


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (3): 332-339.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.03.011
刘博文( ), 王珊珊, 孙倩倩, 梅永霞, 林蓓蕾, 刘腊梅, 张振香(
), 王珊珊, 孙倩倩, 梅永霞, 林蓓蕾, 刘腊梅, 张振香( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-01
出版日期:2025-02-10
发布日期:2025-01-22
通讯作者:
张振香,E-mail:zhangzx666@126.com作者简介:刘博文:女,本科(硕士在读),E-mail:1584155404@qq.com
基金资助:
LIU Bowen( ), WANG Shanshan, SUN Qianqian, MEI Yongxia, LIN Beilei, LIU Lamei, ZHANG Zhenxiang(
), WANG Shanshan, SUN Qianqian, MEI Yongxia, LIN Beilei, LIU Lamei, ZHANG Zhenxiang( )
)
Received:2024-03-01
Online:2025-02-10
Published:2025-01-22
摘要:
目的 探究脑卒中患者及其配偶二元心理资本的潜在剖面特征及相关影响因素,为改善其心理健康提供参考。方法 采用便利抽样法,于2023年3月—8月在河南省某3所三级甲等医院神经内科的脑卒中患者及其配偶作为调查对象。采用一般资料调查表、改良Rankin评分、心理资本量表、凯斯勒心理状况评定量表以及领悟社会支持量表进行调查。潜在剖面分析探索二元心理资本潜在分型,通过多元Logistic回归分析评估各种因素对不同分型的影响。结果 共发放问卷235份,回收有效问卷232份,有效问卷回收率为98.7%。潜在剖面分析结果显示,脑卒中患者及其配偶二元心理资本分为二元低心理资本-低自我效能组(6.0%)、二元高心理资本-低韧性组(15.9%)、二元中心理资本组(78.1%)3个潜在类别。脑卒中患者文化程度、预后情况、患病后工作状况、领悟社会支持量表得分以及配偶工作状况是二元心理资本潜在剖面的影响因素(P<0.05)。结论 脑卒中患者及其配偶二元心理资本水平存在异质性,且存在相依关系,提示医护人员应从二元整体视角出发对不同心理资本特征的脑卒中患者及其配偶制订针对性的干预措施,促进其心理健康。
刘博文, 王珊珊, 孙倩倩, 梅永霞, 林蓓蕾, 刘腊梅, 张振香. 脑卒中患者及其配偶二元心理资本的潜在剖面分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 332-339.
LIU Bowen, WANG Shanshan, SUN Qianqian, MEI Yongxia, LIN Beilei, LIU Lamei, ZHANG Zhenxiang. Latent profile analysis of dyadic psychological capital among stroke patients and their spouses and nursing countermeasures[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(3): 332-339.
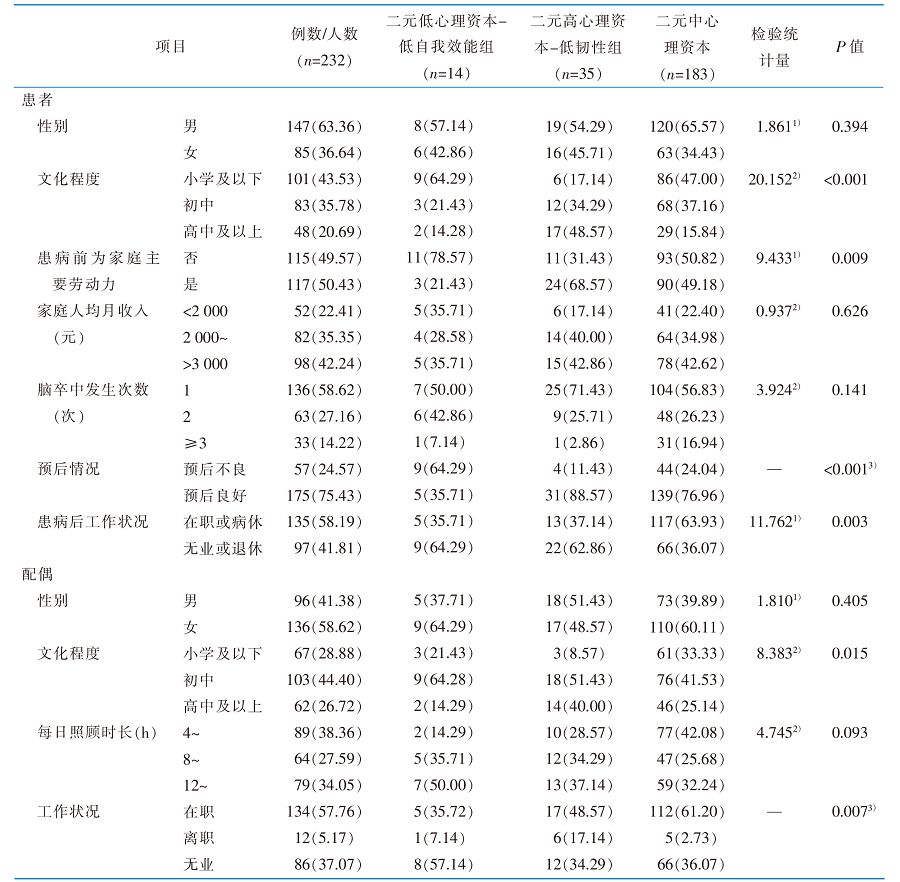 |
表1 脑卒中患者及其配偶的一般资料及二元心理资本潜在剖面的单因素分析[例(百分比,%)]
