


中华护理杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (24): 2976-2983.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.24.005
收稿日期:2023-06-09
出版日期:2023-12-20
发布日期:2023-12-19
通讯作者:
徐蓉,E-mail:1017565070@qq.com作者简介:谢晓冉:女,硕士,护师,E-mail:646343913@qq.com
基金资助:
XIE Xiaoran( ), XU Rong(
), XU Rong( ), ZHANG Jing, TAO Jing, BIAN Xuna, HOU Jinjie
), ZHANG Jing, TAO Jing, BIAN Xuna, HOU Jinjie
Received:2023-06-09
Online:2023-12-20
Published:2023-12-19
摘要:
目的 系统地分析、比较局部氧疗对糖尿病足溃疡患者干预效果的相关研究,为护理实践提供参考依据。 方法 检索PubMed、Embase、Web of Science、CENTRAL、CINAHL、Clinical Trial、中国生物医学文献数据库、中国知网、万方数据库和维普数据库中有关局部氧疗对糖尿病足溃疡患者干预效果的研究,检索时限为建库至2023年2月1日。由2名研究者独立筛选文献和提取数据,应用RevMan 5.4软件对纳入文献进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入8项研究,共计622例糖尿病足溃疡患者。Meta分析结果显示,与常规护理相比,局部氧疗可以提高糖尿病足溃疡患者的治疗有效率[RR=1.59,95%CI(1.16,2.17),P=0.004],提高糖尿病足溃疡面积缩小率[MD=28.78,95%CI(14.83,42.73),P<0.001],且该方法未增加不良事件发生率[RR=0.83,95%CI(0.63,1.10),P=0.190],但在愈合时间[MD=9.86,95%CI(-15.39, 35.11),P=0.440]方面差异无统计学意义。 结论 局部氧疗有助于提高糖尿病足溃疡患者的治疗有效率,缩小溃疡面积,安全性较好,但对愈合时间的干预效果尚不明确。未来应开展高质量随机对照试验以进一步验证局部氧疗对糖尿病足溃疡患者的疗效。
谢晓冉, 徐蓉, 张静, 陶静, 边旭娜, 侯锦杰. 局部氧疗对糖尿病足溃疡患者干预效果的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(24): 2976-2983.
XIE Xiaoran, XU Rong, ZHANG Jing, TAO Jing, BIAN Xuna, HOU Jinjie. The effect of topical oxygen therapy on the intervention of patients with diabetic foot ulcers:a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2023, 58(24): 2976-2983.
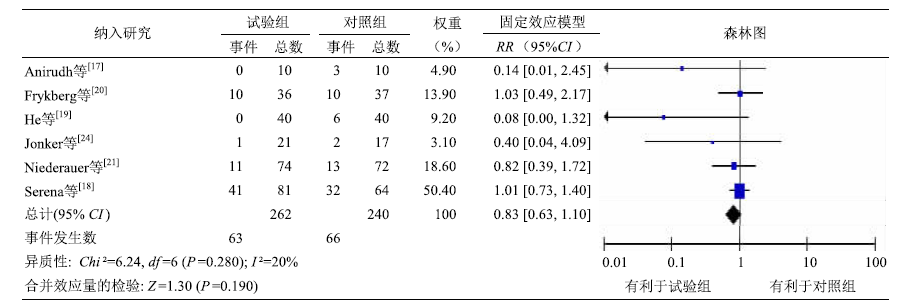
图4 局部氧疗对糖尿病足溃疡患者治疗不良事件发生率的影响
Figure 4 Effect of topical oxygen therapy on the incidence of adverse events in the treatment of patients with diabetic foot ulcers
| [1] |
Bus SA, Lavery LA, Monteiro-Soares M, et al. Guidelines on the prevention of foot ulcers in persons with diabetes(IWGDF 2019 update)[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2020, 36(Suppl 1):e3269.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Jiang YF, Wang XM, Xia L, et al. A cohort study of diabetic patients and diabetic foot ulceration patients in China[J]. Wound Rep And Reg, 2015, 23(2):222-230.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Lipsky BA, Apelqvist J, Bakker K, et al. Diabetic foot disease:moving from roadmap to journey[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2015, 3(9):674-675.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Xu ZR, Ran XW. Diabetic foot care in China:challenges and strategy[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2016, 4(4):297-298.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
谢晓冉, 徐蓉. 糖尿病足发病风险预测模型的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(1):124-131.
