


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (24): 2956-2963.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.24.002
徐雅萍( ), 贾云洋, 易祖玲, 许蕊凤, 佟冰度, 鲁雪梅
), 贾云洋, 易祖玲, 许蕊凤, 佟冰度, 鲁雪梅
收稿日期:2025-04-21
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-19
作者简介:徐雅萍:女,硕士,副主任护师,护士长,E-mail:yaping0535@163.com
基金资助:
XU Yaping( ), JIA Yunyang, YI Zuling, XU Ruifeng, TONG Bingdu, LU Xuemei
), JIA Yunyang, YI Zuling, XU Ruifeng, TONG Bingdu, LU Xuemei
Received:2025-04-21
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-19
摘要:
目的 探究老年髋部骨折患者出院准备度的潜在剖面并分析其影响因素,为临床实施精准化出院准备护理干预提供依据。 方法 采用便利抽样法,选取2024年9月—2025年2月北京市5所三级甲等医院收治的老年髋部骨折患者作为调查对象,通过一般资料调查表、社会支持评定量表、出院指导质量量表、出院准备度量表对其进行问卷调查。采用潜在剖面分析和多元Logistic回归分析进行数据分析。 结果 回收有效问卷215份,有效问卷回收率为93.48%。老年髋部骨折患者出院准备度得分为6.17(5.42,6.75)分,处于中等偏低水平。出院准备度可被分为3个分型:低准备-全面薄弱型(21.86%)、高准备-适应引领型(39.07%)、中准备-支持优势型(39.07%)。家庭年收入水平、出院时日常生活活动能力、社会支持水平是老年髋部骨折患者出院准备度潜在剖面的影响因素(均P<0.05)。 结论 老年髋部骨折患者出院准备度处于中等偏低水平且存在明显异质性,建议对低准备-全面薄弱型患者实施基础需求优先-系统支持强化策略,对高准备-适应引领型患者强化院内支持、优化延续护理,对中准备-支持优势型患者实施支持-效能转化干预。
徐雅萍, 贾云洋, 易祖玲, 许蕊凤, 佟冰度, 鲁雪梅. 老年髋部骨折患者出院准备度的潜在剖面分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(24): 2956-2963.
XU Yaping, JIA Yunyang, YI Zuling, XU Ruifeng, TONG Bingdu, LU Xuemei. Latent profile analysis and influencing factors of discharge readiness among older patients with hip fractures and nursing strategies[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(24): 2956-2963.
