


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (12): 1479-1485.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.12.011
收稿日期:2024-08-23
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-17
通讯作者:
于明明,E-mail:yumm@hsc.pku.edu.cn作者简介:韩冰:女,硕士,副主任护师,护理部副主任,E-mail:bjjstyy2023@163.com
基金资助:
HAN Bing( ), LI Chunmin, GUO Chenming, YU Mingming(
), LI Chunmin, GUO Chenming, YU Mingming( )
)
Received:2024-08-23
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-17
摘要:
目的 调查骨科护士共情疲劳症状的发生现状,分析其影响因素以及影响因素间的作用路径,为制订针对性的干预方案提供参考。方法 采用便利抽样法,于2024年5月—6月采用一般资料调查表、共情疲劳量表、护士职业认同评定量表、社会支持评定量表、护士心理资本问卷,对14个省(区、市)20所三级甲等综合医院的骨科护士进行问卷调查。采用单因素分析、Spearman相关分析、多元线性回归分析探究护士共情疲劳症状的影响因素,并构建结构方程模型。结果 共发放问卷1 441份,回收有效问卷1 397份,有效问卷回收率为96.94%。护士共情疲劳症状得分为(47.41±12.16)分。多元线性回归分析结果显示,职业认同、社会支持、心理资本、工作时间、每周夜班数是骨科护士共情疲劳症状的影响因素(P<0.05)。路径分析结果显示,模型拟合指标良好,心理资本对共情疲劳症状具有直接作用(β=-0.15,P<0.05);职业认同(β=1.46,P<0.001;β=-0.38,P<0.001)、社会支持(β=0.14,P<0.001;β=-0.99,P<0.001)在心理资本与共情疲劳症状间具有中介作用。结论 骨科护士共情疲劳症状较严重。护理管理者应针对相关影响因素制订有效的预防措施,以减轻骨科护士的共情疲劳症状。
韩冰, 李春敏, 郭晨明, 于明明. 骨科护士共情疲劳症状的影响因素及路径分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(12): 1479-1485.
HAN Bing, LI Chunmin, GUO Chenming, YU Mingming. Influencing factors and path analysis of compassion fatigue symptoms in orthopedic nurses[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(12): 1479-1485.
 |
表1 调查对象的一般资料及共情疲劳症状的单因素分析结果(n=1 397)
Table 1 The general characteristics of orthopedic nurses and the results of univariate analysis of compassion fatigue symptoms(n=1 397)
