


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (19): 2396-2403.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.19.013
韩林( ), 李敏敏, 李雨欣, 陆柳伊, 张琦, 王雪婷, 鞠萍, 杨丽娟(
), 李敏敏, 李雨欣, 陆柳伊, 张琦, 王雪婷, 鞠萍, 杨丽娟( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-28
出版日期:2024-10-10
发布日期:2024-10-14
通讯作者:
杨丽娟,E-mail:sdyanglijuan@aliyun.com作者简介:韩林:女,本科(硕士在读),护士,E-mail:710749736@qq.com
HAN Lin( ), LI Minmin, LI Yuxin, LU Liuyi, ZHANG Qi, WANG Xueting, JU Ping, YANG Lijuan(
), LI Minmin, LI Yuxin, LU Liuyi, ZHANG Qi, WANG Xueting, JU Ping, YANG Lijuan( )
)
Received:2024-01-28
Online:2024-10-10
Published:2024-10-14
摘要:
目的 构建先天性心脏病术后患儿营养不良风险预测模型,进行内部及外部验证。 方法 采用便利抽样法,选取2018年1月—2021年12月山东省某三级甲等医院收治的300例6月龄以下的先天性心脏病术后患儿作为建模组,选取2022年1月—2023年6月收治的129例患儿作为验证组。回顾性收集患儿的一般资料、疾病相关资料、治疗和护理相关资料,通过单因素、Logistic回归分析构建先天性心脏病术后患儿营养不良风险预测模型,绘制列线图并评价其预测效果。 结果 先天性心脏病术后患儿营养不良发生率为33.10%,Logistic回归分析结果显示,出生体重<2.5 kg、术前营养不良、术后1周液体负平衡、体外循环时间较长是患儿发生营养不良的危险因素(P<0.05)。该模型建模组受试者操作特征曲线下面积为0.933,灵敏度为83.30%,特异度为90.90%,Hosmer-Lemeshow检验显示,χ2=7.765(P=0.457)。验证组受试者操作特征曲线下面积为0.918,灵敏度为87.20%,特异度为90.00%,Hosmer-Lemeshow检验显示,χ2=4.947(P=0.763)。两组校准曲线均显示,该模型具有较好的校准度;临床决策曲线显示,该模型具有较好的临床实用性。 结论 该研究构建的风险预测模型具有较好的预测能力,可为医护人员早期识别先天性心脏病术后营养不良高危患儿,制订针对性干预措施提供参考。
韩林, 李敏敏, 李雨欣, 陆柳伊, 张琦, 王雪婷, 鞠萍, 杨丽娟. 先天性心脏病术后患儿营养不良风险预测模型的构建及验证研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(19): 2396-2403.
HAN Lin, LI Minmin, LI Yuxin, LU Liuyi, ZHANG Qi, WANG Xueting, JU Ping, YANG Lijuan. Construction and verification of a risk prediction model for postoperative malnutrition in infants with congenital heart disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(19): 2396-2403.
