


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (19): 2309-2318.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.19.001
• Research Paper • Next Articles
MENG Xiaojing( ), LI Xiang, FENG Yingpu(
), LI Xiang, FENG Yingpu( ), FAN Jingli, HUO Xiaoran, ZHANG Chunxia, ZHOU Limin, GAO Min
), FAN Jingli, HUO Xiaoran, ZHANG Chunxia, ZHOU Limin, GAO Min
Received:2023-01-03
Online:2023-10-10
Published:2023-10-12
Contact:
FENG Yingpu
孟晓静( ), 李翔, 冯英璞(
), 李翔, 冯英璞( ), 范晶丽, 霍晓冉, 张春霞, 周立民, 高敏
), 范晶丽, 霍晓冉, 张春霞, 周立民, 高敏
通讯作者:
冯英璞
作者简介:孟晓静:女,硕士,副主任护师,护士长,E-mail:mengxiaojing512@126.com
MENG Xiaojing, LI Xiang, FENG Yingpu, FAN Jingli, HUO Xiaoran, ZHANG Chunxia, ZHOU Limin, GAO Min. Evidence-based practice of target temperature management in patients with traumatic brain injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2023, 58(19): 2309-2318.
孟晓静, 李翔, 冯英璞, 范晶丽, 霍晓冉, 张春霞, 周立民, 高敏. 颅脑损伤患者目标温度管理的循证实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(19): 2309-2318.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.19.001
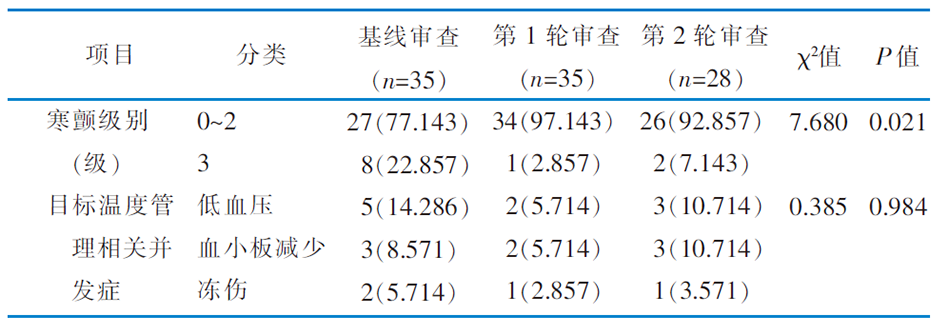 |
Table 4 Comparison of complications related to Grade 3 chills and target temperature management before and after evidence application [case(percent,%)]
 |
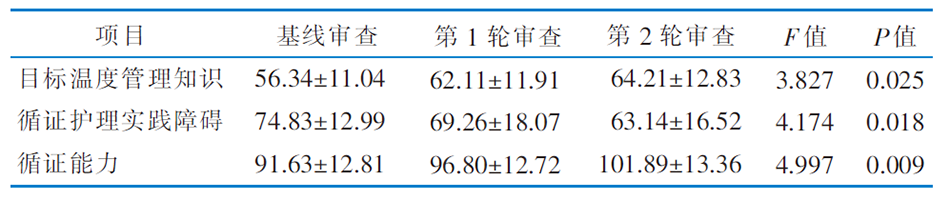 |
Table 5 Comparison of target temperature management knowledge level and evidence-based practice ability of nurses with traumatic brain injury before and after the application of evidence (scores,$ \overline{x}\pm s$,n=27)
 |
| [22] |
Harden SM, Smith ML, Ory MG, et al. RE-AIM in clinical,community,and corporate settings:perspectives,strategies,and recommendations to enhance public health impact[J]. Front Public Health, 2018, 6:71.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Mathisen GE, Einarsen S. A Review of instruments assessing creative and innovative environments within organizations[J]. Creat Res J, 2004, 16(1):119-140.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 刘晓华, 张晋昕, 张振路, 等. 中文版循证护理实践障碍量表信度与效度的评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2008, 43(11):1041-1044. |
| Liu XH, Zhang JX, Zhang ZL, et al. Reliability and validity of Chinese version of Handicap Inventory Short Form about Evaluation of Evidence-Based Nursing Practice[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2008, 43(11):1041-1044. | |
| [25] | 杨如美. 英文版循证实践知识、态度、行为问卷及循证实践影响因素问卷的初步修订与应用[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010. |
| Yang RM. Preliminary revision and application of the English version of the Evidence-Based Practical Knowledge,Attitude,and Behavior Questionnaire and the evidence-based practical influencing factors questionnaire[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010 | |
| [26] | 王薇, 李朝煜, 张敏, 等. 关注实践过程的循证护理模式研究进展[J]. 中国护理管理, 2018, 18(3):428-432. |
