


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (20): 2538-2546.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.20.015
周英凤( ), 杜世正, 张晓菊, 王志稳, 岳丽青, 罗旭飞, 胡雁(
), 杜世正, 张晓菊, 王志稳, 岳丽青, 罗旭飞, 胡雁( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-06
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-10-28
通讯作者:
胡雁,E-mail:huyan@fudan.edu.cn作者简介:周英凤:女,博士,教授,复旦大学循证护理中心副主任,E-mail:zyingfeng@fudan.edu.cn
ZHOU Yingfeng( ), DU Shizheng, ZHANG Xiaoju, WANG Zhiwen, YUE Liqing, LUO Xufei, HU Yan(
), DU Shizheng, ZHANG Xiaoju, WANG Zhiwen, YUE Liqing, LUO Xufei, HU Yan( )
)
Received:2023-11-06
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-10-28
摘要:
目的 对2022年期刊发表的中国护理领域指南及共识的科学性、透明性和适用性进行评价,为提升指南和共识的质量提供依据。方法 计算机检索Medline、Embase、Web of Science、中国知网、万方数据库、中国生物医学文献服务系统、中华医学期刊网,补充检索中国港澳台地区期刊网站,检索时限为2022年1月—12月。每篇指南或共识由3名评价者采用指南科学性、透明性和适用性的评级(STAR)工具进行独立评价,使用总分、各领域及条目得分率对评价结果进行描述性分析。结果 共纳入36篇文献,其中,33篇共识、3篇指南。指南和共识STAR总分为8.7~65.4(33.5±14.3)分,处于低水平。其中,指南的平均分为55.1分,处于中等水平;共识的平均分为31.5分,处于低水平。纳入文献“推荐意见”领域得分率最高,为52.4%。在各条目中,“说明了参与人员的机构”“说明了推荐意见实施过程中的注意事项”“说明了推荐意见共识方法”“主要推荐意见有明确的参考文献”得分率较高,分别为100%、83.3%、77.8%、75.0%;“进行了注册”“提供注册的平台和注册号信息”“计划书能够在公开平台获取”“说明了资助在指南制订中的作用”得分率最低,亟需关注与提升。结论 2022年期刊发表的中国护理领域指南和共识的总体质量为低水平。指南和共识作为临床护理决策的指导性文件,未来应倡导注册、明确利益冲突管理、提高指南制订各环节的严谨性、拓展传播途径,提升护理领域指南和共识的质量。
周英凤, 杜世正, 张晓菊, 王志稳, 岳丽青, 罗旭飞, 胡雁. 2022年期刊发表的中国护理领域指南及共识的质量评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(20): 2538-2546.
ZHOU Yingfeng, DU Shizheng, ZHANG Xiaoju, WANG Zhiwen, YUE Liqing, LUO Xufei, HU Yan. Evaluation of the quality of Chinese guidelines and expert consensuses on nursing published in 2022[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(20): 2538-2546.
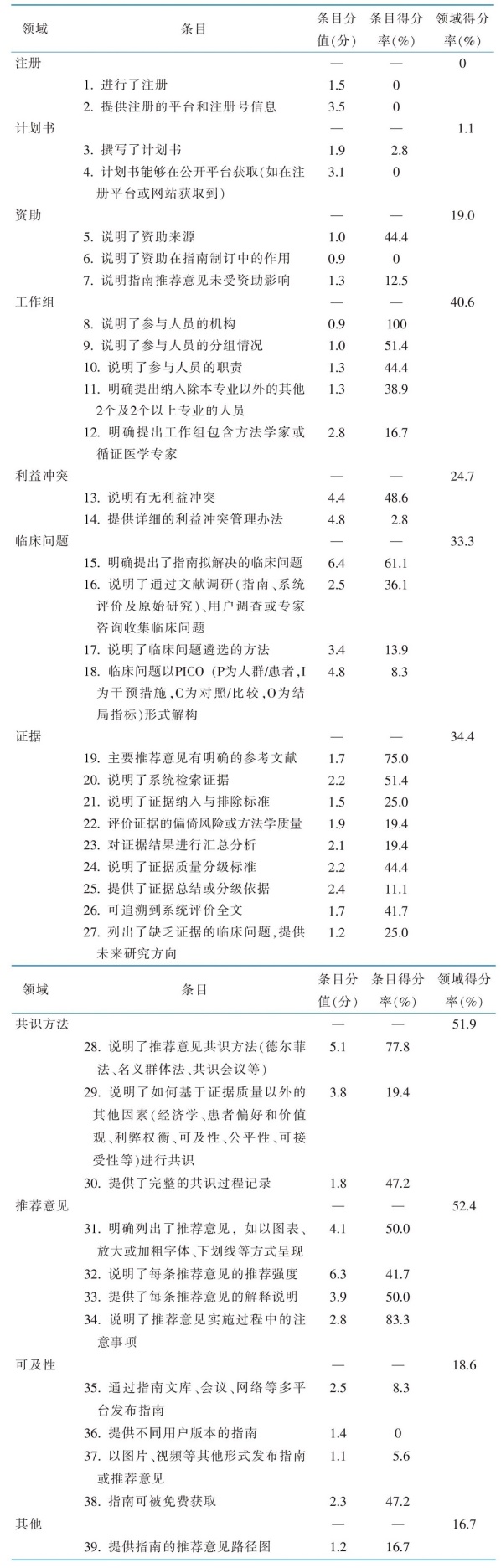 |
表2 2022年期刊发表中国护理领域指南和共识的各领域及条目得分率
Table 2 The scoring rate of domains and items of Chinese guidelines and expert consensuses on nursing published in 2022
 |
| [1] |
Grilli R, Magrini N, Penna A, et al. Practice guidelines deve-loped by specialty societies:the need for a critical appraisal[J]. Lancet, 2000, 355(9198):103-106.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | 中华医学会杂志社指南与标准研究中心, 中国医学科学院循证评价与指南研究创新单元(2021RU017), 世界卫生组织指南实施与知识转化合作中心, 等. 2022年医学期刊发表中国指南和共识的科学性、透明性和适用性的评级[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2023, 103(37):2912-2920. |
| Guidelines and Standards Research Center, Chinese Medical Association Publishing House;Research Unit of Evidence-Based Evaluation and Guidelines(2021RU017), Chinese Aca-demy of Medical Sciences;WHO Collaborating Centre for Guideline Implementation and Knowledge Translation;the Scientific,Transparent and Applicable Rankings(STAR) Work-ing Group, et al. Evaluation and ranking for scientific,transparent and applicable of Chinese guidelines and consensuses published in the medical journals in 2022[J]. Natl Med J China, 2023, 103(37):2912-2920. | |
| [3] | 杨楠, 赵巍, 潘旸, 等. 针对临床实践指南科学性、透明性和适用性的评级工具研发[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2022, 102(30):51-59. |
| Yang N, Zhao W, Pan Y, et al. The development of the Scientific,Transparent and Applicable Rankings(STAR) tool[J]. Natl Med J China, 2022, 102(30):51-59. | |
| [4] | Wang J, Zhang G, Min M, et al. Developing a non-pharma-cological intervention programme for wandering in people with dementia:recommendations for healthcare providers in nursing homes[J]. Brain Sci, 2022, 12(10):1321. |