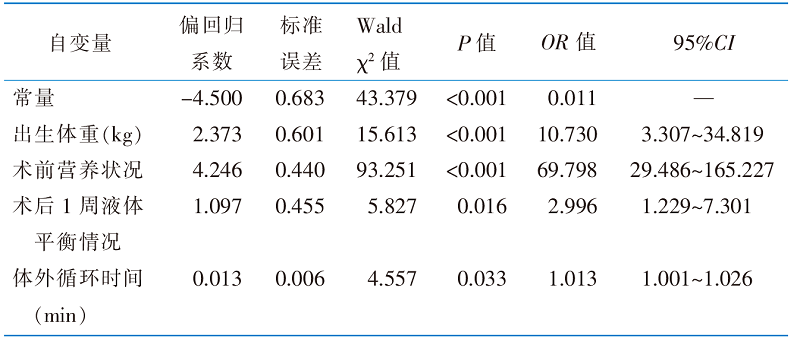 |
表3 先天性心脏病术后患儿营养不良的Logistic回归分析结果(n=300)
Table 3 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of the influencing factors of postoperative malnutrition in children with CHD(n=300)
 |
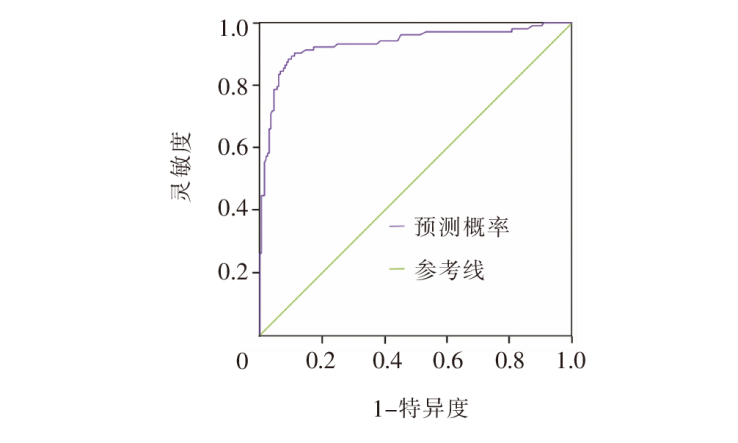
图2 建模组先天性心脏病术后患儿营养不良风险预测模型的受试者操作特征曲线
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curve of the modeling group for predicting the risk of postoperative malnutrition in children with CHD
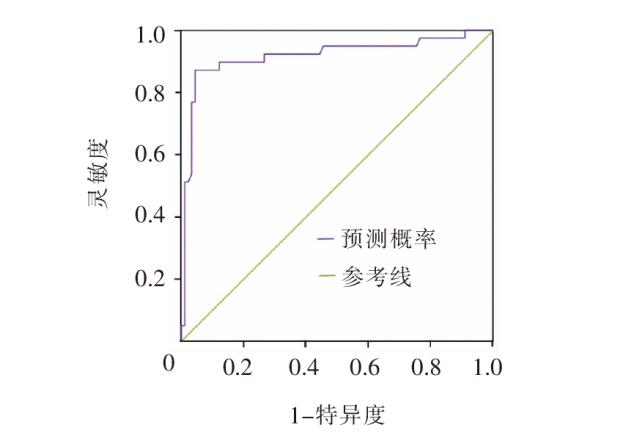
图3 验证组先天性心脏病术后患儿营养不良风险预测模型的受试者操作特征曲线
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curve of the validation group for predicting the risk of postoperative malnutrition in children with CHD
| [1] |
傅唯佳, 顾莺, 杨玉霞, 等. 先天性心脏病患儿营养风险筛查及评估循证决策支持系统的构建与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(17):2059-2066.
DOI URL |
|
Fu WJ, Gu Y, Yang YX, et al. The construction and evaluation of an evidence-based decision support system for the nutrition risk screening of congenital heart disease children[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(17):2059-2066.
DOI URL |
|
| [2] | Mehta NM, Corkins MR, Lyman B, et al. Defining pediatric malnutrition:a paradigm shift toward etiology-related definitions[J]. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2013, 37(4):460-481. |
| [3] | 张媛媛, 王海燕, 杨巧芳. 双重固定式约束衣在先天性心脏病患儿术后的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(1):137-139. |
| Zhang YY, Wang HY, Yang QF. The application effect of double fixed binding cloth in children with congenital heart disease surgery[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(1):137-139. | |
| [4] | Martini S, Beghetti I, Annunziata M, et al. Enteral nutrition in term infants with congenital heart disease:knowledge gaps and future directions to improve clinical practice[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(3):932. |
| [5] |
Brief F, Guimber D, Baudelet JB, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of long-term growth failure in infants with congenital heart disease who underwent cardiac surgery before the age of one[J]. Pediatr Cardiol, 2022, 43(8):1681-1687.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | 顾晓蓉, 陈伟敏, 管咏梅. 6个月以下先天性心脏病患儿术后营养摄入状况的调查[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2016, 33(12):49-50. |
| Gu XR, Chen WM, Guan YM. Investigation of postoperative nutrient intake of children with congenital heart disease aged under 6 months[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2016, 33(12):49-50. | |
| [7] | Ross FJ, Radman M, Jacobs ML, et al. Associations between anthropometric indices and outcomes of congenital heart operations in infants and young children:an analysis of data from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons Database[J]. Am Heart J, 2020, 224:85-97. |
| [8] |
李莉娟, 胡春梅, 龚婷, 等. 先天性心脏病患儿术后1年营养不良影响因素分析[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2023, 61(5):440-445.