| Wang W, Li ZY, Zhang M, et al. Evidence-based nursing models:focusing on the process of evidence-based practice[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2018, 18(3):428-432. | |
| [27] |
Sharp MK, Tyner B, Awang Baki DAB, et al. Evidence synthesis summary formats for clinical guideline development group members:a mixed-methods systematic review protocol[J]. HRB Open Res, 2021, 4:76.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Yoo JY, Kim JH, Kim JS, et al. Clinical nurses’ beliefs,knowledge,organizational readiness and level of implementation of evidence-based practice:the first step to creating an evidence-based practice culture[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(12):e0226742.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 付艳芬, 王春青, 胡雁. 证据临床转化中障碍因素和促进因素的内容分析[J]. 护理学报, 2022, 29(5):64-68. |
| Fu YF, Wang CQ, Hu Y. Content analysis of obstacles and promoters in clinical transformation of evidence[J]. J Nurs China, 2022, 29(5):64-68. | |
| [30] |
Moreda M, Beacham PS, Reese A, et al. Increasing the effectiveness of targeted temperature management[J]. Crit Care Nurse, 2021, 41(5):59-63.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Jain A, Gray M, Slisz S, et al. Shivering treatments for targeted temperature management:a review[J]. J Neurosci Nurs, 2018, 50(2):63-67.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 章梅云, 冯志仙, 邵乐文, 等. 循证护理团队培训方案的制订及应用效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2015, 50(4):446-449. |
| Zhang MY, Feng ZX, Shao LW, et al. The development and outcomes of training program for members of evidence-based nursing team[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2015, 50(4):446-449. | |
| [33] |
胡双, 陈嘉, 陈文俊, 等. 湖南省二三级医院护士长循证实践领导力的现状调查[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(11):1679-1684.
DOI |
| Hu S, Chen J, Chen WJ, et al. Implementation leadership of head nurses in Chinese tertiary and secondary hospitals:a cross-sectional study in Hunan[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(11):1679-1684. | |
| [34] |
Wieringa S, Engebretsen E, Heggen K, et al. Rethinking bias and truth in evidence-based health care[J]. J Eval Clin Pract, 2018, 24(5):930-938.
DOI PMID |
| [1] |
Alcamo AM, Fink EL. Targeted temperature management for everyone[J]. Pediatr Crit Care Med, 2019, 20(2):206-207.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Andrews PJD, Verma V, Healy M, et al. Targeted temperature management in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage,subarachnoid haemorrhage,or acute ischaemic stroke:consensus recommendations[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2018, 121(4):768-775.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Madden LK, Hill M, May TL, et al. The implementation of targeted temperature management:an evidence-based guideline from the neurocritical care society[J]. Neurocritical Care, 2017, 27(3):468-487.