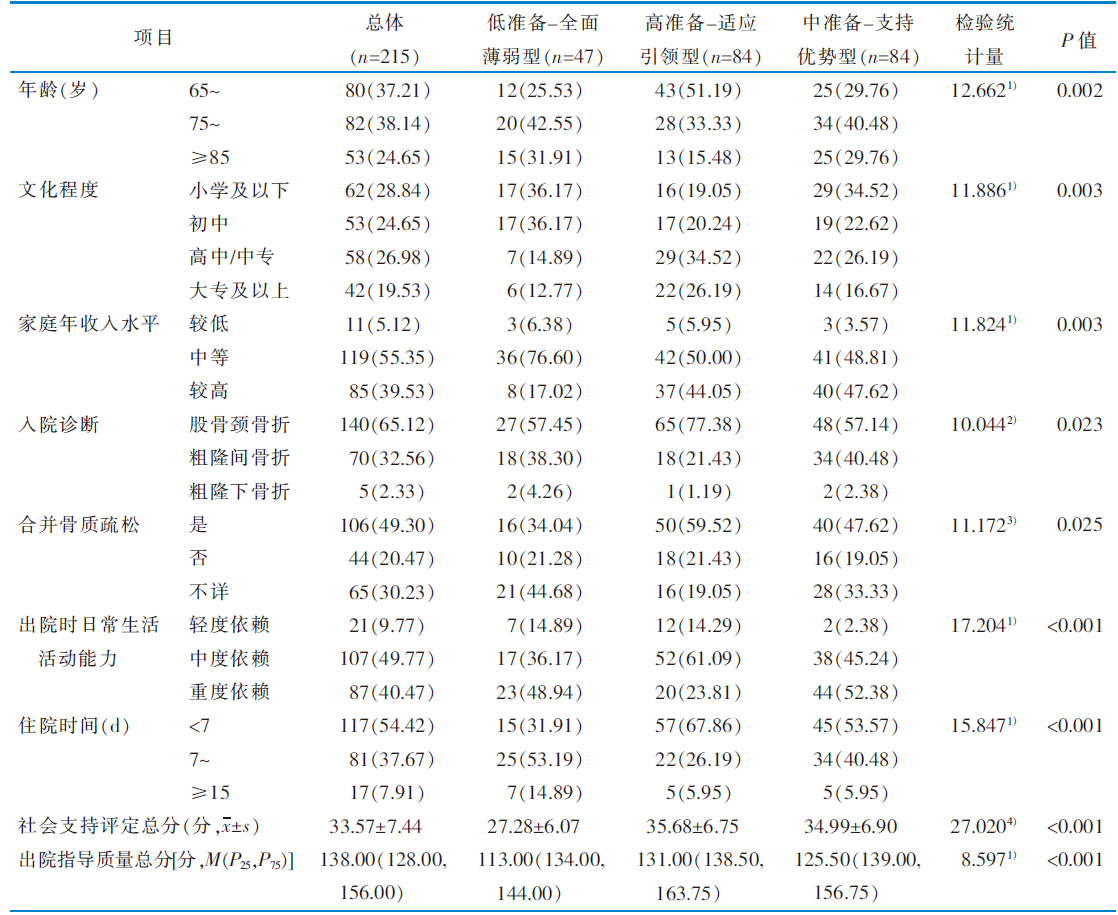 |
表1 老年髋部骨折患者的一般资料及出院准备度潜在剖面的单因素分析
Table 1 General information and univariate analysis of potential profiles of discharge readiness among older patients with hip fractures
 |
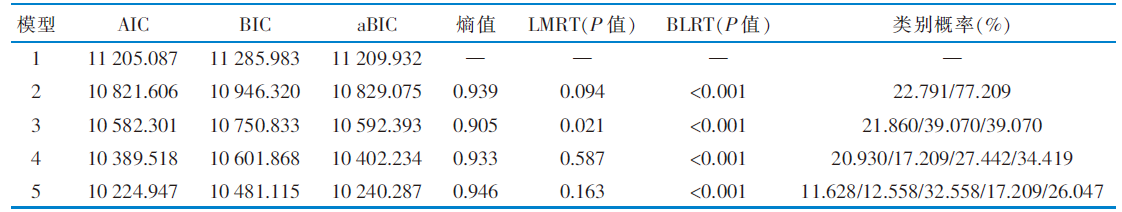 |
表2 老年髋部骨折患者出院准备度潜在剖面模型的拟合指标(n=215)
Table 2 Model fitting results of potential profile analysis model for discharge readiness among older patients with hip fractures(n=215)
 |
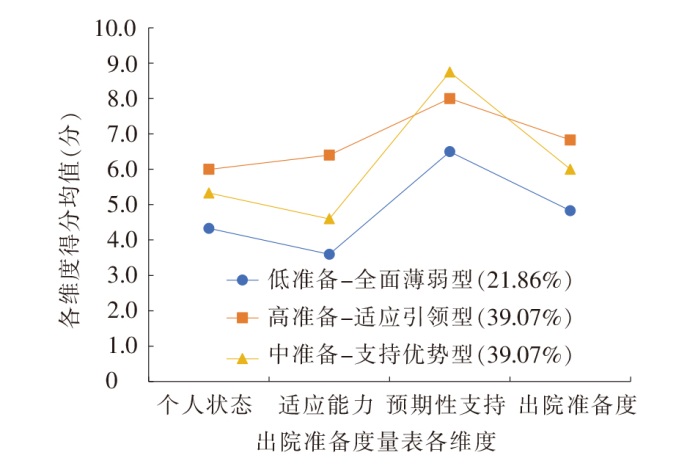
图1 老年髋部骨折患者出院准备度3个潜在剖面的特征分布
Figure 1 The characteristic distribution of 3 potential profiles of discharge readiness among older patients with hip fractures
 |
表4 老年髋部骨折患者出院准备度潜在剖面的多因素分析(n=215)
Table 4 Multifactor analysis of potential profiles of discharge readiness among older patients with hip fractures(n=215)
 |
| [1] | 国家卫生健康委员会医政司. 老年髋部骨折诊疗与管理指南(2022年版)[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2023, 25(4):277-283. |
| Medical Administration Bureau of National Health Commission. Guidelines for treatment and management of hip fractures in the elderly(2022 version)[J]. Chin J Orthop Trauma, 2023, 25(4):277-283. | |
| [2] |
Veronese N, Maggi S. Epidemiology and social costs of hip fracture[J]. Injury, 2018, 49(8):1458-1460.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(14):1671-1691.
