


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (24): 2964-2970.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.24.003
李蕊( ), 宋红(
), 宋红( ), 张春艳, 范晓娟, 王瑶, 耿黎明, 杜颖, 单小天
), 张春艳, 范晓娟, 王瑶, 耿黎明, 杜颖, 单小天
收稿日期:2025-03-13
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
宋红,E-mail:songhong197712@163.com作者简介:李蕊:女,硕士,主管护师,E-mail:vividlee2011@126.com
基金资助:
LI Rui( ), SONG Hong(
), SONG Hong( ), ZHANG Chunyan, FAN Xiaojuan, WANG Yao, GENG Liming, DU Ying, SHAN Xiaotian
), ZHANG Chunyan, FAN Xiaojuan, WANG Yao, GENG Liming, DU Ying, SHAN Xiaotian
Received:2025-03-13
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-19
摘要:
目的 基于主客体互倚模型探讨恶性骨肿瘤患者和其配偶情绪调节困难与抑郁症状的纵向相互作用,为降低双方抑郁症状提供依据。 方法 采用便利抽样法,选择2021年10月—2024年9月徐州市某三级甲等医院骨科收治的188例恶性骨肿瘤患者和其配偶作为调查对象,采用情绪调节状态困难量表、9条目患者健康问卷分别于术后、术后1个月、术后3个月进行调查,采用主客体互倚模型的交叉滞后分析进行统计检验。 结果 回收有效问卷186份,有效问卷回收率为98.94%。恶性骨肿瘤患者和其配偶情绪调节困难对抑郁症状的主体效应具有显著性,即患者和其配偶的情绪调节困难可以正向预测下一阶段自身的抑郁症状。患者和其配偶抑郁症状对情绪调节困难的主体效应具有显著性,即患者和其配偶的抑郁症状可以正向预测一下阶段自身的情绪调节困难。抑郁症状的客体效应具有显著性,即患者和其配偶的抑郁症状可以正向预测下一阶段对方的抑郁症状。 结论 恶性骨肿瘤患者和其配偶情绪调节困难与抑郁症状相互作用,临床应同步干预双方情绪调节能力,阻断抑郁症状的相互影响。
李蕊, 宋红, 张春艳, 范晓娟, 王瑶, 耿黎明, 杜颖, 单小天. 恶性骨肿瘤患者和配偶情绪调节困难与抑郁症状的纵向交互作用及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(24): 2964-2970.
LI Rui, SONG Hong, ZHANG Chunyan, FAN Xiaojuan, WANG Yao, GENG Liming, DU Ying, SHAN Xiaotian. Longitudinal dyadic interactions between emotion dysregulation and depressive symptoms in patients with malignant bone tumors and their spouses[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(24): 2964-2970.
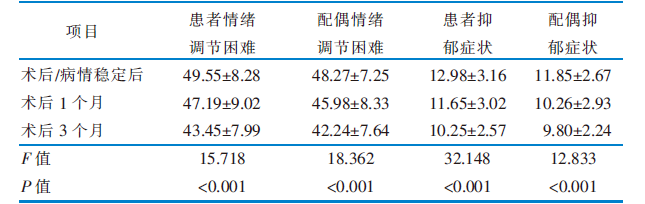 |
表3 恶性骨肿瘤患者和其配偶情绪调节困难、抑郁症状得分(n=186,分,$\bar{x}±s$)
