


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (19): 2346-2352.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.19.006
• Special Planning——Care of Diabetic Foot Chronic Wound • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Jingyi( ), CHEN Xi, ZHU Yanyuan, ZHOU Jiaxin, BAI Jiaojiao(
), CHEN Xi, ZHU Yanyuan, ZHOU Jiaxin, BAI Jiaojiao( )
)
Received:2024-01-10
Online:2024-10-10
Published:2024-10-14
Contact:
BAI Jiaojiao
通讯作者:
白姣姣
作者简介:朱婧怡:女,本科(硕士在读),E-mail:zjyeducation@163.com
基金资助:ZHU Jingyi, CHEN Xi, ZHU Yanyuan, ZHOU Jiaxin, BAI Jiaojiao. A systematic review of risk prediction models for diabetic foot infections[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(19): 2346-2352.
朱婧怡, 陈曦, 朱彦媛, 周嘉欣, 白姣姣. 糖尿病足感染风险预测模型的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(19): 2346-2352.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.19.006
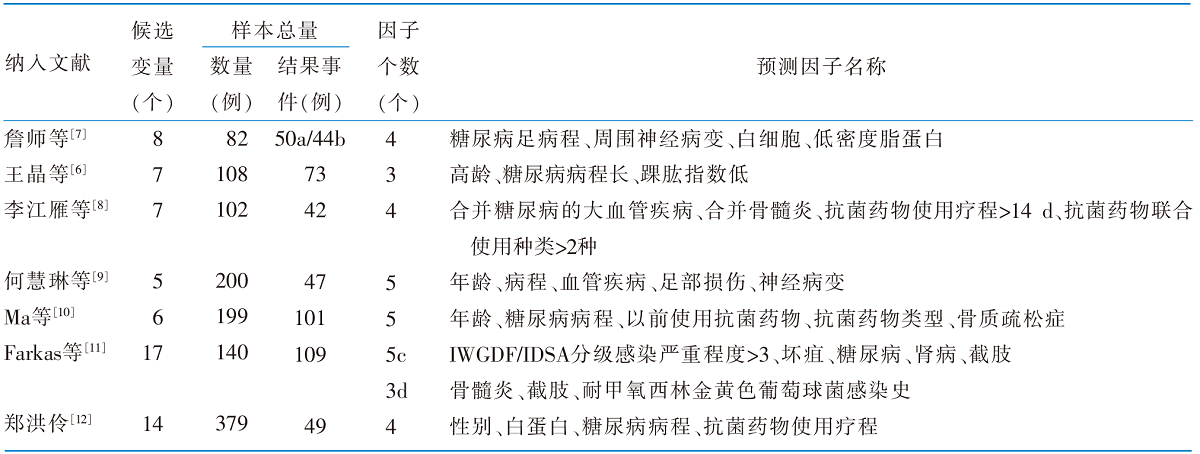 |
Table 2 Establishment of risk prediction models for diabetic foot infections(n=7)
 |
| [1] | van Netten JJ, Bus SA, Apelqvist J, et al. Definitions and criteria for diabetic foot disease[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2020, 36(Suppl 1):e3268. |
| [2] | Mills JP, Patel P, Broekhuizen E, et al. Diabetic foot infections[M]. Ann Arbor(MI): Michigan Medicine University of Michigan, 2019. |
| [3] | Hardjo Lugito NP, Nawangsih C, Moksidy JC, et al. Diabetic foot gangrene patient with multi-drug resistant pseudomonas putida infection in Karawaci district,Indonesia[J]. J Glob Infect Dis, 2015, 7(1):37-39. |
| [4] | Neves JM, Duarte B, Pinto M, et al. Diabetic foot infection:causative pathogens and empiric antibiotherapy considerations-the experience of a tertiary center[J]. Int J Low Extrem Wounds, 2019, 18(2):122-128. |
| [5] | 乐忠宏, 汤晓姣, 崔婷婷, 等. 糖尿病足感染患者病原学特点及耐药性分析[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2017, 27(3):590-592,601. |
| Yue ZH, Tang XJ, Cui TT, et al. Pathogenic bacteriological characteristics and drug resistance of patients with diabetic foot[J]. Chin J Nosocomiology, 2017, 27(3):590-592,601. | |
| [6] | 王晶, 胡岚, 石君, 等. 糖尿病足患者创面感染的影响因素及其模型构建[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2023, 33(24):3733-3737. |
| Wang J, Hu L, Shi J, et al. Influencing factors of wound infection the construction of the model in patients with diabetic foot[J]. Chin J Nosocomiology, 2023, 33(24):3733-3737. | |
| [7] | 詹师, 杨召伍, 陈山, 等. 糖尿病足感染病原微生物分布及风险预测模型的建立[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2023, 33(10):95-100. |
| Zhan S, Yang ZW, Chen S, et al. Distribution of pathogenic microorganisms in diabetic foot infection and construction of risk prediction model[J]. China J Mod Med, 2023, 33(10):95-100. | |
| [8] | 李江雁, 毛小芳, 赵利超, 等. 糖尿病足并发溃疡感染病原菌及其预测模型构建[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2023, 33(17):2619-2623. |
| Li JY, Mao XF, Zhao LC, et al. Pathogens isolated from diabetic foot patients with ulcer infection and establishment of prediction model[J]. Chin J Nosocomiology, 2023, 33(17):2619-2623. | |
| [9] | 何慧琳, 王木, 蒋庆丽, 等. 糖尿病足患者发生伤口严重感染风险预测模型的构建[J]. 当代护士(上旬刊), 2022, 29(12):7-10. |
| He HL, Wang M, Jiang QL, et al. Construction of risk prediction model for severe wound infection in patients with diabetic foot[J]. Mod Nurse, 2022, 29(12):7-10. | |
