


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (21): 2670-2676.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.21.016
• Evidence Synthesis Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Suxiang( ), BIAN Li, ZHANG Yequn, QI Miaomiao
), BIAN Li, ZHANG Yequn, QI Miaomiao
Received:2023-02-17
Online:2023-11-10
Published:2023-11-10
作者简介:刘素香:女,硕士,主管护师,E-mail:liusuxiang97@163.com
基金资助:LIU Suxiang, BIAN Li, ZHANG Yequn, QI Miaomiao. A systematic review of health literacy assessment tools for diabetic patients based on COSMIN guidelines[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2023, 58(21): 2670-2676.
刘素香, 边莉, 张叶群, 齐苗苗. 基于COSMIN指南对糖尿病患者健康素养评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(21): 2670-2676.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.21.016
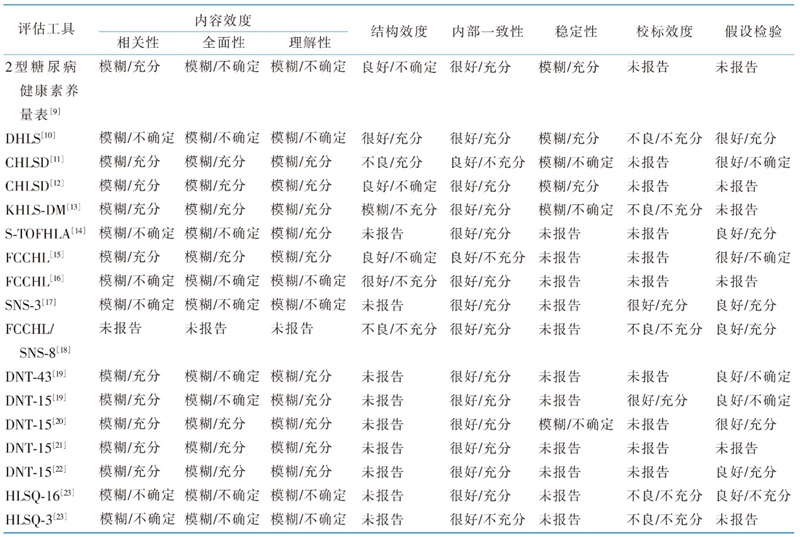 |
Table 2 Psychometric properties and methodological quality evaluation of the included scales (n=17,methodological quality/measurement characteristics quality)
 |
| [1] | International Diabetes Foundation. IDF diabetes atlas-10th edi-tion[EB/OL].(2021-12-06)[2023-05-05]. https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/. |
| [2] | 姜晓雯. 老年2型糖尿病患者健康素养与服药依从性关系:服药信念的中介作用[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2021. |
| Jiang XW. Relationship between health literacy and medication compliance in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus:the mediating role of medication belief[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2021. | |
| [3] |
Souza JG, Apolinario D, Magaldi RM, et al. Functional health literacy and glycaemic control in older adults with type 2 dia-betes:a cross-sectional study[J]. BMJ Open, 2014, 4(2):e004180.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Lee EH, Lee YW, Moon SH. A structural equation model link-ing health literacy to self-efficacy,self-care activities,and heal-th-related quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Asian Nurs Res(Korean Soc Nurs Sci), 2016, 10(1):82-87. |
| [5] | Pleasant A, McKinney J, Rikard RV. Health literacy measure-ment:a proposed research agenda[J]. J Health Commun, 2011, 16(Suppl 3):11-21. |
| [6] |
Prinsen CAC, Mokkink LB, Bouter LM, et al. COSMIN guideline for systematic reviews of patient-reported outcome measures[J]. Qual Life Res, 2018, 27(5):1147-1157.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Mokkink LB, de Vet HCW, Prinsen CAC, et al. COSMIN risk of bias checklist for systematic reviews of patient-reported outcome measures[J]. Qual Life Res, 2018, 27(5):1171-1179.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Alhazzani W, Guyatt G. An overview of the GRADE approach and a peek at the future[J]. Med J Aust, 2018, 209(7):291-292.