DOI |
| Chinese Society of Osteoporosis and Bone Mineral Research. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of primary osteoporosis(2022)[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2023, 26(14):1671-1691. | |
| [4] |
Downey C, Kelly M, Quinlan JF. Changing trends in the mortality rate at 1-year post hip fracture:a systematic review[J]. World J Orthop, 2019, 10(3):166-175.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | 北京市统计局. 北京市2024年国民经济和社会发展统计公报. [EB/OL]. (2025-03-20)[2025-03-26]. https://tjj.beijing.gov.cn/tjsj_31433/tjgb_31445/ndgb_31446/202503/t20250319_4038820.html. |
| Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing 2024 statistical bulletin of national economic and social development[EB/OL].(2025-03-20)[2025-03-26]. https://tjj.beijing.gov.cn/tjsj_31433/tjgb_31445/ndgb_31446/202503/t20250319_4038820.html. | |
| [6] | 刘刚, 杨明辉, 张京, 等. 北京地区老年髋部骨折的流行病学分布特点:多中心2071例患者分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2022, 24(9):759-765. |
| Liu G, Yang MH, Zhang J, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of geriatric hip fracture in Beijing:a multicenter analysis of 2,071 cases[J]. Chin J Orthop Trauma, 2022, 24(9):759-765. | |
| [7] | 宋宏晖, 张鹏, 徐炜, 等. 加速康复外科管理模式对高龄髋部骨折患者护理效果评价[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2021, 37(9):825-832. |
| Song HH, Zhang P, Xu W, et al. Evaluation of nursing effect of enhanced recovery after surgery model in elderly patients with hip fracture[J]. Chin J Trauma, 2021, 37(9):825-832. | |
| [8] | 赵媛, 彭贵凌. 多学科协作下老年髋部骨折围手术期医护一体信息化护理模式的研究[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2021, 37(7):481-486. |
| Zhao Y, Peng GL. Study on the information-based nursing mode of the elderly patients with hip fracture in perioperative period under multidisciplinary cooperation[J]. Chin J Pract Nurs, 2021, 37(7):481-486. | |
| [9] | 张明辉, 郭丽君, 胡玉红, 等. 上海市居家康复治疗项目实施现况及影响因素[J]. 中国卫生资源, 2023, 26(2):203-213. |
| Zhang MH, Guo LJ, Hu YH, et al. Implementation status and influencing factors of home-based rehabilitation treatment project in Shanghai[J]. Chin Health Resour, 2023, 26(2):203-213. | |
| [10] | 安若轩, 陈圆圆, 刘良红, 等. 出院准备度的概念分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2025, 40(2):104-107. |
| An RX, Chen YY, Liu LH, et al. Conceptual analysis of discharge readiness[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2025, 40(2):104-107. | |
| [11] | 何丹, 胡三莲, 周玲, 等. 老年髋部骨折患者出院准备度的现况及影响因素分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2020, 26(27):3732-3737. |
| He D, Hu SL, Zhou L, et al. Current status and influencing factors for discharge readiness in elderly patients with hip fractures[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2020, 26(27):3732-3737. | |
| [12] | 王惠惠, 李娜, 魏民, 等. 老年髋部骨折术后患者出院准备度在社会支持和生活质量间的中介效应分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2022, 28(18):2431-2436. |
| Wang HH, Li N, Wei M, et al. Mediating effect of discharge readiness on social support and quality of life in elderly patients with hip fracture[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2022, 28(18):2431-2436. | |
| [13] |
温忠麟, 谢晋艳, 王惠惠. 潜在类别模型的原理、步骤及程序[J]. 华东师范大学学报(教育科学版), 2023, 41(1):1-15.
DOI |
| Wen ZL, Xie JY, Wang HH. Principles,procedures and programs of latent class models[J]. J East China Norm Univ Educ Sci, 2023, 41(1):1-15. | |
| [14] |
Cohen J. A power primer[J]. Psychol Bull, 1992, 112(1):155-159.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
梅伶俐, 陈朔晖, 胡艳, 等. 社会生态系统理论视角下短肠综合征患儿照护者负担体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(6):718-723.
DOI URL |
| Mei LL, Chen SH, Hu Y, et al. Caring experience of caregivers of children with short bowel syndrome based on the social ecological theory:a qualitative study[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(6):718-723. | |
| [16] |
韩明华, 赵倩, 罗明月, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者社会隔离体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5):532-539.
