


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2026, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (2): 275-282.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.02.018
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2025-01-25
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-14
* Corresponding author:
PENG Qing,E-mail:927411976@qq.com通讯作者:
彭青,E-mail:927411976@qq.com作者简介:陈琳:女,硕士,护师,E-mail:2590165590@qq.com
CHEN Lin, PENG Qing. Research progress on influencing factors and intervention strategies of home-based skin cleansing behaviors in patients with traumatic wounds[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 275-282.
陈琳, 彭青. 创伤性伤口患者居家皮肤清洁行为影响因素及干预策略的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(2): 275-282.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.02.018
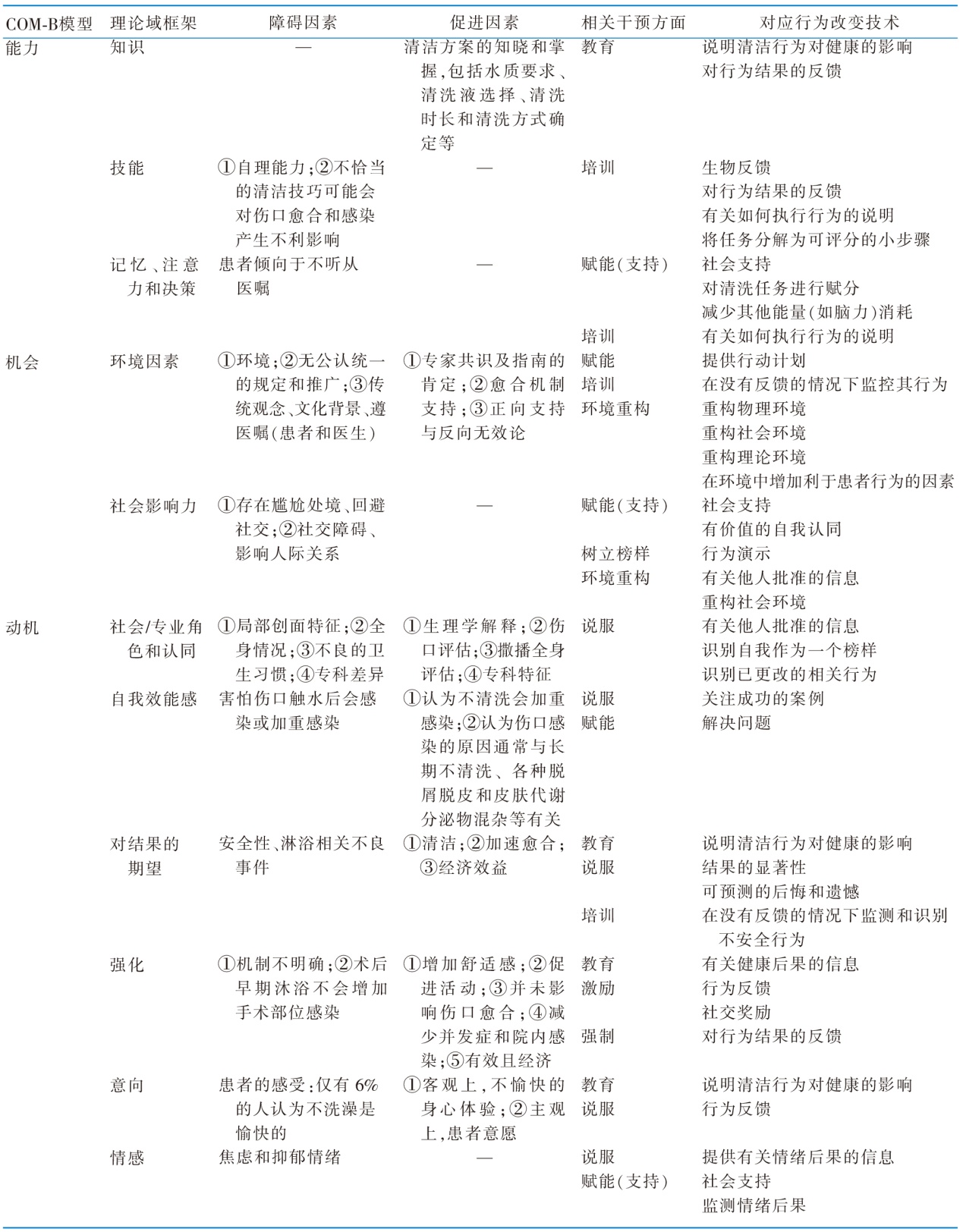 |
Table 2 Information tables of barriers,facilitators,and BCTs-based intervention mapping based on capability,opportunity,motivation,and behavior model and theoretical domain framework
 |
| [1] | Ozgok Kangal MK, Regan JP. Wound healing[M]. Treasure Is-land(FL): StatPearls Publishing Copyrightt, 2021. |
| [2] |
Sartelli M, Guirao X, Hardcastle TC, et al. 2018 WSES/SISE consensus conference:recommendations for the management of skin and soft-tissue infections[J]. World J Emerg Surg, 2018, 13:58.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | 蒋琪霞, 展颖颖, 魏巍, 等. 皮肤损伤患者温水淋浴与伤口感染的相关性及其影响因素[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2021, 34(8):834-839. |
| Jiang QX, Zhan YY, Wei W, et al. Correlation between warm water shower and wound infection in patients with skin injury and its influencing factors[J]. J Med Postgrad, 2021, 34(8):834-839. | |
| [4] | 蒋琪霞, 王亚玲, 解怡洁, 等. 成年创伤患者创面以外皮肤清洗现况及影响因素的多中心横断面调查[J]. 中华烧伤杂志, 2021, 37(5):429-436. |
| Jiang QX, Wang YL, Xie YJ, et al. Multicenter cross-sectional investigation on the cleaning status and influencing factors of skin cleaning outside the wound in adult trauma patients[J]. Chin J Burns, 2021, 37(5):429-436. | |
| [5] | 周晓慧, 季芳, 杨王建. 皮肤创伤急诊处理后皮肤清洗情况与伤口感染的关系研究[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2023, 39(8):625-630. |