| [5] | 中华医学会放射学分会护理工作组. 介入手术室医院感染控制和预防临床实践专家共识[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2022, 31(6):531-537. |
| Nursing Group,Radiology Branch of Chinese Medical Associa-tion. Expert consensus on the clinical infection control and prevention in interventional operating room[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2022, 31(6):531-537. | |
| [6] | 中华护理学会静脉输液治疗专业委员会. 静脉导管常见并发症临床护理实践指南[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2022, 28(18):2381-2395. |
| Intravenous Infusion Therapy Committee of Chinese Nursing Association. Clinical nursing practice guidelines for common complications of intravenous catheters[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2022, 28(18):2381-2395. | |
| [7] | 姚晖, 杨富, 毛晶珏, 等. 超声引导下PICC置管关键技术专家推荐意见及操作细则[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(1):150-153. |
| Yao H, Yang F, Mao JJ, et al. Experts recommendations and operation instructions for key technologies of PICC cathete-rization under ultrasonic guidance[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2022, 36(1):150-153. | |
| [8] | 中华护理学会内科护理专业委员会, 中国医药教育协会炎症性肠病护理专业委员会. 成人活动期炎症性肠病护理专家共识[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(8):1-6. |
| Internal Medicine Nursing Committee of the Chinese Nursing Association,Inflammatory Bowel Disease Nursing Committee of the China Medical Education Association. Expert consensus on nursing care of adults with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(8):1-6. | |
| [9] | 中国研究型医院学会危重医学专委会护理研究学组. 呼吸机雾化吸入疗法护理实践专家共识[J]. 现代临床护理, 2022, 21(4):8-17. |
| The Nursing Research Group of Chinese Research Hospital Association of Critical Care Medicine. Expert consensus on nursing practice in aerosol inhalation therapy with mechanical ventilation[J]. Mod Clin Nurs, 2022, 21(4):8-17. | |
| [10] | 上海市医师协会胸外科医师分会, 上海市肺移植工程技术研究中心. 肺移植手术护理配合专家共识(2022版)[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2022, 29(11):1395-1401. |
| Thoracic Surgery Branch of Shanghai Physicians Association, Shanghai Lung Transplantation Engineering and Technology Research Centre. Expert consensus on lung transplantation nursing(version 2022)[J]. Chin J Clin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2022, 29(11):1395-1401. | |
| [11] |
中华护理学会重症护理专业委员会, 北京医学会肠外肠内营养学会护理学组. 神经重症患者肠内喂养护理专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(3):261-264.
DOI |
|
Intensive Care Committee of Chinese Nursing Association,Beijing Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Nursing Group. Expert consensus on enteral feeding nursing for patients with severe neurological diseases[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(3):261-264.
DOI |
|
| [12] |
中华护理学会精神卫生专业委员会. 精神科保护性约束实施及解除专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(2):146-151.
DOI |
|
Mental Health Professional Committee of Chinese Nursing Association. Expert consensus on the implementation and removal of protective restraints in psychiatry[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(2):146-151.
DOI |
|
| [13] | 冯丽, 张玉侠, 张梦霞, 等. 应用心肺复苏机救治院内心搏骤停患者护理专家共识[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2022, 28(22):2941-2948. |
