


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (1): 52-60.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.01.008
唐佳迎( ), 黄晓霞, 郭芝廷, 刘畅, 陈岚, 封秀琴(
), 黄晓霞, 郭芝廷, 刘畅, 陈岚, 封秀琴( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-31
出版日期:2025-01-10
发布日期:2025-01-05
通讯作者:
封秀琴,E-mail:fengxiuqin@zju.edu.cn作者简介:唐佳迎:女,本科(硕士在读),主管护师,E-mail:157838@zju.edu.cn
基金资助:
TANG Jiaying( ), HUANG Xiaoxia, GUO Zhiting, LIU Chang, CHEN Lan, FENG Xiuqin(
), HUANG Xiaoxia, GUO Zhiting, LIU Chang, CHEN Lan, FENG Xiuqin( )
)
Received:2024-01-31
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2025-01-05
摘要:
目的 基于4R危机管理理论构建气管插管患者拔管后吞咽障碍风险管理方案并探讨其应用效果。 方法 以4R危机管理理论为框架,通过专家会议法,构建气管插管患者拔管后吞咽障碍风险管理方案。采用方便抽样法,将2023年7月—12月收治于浙江省某三级甲等医院急诊ICU、中心ICU及心脏大血管外科ICU的气管插管患者作为研究对象,其中2023年10月—12月收治的68例作为试验组,2023年7月—9月收治的58例作为对照组。试验组采用基于4R危机管理理论的气管插管患者拔管后吞咽障碍风险管理方案进行干预,对照组采用ICU常规气道评估与管理。比较两组拔管后吞咽障碍发生率、首次经口进食时间、首次进食过程中误吸发生率、鼻胃管及鼻肠管留置时间、吸入性肺炎发生率、再次气管插管发生率及ICU重返率。 结果 最终试验组纳入68例,对照组54例。干预后,试验组拔管后吞咽障碍发生率、首次经口进流质饮食的时间、首次进食过程中误吸发生率、鼻胃管及鼻肠管留置时间、吸入性肺炎发生率、ICU重返率均低于对照组(均P<0.05);两组首次经口进普通饮食的时间、再次气管插管发生率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 基于4R危机管理理论的气管插管患者拔管后吞咽障碍风险管理方案具有较好的科学性及安全性,可为临床气管插管患者拔管后的吞咽功能评估与进食管理提供参考。
唐佳迎, 黄晓霞, 郭芝廷, 刘畅, 陈岚, 封秀琴. 气管插管患者拔管后吞咽障碍风险管理研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(1): 52-60.
TANG Jiaying, HUANG Xiaoxia, GUO Zhiting, LIU Chang, CHEN Lan, FENG Xiuqin. Research on a crisis management-based risk management protocol for dysphagia after extubation in pa-tients with tracheal intubation[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(1): 52-60.
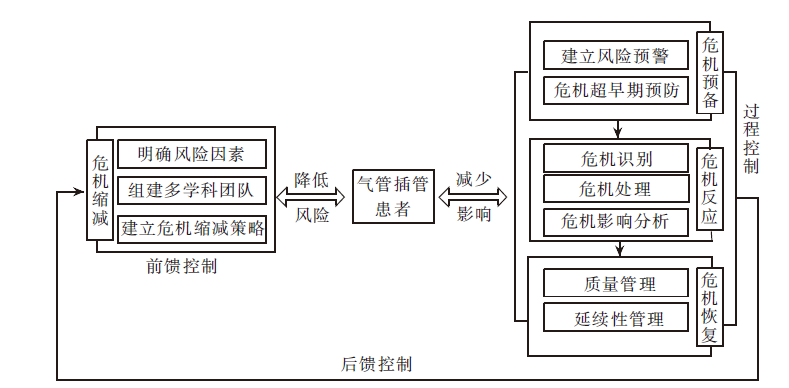
图1 基于4R危机管理论的ICU气管插管患者拔管后吞咽障碍管理概念架构
Figure 1 Conceptual architecture of post-extubation dysphagia management for tracheally intubated patients in ICU based on 4R crisis management theory
 |
表1 基于4R危机管理理论的气管插管患者拔管后吞咽障碍风险管理方案
Table 1 Risk management programme for post-extubation dysphagia in tracheally intubated patients based on the 4R crisis management theory
 |
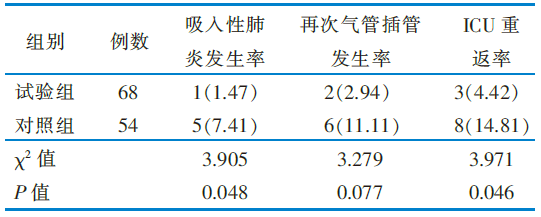 |
表4 两组吸入性肺炎发生率、再次气管插管发生率、ICU重返率的比较[例(百分率,%)]
Table 4 Comparison of aspiration pneumonia, incidence of re-intubation,and ICU return rate between the 2 groups[case(percent,%)]
 |
| [1] |
McIntyre M, Doeltgen S, Dalton N, et al. Post-extubation dysphagia incidence in critically ill patients:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Aust Crit Care, 2021, 34(1):67-75.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Malandraki GA, Markaki V, Georgopoulos VC, et al. Postextubation dysphagia in critical patients:a first report from the largest step-down intensive care unit in Greece[J]. Am J Speech Lang Pathol, 2016, 25(2):150-156.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Brodsky MB, Huang MX, Shanholtz C, et al. Recovery from dysphagia symptoms after oral endotracheal intubation in acute respiratory distress syndrome survivors. A 5-year longitudinal study[J]. Ann Am Thorac Soc, 2017, 14(3):376-383. |
| [4] |