| [10] | Ma YN, Zhang LX, Hu YY, et al. Nomogram model for predicting the risk of multidrug-resistant bacteria infection in diabetic foot patients[J]. Infect Drug Resist, 2021, 14:627-637. |
| [11] |
Farkas A, Lin F, Bui K, et al. Development of predictive nomograms for clinical use to quantify the risk of isolating resistance prone organisms in patients with infected foot ulcers[J]. Epidemiol Infect, 2019, 147:e157.
DOI |
| [12] | 郑洪伶. 糖尿病足住院患者多重耐药菌感染风险预测模型的构建与验证[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2023. |
| Zheng HL. Construction and verification of risk prediction model of multi-drug resistant bacteria infection in diabetic foot inpatients[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Medical University, 2023. | |
| [13] | Moons KG, Hooft L, Williams K, et al. Implementing systematic reviews of prognosis studies in Cochrane[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2018, 10(10):ED000129. |
| [14] | Moons KG, de Groot JA, Bouwmeester W, et al. Critical appraisal and data extraction for systematic reviews of predic-tion modelling studies:the CHARMS checklist[J]. PLoS Med, 2014, 11(10):e1001744. |
| [15] | Moons KGM, Wolff RF, Riley RD, et al. PROBAST:a tool to assess risk of bias and applicability of prediction model studies:explanation and elaboration[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2019, 170(1):W1-W33. |
| [16] | Moons KG, Kengne AP, Woodward M, et al. Risk prediction models:I. Development,internal validation,and assessing the incremental value of a new(bio)marker[J]. Heart, 2012, 98(9):683-690. |
| [17] |
MacCallum RC, Zhang SB, Preacher KJ, et al. On the practice of dichotomization of quantitative variables[J]. Psychol Methods, 2002, 7(1):19-40.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | 陈香萍, 张奕, 庄一渝, 等. PROBAST:诊断或预后多因素预测模型研究偏倚风险的评估工具[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2020, 20(6):737-744. |
| Chen XP, Zhang Y, Zhuang YY, et al. PROBAST:a tool for assessing risk of bias in the study of diagnostic or prognostic multi-factorial predictive models[J]. Chin J Evid Based Med, 2020, 20(6):737-744. | |
| [19] | Hsu L, Li L, Poon LY. Analysis of risk factors of infection in diabetic foot patients[J]. Int Wound J, 2024, 21(1):e14411. |
| [20] |
贾盈盈, 张红燕, 马媛媛, 等. ICU患者压力性损伤风险预测模型的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(8):1242-1248.
DOI URL |
|
Jia YY, Zhang HY, Ma YY, et al. Systematic review of pressure injuries risk prediction models in ICU patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(8):1242-1248.
DOI URL |
|
| [21] |
张占林, 孙勇, 妥小青, 等. 随机森林算法对体检人群糖尿病患病风险的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(9):1021-1026.
DOI |
| Zhang ZL, Sun Y, Tuo XQ, et al. Predictive value of random forest algorithms for diabetic risk in people underwent physical examination[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2019, 22(9):1021-1026. | |
| [22] |
谢晓冉, 徐蓉. 糖尿病足发病风险预测模型的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(1):124-131.
DOI URL |
|
Xie XR, Xu R. A systematic review of risk prediction models for diabetic foot[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(1):124-131.