PMID |
| [9] | 朱冬梅. 2型糖尿病健康素养量表的编制及应用研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2021. |
| Zhu DM. Development and application of Health Literacy Scale for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2021. | |
| [10] |
Lee EH, Lee YW, Lee KW, et al. A new comprehensive dia-betes Health Literacy Scale:development and psychometric evaluation[J]. Int J Nurs Stud, 2018, 88:1-8.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Leung AY, Lou VW, Cheung MK, et al. Development and vali-dation of Chinese Health Literacy Scale for Diabetes[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2013, 22(15/16):2090-2099.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Ahmadi A, Niknami S, Ghaffari M. Type 2 diabetes health li-teracy assessment tool:translation and psychometric evaluation of the Iranian version[J]. Int J Endocrinol Metab, 2022, 20(2):e116983. |
| [13] |
Kang SJ, Sim KH, Song BR, et al. Validation of the Health Literacy Scale for Diabetes as a criterion-referenced test with standard setting procedures[J]. Patient Educ Couns, 2018, 101(8):1468-1476.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Eyübolu E, Schulz PJ. Validation of Turkish health literacy measures[J]. Health Promot Int, 2016, 31(2):355-362.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Ishikawa H, Takeuchi T, Yano E. Measuring functional,com-municative,and critical health literacy among diabetic patients[J]. Diabetes Care, 2008, 31(5):874-879.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | 赵晓燕, 李彦儒, 曾咏梅, 等. 糖尿病健康素养量表的汉化和信效度评价[J]. 中华护理教育, 2021, 18(3):266-269. |
| Zhao XY, Li YR, Zeng YM, et al. Evaluation of the reliability and validity of Health Literacy Scale-Chinese[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2021, 18(3):266-269. | |
| [17] |
McNaughton CD, Cavanaugh KL, Kripalani S, et al. Validation of a short,3-Item version of the Subjective Numeracy Scale[J]. Med Decis Making, 2015, 35(8):932-936.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Luo HB, Patil SP, Wu Q, et al. Validation of a combined health literacy and numeracy instrument for patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Patient Educ Couns, 2018, 101(10):1846-1851.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Huizinga MM, Elasy TA, Wallston KA, et al. Development and validation of the Diabetes Numeracy Test(DNT)[J]. BMC Health Serv Res, 2008, 8:96.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Alghodaier H, Jradi H, Mohammad NS, et al. Validation of a Diabetes Numeracy Test in Arabic[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(5):e0175442.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Moradi Y, Baradaran HR, Khamseh ME. Psychometric proper-ties of the Iranian version of the Diabetes Numeracy Test-15[J]. Int J Prev Med, 2016, 7:43.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
White RO 3rd, Osborn CY, Gebretsadik T, et al. Development and validation of a Spanish diabetes-specific numeracy mea-sure:DNT-15 Latino[J]. Diabetes Technol Ther, 2011, 13(9):893-898.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Al Sayah F, Majumdar SR, Egede LE, et al. Measurement pro-perties and comparative performance of health literacy scree-ning questions in a predominantly low income African American population with diabetes[J]. Patient Educ Couns, 2014, 97(1):88-95.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 彭健, 沈蓝君, 陈祎婷, 等. COSMIN-RoB清单简介及测量工具内部结构研究的偏倚风险清单解读[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2020, 20(10):1234-1240. |
| Peng J, Shen LJ, Chen YT, et al. An overview of the COSMIN-RoB checklist and the interpretation of it in evaluating the risk of bias of studies on internal structure[J]. Chin J Evid Based Med, 2020, 20(10):1234-1240. | |
| [25] |
支婷婷, 王艳波. 认知性访谈在创伤知情照护相关态度量表文化调适中的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(3):343-347.
DOI |
| Zhi TT, Wang YB. Application of cognitive interview in cultu-ral adjustment of Attitudes Related to Trauma-Informed Care Scale[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(3):343-347. | |
| [26] |
王浩云, 高云, 叶君荣, 等. 认知性访谈在精神科护士工作场所暴力管理能力量表构建中的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(17):2126-2133.
DOI |
| Wang HY, Gao Y, Ye JR, et al. Application of cognitive inter-view in the construction of Workplace Violence Management Ability Scale for Psychiatric Nurses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(17):2126-2133. | |
| [27] |
Moreira RS, Bassolli L, Coutinho E, et al. Reproducibility and reliability of the Quality of Life Questionnaire in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation[J]. Arq Bras Cardiol, 2016, 106(3):171-181.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Lee EH, Kim CJ, Lee J, et al. Self-administered health literacy instruments for people with diabetes:systematic review of measurement properties[J]. J Adv Nurs, 2017, 73(9):2035-2048.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
陈欢, 侯朝铭, 高静, 等. 中文版高血压患者服药依从性量表测量学特性的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(2):171-178.
