


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2026, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (3): 361-367.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.03.010
• Specialist Nursing Practice and Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Xiuping1( ), LIANG Jiaojiao1, WANG Lingling2, FU Qin3, HOU Ming4, LI Ping4,*(
), LIANG Jiaojiao1, WANG Lingling2, FU Qin3, HOU Ming4, LI Ping4,*( )
)
Received:2025-09-15
Online:2026-02-10
Published:2026-02-03
* Corresponding author:
LI Ping,E-mail:1483746409@qq.comFunding program:
李修平1( ), 梁娇娇1, 王玲玲2, 付琴3, 侯铭4, 李萍4,*(
), 梁娇娇1, 王玲玲2, 付琴3, 侯铭4, 李萍4,*( )
)
通讯作者:
李萍,E-mail:1483746409@qq.com作者简介:李修平:女,本科(硕士在读),E-mail:1585637652@qq.com
基金资助:LI Xiuping, LIANG Jiaojiao, WANG Lingling, FU Qin, HOU Ming, LI Ping. A study on the relationship between family resilience,care ability,and frailty in middle-aged and older stroke patients and their family caregivers[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(3): 361-367.
李修平, 梁娇娇, 王玲玲, 付琴, 侯铭, 李萍. 中老年脑卒中患者及家庭照顾者家庭弹性、护理能力与衰弱间的关系研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2026, 61(3): 361-367.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2026.03.010
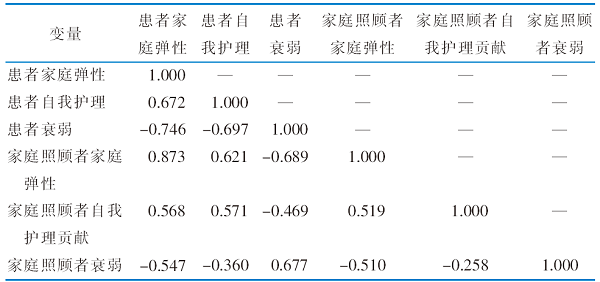 |
Table 2 Correlation between family resilience,care ability,and frailty in middle-aged and older stroke patients and their family caregivers(n=236,r value)
 |
| [1] |
Evans NR, Todd OM, Minhas JS, et al. Frailty and cerebro-vas-cular disease:Concepts and clinical implications for stroke me-dicine[J]. Int J Stroke, 2022, 17(3):251-259.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
李睿, 施雁, 孙晓, 等. 失智患者家庭照顾者衰弱的潜在剖面分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(16):2021-2029.
DOI URL |
|
Li R, Shi Y, Sun X, et al. Latent profile analysis of frailty among family caregivers of patients with dementia[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(16):2021-2029.
DOI URL |
|
| [3] | Burton JK, Stewart J, Blair M, et al. Prevalence and implica-tions of frailty in acute stroke:systematic review & meta-ana-lysis[J]. Age Ageing, 2022, 51(3):afac064. |
| [4] | Máximo RO, Lopes IC, Brigola AG, et al. Pre-frailty,frailty and associated factors in older caregivers of older adults[J]. Rev Saude Publica, 2020,54:17. |
| [5] | 中华医学会老年医学分会,《中华老年医学杂志》编辑委员会. 老年人衰弱预防中国专家共识(2022)[J]. 中华老年医学杂, 2022, 41(5):503-511. |
| Chinese Medical Association Geriatrics Branch,Editorial Com-mittee of Chinese Journal of Geriatrics. Chinese expert consen-sus on prevention of frailty in the elderly(2022)[J]. Chin J Geriatr, 2022, 41(5):503-511. | |
| [6] | 况艺, 王安妮. 社区老年人个体弹性和家庭弹性与衰弱的相关性研究[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2024, 39(7):691-696. |
| Kuang Y, Wang AN. Study on the correlation of individual resilience and family resilience with the frailty of the elderly in community[J]. J Nurses Train, 2024, 39(7):691-696. | |