| Zhou XH, Ji F, Yang WJ. Study on the relationship between skin cleaning and wound infection after emergency treatment of skin trauma[J]. Chin J Pract Nurs, 2023, 39(8):625-630. | |
| [6] | Yu YH, Chao S, Lin YK, et al. The gap between currently avai-lable evidence and awareness in clinical practice of wound care:it is the time to shower earlier[J]. Surgery,2018:S0039-6060(18)30029-1. |
| [7] | 郭丽娜, 谢钰莹, 张孟羽, 等. 脑卒中患者能力-机会-动机-行为潜剖面特征及影响因素研究[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2024, 30(25):3374-3381. |
| Guo LN, Xie YY, Zhang MY, et al. Study on the characteristics and influencing factors of the capability-opportunity-motiva-tion-behaviour profile of stroke patients[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2024, 30(25):3374-3381. | |
| [8] | 魏燕. 理论域框架在理解患者安全问题中的应用[J]. 南京医科大学学报(社会科学版), 2020, 20(6):564-567. |
| Wei Y. Application of theoretical domains framework in under-standing patient safety issues[J]. J Nanjing Med Univ Soc Sci, 2020, 20(6):564-567. | |
| [9] |
Lockwood C, Munn Z, Porritt K. Qualitative research synthesis:methodological guidance for systematic reviewers utilizing meta-aggregation[J]. Int J Evid Based Healthc, 2015, 13(3):179-187.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Hong QN, Gonzalez-Reyes A, Pluye P. Improving the useful-ness of a tool for appraising the quality of qualitative,quantitative and mixed methods studies,the mixed methods appraisal tool(MMAT)[J]. J Eval Clin Pract, 2018, 24(3):459-467.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 胡雁. 如何开展质性研究的系统评价和Meta整合[J]. 上海护理, 2020, 20(7):1-5. |
| Hu Y. How to carry out systematic review and meta-synthesis of qualitative studies[J]. Shanghai Nurs, 2020, 20(7):1-5. | |
| [12] | 刘晓晴, 蒋琪霞, 宋思平. 伤口患者皮肤清洗研究进展[J]. 中西医结合护理(中英文), 2020, 6(8):295-299. |
| Liu XQ, Jiang QX, Song SP. Research progress on the clean-ing of the skin and wounds[J]. Nurs Integr Tradit Chin West Med, 2020, 6(8):295-299. | |
| [13] | 魏林立, 周琴, 邹小梅, 等. 烧伤患者浸浴室的安全管理[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2013, 19(22):2713-2714. |
| Wei LL, Zhou Q, Zou XM, et al. Safety management of bath-room for burn patients[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2013, 19(22):2713-2714. | |
| [14] |
仲宇, 魏惠燕, 林淑洁, 等. 下肢静脉溃疡周围皮肤护理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(12):1446-1453.
