


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2026, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (2): 229-236.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.02.011
• Human Resource Management and Career Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Ping( ), YU Wanchen, LIU Jiayi, YIN Siwen, WANG Shanshan*(
), YU Wanchen, LIU Jiayi, YIN Siwen, WANG Shanshan*( )
)
Received:2025-06-23
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-14
* Corresponding author:
WANG Shanshan,E-mail:rainshan_shan@163.comFunding program:通讯作者:
王汕珊,E-mail:rainshan_shan@163.com作者简介:吴萍:女,本科(硕士在读),护士,E-mail:2123017129@qq.com
基金资助:WU Ping, YU Wanchen, LIU Jiayi, YIN Siwen, WANG Shanshan. Latent profile analysis of nursing assistants’ death cognition and coping abilities[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 229-236.
吴萍, 于宛辰, 柳嘉怡, 尹思文, 王汕珊. 养老护理员死亡认知及应对能力的潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 229-236.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.02.011
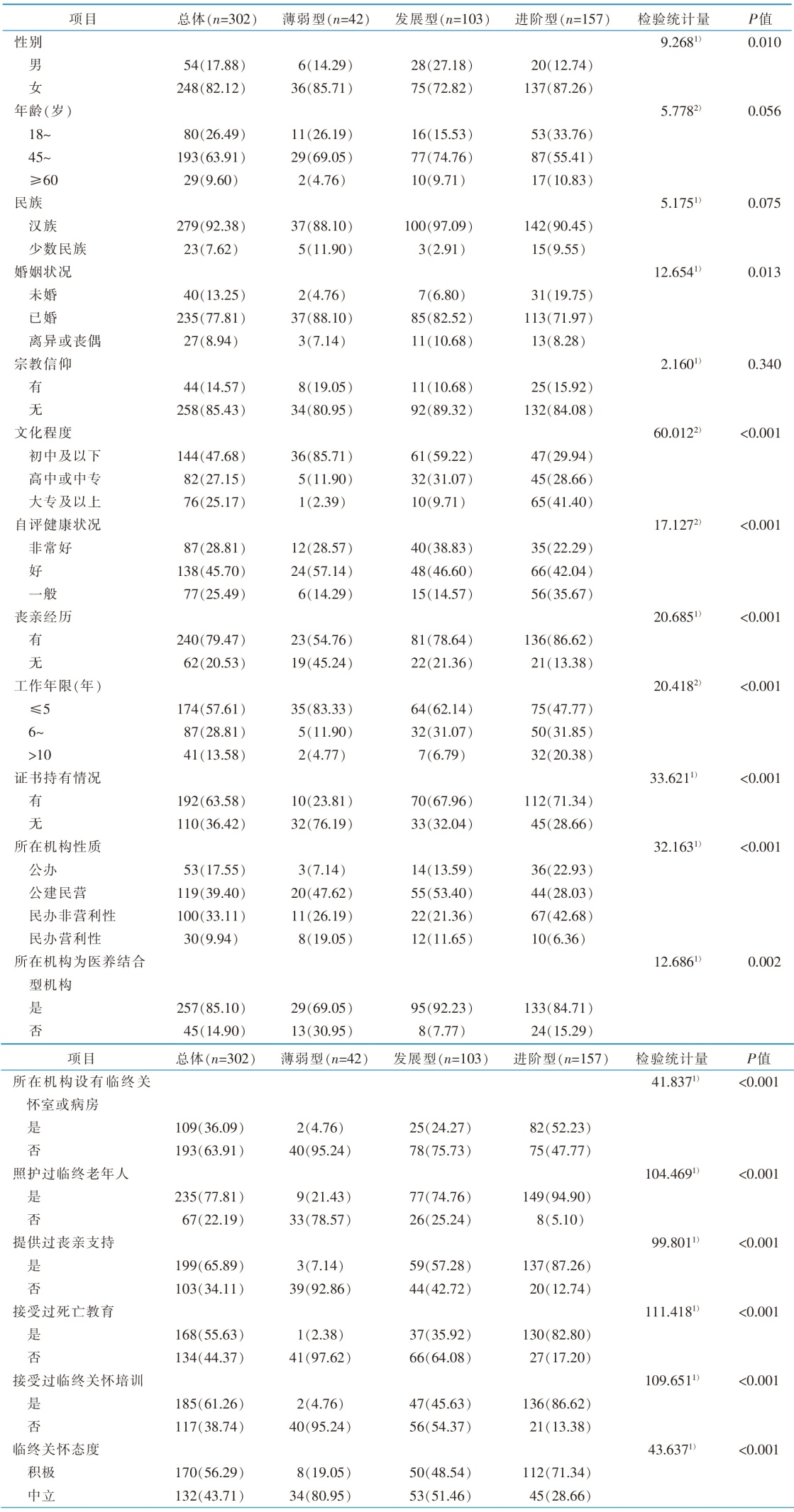 |
Table 1 Demographic characteristics of nursing assistants and their single-factor analysis on the latent profiles of death cognition and coping abilities[case(percentage,%)]
 |
| [1] | 人力资源社会保障部民政部. 养老护理员国家职业技能标准(2019年版)[EB/OL].(2019-09-25)[2025-06-07]. https://www.gov.cnzhengcelconent2022-02121/content5674844.htm. |
| Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security,Ministry of Civil Affairs. National vocational skills standard for nursing assistants(2019 edition)[EB/OL].(2019-09-25)[2025-06-07]. https://www.gov.cnzhengcelconent2022-02121/content5674844.htm. | |