| [7] | 孙凯旋, 刘永兵, 薛谨, 等. 住院患者老年衰弱综合征与自我护理能力的调查分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2017, 23(20):2588-2592. |
| Sun KX, Liu YB, Xue J, et al. Investigation of frailty syndrome and self-care agency among hospitalized elderly patients[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2017, 23(20):2588-2592. | |
| [8] | 王文娜, 张振香, 梅永霞, 等. 脑卒中患者与照顾者自我护理体验的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(10):1247-1255. |
| Wang WN,Zhang ZX,Mei YX,et al. Experience of stroke survivors and caregivers on self-care:a Meta-synthesis of qualitative research[J]. Chin J Nurs,2022,57(10):1247-1255. | |
| [9] |
Ledermann T,Macho S. Mediation in dyadic data at the level of the dyads:a structural equation modeling approach[J]. J Fam Psychol,2009, 23(5):661-670.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国各类主要脑血管病诊断要点2019[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2019, 52(9):710-715. |
| Cerebrovascular Disease Group of the Neurological Branch of the Chinese Medical Association,Chinese Medical Associa-tion,Neurological Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute intra-cerebral hemorrhage 2019[J]. Chin J Neurol, 2019, 52(9):710-715. | |
| [11] | WHO. 世卫组织确定新年龄分段:44岁以下为青年人[EB/OL].[2025-11-07]. https://www.huanqiu.com/article/9CaKrnJAukl. |
| WHO. WHO defines new age segments:youth up to 44 years old[EB/OL].[2025-11-07]. https://www.huanqiu.com/article/9Ca-KrnJAukl. | |
| [12] | 吴明隆. 结构方程模型-AMOS的操作与应用[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2010. |
| Wu ML. Structural equation modeling-operation and applica-tion of AMOS[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 2010. | |
| [13] | Sixbey MT. Development of the Family Resilience Assessment Scale to identify family resilience constructs[D]. Gainesville: University of Florida, 2005. |
| [14] | 杨丽娜, 钱英, 叶安琪, 等. 家庭弹性评估量表在脑卒中患者中的修订及信效度检验[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志, 2023, 32(10):945-950. |
| Yang LN, Qian Y, Ye AQ, et al. Revision of the Family Resi-lience Assessment Scale in patients with stroke and its relia-bility and validity test[J]. Chin J Behav Med and Brain Sci, 2023, 32(10):945-950. | |
| [15] |
Evers GC, Isenberg MA, Philipsen H, et al. Validity testing of the Dutch translation of the appraisal of the Self-Care Agency A.S.A.-Scale[J]. Int J Nurs Stud, 1993, 30(4):331-342.
PMID |
| [16] | 郭丽娜, 高涵, 郭启云, 等. 修正版自我护理能力评估量表汉化后的信效度评价[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2014, 30(30):64-66. |
| Guo LN, Gao H, Guo QY, et al. Reliability and validity of Chinese version of the Appraisal of Self-Care Agency Assess-ment Scale-Revised[J]. Chin J Prac Nurs, 2014,30(30):64-66. | |
| [17] | 王文娜, 张振香, 张杜杜, 等. 照顾者对脑卒中患者自我护理贡献量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志,2023, 58(1):39-45. |
|
Wang WN, Zhang ZX, Zhang DD, et al. Development and psychometric test of the Caregiver Contribution to Self-Care of Stroke Patient Scale[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(1):39-45.