Omura K, Komine A, Yanagigawa M, et al. Frequency and outcome of post-extubation dysphagia using nurse-performed swallowing screening protocol[J]. Nurs Crit Care, 2019, 24(2):70-75.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Hongo T, Yamamoto R, Liu K, et al. Association between timing of speech and language therapy initiation and outcomes among post-extubation dysphagia patients:a multicenter retrospective cohort study[J]. Crit Care, 2022, 26(1):98. |
| [6] |
Johnson KL, Speirs L, Mitchell A, et al. Validation of a postextubation dysphagia screening tool for patients after prolonged endotracheal intubation[J]. Am J Crit Care, 2018, 27(2):89-96.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Heath RL, Lee J, Ni L. Crisis and risk approaches to emergency management planning and communication:the role of similarity and sensitivity[J]. J Public Relat Res, 2009, 21(2):123-141. |
| [8] |
程婷, 涂惠, 熊晓云, 等. 经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后老年患者多重用药管理方案的构建[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(12):1476-1482.
DOI URL |
|
Cheng T, Tu H, Xiong XY, et al. Construction of a medication management program of elderly patients with polypharmacy after percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(12):1476-1482.
DOI URL |
|
| [9] | 陈露, 乔建峰, 李亚敏, 等. 4R危机理论在全麻胸腔镜术后胸腔闭式引流的护理效果及学习曲线分析[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2023, 38(15):1412-1416. |
| Chen L, Qiao JF, Li YM, et al. Effect of 4R-crisis nursing for patients with closed thoracic drainage after thoracoscopic surgery under general anesthesia and its learning curve analysis[J]. J Nurses Train, 2023, 38(15):1412-1416. | |
| [10] |
Lu DY, Yeun-Sim Jeong S, Zhu LY. Development and validation of a management of workplace violence competence scale for nursing practicum students[J]. Asian Nurs Res, 2021, 15(1):23-29.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Tang JY, Feng XQ, Huang XX, et al. Development and validation of a predictive model for patients with post-extubation dysphagia[J]. World J Emerg Med, 2023, 14(1):49-55. |
| [12] | Robert CH. Extubation management in the adult intensive care unit[EB/OL]. (2023-04-27)[2023-06-16]. https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/extubation-management-in-the-adult-intensive-care-unit?search=%E5%90%9E%E5%92%BD%E9%9A%9C%E7%A2%8D%20%E6%B0%94%E7%AE%A1%E6%8F%92%E7%AE%A1&source=Out%20of%20date%20-%20zh-Hans&selectedTitle=4-150. |
| [13] | Lauren CB. Complications of airway management in adults[EB/OL]. (2022-08-17)[2023-06-16]. https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/complications-of-airway-management-in-adults. |
| [14] | Anthony JL. Oropharyngeal dysphagia:clinical features,diagnosis,and management[EB/OL]. (2023-04-18)[2023-06-16]. https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/oropharyngeal-dysphagia-clini-cal-features-diagnosis-and-management?search=Dyspha-gia%20en-dotracheal%20intubation&source=Out%20of%20date%20-%20zh-Hans&selectedTitle=5-150. |
| [15] |
Higgs A, McGrath BA, Goddard C, et al. Guidelines for the management of tracheal intubation in critically ill adults[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2018, 120(2):323-352.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | 中国康复医学会康复护理专业委员会. 吞咽障碍康复护理专家共识[J]. 护理学杂志, 2021, 36(15):1-4. |
