719a65f94.pdf. | |
| [25] |
徐元元, 史广玲, 张燕红, 等. 预防ICU患者大便失禁性皮炎的循证实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(6):811-817.
DOI URL |
|
Xu YY, Shi GL, Zhang YH, et al. Evidence-based practice in prevention of fecal incontinence associated dermatitis in ICU patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(6):811-817.
DOI URL |
|
| [26] | 唐青青, 李秀云. 血糖在目标范围内时间作为糖尿病血糖管理新指标的研究进展[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2023, 31(4):316-320. |
| Tang QQ, Li XY. Research progress of blood glucose time in range as a new indicator of glycemic management in diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin J Diabetes, 2023, 31(4):316-320. | |
| [27] |
胡双, 陈嘉, 陈文俊, 等. 湖南省二三级医院护士长循证实践领导力的现状调查[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(11):1679-1684.
DOI URL |
| Hu S, Chen J, Chen WJ, et al. Implementation leadership of head nurses in Chinese tertiary and secondary hospitals:a cross-sectional study in Hunan[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(11):1679-1684. | |
| [28] |
林菁菁, 王碧芬, 陈晓怡, 等. 代谢相关脂肪性肝病患者运动管理的循证实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(1):69-76.
DOI URL |
|
Lin JJ, Wang BF, Chen XY, et al. Evidence-based practices for exercise management in patients with metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(1):69-76.
DOI URL |
|
| [29] |
吕银雪, 方晓霞, 韩玲, 等. 基于跨理论模型的运动饮食行为干预在减重手术患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(18):2197-2205.
DOI URL |
|
Lü YX, Fang XX, Han L, et al. Application of exercise-diet behavior intervention based on the transtheoretical model in patients undergoing weight loss surgery[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(18):2197-2205.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 周淼, 陈星, 彭飞, 孙尚雪, 李阳洋. ICU患者中心静脉导管相关血流感染风险预测工具的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1132-1139. |
| [2] | 梁元元, 高兴莲, 戴张章, 周荣超, 胡娟娟, 王曾妍, 沈剑辉. 医院手术器械管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 1005-1011. |
| [3] | 王婷, 王佳婷, 金爱云, 朱霞明, 方云, 汪靖, 田菲, 濮益琴, 万滢, 贺瑾, 颜霞. 自体造血干细胞移植术后患者护理随访清单的构建及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 914-920. |
| [4] | 盛婉婷, 王蕊, 赵玉晓, 戚鹏菲, 高祀龙, 冯娟, 吕伯瀚, 牛群, 王刚. 中等长度静脉导管不同尖端位置应用效果的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 990-997. |
| [5] | 严雪芹, 曹松梅, 周芳芳, 朱丽群, 陈成, 朱梦雪, 张艳红, 梁怡青, 柏素萍. 手部烧伤患者手功能早期康复管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 998-1004. |
| [6] | 李红颐, 李雪, 范宇莹, 赵一莎, 李京淑. ICU患者创伤心理反应的潜在剖面及影响因素的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 842-848. |
| [7] | 魏永婷, 田书梅, 杨娇, 余良欢, 倪福, 范雨晴, 肖瑶, 席祖洋, 沙菊艳, 刘聪. 护士循证决策能力量表的汉化及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 736-742. |
| [8] | 黄真真, 隋伟静, 董婧, 张君如, 张楚楚, 周泓廷, 张佳宇, 张娜, 庄一渝. 眼动追踪在ICU言语不能患者中应用的范围综述[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 757-763. |
| [9] | 王雯静, 郝妩媚, 台靖宇, 董倩, 郭爱敏. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者吸入药物治疗体验的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 545-551. |
| [10] | 唐佳怡, 唐桂清, 张娜, 李晓波. 慢加急性肝衰竭患者营养管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 581-588. |
| [11] | 刘婷婷, 牛巧红, 焦雪萍, 卫嘉玮, 段少铭, 胡聪丽, 苏芮. 直肠癌保肛术后患者肠道症状体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 603-610. |
| [12] | 蒋思珊, 成琴琴, 罗听薇, 张娜, 郭俊晨, 李东雅, 李丹丹, 朱丽辉. 儿童安宁疗护质量评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 611-618. |
| [13] | 中华护理学会老年护理专业委员会, 北京医院 国家老年医学中心, 中国医学科学院老年医学研究院, 北京大学护理学院(执笔:刘文静 王志稳 余跃琳 任欣 琚慧 陈宏 王君鑫 陈闪闪 周佳 伊默 王文霞 张玲娟 陈思烨 杨宇帆 王小萌 孙红). 老年人内在能力评估与维护指南[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 261-265. |
| [14] | 段煜, 郭张慧, 张洁, 焦萌, 屈简妮, 刘桂英, 赵丹, 陈颖宇, 郭红. 衰弱老年人运动锻炼促进与阻碍因素的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 288-296. |
| [15] | 宗小燕, 李红燕, 韩小云, 景新华. 胃癌患者围手术期口服营养补充管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 355-363. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||