Table 1 General information of stroke patients and their spouses and univariate analysis of potential categories [cases(percentage,%)]
 |
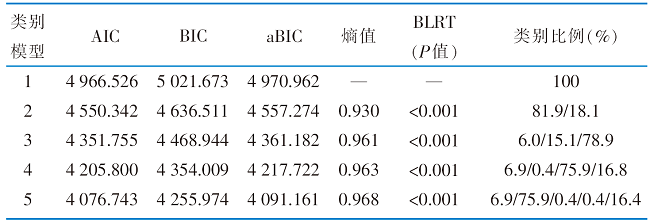 |
表2 脑卒中患者及其配偶二元心理资本的潜在剖面分析结果(n=232)
Table 2 Results of latent profile analysis of dyadic psychological capital among stroke patients and their spouses(n=232)
 |
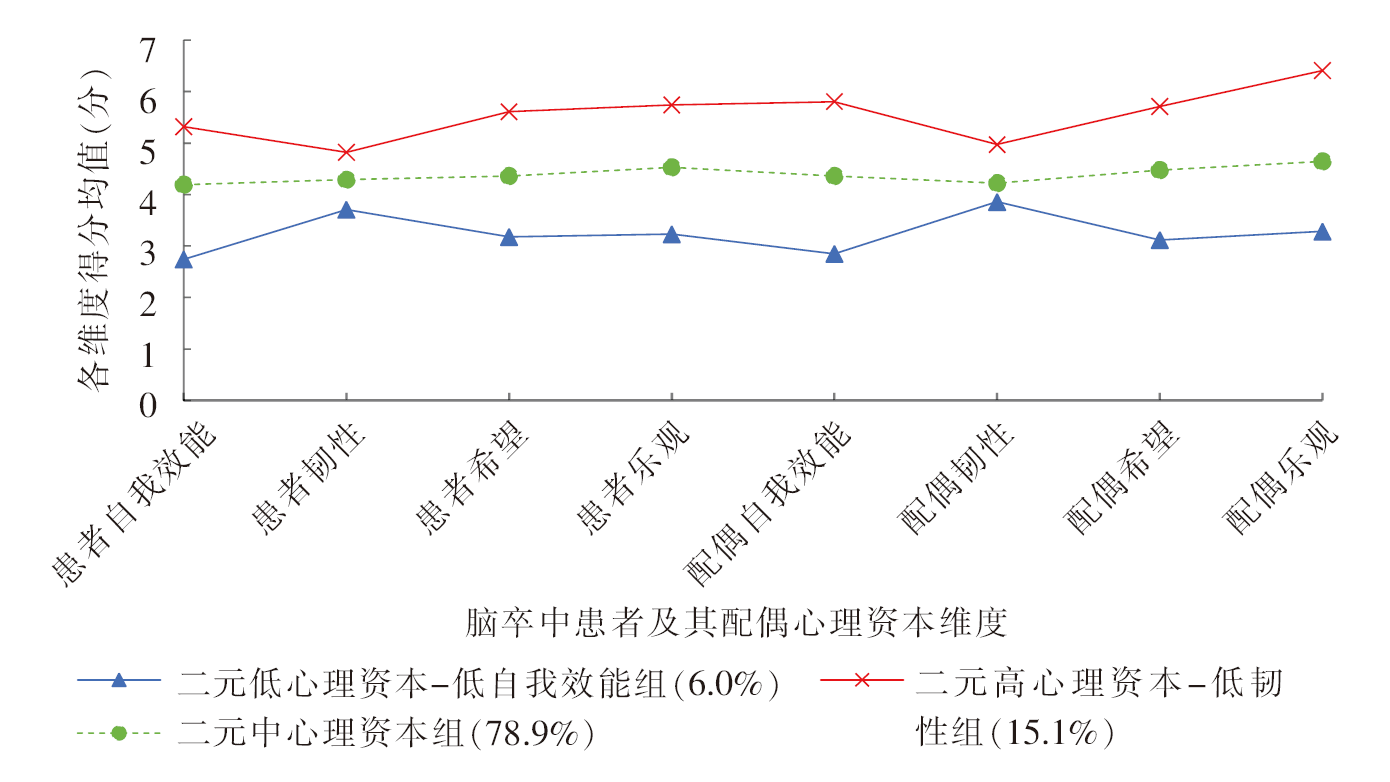
图1 脑卒中患者及其配偶二元心理资本3个潜在剖面的特征分布
Figure 1 The characteristic distribution of 3 potential categories of dyadic psychological capital among stroke patients and their spouses
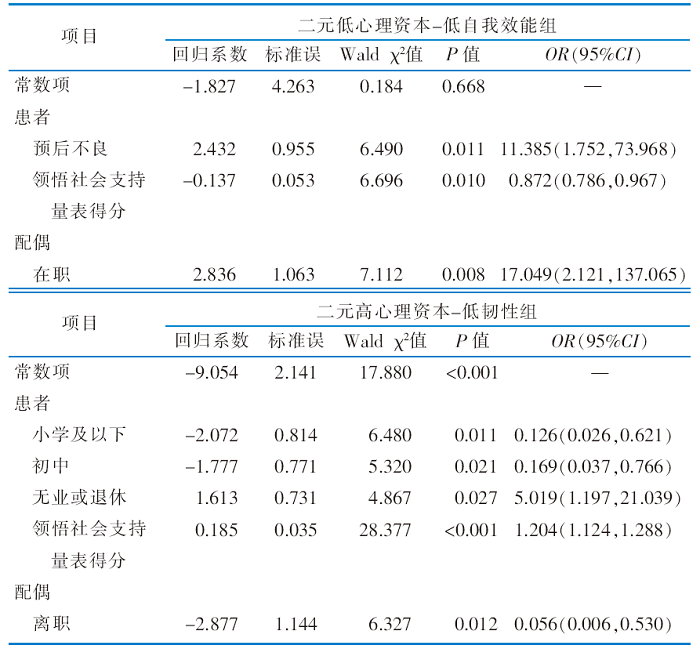 |
表4 脑卒中患者及其配偶二元潜在类别的多元Logistic回归分析(n=232)
Table 4 Results of multiple logistic regression of dyadic potential category influencing factors among stroke patients and their spouses(n=232)
 |
| [1] | Labori F, Persson J, Svensson M, et al. The impact of stroke on spousal and family income:a difference-in-difference study from Swedish national registries[J]. Top Stroke Rehabil, 2024, 31(4):381-389. |
| [2] | Luthans F, Youssef-Morgan C, Avolio B. 心理资本(第二版)[M]. 王垒,译. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2018. |
| Luthans F, Youssef-Morgan C, Avolio B. Psychological capital (second edition)[M]. Wang L,trans. Beijing: China Light Indu-stry Press, 2018. | |
| [3] | 张阔, 张赛, 董颖红. 积极心理资本:测量及其与心理健康的关系[J]. 心理与行为研究, 2010, 8(1):58-64. |
| Zhang K, Zhang S, Dong YH. Positive psychological capital:measurement and relationship with mental health[J]. Stud Psy-chol Behav, 2010, 8(1):58-64. | |
| [4] | 何叶, 王元姣, 谢珺, 等. 心理资本在恢复期脑卒中患者领悟社会支持与患者积极度的中介效应分析[J]. 护理学报, 2023, 30(7):65-70. |
| He Y, Wang YJ, Xie J, et al. Analysis on the mediating effect of psychological capital on perceived social support and patient’s positive degree of stroke patients in recovery period[J]. J Nurs(China), 2023, 30(7):65-70. | |