DOI |
| Chen H, Hou CM, Gao J, et al. Chinese version of the Medication Adherence Scale for Patients with Hypertension:a systematic review of psychometric properties[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(2):171-178. | |
| [30] | 罗欢, 侯朝铭, 高静, 等. 中文版2型糖尿病患者自我管理评估工具测量属性的系统评价[J]. 中华护理教育, 2023, 20(3):349-355. |
| Luo H, Hou CM, Gao J, et al. Chinese version of the self-management assessment tools for patients with type 2 diabe-tes:a systematic review[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2023, 20(3):349-355. | |
| [31] | De Vet HCW, Terwee CB, Mokkink LB, et al. Measurement in medicine:a practical guide[J]. Meas Med A Pract Guide, 2011:1-338. |
| [32] | 陈艺蕾, 张晟, 柴菽彬, 等. 糖尿病中医疗效评价PRO量表的反应度研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2020, 35(4):2031-2033. |
| Chen YL, Zhang S, Chai SB, et al. Responsiveness of diabetes PRO scale of the evaluation for the efficacy of TCM[J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2020, 35(4):2031-2033. | |
| [33] |
AADE. AADE7 self-care behaviors[J]. Diabetes Educ, 2008, 34(3):445-449.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LIU Haiting, WANG Yongmei, ZHENG Beibei, CAI Lili, YE Linbin, WU Jiayun, NING Li, LI Yimin, CHEN Weixia. Development and reliability and validity test of a Self-Assessment Scale for Medication Literacy in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease Comorbidity Diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(9): 1065-1071. |
| [2] | Center for Evidence-based Nursing, Fudan University, (Writing Committee:XING Nianlu, ZHOU Yingfeng, CHEN Shuyu, FANG Yuan, LI Li, GU Yanhong, ZHAO Minhui, PAN Xiuhong). The development of a patient guideline on non-pharmacological management of gestational diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(6): 662-668. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xin, YIN Wei, LIU Qiaoyan, JIN Huayi, ZU Houjuan. Longitudinal relationship between family support and glucose management decision-making behaviours in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(6): 669-676. |
| [4] | CHEN Yumei, ZHAO Huifen, ZHAO Xiaoshan, ZHAO Meijing, PENG Yumei, SHEN Liqin. Development and reliability and validity test of a risk perception scale for pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(6): 677-684. |
| [5] | TANG Yalin, WEI Lili, LI Qianqian, KUANG Guofang, YUE Chongyu, ZHANG Xinwei, ZHANG Yan, GU Ruting, LÜ Bohan, ZHAO Yafei. Analysis on the current situation and influencing factors of social network among pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(6): 685-690. |
| [6] | WANG Qiaosong, ZHANG Kun, ZHENG Qirong, LIN Jingjing, ZHANG Xueling, FANG Yan, YANG Jingping, LIN Rong, LIN Rongjin. Evidence summary for maternal postpartum management of gestational diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(6): 691-698. |
| [7] | WANG Xuan, WEN Xianxiu, GOU Li, ZHOU Lijuan, CHEN Fuli, WU Haiyan, WANG Liang. The cardiac rehabilitation adherence assessment tools:a systematic review of psychometric properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(6): 736-743. |
| [8] | ZHAO Qiaomei, HUANG Bingying, XU Hongxia, CAI Lingyun, ZHOU Donger, ZHU Huanbing, DING Chao. Nursing care of a patient with infection of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae:a case report [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(5): 601-605. |
| [9] | FAN Lei, SONG Jihong, CHEN Shaohua, YANG Xinru, ZHAO Yaman, WU Jieling. Basic procedures and issue analysis of nursing systematic reviews [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(3): 281-286. |
| [10] | ZHANG Ruoxuan, ZHAO Jian, MU Lining. Meta-analysis and nursing implications of ketoacidosis caused by sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(3): 353-361. |
| [11] | ZHU Dongge, WANG Juzi, ZHAO Qian, HE Yapeng, ZHANG Zhuanzhuan, YANG Yutong. Systematic review of risk prediction models for intradialytic hypotension in patients with maintenance hemodialysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(2): 174-183. |
| [12] | LUO Yaping, YU Shujuan, ZHU Miaomiao, PAN Hongying. Self-neglect in elderly diabetic patients in the community:an interpretive phenomenological study [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(2): 203-209. |
| [13] | CAI Lingyun, ZENG Fei, GUO Luyao, LAN Meijuan, LIANG Jiangshuyuan, GU Peipei, ZHU Yan, GUO Ge. Analysis and nursing enlightenment of influencing factors of post-transplant diabetes mellitus in lung transplant recipients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(16): 1987-1992. |
| [14] | CHU Yunyi, JIANG Zifang, HE Zefan, ZHANG Jiaxin, CHEN Yanfei. Palliative care quality assessment tools based on the cancer patient experience:a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(13): 1657-1665. |
| [15] | WANG Qiaosong, ZHANG Kun, ZHANG Xueling, ZHENG Qirong, YANG Jingping, LIN Jingjing, LIN Rongjin. The application of mobile blood glucose management in pregnant women with gestational diabetes:a scoping review [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(10): 1270-1276. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||