DOI URL |
| Han MH, Zhao Q, Luo MY, et al. Experience of social isolation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:a qualitative study[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(5):532-539. | |
| [17] |
Welsh A, Hanson S, Pfeiffer K, et al. Facilitating the transition from hospital to home after hip fracture surgery:a qualitative study from the HIP HELPER trial[J]. BMC Geriatr, 2024, 24(1):948.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | 肖水源. 《社会支持评定量表》的理论基础与研究应用[J]. 临床精神医学杂志, 1994, 4(2):98-100. |
| Xiao SY. Theoretical basis and research application of Social Support Rating Scale[J]. J Clin Psychiatry, 1994, 4(2):98-100. | |
| [19] |
李莉, 申雅文, 李德龙, 等. 脆性骨折术后患者康复自我效能感的影响因素及路径分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(24):3003-3008.
DOI URL |
|
Li L, Shen YW, Li DL, et al. Analysis of influencing factors and pathways of postoperative self-efficacy in patients with fragility fracture[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(24):3003-3008.
DOI URL |
|
| [20] | 王婧怡, 孔晓倩, 王莉, 等. 失能老年人及家庭照顾者衰弱与社会支持、自我效能的主客体效应分析[J]. 中国护理管理, 2024, 24(12):1836-1841. |
| Wang JY, Kong XQ, Wang L, et al. Relationships among social support,self-efficacy,and frailty in disabled older adults and their family caregivers:the actor-partner interdependence analysis[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2024, 24(12):1836-1841. | |
| [21] | 李竹梅, 孙念梅. 妊娠晚期孕妇创伤后应激障碍与分娩恐惧、社会支持的相关性[J]. 护理研究, 2024, 38(16):2985-2991. |
| Li ZM, Sun NM. Correlation of post-traumatic stress disorder with fear of childbirth and social support in pregnant women in the third trimester[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2024, 38(16):2985-2991. | |
| [22] |
Weiss ME, Piacentine LB, Lokken L, et al. Perceived readiness for hospital discharge in adult medical-surgical patients[J]. Clin Nurse Spec, 2007, 21(1):31-42.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | 王冰花, 汪晖, 杨纯子. 中文版出院指导质量量表的信效度测评[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2016, 51(6):752-755. |
| Wang BH, Wang H, Yang CZ. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Quality of Discharge Teaching Scale[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2016, 51(6):752-755. | |
| [24] |
Weiss ME, Piacentine LB. Psychometric properties of the Readiness for Hospital Discharge Scale[J]. J Nurs Meas, 2006, 14(3):163-180.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | 林佑樺, 高家常, 黄阿美, 等. 中文版医院出院准备度量表之信效度检定[J]. 护理杂志, 2024, 61(4):56-65. |
| Lin YH, Gao CC, Huang AM, et al. Psychometric testing of the Chinese version of the Readiness for Hospital Discharge Scale[J]. The Journal of Nursing, 2014, 61(4):56-65. | |
| [26] |
韩琳, 闫楚楚, 单亚维, 等. 髋关节置换患者出院准备服务的循证实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(10):1157-1164.
DOI URL |
|
Han L, Yan CC, Shan YW, et al. Evidence-based practice of discharge preparation services for hip replacement patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(10):1157-1164.
DOI URL |
|
| [27] |
李红颐, 李雪, 范宇莹, 等. ICU患者创伤心理反应的潜在剖面及影响因素的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7):842-849.
DOI URL |
|
Li HY, Li X, Fan YY, et al. A mixed study of latent profile analysis and influencing factors of psychological responses to trauma in ICU patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(7):842-849.
DOI URL |
|
| [28] |
张文忠, 季红, 王宁, 等. 全膝关节置换术后患者康复治疗体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(24):3028-3036.
DOI URL |
| Zhang WZ, Ji H, Wang N, et al. Rehabilitation experience of patients after total knee arthroplasty:a qualitative meta-synthesis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(24):3028-3036. | |
| [29] | 乔晓春. 对未来中国养老照护需求的估计[J]. 人口与发展, 2021, 27(1):105-116. |
| Qiao XC. Estimation of care needs of Chinese elderly in the future[J]. Popul Dev, 2021, 27(1):105-116. | |
| [30] | 汤叶丛, 庄丽丽, 李秀文, 等. 医患共同决策在临床实践中的困境及对策[J]. 医学与哲学, 2025, 46(4):19-23. |
| Tang YC, Zhuang LL, Li XW, et al. Challenges and strategies of shared decision-making in clinical practice[J]. Med Philos, 2025, 46(4):19-23. | |
| [31] |
Bandura A. Self-efficacy:toward a unifying theory of behavioral change[J]. Psychol Rev, 1977, 84(2):191-215.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||