| [5] |
黄竞仪, 许严江, 岳秋菊, 等. 心理资本在肝癌患者的照顾者负担与焦虑间的中介效应[J]. 心理月刊, 2023, 18(13):20-22.
DOI |
| Huang JY, Xu YJ, Yue QJ, et al. The mediating effect of psychological capital on caregiver burden and anxiety in liver cancer patients[J]. Psychol Monthly, 2023, 18(13):20-22. | |
| [6] |
Czikmantori T, Hagemeyer B, Engeser S. A dyadic typology of social desires in couples[J]. J Pers, 2018, 86(4):590-603.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | 彭斌, 刘鸣, 崔丽英. 与时俱进的新指南:《中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018》解读[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2018, 51(9):657-659. |
| Peng B, Liu M, Cui LY. New evidence,new guideline:inter-pretation of the Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke 2018[J]. Chin J Neurol, 2018, 51(9):657-659. | |
| [8] | 方积乾. 生物医学研究的统计方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007. |
| Fang JQ. Statistical methods for biomedical research[M]. Bei-jing: Higher Education Press, 2007. | |
| [9] | 范玉华, 姬晓昙, 蓝琳芳. 国内脑卒中临床试验疗效判断方法中改良Rankin评分的应用现状[J]. 中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2015, 41(7):412-415. |
| Fan YH, Ji XT, Lan LF. The application of mRS in the methods of outcome assessment in Chinese stroke trials[J]. Chin J Nerv Ment Dis, 2015, 41(7):412-415. | |
| [10] | 张世洪, 吴波, 谈颂. 卒中登记研究中Barthel指数和改良的Rankin量表的适用性与相关性研究[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2004, 4(12):871-874. |
| Zhang SH, Wu B, Tan S. Appropriateness assessment and cor-relation analysis of Barthel Index and Modified Rankin Scales in a stroke data register[J]. Chin J Evid Based Med, 2004, 4(12):871-874. | |