DOI |
| [4] |
Cariou A, Payen JF, Asehnoune K, et al. Targeted temperature management in the ICU:guidelines from a French expert panel[J]. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med, 2018, 37(5):481-491.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Picetti E, Iaccarino C, Servadei F. Letter:guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury fourth edition[J]. Neurosurgery, 2017, 81(1):E2.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Huang HP, Zhao WJ, Pu J. Effect of mild hypothermia on prognosis of patients with severe traumatic brain injury:a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis[J]. Aust Crit Care, 2020, 33(4):375-381.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Pegoli M, Zurlo Z, Bilotta F. Temperature management in acute brain injury:a systematic review of clinical evidence[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2020, 197:106-165. |
| [8] |
Crompton EM, Lubomirova I, Cotlarciuc I, et al. Meta-analysis of therapeutic hypothermia for traumatic brain injury in adult and pediatric patients[J]. Crit Care Med, 2017, 45(4):575-583.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Lewis SR, Evans DJ, Butler AR, et al. Hypothermia for traumatic brain injury[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2017, 9(9):CD001048. |
| [10] | 中国医师协会急诊医师分会, 中国医药教育协会急诊医学专业委员会, 成人急危重症脑损伤患者目标温度管理临床实践专家共识组, 等. 成人急危重症脑损伤患者目标温度管理临床实践专家共识[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2019, 28(3):282-291. |
| Branch of Emergency Physicians of Chinese Medical Doctor Association,Professional Committee of Emergency Medicine of Chinese Medical Education Association, Expert Consensus Group on Clinical Practice of Target Temperature Management for Adult Patients with Acute and Severe Brain Injury. Clinical practice expert consensus on target temperature management in adult patients with acute and severe brain injury[J]. Chin J Emerg Med, 2019, 28(3):282-291. | |
| [11] | 宿英英, 黄旭升, 潘速跃, 等. 神经重症低温治疗中国专家共识[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2015, 48(6):453-458. |
| Su YY, Huang XS, Pan SY, et al. Chinese expert consensus on severe neurohypothermia treatment[J]. Chin J Neurol, 2015, 48(6):453-458. | |
| [12] | 中国研究型医院学会神经再生与修复专业委员会心脏重症脑保护学组, 中国研究型医院学会神经再生与修复专业委员会神经重症护理与康复学组. 亚低温脑保护中国专家共识[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2020, 32(4):385-391. |
| Cardiac Critical Brain Protection Group, Neurological Regen-eration and Repair Professional Committee of Chinese Society of Research Hospitals, Neurological Critical Care and Reha-bilitation Group of Neurological Regeneration and Repair Professional Committee of Chinese Society of Research Hos-pitals. Chinese expert consensus on mild hypothermia brain protection[J]. Chin J Crit Care Emerg Med, 20, 32(4):385-391. | |
| [13] | 贺亚龙, 刘文博. 颅脑创伤后加重继发性脑损伤的危险因素防治专家共识[J]. 临床神经外科杂志, 2020, 17(3):241-249,253. |
| He YL, Liu WB. Experts consensus on the management of factors of secondary brain insults following traumatic brain injury[J]. J Clin Neurosurg, 2020, 17(3):241-249,253. | |
| [14] | 王琦, 袁莉莉, 丁贤慧, 等. 低温干预对成人严重颅脑损伤患者疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2020, 20(10):1180-1186. |
| Wang Q, Yuan LL, Ding XH, et al. Efficacy of hypothermia intervention on adult severe craniocerebral injury:a metaanalysis[J]. Chin J Evid Based Med, 2020, 20(10):1180-1186. | |
| [15] | 宋向奇, 陈通, 付爱军, 等. 长期亚低温对比短期亚低温治疗重型颅脑损伤的系统评价[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2014, 27(11):1184-1187. |
| Song XQ, Chen T, Fu AJ, et al. Comparison of long-term and short-term mild hypothermia on severe traumatic brain injury:a systematic review[J]. J Med Postgrad, 2014, 27(11):1184-1187. | |
| [16] | 荀静, 祁静, 周梦良, 等. 颅脑创伤患者目标温度管理护理实践最佳证据总结[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2021, 38(4):70-73,88. |
| Xun J, Qi J, Zhou ML, et al. Best evidence summary of nurs-ing practice of targeted temperature management in traumatic brain injury patients[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2021, 38(4):70-73,88. | |
| [17] |
Ranegger R, Haug S, Vetsch J, et al. Providing evidence-based knowledge on nursing interventions at the point of care:findings from a mapping project[J]. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak, 2022, 22(1):308.