DOI URL |
|
| [18] |
Gobbens RJJ, Luijkx KG, Wijnen-Sponselee MT, et al. In search of an integral conceptual definition of frailty:opinions of experts[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2010, 11(5):338-343.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 奚兴, 郭桂芳, 孙静. 中文版Tilburg衰弱评估量表的信效度研究[J]. 护理学报, 2013,20(16):1-5. |
| Xi X, Guo GF, Sun J. Reliability and validity of Chinese ver-sion of Tilburg Frailty Indicator[J]. J Nurs,2013,20(16):1-5. | |
| [20] | Qin F, Wei TQ, Zhao XY. et al. Relationship between family resilience and dyadic coping in colorectal cancer patients and their spouses,based on the actor-partner interdependence model[J]. Eur J Oncol Nurs,2024,70:102622. |
| [21] |
刘雪华, 王建虹, 杨丽红, 等. 血液肿瘤患者及其配偶二元应对与恐惧疾病进展的相关性分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6):717-722.
DOI URL |
|
Liu XH, Wang JH, Yang LH, et al. An analysis of correlation between dyadic coping in patients with hematological tumors and their spouses and fear of progression[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(6):717-722.
DOI URL |
|
| [22] | 丁璐. 基于5A模式的脑卒中患者护理干预方案构建及效果研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2023. |
| Ding L. Construction of nursing intervention program for stroke patients based on 5A model and effect research[D]. Kunming: Kunming Medical University, 2023. | |
| [23] | 滕慧, 李春梅, 田杨君, 等. 基于随机森林模型的脑卒中照顾者自我护理贡献现状及影响因素研究[J]. 军事护理, 2025, 42(3):1-5. |
| Teng H, Li CM, Tian YJ, et al. Study on the status quo and influencing factors of stroke caregiver contributions to self-care based on random forest model[J]. Mil Nurs, 2025, 42(3):1-5. | |
| [24] |
Lana A, Rodriguez-Artalejo F, Lopez-Garcia E. Dairy consump-tion and risk of frailty in older adults:a prospective cohort study[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2015, 63(9):1852-1860.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 张鑫宇, 张磊, 隋汝波. 基于Logistic回归和人工神经网络构建老年脑卒中患者衰弱预测模型[J]. 军事护理, 2023, 40(2):10-14,19. |
| Zhang XY, Zhang L, Sui RB. Prediction model for frailty in elderly stroke patients based on logistic regression and artifi-cial neural network[J]. Mil Nurs, 2023, 40(2):10-14,19. | |
| [26] | 林卫, 苏俐莉, 余天智, 等. 老年缺血性脑卒中后遗症患者衰弱状况调查及其危险因素分析[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2021, 23(5):499-502. |
| Lin W, Su LL, Yu TZ, et al. Frailty and its risk factors in elderly ischemic stroke patients with sequelae[J]. Chin J Ge-riatr Heart Brain Vessel Dis, 2021, 23(5):499-502. | |
| [27] | Wang YJ, Chen YW, Xu JX, et al. Association between resilie-nce and frailty among Chinese older adults[J]. Front Psychia-try, 2022,13:948958. |
| [28] |
Nakhjiri LZ, Darvishpour A, Pourghane P, et al. The relation-ship between frailty syndrome and self-care ability in the elderly with heart failure[J]. J Educ Health Promot, 2021, 10:475.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | 张相醇, 王安妮, 管婷玉, 等. 照顾者照顾能力与失能老人抑郁:家庭弹性与心理弹性链式中介作用分析[J]. 军事护理, 2023, 40(6):43-47,52. |
| Zhang XC, Wang AN, Guan TY, et al. Caregivers’ caring abi-lity and disabled elderly’s depression:a chain mediating effect analysis of family resilience and psychological resilience[J]. Mil Nurs, 2023, 40(6):43-47,52. | |
| [30] | 孟盈彤, 张婷婷, 陆思宇, 等. 慢性心力衰竭患者及家庭照顾者相依关系在家庭弹性和自我护理间的主客体互倚中介模型研究[C]. 第六届上海国际护理大会论文汇编(下),2024:111-112. |
| Meng YT, Zhang TT, Lu SY, et al. A study on the actor-partner interdependence mediation model of dyadic interdependence between family resilience and self-care in patients with chronic heart failure and their family caregivers[C]. Proc 6th Shanghai Int Nurs Conference(Vol. 2),2024:111-112. |
| [1] | HUANG Chunyan, SHEN Xiaoxing, ZHU Haiqiong, CHEN Yun, OUYANG Wenhui, YANG Chen, OUYANG Xiaojun. Development and efficacy assessment of oral exercise interventions in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(3): 326-331. |