| Feng L, Zhang YX, Zhang MX, et al. Nursing expert consensus on application of cardiopulmonary resuscitation machine in treating patients with in-hospital cardiac arrest[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2022, 28(22):2941-2948. | |
| [14] |
中华护理学会外科护理专业委员会, 中华医学会外科学分会护理学组. 普通外科患者静脉血栓栓塞症风险评估与预防护理专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(4):444-449.
DOI |
|
The Surgical Nursing Committee of Chinese Nursing Associa-tion,the Nursing Group of Chinese Society of Surgical of Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on risk assess-ment and prevention of venous thromboembolism in general surgical patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(4):444-449.
DOI |
|
| [15] |
中华医学会肠外肠内营养学会护理学组. 肠外营养安全输注专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(12):1421-1426.
DOI |
|
Chinese Medical Association of Parenteral and Enteral Nutri- tion Nursing Group. Expert consensus on parenteral nutrition safety infusion[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(12):1421-1426.
DOI |
|
| [16] | 中华医学会放射学分会护理工作组. 门静脉高压患者经颈静脉肝内门体分流术护理管理专家共识[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2022, 31(2):117-124. |
| Nursing Group,Radiology Society of Chinese Medical Associa-tion. Expert consensus on nursing management for patients with portal hypertension after transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2022, 31(2):117-124. | |
| [17] | 中国抗癌协会甲状腺癌专业委员会护理学组. 甲状腺癌加速康复外科围手术期护理专家共识[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(1):1-7. |
| Nursing Committee of Chinese Association of Thyroid Onco-logy. Enhanced recovery after surgery(ERAS) of perioperative nursing in thyroid oncology:an experts consensus[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2022, 36(1):1-7. | |
| [18] | 北京护理学会心血管专业委员会. 冠心病患者心脏康复健康教育处方护理专家共识[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2022, 28(9):1121-1127. |
| Cardiovascular Professional Committee. Expert consensus on prescription nursing of cardiac rehabilitation health education for patients with coronary heart disease[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2022, 28(9):1121-1127. | |
| [19] | Wang YL, Li YC, Shen BY, et al. Nursing ethics for preven-tion and control of major infectious disease outbreaks:Chinese expert consensus[J]. Int J Nurs Sci, 2022, 9(1):5-10. |
| [20] | 中国康复医学会脊柱脊髓专业委员会护理学组, 四川省医学会骨科专业委员会护理学组. 颈椎病患者围手术期睡眠护理管理专家共识[J]. 华西医学, 2022, 37(10):1454-1459. |
| Nursing Group,Professional Committee of Spine and Spinal Cord,, Chinese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine,Nursing Group,Professional Committee of Orthopaedics,Sichuan Medical Association. Expert consensus on perioperative sleep care ma-nagement for patients with cervical spondylosis[J]. West China Med J, 2022, 37(10):1454-1459. | |
| [21] | 中国抗癌协会脑胶质瘤专业委员会. 胶质母细胞瘤肿瘤电场治疗头皮护理专家共识[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2022, 28(21):2801-2807. |
| Brain Glioma Committee of China Anti-Cancer Association. Expert consensus on scalp nursing in glioblastoma tumor-treating fields[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2022, 28(21):2801-2807. | |
| [22] | 湖北省医学会介入医学分会护理学组. 肝细胞癌经动脉化疗栓塞治疗围手术期护理策略专家共识[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2022, 41(2):212-216. |