| Rehabilitation Nursing Specialized Committee of Chinese Society of Rehabilitation Medicine. Expert consensus on dysphagia rehabilitation care[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2021, 36(15):1-4. | |
| [17] | 中国吞咽障碍膳食营养管理专家共识组. 吞咽障碍膳食营养管理中国专家共识(2019版)[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2019, 41(12):881-888. |
| Chinese Expert Consensus Group on Dietary and Nutritional Management of Dysphagia. Chinese expert consensus on dietary and nutritional management of dysphagia[J]. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil, 2019, 41(12):881-888. | |
| [18] | McIntyre M, Chimunda T, Koppa M, et al. Risk factors for postextubation dysphagia:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2022, 132(2):364-374. |
| [19] | 蒋玲洁, 杨琳, 张志刚, 等. ICU患者获得性吞咽障碍危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国护理管理, 2021, 21(2):232-237. |
| Jiang LJ, Yang L, Zhang ZG, et al. Meta-analysis of risk factors for acquired dysphagia in ICU patients[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2021, 21(2):232-237. | |
| [20] |
戚春霞, 厉春林, 张雅芝, 等. 重症患者ICU获得性吞咽障碍影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(8):1236-1241.
DOI URL |
| Qi CX, Li CL, Zhang YZ, et al. Dysphagia in the intensive care unit:a meta-analysis of risk factors[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(8):1236-1241. | |
| [21] |
余金甜, 陈俊杉, 张爱琴. 心脏术后患者发生获得性吞咽障碍危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(3):451-456.
DOI URL |
|
Yu JT, Chen JS, Zhang AQ. A meta-analysis of risk factors for acquired swallowing disorders among patients after cardiac surgery[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(3):451-456.
DOI URL |
|
| [22] |
Expanded explanation of the sample size calculation[J]. JAMA, 2016, 316(7):775.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | 刘彩云, 王晓晶, 闫丽, 等. 护士主导的吞咽训练对拔管后吞咽障碍患者的影响[J]. 护理学杂志, 2023, 38(2):12-15. |
| Liu CY, Wang XJ, Yan L, et al. Effect of nurse-led swallowing training on patients with post-extubation dysphagia[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2023, 38(2):12-15. | |
| [24] |
张滢滢, 王海芳, 王玉宇, 等. ICU不同进食方式的患者误吸发生现状及特征比较[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(3):265-271.
DOI URL |
|
Zhang YY, Wang HF, Wang YY, et al. Comparative study on the characteristics of aspiration in ICU patients with different feeding patterns[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(3):265-271.
DOI URL |
|
| [25] | 佘君, 丁建文, 申捷. 成人吸入性肺炎诊断和治疗专家建议[J]. 国际呼吸杂志, 2022, 42(2):86-96. |
| She J, Ding JW, Shen J. Expert task force on diagnosis and treatment of aspiration pneumonia in adults[J]. Int J Respir, 2022, 42(2):86-96. | |
| [26] |
Reintam Blaser A, Starkopf J, Alhazzani W, et al. Early enteral nutrition in critically ill patients:ESICM clinical practice guidelines[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2017, 43(3):380-398.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
中国老年医学学会,中国老年医学学会重症医学分会. 中国老年重症患者肠内营养支持专家共识(2022)[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2022, 34(4):337-342.
PMID |
|
Chinese Society of Geriatrics,Sub-branch of Critical Care Medicine,Chinese Society of Geriatrics. Expert consensus on enteral nutrition support for elderly patients with critical illness in China(2022)[J]. Chin Crit Care Med, 2022, 34(4):337-342.