 |
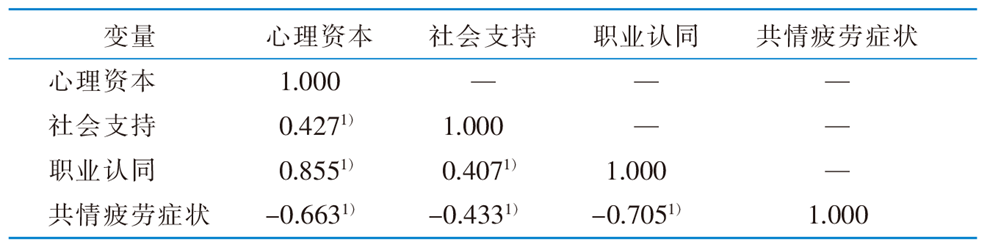 |
表2 骨科护士心理资本、职业认同、社会支持与共情疲劳症状的相关分析 (r 值,n=1 397)
Table 2 Correlations of psychological capital, professional identity,social support and compassion fatigue symptoms in orthopedic nurses(r value,n=1 397)
 |
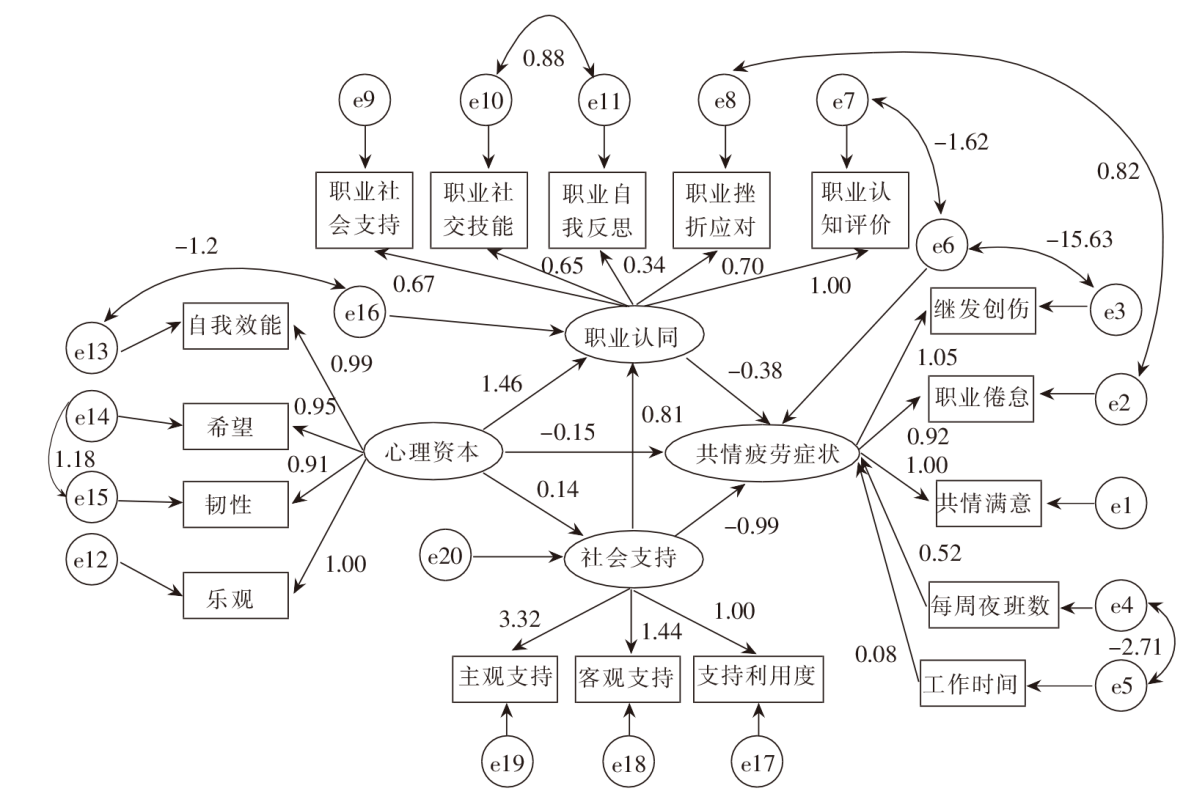
图1 骨科护士心理资本、社会支持和职业认同与共情疲劳症状的结构方程模型
Figure 1 Mediating effect model of psychological capital, social support, professional identity and compassion fatigue symptoms in orthopedic nurses
| [1] | Figley CR. Compassion fatigue:psychotherapists' chronic lack of self care[J]. J Clin Psychol, 2002, 58(11):1433-1441. |
| [2] |
Wijdenes KL, Badger TA, Sheppard KG. Assessing compassion fatigue risk among nurses in a large urban trauma center[J]. J Nurs Adm, 2019, 49(1):19-23.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Zhang YY, Han WL, Qin W, et al. Extent of compassion sati-sfaction,compassion fatigue and burnout in nursing:a meta-analysis[J]. J Nurs Manag, 2018, 26(7):810-819. |
| [4] |
Demerouti E, Bakker AB, Nachreiner F, et al. The job demands-resources model of burnout[J]. J Appl Psychol, 2001, 86(3):499-512.
PMID |
| [5] |
丛胜楠, 张爱霞, 刘颖, 等. 江苏省妇产专科医院护士共情疲劳的影响因素及路径分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(8):977-984.
DOI URL |
|
Cong SN, Zhang AX, Liu Y, et al. Analysis of influencing factors and impact path of compassion fatigue in nurses from maternity hospitals in Jiangsu[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(8):977-984.