DOI URL |
|
| [23] | 李琳琳, 霍磊, 李品川, 等. 糖尿病足病不同程度感染患者临床特点分析[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2020, 26(2):290-295. |
| Li LL, Huo L, Li PC, et al. Analysis of clinical characteristics of different degrees of infection in patients with diabetic foot disease[J]. Chin J Surg Integr Tradit West Med, 2020, 26(2):290-295. | |
| [24] | Chastain CA, Klopfenstein N, Serezani CH, et al. A clinical review of diabetic foot infections[J]. Clin Podiatr Med Surg, 2019, 36(3):381-395. |
| [1] | ZHOU Miao, CHEN Xing, PENG Fei, SUN Shangxue, LI Yangyang. Systematic review of risk prediction instruments for central line associated bloodstream infections in ICU patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1132-1139. |
| [2] | PENG Yingjie, LIU Aihong, ZHU Wenli, MEI Yuxin, ZHOU Meng, GUAN Wenjing. Systematic review of readiness assessment tools for advance care planning in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1146-1153. |
| [3] | LIANG Yuanyuan, GAO Xinglian, DAI Zhangzhang, ZHOU Rongchao, HU Juanjuan, WANG Zengyan, SHEN Jianhui. Summary of the best evidence for surgical instrument management strategies in medical institutions [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 1005-1011. |
| [4] | WANG Ting, WANG Jiating, JIN Aiyun, ZHU Xiaming, FANG Yun, WANG Jing, TIAN Fei, PU Yiqin, WAN Ying, HE Jin, YAN Xia. Construction of a nursing follow-up checklist for patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 914-920. |
| [5] | SHENG Wanting, WANG Rui, ZHAO Yuxiao, QI Pengfei, GAO Silong, FENG Juan, LÜ Bohan, NIU Qun, WANG Gang. The effectiveness of applying different tip positions of midline catheters:a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 990-997. |
| [6] | YAN Xueqin, CAO Songmei, ZHOU Fangfang, ZHU Liqun, CHEN Cheng, ZHU Mengxue, ZHANG Yanhong, LIANG Yiqing, BAI Suping. Summary of best evidence for early rehabilitation management of hand function in patients with hand burns [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 998-1004. |
| [7] | WEI Yongting, TIAN Shumei, YANG Jiao, YU Lianghuan, NI Fu, FAN Yuqing, XIAO Yao, XI Zuyang, SHA Juyan, LIU Cong. Sinicization of Evidence-Informed Decision-Making Competence Measure for nurses and its reliability and validity test [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(6): 736-742. |
| [8] | WANG Wenjing, HAO Wumei, TAI Jingyu, DONG Qian, GUO Aimin. Experience of inhalation therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:a Meta-synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 545-551. |
| [9] | TANG Jiayi, TANG Guiqing, ZHANG Na, LI Xiaobo. Best evidence summary of nutritional management in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 581-588. |
| [10] | CUI Yuzhen, YAO Zhuoya, GENG Junhui, LI Manchun, ZHAN Meng, DING Lina, JIANG Enshe. Investigation and nursing countermeasures on the current situation of oral instrument cleaning,disinfection,and sterilization management in 348 medical institutions in Henan Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 596-602. |
| [11] | LIU Tingting, NIU Qiaohong, JIAO Xueping, WEI Jiawei, DUAN Shaoming, HU Congli, SU Rui. Meta-synthesis of qualitative studies on the experience of bowel symptoms in patients undergoing sphincter-preserving surgery for rectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 603-610. |
| [12] | JIANG Sishan, CHENG Qinqin, LUO Tingwei, ZHANG Na, GUO Junchen, LI Dongya, LI Dandan, ZHU Lihui. A systematic review of quality assessment tools for pediatric palliative care based on COSMlN guidelines [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(5): 611-618. |
| [13] | WANG Sa, MIAO Huali, LI Yuwei, WANG Hongwei, QIAO Caicai, SONG Weiting. A systematic review of tools for assessing the readiness of patients with chronic diseases aged 10-19 to transition to adulthood [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(4): 469-477. |
| [14] | LIU Ning, LI Jingling, ZUO Shunli, ZHU Xiuyuan, FANG Yiping, QIU Lihong. Systematic review of a body image assessment tool for burn patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(4): 478-485. |
| [15] | Chinese Nursing Association Geriatric Nursing Committee, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, School of Nursing, Peking University(Writing Committee:LIU Wenjing, WANG Zhiwen, YU Yuelin, REN Xin, JU Hui, CHEN Hong WANG Junxin, CHEN Shanshan, ZHOU Jia, YI Mo, WANG Wenxia, ZHANG Lingjuan, CHEN Siye, YANG Yufan, WANG Xiaomeng, SUN Hong). Guideline for assessment and maintenance of intrinsic capacity in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(3): 261-265. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||