Table 3 Scores of emotion dysregulation and depressive symptoms in patients with malignant bone tumors and their spouses(n=186,scores,$\bar{x}±s$)
 |
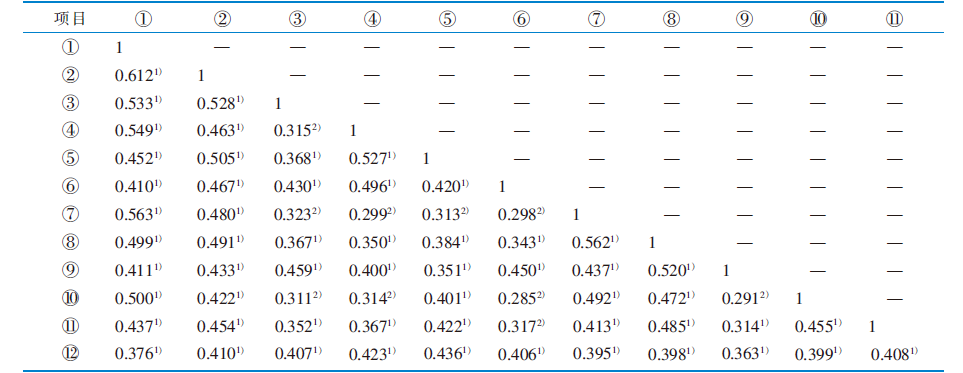 |
表4 恶性骨肿瘤患者和其配偶情绪调节困难、抑郁症状得分及相关分析(r值,n=186)
Table 4 Scores and bivariate correlations for emotion dysregulation and depressive symptoms in patients with malignant bone tumors and their spouses(r values,n=186)
 |
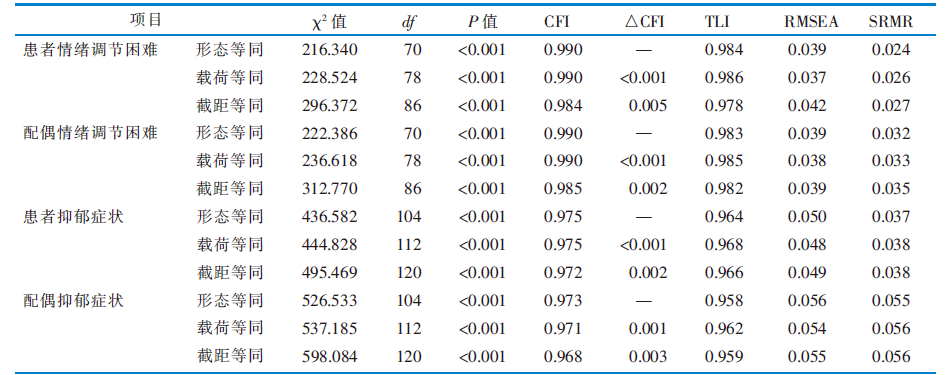 |
表5 恶性骨肿瘤患者和其配偶情绪调节困难及抑郁症状3次测量的等价性模型拟合结果
Table 5 Model fit indices for testing measurement invariance of emotion dysregulation and depressive symptoms across 3 time points in malignant bone tumor patients and their spouses
 |
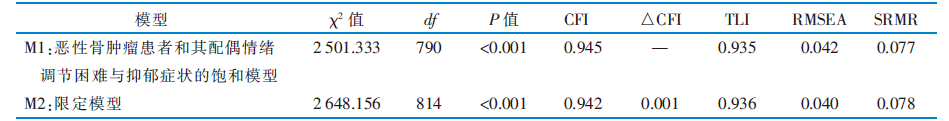 |
表6 恶性骨肿瘤患者和其配偶情绪调节困难、抑郁症状主客体互倚模型限定后的拟合结果
Table 6 Goodness-of-fit indices for the constrained actor-partner interdependence model(APIM) of emotion dysregulation and depressive symptoms in malignant bone tumor patients and their spouses
 |
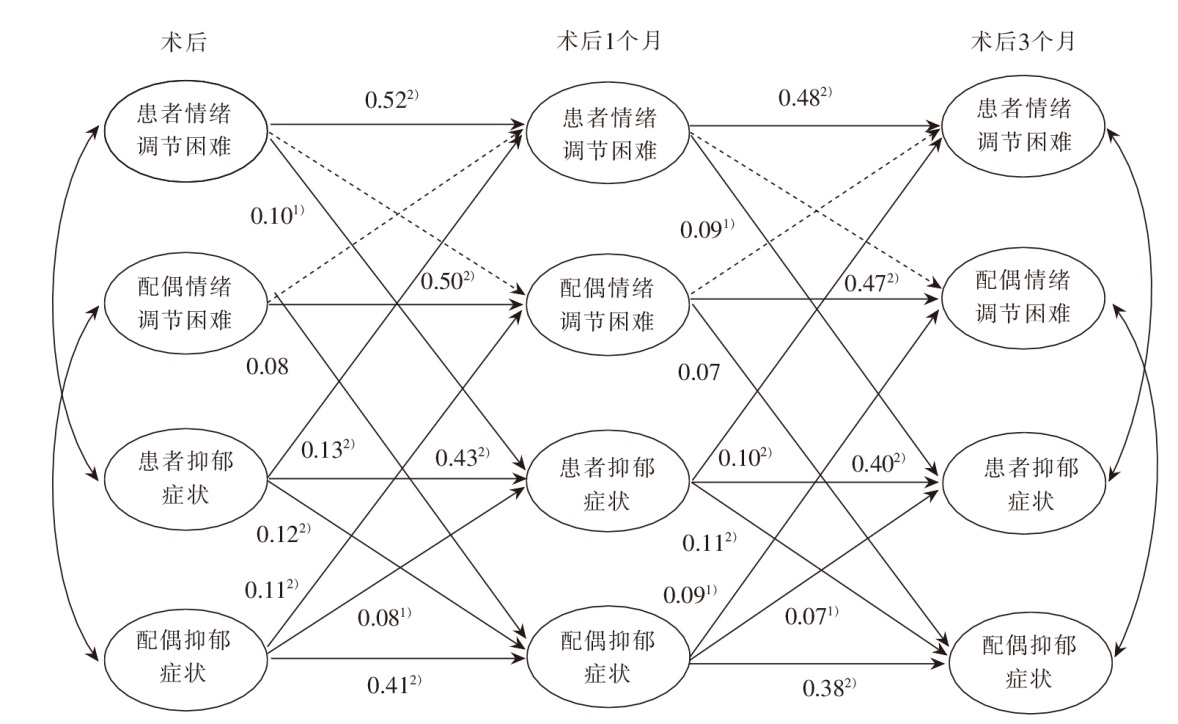
图1 恶性骨肿瘤患者和其配偶情绪调节困难、抑郁症状的交叉滞后主客体互倚模型图
Figure 1 Cross-lagged actor-partner interdependence model(APIM) of emotion dysregulation and depressive symptoms in patients with malignant bone tumors and their spouses 1)P<0.01,2)P<0.001。
| [1] |
Nacev BA, Sanchez-Vega F, Smith SA, et al. Clinical sequencing of soft tissue and bone sarcomas delineates diverse genomic landscapes and potential therapeutic targets[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1):3405.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Smolle MA, Kogler A, Andreou D, et al. Prognostic impact of pulmonary metastasectomy in bone sarcoma patients:a retrospective,single-centre study[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(6):1733.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Grassi L, Caruso R, Riba MB, et al. Anxiety and depression in adult cancer patients:ESMO clinical practice guideline[J]. ESMO Open, 2023, 8(2):101155.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