| [11] | 刘志薇, 张振香, 梅永霞, 等. 脑卒中患者配偶照顾者抑郁症状潜在类别分析及影响因素[J]. 军事护理, 2023, 40(4):56-59. |
| Liu ZW, Zhang ZX, Mei YX, et al. Latent class analysis of depressive symptoms in spouse caregivers of stroke patients and the influencing factors[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2023, 40(4):56-59. | |
| [12] |
Kessler RC, Andrews G, Colpe LJ, et al. Short screening scales to monitor population prevalences and trends in non-specific psychological distress[J]. Psychol Med, 2002, 32(6):959-976.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | 周成超, 楚洁, 王婷, 等. 简易心理状况评定量表Kessler10中文版的信度和效度评价[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2008, 16(6):627-629. |
| Zhou CC, Chu J, Wang T, et al. Reliability and validity of 10-item Kessler scale(K10) Chinese version in evaluation of men-tal health status of Chinese population[J]. Chin J Clin Psy-chol, 2008, 16(6):627-629. | |
| [14] |
Zimet GD, Powell SS, Farley GK, et al. Psychometric charac-teristics of the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support[J]. J Pers Assess, 1990, 55(3-4):610-617.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | 姜乾金. 领悟社会支持量表[J]. 中国行为医学科学, 2001, 10(10):41-43. |
| Jiang QJ. Perceived Social Support Scale[J]. Chin J Behav Med Sci, 2001, 10(10):41-43. | |
| [16] | 王孟成. 潜变量建模与Mplus应用[M]. 重庆大学出版社, 2014. |
| Wang MC. Latent variable modeling using Mplus[M]. Chong-ging: Chonging University Press, 2014. | |
| [17] | 孙倩倩, 李婷, 梅永霞, 等. 基于交叉滞后分析的脑卒中患者夫妻二元应对与抑郁关系研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2023, 38(19):71-76. |