DOI |
| Zhong Y, Wei HY, Lin SJ, et al. Summary of the best evide-nce for surrounding skin management in venous leg ulcers[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(12):1446-1453. | |
| [15] |
Mdoe MB, Mselle LT, Kibusi SM. An integrative review of home care recommendations for women after Caesarean section[J]. Nurs Open, 2024, 11(3):e2145.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Chang IW. Early versus delayed post-operative bathing or show-ering to prevent wound complications:a Cochrane review sum-mary[J]. Int J Nurs Stud, 2016, 61:258-259.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Dayton P, Feilmeier M, Sedberry S. Does postoperative shower-ing or bathing of a surgical site increase the incidence of infection? A systematic review of the literature[J]. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2013, 52(5):612-614.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Milne J. The importance of skin cleansing in wound care[J]. Br J Nurs, 2019, 28(12):S20-S22.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | 赵婷, 蒋琪霞, 徐慧黎, 等. 创伤性伤口患者居家带伤洗浴方案的安全性及有效性研究[J]. 医学研究与战创伤救治, 2023, 36(10):1077-1081. |
| Zhao T, Jiang QX, Xu HL, et al. The safety and efficacy of bath at home in patients with trauma[J]. J Med Res Combat Trauma Care, 2023, 36(10):1077-1081. | |
| [20] | 邓茹, 王艳霞. 浸浴疗法在烧伤病人难愈创面治疗中的应用[J]. 护理研究, 2018, 32(2):276-277. |
| Deng R, Wang YX. Application of immersion therapy in treat-ing refractory wound among patients with burn[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2018, 32(2):276-277. | |
| [21] |
姜明敏, 王军, 张宁, 等. 温泉水疗综合训练法对军事训练伤的康复治疗效果探讨[J]. 中国疗养医学, 2023, 32(7):717-720.
DOI |
| Jiang MM, Wang J, Zhang N, et al. Exploration of the rehabi-litation treatment effect of hot spring hydrotherapy compre-hensive training method on military training injuries[J]. Chin J Conval Med, 2023, 32(7):717-720. | |
| [22] |
Hsieh PY, Chen KY, Chen HY, et al. Postoperative showering for clean and clean-contaminated wounds:a prospective,rando-mized controlled trial[J]. Ann Surg, 2016, 263(5):931-936.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Neues C, Haas E. Beeinflussung der postoperativen wundhei-lung durch duschen[J]. Der Chir, 2000, 71(2):234-236. |
| [24] | Riederer SR, Inderbitzi R. Gefährdet das duschen die postope-rative wundheilung?[J]. Der Chir, 1997, 68(7):715-717. |
| [25] |
赵婷, 蒋琪霞, 徐慧黎, 等. 创伤性伤口患者居家带伤洗浴方案的构建与初步验证研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(14):1729-1734.
DOI |
| Zhao T, Jiang QX, Xu HL, et al. Construction and preliminary validation of bathing with wounds at home scheme for patients with traumatic wounds[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2024, 27(14):1729-1734. | |
| [26] |
蒋琪霞, 徐娟, 王亚玲, 等. 创伤伤口患者居家洗浴与伤口感染现况调查及伤口感染影响因素分析:一项多中心研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(29):3757-3762.