DOI PMID |
|
| [28] | Alenazi A, Alshibani A. Confirmatory methods for endotracheal tube placement in out-of-hospital settings:a systematic review of the literature[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(7):e28479. |
| [29] |
Jolley SE, Bunnell AE, Hough CL. ICU-acquired weakness[J]. Chest, 2016, 150(5):1129-1140.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Shinn JR, Kimura KS, Campbell BR, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute laryngeal injury after prolonged mechanical ventilation[J]. Crit Care Med, 2019, 47(12):1699-1706.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Marvin S, Thibeault S, Ehlenbach WJ. Post-extubation dysphagia:does timing of evaluation matter?[J]. Dysphagia, 2019, 34(2):210-219. |
| [32] |
Schefold JC, Berger D, Zürcher P, et al. Dysphagia in Mechani-cally Ventilated ICU Patients(DYnAMICS):a prospective observational trial[J]. Crit Care Med, 2017, 45(12):2061-2069.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Depolli GT, Oliveira GB, Oliveira TJ, et al. Quality of life in dysphagia and anxiety and depression symptoms pre and post-thyroidectomy[J]. Codas, 2023, 35(5):e20220099. |
| [1] | 陈玲欣, 董莲莲, 魏文静, 罗雪莉, 俞逢慧. 1例注射性肉毒毒素急性中毒合并呼吸衰竭患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 986-989. |
| [2] | 谭雨婷, 张志霞, 许梦莉, 郭沛然, 肖琴, 乔林茹, 宋飞云, 余巧君. 中年脑卒中患者自主康复行为与相关症状关系的研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 773-778. |
| [3] | 孙丹萍, 王华芬, 黄莺, 邵丽芳, 鲁慧琴, 詹晓琴. HIV感染者继发口咽念珠菌病风险评估量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 723-728. |
| [4] | 蒋思珊, 成琴琴, 罗听薇, 张娜, 郭俊晨, 李东雅, 李丹丹, 朱丽辉. 儿童安宁疗护质量评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 611-618. |
| [5] | 王飒, 苗华丽, 李雨蔚, 王鸿伟, 乔彩彩, 宋炜婷. 10~19岁慢性病患者向成人过渡期准备度评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4): 469-477. |
| [6] | 刘宁, 李婧菱, 左顺利, 朱秀媛, 方亦萍, 丘丽红. 烧伤患者身体意象特异性评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4): 478-485. |
| [7] | 肖瑶, 张晓天, 魏永婷, 马迎辉, 龚霓, 杨晶, 王梓珅, 岳鹏. 终末期患者居家社会照护需求评估工具的构建及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(1): 99-105. |
| [8] | 陈丽霞, 施慧, 朱德政, 曾莹. 成人低血糖恐惧评估工具的质量评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1072-1079. |
| [9] | 宋晓安, 卢兴泉, 马静, 王亚凡, 王晓华, 任红, 高俊. 新入职护士考核评估管理信息系统的开发与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 974-979. |
| [10] | 周樊华, 甘霖, 梅艳丽, 杜芬, 严冶, 熊莉娟. 中西医结合病房患者入院护理评估单的研制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(7): 802-807. |
| [11] | 熊桃, 谭雪梅, 罗静, 李阳, 郑予希, 李奉玲, 魏雪梅, 崔丽君, 罗澜峻. 脑卒中患者康复动机评估工具的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(7): 890-896. |
| [12] | 陈钰妹, 赵惠芬, 赵晓珊, 赵梅晶, 彭玉美, 沈丽琴. 妊娠期糖尿病孕妇风险感知量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(6): 677-684. |
| [13] | 王旋, 温贤秀, 苟莉, 周丽娟, 陈付利, 吴海燕, 王良. 心脏康复依从性评估工具测量学属性的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(6): 736-743. |
| [14] | 饶淼, 韦荣泉, 李霞, 宁家杰, 王素婷, 蔡玉萍. 癌症相关认知障碍评估工具的范围综述[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(23): 2919-2927. |
| [15] | 朱凤, 庄一渝, 魏丽, 徐红贞, 秦建芬, 林迦密, 丁文雯. 早产儿母亲泌乳激活评估及护理干预的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(23): 2928-2932. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 40
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 824
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||