彭涛, 贺开麒, 雷一鹏, 等. 恶性骨肿瘤患者照护者真实照护体验的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(22):2785-2791.
DOI URL |
| Peng T, He KQ, Lei YP, et al. Meta-integration of real care experiences of caregivers of patients with malignant bone tumors[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(22):2785-2791. | |
| [5] |
Raposo CF, Pascoal PM, Faustino B, et al. The effect of emotional regulation difficulties on sexual and psychological distress using repetitive negative thinking as a mediator[J]. J Sex Med, 2023, 20(12):1466-1469.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
刘颖, 陈佳丽, 宁宁, 等. 骨肿瘤手术患者创伤后成长的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(10):1184-1190.
DOI URL |
| Liu Y, Chen JL, Ning N, et al. Investigation and research on post-traumatic growth in patients undergoing bone tumor surgery[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(10):1184-1190. | |
| [7] |
Vizin G, Szekeres T, Juhász A, et al. The role of stigma and depression in the reduced adherence among young breast cancer patients in Hungary[J]. BMC Psychol, 2023, 11(1):319.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
刘雪华, 王建虹, 杨丽红, 等. 血液肿瘤患者及其配偶二元应对与恐惧疾病进展的相关性分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6):717-722.
DOI URL |
|
Liu XH, Wang JH, Yang LH, et al. An analysis of correlation between dyadic coping in patients with hematological tumors and their spouses and fear of progression[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(6):717-722.