PMID |
|
Li LJ, Hu CM, Gong T, et al. Factors associated with malnutrition in infants with congenital heart disease within one year after surgery[J]. Chin J Pediatr, 2023, 61(5):440-445.
DOI PMID |
|
| [9] |
Shi H, Yang D, Tang KC, et al. Explainable machine learning model for predicting the occurrence of postoperative malnutrition in children with congenital heart disease[J]. Clin Nutr, 2022, 41(1):202-210.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | 左茜, 苏洁, 陶柯宏, 等. 需体外循环手术干预的先天性心脏病婴幼儿的营养评估[J]. 心脏杂志, 2024, 36(2):191-195. |
| Zuo Q, Su J, Tao KH, et al. Nutritional assessment of infants with congenital heart disease requiring surgical intervention with extracorporeal circulation[J]. Chin Heart J, 2024, 36(2):191-195. | |
| [11] |
Centeno-Malfaz F, Moráis-López A, Caro-Barri A, et al. Nutrition in congenital heart disease:consensus document[J]. An Pediatr, 2023, 98(5):373-383.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | El-Chouli M, Meddis A, Christensen DM, et al. Lifetime risk of comorbidity in patients with simple congenital heart disease:a Danish nationwide study[J]. Eur Heart J, 2023, 44(9):741-748. |
| [13] |
Hansson L, Lind T, Wiklund U, et al. Fluid restriction negatively affects energy intake and growth in very low birthweight infants with haemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus[J]. Acta Paediatr, 2019, 108(11):1985-1992.
DOI |
| [14] |
高华炜, 陈求名, 赵韡, 等. 三种先天性心脏病手术风险评分系统预测效能的比较[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2019, 47(5):388-392.
PMID |
|
Gao HW, Chen QM, Zhao W, et al. Predictive value of 3 different risk stratification models for patients after congenital heart surgeries[J]. Chin J Cardiol, 2019, 47(5):388-392.
DOI PMID |
|
| [15] | 何洋, 李文星, 唐军, 等. 早产儿喂养不耐受临床诊疗指南(2020)[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2020, 22(10):1047-1055. |
| He Y, Li WX, Tang J, et al. Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of feeding intolerance in preterm infants(2020)[J]. Chin J Contemp Pediatr, 2020, 22(10):1047-1055. | |
| [16] |
Eveleens RD, Joosten KFM, et al. Definitions,predictors and outcomes of feeding intolerance in critically ill children:a systematic review[J]. Clin Nutr, 2020, 39(3):685-693.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | 丁文雯, 向奕瑾, 马佳莉, 等. 极低出生体重早产儿校正月龄12个月内体格生长情况及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(1):52-57. |
| Ding WW, Xiang YJ, Ma JL, et al. Analysis on features and related factors of physical growth in very low birth weight preterm infants in 12 months of corrected age[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(1):52-57. | |
| [18] | 林淑皖, 张红, 涂惠琼. 母乳口腔运动干预对婴儿体外循环术后胃肠功能恢复的影响[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(21):36-39. |
| Lin SW, Zhang H, Tu HQ. Impact of olfactory stimulation with breast milk on digestive function recovery in infants after cardiopulmonary bypass[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(21):36-39. | |