| Medicine Branch of Hubei Medical Association. Expert con-sensus on perioperative nursing strategy of hepatocellular carcinoma treated by arterial chemoembolization[J]. J Clin Ra-diol, 2022, 41(2):212-216. | |
| [23] |
Xu Y, Fei XY, Xue YH, et al. Chinese expert consensus on the nursing management of the totally implantable venous access device[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2022, 18(5):1231-1240.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | 上海现代服务业联合会医疗服务专业委员会. 医疗机构护理员工作内容的专家建议[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2022, 28(14):1821-1825. |
| Medical Service Professional Committee of Shanghai Modern Service Industry Federation. Expert recommendations on the job content of nursing workers in medical institutions[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2022, 28(14):1821-1825. | |
| [25] |
中华护理学会血液净化专业委员会, 上海市护理学会血液净化专业委员会. 血液透析安全注射临床实践专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(7):785-790.
DOI |
|
Blood Purification Committee of Chinese Nursing Association,Blood Purification Committee of Shanghai Nursing Associa-tion. Expert consensus on clinical practice of injection safety in hemodialysis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(7):785-790.
DOI |
|
| [26] | 国家儿童医学中心儿科护理联盟《危重症儿童临终关怀专家共识》制作组. 中国危重症儿童临终关怀专家共识(2022版)[J]. 中国小儿急救医学, 2022, 29(8):600-605. |
| The Expert Development Consensus Group from the Commit-tee of Pediatric Nursing of National Children’s Medical Center. Expert consensus on hospice care for critically ill children in China(2022 edition)[J]. Chin Pediatr Emerg Med, 2022, 29(8):600-605. | |
| [27] | 北京护理学会手术室专业委员会. 手术室静脉血栓栓塞症预防与护理专家共识[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2022, 28(20):2661-2669. |
| Professional Committee of Operating Room,Beijing Nursing Association,China-Japan Friendship Hospital. Expert consensus on prevention and nursing of venous thromboembolism in operating room[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2022, 28(20):2661-2669. | |
| [28] | 上海市肺栓塞和深静脉血栓防治联盟, 国际血管联盟中国分部护理专业委员会, 上海市护理学会外科护理专业委员会. 间歇充气加压用于静脉血栓栓塞症预防的中国专家共识[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2022, 37(7):549-553. |
| Shanghai Federation on Prevention and Treatment of Pulmo-nary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis,Nursing Professio-nal Committee of China Branch of the International Vascular Alliance, Surgical Nursing Professional Committee of Shanghai Nursing Society. China expert consensus on intermittent inflating and pressurizing for prevention of venous thromboe-mbolism[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2022, 37(7):549-553. | |
| [29] | 中国研究型医院学会护理分会. 成人肠造口皮肤黏膜分离护理专家共识[J]. 中国研究型医院, 2022, 9(5):9-12. |
| Nursing Branch of Chinese Research Hospital Association. Expert consensus on mucocutaneous separation nursing for adult enterostomy[J]. Chin Res Hosp, 2022, 9(5):9-12. | |
| [30] | 中华护理学会精神卫生专业委员会. 精神科住院抑郁症患者自杀预防及护理干预措施专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(18):2181-2185. |
| Mental Health Professional Committee of Chinese Nursing Association. Expert consensus of suicide care interventions for psychiatric inpatients with depression[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(18):2181-2185. | |
| [31] |
广东省医学会泌尿外科学分会. 尿路结石腔内碎石患者围手术期并发尿脓毒症护理专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(8):914-917.