DOI URL |
|
| [6] | 庄琳丽. 三甲医院临床护士共情疲劳现状及其影响因素研究[D]. 成都: 成都中医药大学, 2020. |
| Zhuang LL. Study on the status quo and influencing factors of empathic fatigue among clinical nurses in 3A hospitals[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of TCM, 2020. | |
| [7] | 张慧, 许翠萍, 薛秀娟, 等. ICU护士同情心疲乏对其职业认同的影响[J]. 中国护理管理, 2014, 14(3):246-249. |
| Zhang H, Xu CP, Xue XJ, et al. Impact of compassion fatigue on professional identity in intensive care unit nurses[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2014, 14(3):246-249. | |
| [8] | 王建华. 实用医学科研方法[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2003:56-57. |
| Wang JH. Practical medical research methods[M]. Beijing: Peo-ple's Medical Publishing House, 2003:56-57. | |
| [9] | 吴明隆. 结构方程模型:AMOS的操作与应用[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2009. |
| Wu ML. Structural equation modeling:operation and application with AMOS[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 2009. | |
| [10] | Stamm B. The concise ProQOL manual:the concise manual for the Professional Quality of Life Scale,2nd edition[M/OL].(2010)[2024-08-01]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/340033923_The_Concise_ProQOL_Manual_The_concise_manual_for_the_Professional_Quality_of_Life_Scale_2_nd_Edition. |
| [11] | 陈华英, 王卫红. 中文版同情疲劳量表的信度、效度研究[J]. 中国护理管理, 2013, 13(4):39-41. |
| Chen HY, Wang WH. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Compassion Fatigue Scale[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2013, 13(4):39-41. | |
| [12] | 刘玲, 郝玉芳, 刘晓虹. 护士职业认同评定量表的研制[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2011, 28(3):18-20. |
| Liu L, Hao YF, Liu XH. Development of Professional Identity Scale for Nurses[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2011, 28(3):18-20. | |
| [13] | 肖水源. 《社会支持评定量表》的理论基础与研究应用[J]. 临床精神医学杂志, 1994, 4(2):98-100. |
| Xiao SY. Theoretical basis and research application of Social Support Rating Scale[J]. J Clin Psychiatry, 1994, 4(2):98-100. | |
| [14] | Luthans F, Youssef CM, Avolio BJ. Psychological capital deve-loping the human competitive edge[M]. Oxford: Oxford Univer-sity Press, 2007. |
| [15] | 骆宏, 赫中华. 466名护士心理资本与职业倦怠及离职意愿的关系[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010, 45(10):933-935. |
| Luo H, He ZH. The relationships among psychological capital,job burnout and turnover intention in 466 nurses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010, 45(10):933-935. | |
| [16] | 修晓萍. 急诊儿科护士共情疲乏的现状调查及认知重评干预研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2020. |
| Xiu XP. Investigation on the current situation of empathy fatigue of emergency pediatric nurses and intervention study on cognitive reappraisal[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2020. | |
| [17] | Kwon J, Coimbra R. Fat embolism syndrome after trauma:what you need to know[J]. J Trauma Acute Care Surg, 2024, 97(4):505-513. |
| [18] |
肖万莲, 李娜, 陈晓玲, 等. 集束化护理在高龄髋部骨折患者围手术期的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(22):2734-2740.
DOI URL |
|
Xiao WL, Li N, Chen XL, et al. Application of cluster nursing mode in perioperative period of elderly patients with hip fracture[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(22):2734-2740.
DOI URL |
|
| [19] | Luthans F, Avolio BJ, Avey JB, et al. Positive psychological capital:measurement and relationship with performance and satisfaction[J]. Pers Psychol, 2007, 60(3):541-572. |
| [20] | 田梅梅, 范霖, 施雁, 等. 临床护士共情疲劳的现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(1):76-82. |
| Tian MM, Fan L, Shi Y, et al. The current status and in-fluencing factors of compassion fatigue in clinical nurses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(1):76-82. | |
| [21] |