| [2] | Just DT, O’Rourke HM, Berta WB, et al. Expanding the concept of end-of-life care in long-term care:a scoping review explor-ing the role of healthcare assistants[J]. Int J Older People Nurs, 2021, 16(2):e12353. |
| [3] | 杨红, 李攀, 胡茂荣. 论死亡的认知与接纳[J]. 医学与哲学, 2023, 44(5):54-58. |
| Yang H, Li P, Hu MR. The cognition and acceptance of death[J]. Med Philos, 2023, 44(5):54-58. | |
| [4] |
陈炜琳, 马红梅, 王萧, 等. 护士死亡应对能力的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(12):1795-1799.
DOI |
| Chen WL, Ma HM, Wang X, et al. Research progress on death competence of nurses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(12):1795-1799. | |
| [5] |
Puente-Fernández D, Lozano-Romero MM, Montoya-Juárez R, et al. Nursing professionals’ attitudes,strategies,and care practices towards death:a systematic review of qualitative studies[J]. J Nurs Scholarsh, 2020, 52(3):301-310.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Eichorst MK, Fromenthal AL, Harris GM, et al. In the presence of death and dying:death attitudes and compassion fatigue among certified nursing assistants in skilled care[J]. Aging Ment Health, 2025, 29(3):452-461. |
| [7] |
尹奎, 彭坚, 张君. 潜在剖面分析在组织行为领域中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7):1056-1070.
DOI |
|
Yin K, Peng J, Zhang J. The application of latent profile analy-sis in organizational behavior research[J]. Adv Psychol Sci, 2020, 28(7):1056-1070.