| Sun QQ, Li T, Mei YX, et al. Relationship between dyadic coping and depression in stroke patients and their spouses:a cross lagged panel analysis[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2023, 38(19):71-76. | |
| [18] | Zhang LY, Zhang ZX, Mei YX, et al. Dyadic appraisals,dyadic coping,and mental health among couples coping with stroke:a longitudinal study protocol[J]. J Adv Nurs, 2020, 76(11):3164-3170. |
| [19] | Wang JY, Cui J, Tu SY, et al. Resilience and caregiving ability among caregivers of people with stroke:the mediating role of uncertainty in illness[J]. Front Psychiatry, 2022, 13:788737. |
| [20] |
Liu Z, King M. The influencing factors and coping styles of mental health stress responses of stroke caregivers[J]. Work, 2021, 69(2):499-513.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Terrill AL, Reblin M, MacKenzie JJ, et al. Intimate relation-ships and stroke:piloting a dyadic intervention to improve depression[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(3):1804. |
| [22] | 庞晨晨. 中青年脑卒中患者积极心理资本、应对方式与健康行为的相关性研究[D]. 开封: 河南大学, 2020. |
| Pang CC. Study on the correlation between positive psycholo-gical capital,coping style and health behavior in young and middle-aged stroke patients[D]. Kaifeng: Henan University, 2020. | |
| [23] |
刘志薇, 梅永霞, 张振香, 等. 脑卒中患者夫妻疾病沟通体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(5):576-581.
DOI URL |
|
Liu ZW, Mei YX, Zhang ZX, et al. A qualitative study of disease communication experiences in couples with stroke[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(5):576-581.
DOI URL |
|
| [24] |
徐广怡, 刘婷, 徐颜红, 等. 炎症性肠病患者心理韧性的潜在剖面分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(10):1212-1218.