DOI URL |
|
| [9] |
Kenny DA, Ledermann T. Detecting,measuring,and testing dyadic patterns in the actor-partner interdependence model[J]. J Fam Psychol, 2010, 24(3):359-366.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 费菲, 赵海, 曲莉莉. 我国骨肿瘤循证临床诊疗指南2015最新解读恶性骨肿瘤化疗等相关新药进展综述(下)[J]. 中国医药科学, 2016, 6(2):5-6. |
| Fei F, Zhao H, Qu LL. The latest interpretation of evidence-based clinical diagnosis and treatment guidelines for bone tumors in China in 2015(Ⅱ)[J]. China Med Pharm, 2016, 6(2):5-6. | |
| [11] | 王家良. 临床流行病学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2014. |
| Wang JL. Clinical epidemiology[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2014. | |
| [12] |
Gratz KL. Targeting emotion dysregulation in the treatment of self-injury[J]. J Clin Psychol, 2007, 63(11):1091-1103.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | 刘奇勤, 武厚, 刘明矾. 情绪调节状态困难量表的修订及信效度检验[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2017, 38(10):1571-1574. |
| Liu QQ, Wu H, Liu MF. Revision and reliability and validity test of Emotional Adjustment State Difficulty Scale[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2017, 38(10):1571-1574. | |
| [14] |
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9:validity of a brief depression severity measure[J]. J Gen Intern Med, 2001, 16(9):606-613.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | 卞崔冬, 何筱衍, 钱洁, 等. 患者健康问卷抑郁症状群量表在综合性医院中的应用研究[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版), 2009, 30(5):136-140. |
| Bian CD, He XY, Qian J, et al. The reliability and validity of a modified Patient Health Questionnaire for Screening Depressive Syndrome in general hospital outpatients[J]. J Tongji Univ Med Sci, 2009, 30(5):136-140. | |
| [16] |
Roepke AM, Turner AP, Henderson AW, et al. A prospective longitudinal study of trajectories of depressive symptoms after dysvascular amputation[J]. Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 2019, 100(8):1426-1433.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 汤丹丹, 温忠麟. 共同方法偏差检验:问题与建议[J]. 心理科学, 2020, 43(1):215-223. |
| Tang DD, Wen ZL. Statistical approaches for testing common method bias:problems and suggestions[J]. J Psychol Sci, 2020, 43(1):215-223. | |
| [18] |
Lim DW, Retrouvey H, Kerrebijn I, et al. Longitudinal study of psychosocial outcomes following surgery in women with unilateral nonhereditary breast cancer[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2021, 28(11):5985-5998.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
O’Brien AL, West JM, Gokun Y, et al. Longitudinal durability of patient-reported pain outcomes after targeted muscle reinnervation at the time of major limb amputation[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 2022, 234(5):883-889.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Weissman S, Ghoneim S, Sanayei A, et al. New-onset depression after colorectal cancer diagnosis:a population-based longitudinal study[J]. Int J Colorectal Dis, 2021, 36(12):2599-2602.
DOI |
| [21] | 蓝慧玉, 农小莲, 黄仕环, 等. 癌症患者抑郁轨迹的研究进展[J]. 实用肿瘤学杂志, 2024, 38(4):262-267. |
| Lan HY, Nong XL, Huang SH, et al. Research progress of depression trajectory in cancer patients[J]. Pract Oncol J, 2024, 38(4):262-267. | |
| [22] |
杨阳, 刘美, 熊沫, 等. 中青年肠造口患者及其主要照护者护理依赖二元应对体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4):389-395.
DOI URL |
| Yang Y, Liu M, Xiong M, et al. A qualitative study on the dual coping experience of nursing dependence in young and middle-aged enterostomy patients and their primary caregivers[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(4):389-395. | |
| [23] |
Sullivan MJL, Adams H, Yamada K, et al. The relation between perceived injustice and symptom severity in individuals with major depression:a cross-lagged panel study[J]. J Affect Disord, 2020, 274:289-297.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 陈静, 施旭爱. 抑郁症患者自杀意念调查及其与家庭功能的关系:情绪调节自我效能感的中介作用[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2024, 32(11):1647-1652. |
| Chen J, Shi XA. Investigation of suicidal ideation in patients with depression and its relationship with family function:the mediating role of emotional regulation self-efficacy[J]. China J Health Psychol, 2024, 32(11):1647-1652. | |
| [25] |
Greene T, West M, Somer E. Maladaptive daydreaming and emotional regulation difficulties:a network analysis[J]. Psychiatry Res, 2020, 285:112799.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Cox MJ, Paley B. Families as systems[J]. Annu Rev Psychol, 1997, 48:243-267.
PMID |
| [27] |
Lo CZ, Su TW, Huang CC, et al. Randomization and resilience of brain functional networks as systems-level endophenotypes of schizophrenia[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015, 112(29):9123-9128.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 刘博文, 王珊珊, 孙倩倩, 等. 脑卒中患者及其配偶二元心理资本的潜在剖面分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3):332-339. |
| Liu BW, Wang SS, Sun QQ, et al. Latent profile analysis of dyadic psychological capital among stroke patients and their spouses and nursing countermeasures[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(3):332-339. |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||