| [19] | Yilmaz Ferhatoglu S, Yurdakok O, Yurtseven N. Malnutrition on admission to the paediatric cardiac intensive care unit increases the risk of mortality and adverse outcomes following paediatric congenital heart surgery:a prospective cohort study[J]. Aust Crit Care, 2022, 35(5):550-556. |
| [20] | Wen BJ, Njunge JM, Bourdon C, et al. Systemic inflammation and metabolic disturbances underlie inpatient mortality among ill children with severe malnutrition[J]. Sci Adv, 2022, 8(7):eabj6779. |
| [21] |
Tsintoni A, Dimitriou G, Karatza AA. Nutrition of neonates with congenital heart disease:existing evidence,conflicts and concerns[J]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2020, 33(14):2487-2492.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | 吴珍, 富智, 缪红军. 先天性心脏病新生儿围手术期营养支持的研究[J]. 肠外与肠内营养, 2017, 24(6):365-368,373. |
| Wu Z, Fu Z, Miu HJ. Nutrition support in neonates with congenital heart disease during the perioperative period[J]. Parenter Enter Nutr, 2017, 24(6):365-368,373. | |
| [23] |
Banerji N, Sudhakar A, Balachandran R, et al. Early weight trends after congenital heart surgery and their determinants[J]. Cardiol Young, 2020, 30(1):89-94.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Hatami S, Hefler J, Freed DH. Inflammation and oxidative stress in the context of extracorporeal cardiac and pulmonary support[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13:831930. |
| [25] | Floh AA, McCrindle BW, Manlhiot C, et al. Feeding may modu-late the relationship between systemic inflammation,insulin resistance,and poor outcome following cardiopulmonary bypass for pediatric cardiac surgery[J]. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2020, 44(2):308-317. |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [6] | 韩姗姗, 秦永平, 屈虹, 郑显兰. 神经外科患儿术中获得性压力性损伤风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 928-933. |
| [7] | 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培. 14例造血干细胞移植后继发闭塞性细支气管炎行双肺移植术患儿的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 972-976. |
| [8] | 张聚, 魏丽丽, 辛晨, 王静, 韩艳, 杨岩岩, 孙梦竹. 沉浸式虚拟现实技术在择期手术全身麻醉患儿中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 671-676. |
| [9] | 韩文文, 胡春霞, 张凯, 隋伟静, 黄美丽, 潘红英, 宫晓艳, 庄一渝. 1例特重度烧伤患儿基于增强现实技术的远程护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 677-679. |
| [10] | 杨童玲, 陈玉莹, 万凡, 窦亚兰, 胡晓静. 新生儿居家皮肤护理指导方案的构建及初步应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 680-687. |
| [11] | 国家心血管病中心 中华护理学会心血管专业委员会(执笔:张茜 刘亚飞 李梦然 王娜 王艳娇 王诗瑜 李庆印). 先天性心脏病患儿围生期护理管理专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 552-557. |
| [12] | 陈千禾, 陈军, 蒋凯瑶, 吴晓楠, 洪婉婷, 张春梅. 儿科护士实施儿童医疗恐惧干预的促进与障碍因素质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 575-580. |
| [13] | 蒋思珊, 成琴琴, 罗听薇, 张娜, 郭俊晨, 李东雅, 李丹丹, 朱丽辉. 儿童安宁疗护质量评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 611-618. |
| [14] | 杨福娜, 杨瑞, 秦妍, 陈军翰, 郭兰伟, 王永琦, 何家欣, 刘琪, 毛婷, 梅萧萧, 王文颖, 徐晓霞, 石红英. 癌症患儿家庭复原力现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4): 446-452. |
| [15] | 王飒, 苗华丽, 李雨蔚, 王鸿伟, 乔彩彩, 宋炜婷. 10~19岁慢性病患者向成人过渡期准备度评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4): 469-477. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||