DOI |
| Jiang QX, Xu J, Wang YL, et al. Inventory survey of home bathing and wound infection in patients with traumatic wounds and analysis of the influencing factors of wound infection:a multicenter study[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2021, 24(29):3757-3762. | |
| [27] | 蒋琪霞, 徐娟, 刘晓晴, 等. 创伤性伤口患者皮肤清洗现况及原因的多中心横断面研究[J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2020, 22(9):646-650,654. |
| Jiang QX, Xu J, Liu XQ, et al. A multicenter cross-sectional study on the current situation and causes of skin cleaning in patients with traumatic wounds[J]. J Trauma Surg, 2020, 22(9):646-650,654. | |
| [28] |
Alheggi A, Alzakry L, Khunayn RB, et al. Skin cleansing and wound care practice in patients with epidermolysis bullosa[J]. J Dermatol Dermatol Surg, 2022, 26(1):13-17.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Takehara K, Amemiya A, Mugita Y, et al. The association bet-ween tinea pedis and feet-washing behavior in patients with diabetes:a cross-sectional study[J]. Adv Skin Wound Care, 2017, 30(11):510-516.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | 蒋琪霞, 周济宏, 程东瑞, 等. 132例手术切口感染患者临床特征及干预效果分析[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2020, 33(2):178-183. |
| Jiang QX, Zhou JH, Cheng DR, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of 132 patients with surgical site infection[J]. J Med Postgrad, 2020, 33(2):178-183. | |
| [31] |
Yoo JS, Lee H, Kim SE, et al. Effects of early postoperative shower after cardiac surgery[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2022, 11(8):2562-2568.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 刘晓晴, 蒋琪霞, 宋思平. 皮肤清洗对术后切口感染影响的病例对照研究[J]. 中西医结合护理(中英文), 2020, 6(10):216-218. |
| Liu XQ, Jiang QX, Song SP. Effect of skin cleaning on pre-venting incisional wound infection after surgery:a case-control study[J]. Nurs Integr Tradit Chin West Med, 2020, 6(10):216-218. | |
| [33] |
Sano H, Ichioka S. Which cleansing care is better,foot bath or shower? Analysis of 236 limb ulcers[J]. Int Wound J, 2015, 12(5):577-580.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Jayathilake A, Jayaweera JAAS, Kumbukgolla WW, et al. Inf-luence of early postoperative showering in undressed surgical wound for better clinical outcome[J]. J Perioper Pract, 2020, 30(6):163-169.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Ferhatoglu MF, Kartal A, Ekici U, et al. Effects of bathing habits on postoperative wound complications following sacro-coccygeal pilonidal sinus surgery:a retrospective analysis of 67 adolescent patients[J]. Wounds, 2019, 31(11):292-296.
PMID |
| [36] | Ogawa H, Tahara S. Postoperative showering for patients with closed suction drainage:a retrospective cohort study of deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstructions[J]. Cu-reus, 2022, 14(3):e23665. |
| [37] |
Feilmeier M, Dayton P, Sedberry S, et al. Incidence of surgical site infection in the foot and ankle with early exposure and showering of surgical sites:a prospective observation[J]. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2014, 53(2):173-175.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | 王盈, 强万敏, 李静, 等. 皮肤清洁对癌症患者放射性皮炎影响效果的系统评价[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2020, 35(5):426-432. |
| Wang Y, Qiang WM, Li J, et al. Skin cleanness for radiation induced skin reaction in cancer patients:a systematic review[J]. J Nurses Train, 2020, 35(5):426-432. | |
| [39] | Copeland-Halperin LR, Reategui Via Y Rada ML, Levy J, et al. Does the timing of postoperative showering impact infection rates? A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Plast Re-constr Aesthet Surg, 2020, 73(7):1306-1311. |
| [40] | 张媛, 郭锦丽, 刘宏, 等. 慢性伤口患者创面操作性疼痛管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(14):1761-1768. |
| Zhang Y, Guo JL, Liu H, et al. The best evidence summary of wound procedural pain management in patients with chronic wounds[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(14):1761-1768. | |
| [41] |
张媛, 郭锦丽. 沉浸式虚拟现实技术在创面操作性疼痛管理中的应用进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(2):243-249.
DOI |
|
Zhang Y, Guo JL. Application progress of immersive virtual reality technology in wound procedural pain management[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(2):243-249.
DOI |
|
| [42] |
孙红玲, 兰美娟, 王惠, 等. 医联体内慢性伤口护理联动管理障碍因素的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(18):2246-2251.