DOI URL |
|
| [8] | 方积乾. 生物医学研究的统计方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007. |
| Fang JQ. Statistical methods for biomedical research[M]. Bei-jing: Higher Education Press, 2007. | |
| [9] |
Leonard R, Noonan K, Horsfall D, et al. Developing a Death Literacy Index[J]. Death Stud, 2022, 46(9):2110-2122.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Che SL, Li X, Zhu MX, et al. The Death Literacy Index:tran-slation,cultural adaptation,and validation of the Chinese ver-sion[J]. Front Public Health, 2023, 11:1140475.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 史静琤, 莫显昆, 孙振球. 量表编制中内容效度指数的应用[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2012, 37(2):49-52. |
| Shi JC, Mo XK, Sun ZQ. Content validity index in scale deve-lopment[J]. J Cent South Univ Med Sci, 2012, 37(2):49-52. | |
| [12] | Frommelt KH. The effects of death education on nurses’ atti-tudes toward caring for terminally ill persons and their fami-lies[J]. Am J Hosp Palliat Care, 1991, 8(5):37-43. |
| [13] | 王丽萍. 中文版佛罗梅尔特临终关怀态度量表(FATCOD-B)的修订及应用研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2016. |
| Wang LP. Study on the revision and application of Chinese version of Fromelter’s Attitude Scale for Hospice Care (FATCOD-B)[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2016. | |
| [14] | 唐鲁, 周玲君, 李玉香, 等. 死亡教育课程方案的设计及实施[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2015, 50(2):223-229. |
| Tang L, Zhou LJ, Li YX, et al. Construction and implemen-tation of the death education curriculum[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2015, 50(2):223-229. | |
| [15] |
Graham-Wisener L, Toner P, Leonard R, et al. Psychometric validation of the Death Literacy Index and benchmarking of death literacy level in a representative UK population sample[J]. BMC Palliat Care, 2022, 21(1):145.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Johansson T, Tishelman C, Eriksson LE, et al. Factors associa-ted with death literacy among Swedish adults:a cross-sectio-nal exploratory study[J]. Palliat Support Care, 2024, 22(6):1573-1583.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 冯小君, 李静静. 养老机构护理员临终关怀知识、态度、行为现状及其影响因素[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2017, 34(6):7-12. |
| Feng XJ, Li JJ. Investigation of the knowledge,attitude and behavior of hospice palliative care and influencing factors among old-age care providers[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2017, 34(6):7-12. | |
| [18] | 罗稀, 江宾, 廖佳, 等. 四川地区肿瘤科护士照顾临终病人态度及其影响因素[J]. 护理研究, 2019, 33(22):3830-3835. |
| Luo X, Jiang B, Liao J, et al. Status and influencing factors of caring attitude toward dying patients among oncology nurses in Sichuan[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2019, 33(22):3830-3835. | |
| [19] |
Eagly AH, Nater C, Miller DI, et al. Gender stereotypes have changed:a cross-temporal meta-analysis of U.S. public opinion polls from 1946 to 2018[J]. Am Psychol, 2020, 75(3):301-315.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Almarwani AM, Alzahrani NS. Factors affecting the develop-ment of clinical nurses’ competency:a systematic review[J]. Nurse Educ Pract, 2023, 73:103826.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 朱明霞, 谢淑玲, 黎想, 等. 粤港澳大湾区华人居民死亡素养现状及当代生死教育初探[J]. 中国医学伦理学, 2024, 37(4):491-498. |
| Zhu MX, Xie SL, Li X, et al. The current situation of death literacy among Chinese residents in the Guangdong-Hong-Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and its preliminary exploration on contemporary life and death education[J]. Chin Med Ethics, 2024, 37(4):491-498. | |
| [22] |
Zhang XK, Zhang HL, Zhu MX, et al. The mediating effects of death reflection on death literacy and death anxiety among Chinese nurses:a cross-sectional study[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1):31153.
DOI |
| [23] |
Fishbein M. An investigation of the relationships between beliefs about an object and the attitude toward that object[J]. Hum Relat, 1963, 16(3):233-239.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Oba K, Tanimura C, Noguchi Y, et al. Perspectives of nursing students on end-of-life nurse education:a qualitative study of the guided death experience[J]. Nurse Educ Today, 2023, 126:105834.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Li WW, Chhabra J, Singh S. Palliative care education and its effectiveness:a systematic review[J]. Public Health, 2021, 194:96-108.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Romão ME, Belli G, Jumayeva S, et al. Death education in prac-tice:a scoping review of interventions,strategies,and psychoso-cial impact[J]. Omega(Westport), 2025:30222825133-8643. |
| [27] |
李凤侠, 刘筝筝, 胡成文, 等. 基于建构主义学习理论构建护士的死亡教育方案[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(11):1685-1690.