O'Mahony S, Ziadni M, Hoerger M, et al. Compassion fatigue among palliative care clinicians:findings on personality factors and years of service[J]. Am J Hosp Palliat Care, 2018, 35(2):343-347.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | 陈莉, 陈松, 梅俊华, 等. 新冠肺炎疫情下医护人员共情疲劳干预策略研究[J]. 医学与哲学, 2020, 41(16):50-53. |
| Chen L, Chen S, Mei JH, et al. Study on the interventional strategy of empathy fatigue of medical staff in the epidemic of COVID19[J]. Med Philos, 2020, 41(16):50-53. | |
| [23] | Yazdankhahfard M, Haghani F, Omid A. The Balint group and its application in medical education:a systematic review[J]. J Educ Health Promot, 2019,8:124. |
| [24] | 徐永娟, 刘志梅, 位兰玲, 等. 急诊护士工作压力源和心理资本对共情疲劳影响的路径分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2020, 26(16):2162-2167. |
| Xu YJ, Liu ZM, Wei LL, et al. Path analysis of the influence of work stressors and psychological capital on compassion fatigue in emergency nurses[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2020, 26(16):2162-2167. | |
| [25] | 魏华, 董越娟, 邹涛, 等. 新入职院前急救护士职业应激、心理资本与共情疲劳感的关系分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2015, 21(15):1798-1801,1802. |
| Wei H, Dong YJ, Zou T, et al. Relationship of compassion fatigue,occupational stress and psychological capital among new graduate ambulance nurses[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2015, 21(15):1798-1801,1802. | |
| [26] | 张菊花. 护士心理资本、组织支持及工作满意度的相关性研究[D]. 延吉: 延边大学, 2016. |
| Zhang JH. Study on the correlation among psychological capi-tal,organizational support and job satisfaction of nurses[D]. Yanji: Yanbian University, 2016. | |
| [27] | Yu HR, Jiang AL, Shen J. Prevalence and predictors of com-passion fatigue,burnout and compassion satisfaction among oncology nurses:a cross-sectional survey[J]. Int J Nurs Stud, 2016,57:28-38. |
| [28] | Hunsaker S, Chen HC, Maughan D, et al. Factors that influen-ce the development of compassion fatigue,burnout,and compas-sion satisfaction in emergency department nurses[J]. J Nurs Scholarsh, 2015, 47(2):186-194. |
| [1] | 何梅, 熊杰, 黄素芳, 李芳芳, 李进, 任兰兰, 陈敏. 急性A型主动脉夹层患者症状网络分析及对预检分诊的启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1075-1079. |
| [2] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [3] | 刘晓熠, 王红, 周智聪, 孙旭, 王意茹, 仝紫薇, 刘晓莹. 沉浸式虚拟现实技术对外周性前庭功能障碍患者康复效果的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1140-1145. |
| [4] | 刘方, 刘云访, 德宗, 皮蓉, 何子涵, 李素云. 肝硬化患者口渴感现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 934-939. |
| [5] | 谭雨婷, 张志霞, 许梦莉, 郭沛然, 肖琴, 乔林茹, 宋飞云, 余巧君. 中年脑卒中患者自主康复行为与相关症状关系的研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 773-778. |
| [6] | 周柯冰, 黄晓娇, 闫凤侠. 首发脑卒中恢复期患者症状负担及其影响因素的网络分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 792-798. |
| [7] | 陈丽花, 黄瑶, 盛青青, 谭玉凤, 张书琴, 黄小群, 徐蒙蒙. 肺移植术后肠内营养患者喂养不耐受的现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 849-855. |
| [8] | 田君叶, 张霞, 苏莉, 孙路路, 赵瑾, 丁炎明. 专科护士培训信息管理平台的建设与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 652-658. |
| [9] | 雷丹, 卞薇, 王宗华, 苏君, 万君丽, 王露. 角膜溃疡患者互联网+精准症状管理方案的构建及应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 688-695. |
| [10] | 王衍蝶, 曾妃, 梁江淑渊, 顾培培. 肺移植患者骨代谢异常影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 703-709. |
| [11] | 唐楠, 高远, 苏清清, 宋咪, 邱晨, 邵梦琪. 老年骨质疏松患者再骨折影响因素分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 710-716. |
| [12] | 李燕, 吴雪, 庞建美, 强万敏, 杨川川, 孙盛楠, 李静. 24个省份胸外科护士围手术期肺康复知信行的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 569-574. |
| [13] | 陈千禾, 陈军, 蒋凯瑶, 吴晓楠, 洪婉婷, 张春梅. 儿科护士实施儿童医疗恐惧干预的促进与障碍因素质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 575-580. |
| [14] | 刘婷婷, 牛巧红, 焦雪萍, 卫嘉玮, 段少铭, 胡聪丽, 苏芮. 直肠癌保肛术后患者肠道症状体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 603-610. |
| [15] | 梁轶岚, 姜伟, 何小爽, 王婷, 吕亚旎. 症状科学模型在慢性肾脏疾病患者中的研究进展及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 624-628. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||