DOI URL |
| Xu GY, Liu T, Xu YH, et al. Latent profile analysis and nursing decision-making of psychological resilience among patients with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(10):1212-1218. | |
| [25] | 车洪, 关晋英, 许叶华, 等. 五种干预措施对癌症儿童主要照顾者心理韧性影响的网状Meta分析[J]. 医学与哲学, 2022, 43(24):46-50+56. |
| Che H, Guan JY, Xu YH, et al. Effectiveness of five inter-ventions on resilience of primary caregivers of children with cancer:a network Meta-analysis[J]. Med Philos, 2022, 43(24):46-50+56. | |
| [26] | 李怡璇. 脑卒中患者积极心理资本、照护依赖、自我护理能力与生活质量的相关性研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃中医药大学, 2024. |
| Li YX. Correlation between positive psychological capital,care-dependent,self-care ability and quality of life in stroke patients[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, 2024. | |
| [27] | 司雨朦, 杜静, 余红, 等. 卒中后疲劳患者疲劳体验及应对策略的质性研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2024, 39(07):109-112. |
| Si MY, Du J, Yu H, et al. Experience of fatigue and coping strategies among patients with post-stroke fatigue:a qualitative study[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2024, 39(07):109-112. | |
| [28] | Gao C, Li M, Guo L, et al. Developing a conceptual model for understanding caregiving experience and their impacts on quality of life for Chinese breast cancer family caregivers:a qualitative study[J]. Nurs Open, 2024, 11(3),e2139. |
| [29] |
Hassan M, Fang SH, Malik AA, et al. Impact of perceived so-cial support and psychological capital on university students’ academic success:testing the role of academic adjustment as a moderator[J]. BMC Psychol, 2023, 11(1):340.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | 杨梦竹. 老年维持性血液透析患者积极心理资本、社会支持与生活质量的相关性研究[D]. 开封: 河南大学, 2021. |
| Yang MZ. Correlation between positive psychological capital,social support and quality of life in elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients[D]. Kaifeng: Henan University, 2021. | |
| [31] |
孙倩倩, 梅永霞, 宋王涛, 等. 脑卒中患者及其配偶获益感与积极心理资本的二元关系研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(17):2116-2122.
DOI URL |
| Sun QQ, Mei YX, Song WT, et al. A study on dyadic relation-ship between benefit finding and positive psychological capital in stroke patients and their spouses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(17):2116-2122. |
| [1] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [2] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [3] | 章子怡, 杜冰, 张荩之, 尹敏. 青少年心境障碍患者心理求助体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 947-952. |
| [4] | 谭雨婷, 张志霞, 许梦莉, 郭沛然, 肖琴, 乔林茹, 宋飞云, 余巧君. 中年脑卒中患者自主康复行为与相关症状关系的研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 773-778. |
| [5] | 周辰茜, 林蓓蕾, 张杰, 任慧, 王辉, 张振香. 脑卒中发病风险感知与客观发病风险的关系及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 779-784. |
| [6] | 苏炫, 成巧梅, 李晓婉, 王珂心, 王培席, 肖梦伟, 王语, 李楠楠, 谢丹莹. 急性期脑卒中患者卒中后抑郁的潜在类别及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 785-791. |
| [7] | 周柯冰, 黄晓娇, 闫凤侠. 首发脑卒中恢复期患者症状负担及其影响因素的网络分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 792-798. |
| [8] | 张程, 王霄一, 杨文娟, 刘梦如, 贺飞. 双向社会支持在老年维持性血液透析患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 813-818. |
| [9] | 李红颐, 李雪, 范宇莹, 赵一莎, 李京淑. ICU患者创伤心理反应的潜在剖面及影响因素的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 842-848. |
| [10] | 刘雪华, 王建虹, 杨丽红, 刘佳丽, 乔艳萍, 李晓燕. 血液肿瘤患者及其配偶二元应对与恐惧疾病进展的相关性分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 717-722. |
| [11] | 任雅钰, 高春华, 卢芳燕, 郑力, 王华芬. 虚拟现实技术在癌症患者心理干预中应用的范围综述[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4): 486-492. |
| [12] | 蒲江锋, 王婉儿, 李格格, 谢章浩, 许怡璇, 詹宁静, 黄惠根. 护士组织支持感现状及潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 340-346. |
| [13] | 况嘉茜, 陈淳, 张倩. 脑卒中患者运动功能预后预测模型的范围综述及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 364-372. |
| [14] | 铁万琴, 张曦, 王永琦, 许洋, 陈雪丰, 潘璐, 陈思羽. 乳腺癌患者化疗前后症状特征的潜在转变分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(2): 193-200. |
| [15] | 徐萍, 闫荣, 张淼淼, 柳文慧, 姜凯. 头颈部肿瘤患者身体意象潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(2): 215-222. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||