DOI |
|
Li FX, Liu ZZ, Hu CW, et al. Construction of a death education program for nursing staff based on constructivism learning theory[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(11):1685-1690.
DOI |
| [1] | ZHU Haixiang, LI Yan, XU Qijin, CHEN Jinxuan, HAN Xiaoxue, WU Yuan. Development and application research of a Graded and Categorized Symptom Recognition Tool in patients with chronic heart failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 149-156. |
| [2] | WANG Weiyun, GU Zejuan, TANG Yifan, SU Ziwen, LIU Changhong. Research on fluid balance thresholds in heart failure patients and nursing strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 157-165. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yingying, MA Yan, WU Lili, ZHANG Li, SUN Ying, LIU Lu, ZHUANG Yiyu. Development and validation of a Symptom Perception Distress Scale for patients with cardiovascular diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 174-181. |
| [4] | LI Fang, XU Cuirong, JIANG Lin, ZHANG Lixia, XIAO Yanhua, YUAN Xiao, HUANG Chaoyang, BAO Jiawei. Construction and verification of a risk prediction model for venous inflammation in preterm neonates with PICC placed in lower limbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 190-197. |
| [5] | DING Jiarong, CHEN Hui, WANG Xuerui, SUN Xiaoling, ZHANG Yin. A longitudinal qualitative study on self-management experiences and needs of patients with urinary incontinence after orthotopic neobladder surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 205-212. |
| [6] | DU Xuelian, CHEN Huajian, HUANG Shaojuan, LI Canhui, DONG Peiwen, LIAO Jiangbo, OU Bowei. Development and application study of a pelvic fracture patient risk assessment system [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 213-219. |
| [7] | CHEN Lin, PENG Qing. Research progress on influencing factors and intervention strategies of home-based skin cleansing behaviors in patients with traumatic wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 275-282. |
| [8] | TAO Binbin, YIN Qianyu, CHAI Zhaowu, AO Chunyan, LIU Ping, ZHANG Qian, YANG Bing. Construction and implementation of an online oral health education program for community-dwelling elder adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 9-16. |
| [9] | LU Qinyi, LU Chengqian, ZHAO Yafen, JIN Xueqin. The impact of fear of falling on self-awareness of falls in community-dwelling older adults with type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 23-29. |
| [10] | GAO Weijie, SUN Yumei. Barriers to the use of respite care by home-dwelling older adults with dementia and family caregivers:a meta-synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 30-37. |
| [11] | Palliative Care Professional Committee of Chinese Nursing Association(Writing Committee:GUO Junchen, CHEN Yongyi, YING Wenjuan, LÜ Yinyin, ZHAO Yun, QIANG Wanmin, XU Xiaoxia, HU Yonghong. Expert consensus on shared care management for adult palliative care patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 53-56. |
| [12] | ZHENG Cuiyan, FENG Yaping, LIU Zhimei, HU Huiqun. Comparative study on bilateral and unilateral ball-squeezing exercise in patients with PICC [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 57-62. |
| [13] | GAO Dan, YAO Liwei, HUANG Jinpeng, LIU Xiaoxia, ZHANG Yue, MAO Xiaoxiao. Study on the application of augmented reality somatosensory exercise training on early mobilization in patients after debridement and decortication for tuberculous empyema [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 70-77. |
| [14] | PENG Yuan, YANG Zhengwei, HE Chuan, CHEN Yuqin. Effectiveness of lower limb compression therapy in preventing chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in breast cancer patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 78-84. |
| [15] | JIANG Xiangling, LU Huifen, YU Youjun, LIN Xiaoli, HUANG Peiling. Influencing factors and nursing implications of hearing impairment in patients with post-radiotherapy nasopharyngeal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 85-92. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||