DOI |
|
Sun HL, Lan MJ, Wang H, et al. Qualitative research on the barriers of chronic wound linkage management in medical consortium[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(18):2246-2251.
DOI |
|
| [43] |
严雪芹, 柏素萍, 刘巧艳, 等. 烧伤后创面瘙痒患者非药物干预的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(5):610-617.
DOI |
|
Yan XQ, Bai SP, Liu QY, et al. Best evidence summary of non-pharmacological interventions in post-burn itch[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(5):610-617.
DOI |
| [1] | ZHU Haixiang, LI Yan, XU Qijin, CHEN Jinxuan, HAN Xiaoxue, WU Yuan. Development and application research of a Graded and Categorized Symptom Recognition Tool in patients with chronic heart failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 149-156. |
| [2] | WANG Weiyun, GU Zejuan, TANG Yifan, SU Ziwen, LIU Changhong. Research on fluid balance thresholds in heart failure patients and nursing strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 157-165. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yingying, MA Yan, WU Lili, ZHANG Li, SUN Ying, LIU Lu, ZHUANG Yiyu. Development and validation of a Symptom Perception Distress Scale for patients with cardiovascular diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 174-181. |
| [4] | LI Fang, XU Cuirong, JIANG Lin, ZHANG Lixia, XIAO Yanhua, YUAN Xiao, HUANG Chaoyang, BAO Jiawei. Construction and verification of a risk prediction model for venous inflammation in preterm neonates with PICC placed in lower limbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 190-197. |
| [5] | DING Jiarong, CHEN Hui, WANG Xuerui, SUN Xiaoling, ZHANG Yin. A longitudinal qualitative study on self-management experiences and needs of patients with urinary incontinence after orthotopic neobladder surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 205-212. |
| [6] | DU Xuelian, CHEN Huajian, HUANG Shaojuan, LI Canhui, DONG Peiwen, LIAO Jiangbo, OU Bowei. Development and application study of a pelvic fracture patient risk assessment system [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 213-219. |
| [7] | WU Ping, YU Wanchen, LIU Jiayi, YIN Siwen, WANG Shanshan. Latent profile analysis of nursing assistants’ death cognition and coping abilities [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 229-236. |
| [8] | TAO Binbin, YIN Qianyu, CHAI Zhaowu, AO Chunyan, LIU Ping, ZHANG Qian, YANG Bing. Construction and implementation of an online oral health education program for community-dwelling elder adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 9-16. |
| [9] | LU Qinyi, LU Chengqian, ZHAO Yafen, JIN Xueqin. The impact of fear of falling on self-awareness of falls in community-dwelling older adults with type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 23-29. |
| [10] | GAO Weijie, SUN Yumei. Barriers to the use of respite care by home-dwelling older adults with dementia and family caregivers:a meta-synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 30-37. |
| [11] | Palliative Care Professional Committee of Chinese Nursing Association(Writing Committee:GUO Junchen, CHEN Yongyi, YING Wenjuan, LÜ Yinyin, ZHAO Yun, QIANG Wanmin, XU Xiaoxia, HU Yonghong. Expert consensus on shared care management for adult palliative care patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 53-56. |
| [12] | ZHENG Cuiyan, FENG Yaping, LIU Zhimei, HU Huiqun. Comparative study on bilateral and unilateral ball-squeezing exercise in patients with PICC [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 57-62. |
| [13] | GAO Dan, YAO Liwei, HUANG Jinpeng, LIU Xiaoxia, ZHANG Yue, MAO Xiaoxiao. Study on the application of augmented reality somatosensory exercise training on early mobilization in patients after debridement and decortication for tuberculous empyema [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 70-77. |
| [14] | PENG Yuan, YANG Zhengwei, HE Chuan, CHEN Yuqin. Effectiveness of lower limb compression therapy in preventing chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in breast cancer patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 78-84. |
| [15] | JIANG Xiangling, LU Huifen, YU Youjun, LIN Xiaoli, HUANG Peiling. Influencing factors and nursing implications of hearing impairment in patients with post-radiotherapy nasopharyngeal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 85-92. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