| [2] | WANG Weiyun, GU Zejuan, TANG Yifan, SU Ziwen, LIU Changhong. Research on fluid balance thresholds in heart failure patients and nursing strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 157-165. |
| [3] | TAO Juan, YIN Yongtian, QIN Yuting, WANG Shiyuan, HAN Rong, ZHANG Handan. Home care experiences of caregivers of patients with left ventricular assist device implantation:a qualitative Meta-synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(2): 182-189. |
| [4] | RU Xiuli, HAN Mengdan, JI Lili, ZHOU Lina, LI Xuewen, ZHANG Yishuang. Effect of medication self-management behavior on frailty among community-dwelling older adults with chronic multimorbidity [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 17-22. |
| [5] | WANG Yangyang, YIN Na, LI Jiaqi, ZHANG Ju, GONG Tingting, YANG Minfei. Construction and validation of a frailty risk prediction model for elderly patients with traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 106-112. |
| [6] | LIAO Rongrong, XU Wang, ZHENG Zhouxue, QIN Huimin, WU Wen, TANG Danzhe. Nursing practice of brain-computer interface-guided active rehabilitation in a patient with post-stroke hemiplegia during the recovery phase [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2026, 61(1): 121-124. |
| [7] | CAO Yun, SUN Guozhen, CHEN Feng, JI Xueli, YAN Mengwan, JING Lei, QIAN Kun. A study of modified ankle pump exercise in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | TAN Yuting, ZHANG Zhixia, XU Mengli, GUO Peiran, XIAO Qin, QIAO Linru, SONG Feiyun, YU Qiaojun. Relationship between autonomous rehabilitation behavior and related symptoms of middle-aged stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(7): 773-778. |
| [9] | ZHOU Chenxi, LIN Beilei, ZHANG Jie, REN Hui, WANG Hui, ZHANG Zhenxiang. Dose-response relationship between disease risk perception and objective risk of stroke and nursing strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(7): 779-784. |
| [10] | SU Xuan, CHENG Qiaomei, LI Xiaowan, WANG Kexin, WANG Peixi, XIAO Mengwei, WANG Yu, LI Nannan, XIE Danying. Study on the latent classes of post-stroke depression in patients with acute stroke and nursing insights [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(7): 785-791. |
| [11] | ZHOU Kebing, HUANG Xiaojiao, YAN Fengxia. Network analysis of symptom burden and its influencing factors in first-ever subacute stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(7): 792-798. |
| [12] | FENG Weiqing, CHEN Yanbo, CAI Huan, RUAN Jiahui, HE Xiuxian, LI Kun. A scoping review of the longitudinal studies on post stroke fatigue [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(7): 799-805. |
| [13] | CHEN Lan, MA Huimin, FANG Yuan, ZHANG Huan, REN Jingnan, LU Liyun, WU Xiangliang, LIU Chang, JIN Dingping, FENG Xiuqin. Construction and application of an early in-hospital temperature management protocol for patients with heat stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 561-568. |
| [14] | YANG Yang, LIU Mei, XIONG Mo, FENG Lijuan, YANG Chunzi. A qualitative study on the dual coping experience of nursing dependence among middle-aged and young patients with enterostomy and their primary caregivers [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(4): 389-395. |
| [15] | YANG Funa, YANG Rui, QIN Yan, CHEN Junhan, GUO Lanwei, WANG Yongqi, HO Kayan, LIU Qi, MAO Ting, MEI Xiaoxiao, WANG Wenying, XU Xiaoxia, SHI Hongying. Current situation and influencing factors of family resilience of children with cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(4): 446-452. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||