DOI |
|
Urology Branch of Guangdong Medical Association. Expert consensus on perioperative urosepsis nursing of patients with intracavitary surgery for urinary tract calculi[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(8):914-917.
DOI |
|
| [32] | 刘义兰, 金艳, 陈秋香, 等. 医院参与全员新冠病毒核酸检测样本采集管理专家共识[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(5):1-4. |
| Liu YL, Jin Y, Chen QX, et al. Expert consensus on hospital participation in population-wide specimen collection for COVID-19 testing[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(5):1-4. | |
| [33] | 国际血管联盟中国分部护理专业委员会. 周围血管血栓性疾病置管溶栓护理专家共识[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2022, 31(11):1045-1051. |
| Professional Committee of Nursing Care,Chinese Chapter of International Union of Angiology. Expert consensus on the nursing care for patients with peripheral vascular thrombotic diseases treated with catheter-directed thrombolysis[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2022, 31(11):1045-1051. | |
| [34] | 中华护理学会眼科护理专业委员会. 《超声乳化手术专用手术器械清洗、消毒、灭菌操作流程》专家共识[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(23):4137-4140. |
| Ophthalmic Nursing Committee of Chinese Nursing Associa-tion. Experts consensus on “operation procedures of cleaning,disinfection and sterilization of special surgical instruments for phacoemulsification surgery”[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2022, 36(23):4137-4140. | |
| [35] | 王正国创伤医学基金会围手术期加速康复护理联盟. 成人术后口渴症状评估与管理的专家共识[J]. 军事护理, 2022, 39(12):1-4. |
| Wang Zhengguo Trauma Medicine Foundation Perioperative Accelerated Rehabilitation Care Coalition. Expert consensus on the assessment and management of postoperative thirst symptoms in adults[J]. Mil Nurs, 2022, 39(12):1-4. | |
| [36] | 许娟, 莫蓓蓉, 胡玉娜, 等. 重症监护病房成人患者护理人文关怀专家共识[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(18):1-4. |
| Xu J, Mo BR, Hu YN, et al. Expert consensus on nursing human caring for ICU adult patients[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(18):1-4. | |
| [37] | 中华护理学会传染病护理专业委员会, 湖南省护理学会传染病护理专业委员会, 湖南省医学会感染病学专业委员会肝衰竭和人工肝学组, 等. 经皮股静脉人工肝临时血管通路管理的专家共识[J]. 循证护理, 2022, 8(5):614-619. |
| Infectious Disease Nursing Professional Committee of Chinese Nursing Association,Infectious Disease Nursing Professional Committee of Hunan Nursing Association, Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group of Infectious Diseases Professional Committee of Hunan Medical Association, et al. Expert con-sensus on management of transcutaneous femoral vein as temporary vascular access for artificial liver[J]. Chin Evid Based Nurs, 2022, 8(5):614-619. | |
| [38] | 中国医师协会介入医师分会外周血管介入专业学组, 中国静脉介入联盟, 国际血管联盟中国分部护理专业委员会, 等. 布-加综合征介入治疗护理规范专家共识[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2022, 31(5):429-437. |
| Professional Committee on Peripheral Vascular Intervention of Interventional Physician Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association,Chinese Intravenous Intervention Alliance, Profes-sional Committee on Nursing Care, Chinese Chapter of Inter-national Union of Angiology, et al. Expert consensus on nursing standards for patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome receiving interventional treatment[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2022, 31(5):429-437. | |