DOI |
| [18] | 胡雁, 郝玉芳. 循证护理学[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018:219-221. |
| Hu Y, Hao YF. Evidence-based nursing[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2018:219-221. | |
| [19] | 朱政, 胡雁, 周英凤, 等. 推动证据向临床转化(三)研究的选题和问题构建[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2020, 35(9):796-799. |
| Zhu Z, Hu Y, Zhou YF, et al. Promoting the transformation of evidence to clinical practice:research topic selection and problem construction[J]. J Nurses Train, 2020, 35(9):796-799. | |
| [20] | 周英凤, 朱政, 胡雁, 等. 推动证据向临床转化(七)证据的可用性评价[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2020, 35(13):1193-1196. |
| Zhou YF, Zhu Z, Hu Y, et al. Implementing evidence into practice:how to evaluate the applicability of evidence[J]. J Nurses Train, 2020, 35(13):1193-1196. | |
| [21] | 王强, 李幼平, 张伯礼, 等. 指南临床适用性评价的问题与需求[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2020, 20(3):249-251. |
| Wang Q, Li YP, Zhang BL, et al. Issues and demands for clinical applicability evaluation of clinical guidelines[J]. Chin J Evid Based Med, 2020, 20(3):249-251. |
| [1] | LIANG Yuanyuan, GAO Xinglian, DAI Zhangzhang, ZHOU Rongchao, HU Juanjuan, WANG Zengyan, SHEN Jianhui. Summary of the best evidence for surgical instrument management strategies in medical institutions [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 1005-1011. |
| [2] | WANG Ting, WANG Jiating, JIN Aiyun, ZHU Xiaming, FANG Yun, WANG Jing, TIAN Fei, PU Yiqin, WAN Ying, HE Jin, YAN Xia. Construction of a nursing follow-up checklist for patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 914-920. |
| [3] | SHENG Wanting, WANG Rui, ZHAO Yuxiao, QI Pengfei, GAO Silong, FENG Juan, LÜ Bohan, NIU Qun, WANG Gang. The effectiveness of applying different tip positions of midline catheters:a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 990-997. |
| [4] | YAN Xueqin, CAO Songmei, ZHOU Fangfang, ZHU Liqun, CHEN Cheng, ZHU Mengxue, ZHANG Yanhong, LIANG Yiqing, BAI Suping. Summary of best evidence for early rehabilitation management of hand function in patients with hand burns [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 998-1004. |
| [5] | WEI Yongting, TIAN Shumei, YANG Jiao, YU Lianghuan, NI Fu, FAN Yuqing, XIAO Yao, XI Zuyang, SHA Juyan, LIU Cong. Sinicization of Evidence-Informed Decision-Making Competence Measure for nurses and its reliability and validity test [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(6): 736-742. |
| [6] | WANG Wenjing, HAO Wumei, TAI Jingyu, DONG Qian, GUO Aimin. Experience of inhalation therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:a Meta-synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 545-551. |
| [7] | TANG Jiayi, TANG Guiqing, ZHANG Na, LI Xiaobo. Best evidence summary of nutritional management in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 581-588. |
| [8] | LIU Tingting, NIU Qiaohong, JIAO Xueping, WEI Jiawei, DUAN Shaoming, HU Congli, SU Rui. Meta-synthesis of qualitative studies on the experience of bowel symptoms in patients undergoing sphincter-preserving surgery for rectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 603-610. |
| [9] | JIANG Sishan, CHENG Qinqin, LUO Tingwei, ZHANG Na, GUO Junchen, LI Dongya, LI Dandan, ZHU Lihui. A systematic review of quality assessment tools for pediatric palliative care based on COSMlN guidelines [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 611-618. |
| [10] | Chinese Nursing Association Geriatric Nursing Committee, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, School of Nursing, Peking University(Writing Committee:LIU Wenjing, WANG Zhiwen, YU Yuelin, REN Xin, JU Hui, CHEN Hong WANG Junxin, CHEN Shanshan, ZHOU Jia, YI Mo, WANG Wenxia, ZHANG Lingjuan, CHEN Siye, YANG Yufan, WANG Xiaomeng, SUN Hong). Guideline for assessment and maintenance of intrinsic capacity in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(3): 261-265. |
| [11] | DUAN Yu, GUO Zhanghui, ZHANG Jie, JIAO Meng, QU Jianni, LIU Guiying, ZHAO Dan, CHEN Yingyu, GUO Hong. Facilitators and barriers to the implementation of exercise for elderly patients with frailty:a qualitative Meta-synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(3): 288-296. |
| [12] | ZONG Xiaoyan, LI Hongyan, HAN Xiaoyun, JING Xinhua. Summary of the best evidence for perioperative management of oral nutritional supplementation in patients with gastric cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(3): 355-363. |
| [13] | LI Jing, MAO Qiuting, HUANG Yi, ZENG Fan, XIONG Mo, LI Qianqian, ZHOU Shuanghong. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of factors influencing taste alterations in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(14): 1778-1785. |
| [14] | YANG Shu, LIN Yihui, HAN Zhihao, TANG Linxia, QIU Yunxia, MA Xiaoqin. Meta-integration of qualitative studies on body image experience in breast cancer patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(14): 1786-1792. |
| [15] | HAN Lin, YAN Chuchu, SHAN Yawei, LU Haiying, CHEN Ru, GAN Fei, JIN Lijuan. Evidence-based practice of discharge preparation services for hip replacement patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(10): 1157-1163. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||