| [39] | 中华护理学会老年护理专业委员会, 中国康复医学会心血管疾病预防与康复专业委员会, 中国老年保健协会脏器康复专业委员会, 等. 心脏康复护理专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(16):1937-1941. |
| Geriatric Nursing Committee of Chinese Nursing Association,Committee of Cardiac Rehabilitation and Prevention of Chinese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine, Organ Reha-bilitation Committee of Chinese Elder Health Care Associa-tion, et al. Chinese expert consensus on cardiac rehabilitation nursing care[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(16):1937-1941. | |
| [40] | 中华医学会杂志社指南与标准研究中心, 中国医学科学院循证评价与指南研究创新单元, 世界卫生组织指南实施与知识转化合作中心. 2021年医学期刊发表中国指南和共识的科学性、透明性和适用性的评级[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2022, 102(30):10-19. |
| Guidelines and Standards Research Center, Chinese Medical Association Publishing House;Research Unit of Evidence-Based Evaluation and Guidelines, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences,WHO Collaborating Centre for Guideline Implementation and Knowledge Translation. Evaluation and ranking for scientificity,transparency and applicability of Chinese guidelines and consensuses published in the medical journals in 2021[J]. Natl Med J China, 2022, 102(30):10-19. |
| [1] | 梁元元, 高兴莲, 戴张章, 周荣超, 胡娟娟, 王曾妍, 沈剑辉. 医院手术器械管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 1005-1011. |
| [2] | 王婷, 王佳婷, 金爱云, 朱霞明, 方云, 汪靖, 田菲, 濮益琴, 万滢, 贺瑾, 颜霞. 自体造血干细胞移植术后患者护理随访清单的构建及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 914-920. |
| [3] | 盛婉婷, 王蕊, 赵玉晓, 戚鹏菲, 高祀龙, 冯娟, 吕伯瀚, 牛群, 王刚. 中等长度静脉导管不同尖端位置应用效果的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 990-997. |
| [4] | 严雪芹, 曹松梅, 周芳芳, 朱丽群, 陈成, 朱梦雪, 张艳红, 梁怡青, 柏素萍. 手部烧伤患者手功能早期康复管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 998-1004. |
| [5] | 魏永婷, 田书梅, 杨娇, 余良欢, 倪福, 范雨晴, 肖瑶, 席祖洋, 沙菊艳, 刘聪. 护士循证决策能力量表的汉化及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 736-742. |
| [6] | 王雯静, 郝妩媚, 台靖宇, 董倩, 郭爱敏. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者吸入药物治疗体验的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 545-551. |
| [7] | 国家心血管病中心 中华护理学会心血管专业委员会(执笔:张茜 刘亚飞 李梦然 王娜 王艳娇 王诗瑜 李庆印). 先天性心脏病患儿围生期护理管理专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 552-557. |
| [8] | 中国抗癌协会肿瘤康复整合护理专业委员会(执笔:王影新 刘飞 武佩佩 张丽娟 杨福娜 叶丽). 乳腺癌术后患者淋巴水肿防治的居家运动专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 558-560. |
| [9] | 唐佳怡, 唐桂清, 张娜, 李晓波. 慢加急性肝衰竭患者营养管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 581-588. |
| [10] | 刘婷婷, 牛巧红, 焦雪萍, 卫嘉玮, 段少铭, 胡聪丽, 苏芮. 直肠癌保肛术后患者肠道症状体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 603-610. |
| [11] | 蒋思珊, 成琴琴, 罗听薇, 张娜, 郭俊晨, 李东雅, 李丹丹, 朱丽辉. 儿童安宁疗护质量评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 611-618. |
| [12] | 中华护理学会老年护理专业委员会, 北京医院 国家老年医学中心, 中国医学科学院老年医学研究院, 北京大学护理学院(执笔:刘文静 王志稳 余跃琳 任欣 琚慧 陈宏 王君鑫 陈闪闪 周佳 伊默 王文霞 张玲娟 陈思烨 杨宇帆 王小萌 孙红). 老年人内在能力评估与维护指南[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 261-265. |
| [13] | 段煜, 郭张慧, 张洁, 焦萌, 屈简妮, 刘桂英, 赵丹, 陈颖宇, 郭红. 衰弱老年人运动锻炼促进与阻碍因素的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 288-296. |
| [14] | 宗小燕, 李红燕, 韩小云, 景新华. 胃癌患者围手术期口服营养补充管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 355-363. |
| [15] | 国家儿童医学中心儿科护理联盟急危重症护理学组 国家儿童医学中心儿科护理联盟消化护理学组(执笔:邹瑜 顾莺 余卓文 黄艳 杨玉霞 李素云 王颖雯). 儿童胃管及肠管置管专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(14): 1700-1704. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||