DOI URL |
|
Xie XR, Xu R. A systematic review of risk prediction models for diabetic foot[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(1):124-131.
DOI URL |
|
| [6] |
吴佳芸, 宁丽, 葛华英, 等. 糖尿病足风险自评工具的构建与验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(15):1811-1817.
DOI URL |
|
Wu JY, Ning L, Ge HY, et al. Construction and validation of diabetic foot risk self-assessment tool[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(15):1811-1817.
DOI URL |
|
| [7] |
Patel S, Srivastava S, Singh MR, et al. Mechanistic insight into diabetic wounds:pathogenesis,molecular targets and treatment strategies to pace wound healing[J]. Biomed Pharmacoth, 2019, 112:108615.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Lantis J. Oxygen therapy:evidence base[J]. J Wound Care, 2020, 29(Sup5b):S11-S22. |
| [9] |
Guan Y, Niu H, Liu ZT, et al. Sustained oxygenation accelerates diabetic wound healing by promoting epithelialization and angiogenesis and decreasing inflammation[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(35):eabj0153.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 黄荣曦, 杨刚毅, 李伶, 等. 高压氧辅助治疗糖尿病足溃疡有效性及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2013, 21(12):1081-1087. |
| Huang RX, Yang GY, Li L, et al. Efficacy and safety of adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen therapy for diabetic foot ulcer:a Meta-analysis[J]. Chin J Diabetes, 2013, 21(12):1081-1087. | |
| [11] |
Howard MA, Asmis R, Evans KK, et al. Oxygen and wound care:a review of current therapeutic modalities and future direction[J]. Wound Repair Regen, 2013, 21(4):503-511.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Lindenmann J, Smolle C, Kamolz LP, et al. Survey of molecu-lar mechanisms of hyperbaric oxygen in tissue repair[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(21):11754.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
de Smet GHJ, Kroese LF, Menon AG, et al. Oxygen therapies and their effects on wound healing[J]. Wound Repair Regen, 2017, 25(4):591-608.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | 孙献坤, 袁丽, 李饶, 等. 糖尿病足溃疡患者局部氧疗的研究进展[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2021, 13(2):183-186. |
| Sun XK, Yuan L, Li R, et al. Research progress on topical oxygen therapy for patients with diabetic foot ulcer[J]. Chin J Diabetes Mellitus, 2021, 13(2):183-186. | |
| [15] | Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.2[EB/OL]. (2021-02-01)[2022-10-22]. https://training.cochran-e.org/handbook. |
| [16] | Sterne J, Savovic J, Page MJ, et al. RoB 2:a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials[J]. BMJ, 2019, |
| [17] |
Anirudh V, Kamath DY, Ghosh S, et al. Topical controlled warm oxygen therapy delivered through a novel device(KADAMTM) to treat diabetic foot ulcers:a randomized controlled,open,pilot trial[J]. Indian J Surg, 2021, 83(4):907-914.
DOI |
| [18] |
Serena TE, Bullock NM, Cole W, et al. Topical oxygen therapy in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers:a multicentre,open,randomised controlled clinical trial[J]. J Wound Care, 2021, 30(Sup 5):S7-S14.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
He SM, Liang CY, Yi CL, et al. Therapeutic effect of continuous diffusion of oxygen therapy combined with traditional moist wound dressing therapy in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2021, 174:108743.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Frykberg RG, Franks PJ, Edmonds M, et al. A multinational,multicenter,randomized,double-blinded,placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of cyclical topical wound oxygen (TWO2) therapy in the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers:the TWO2 study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2020, 43(3):616-624.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Niederauer MQ, Michalek JE, Liu QQ, et al. Continuous diffusion of oxygen improves diabetic foot ulcer healing when compared with a placebo control:a randomised,double-blind,multicentre study[J]. J Wound Care, 2018, 27(Sup9):S30-S45.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Yu J, Lu S, McLaren AM, et al. Topical oxygen therapy results in complete wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers[J]. Wound Repair Regen, 2016, 24(6):1066-1072.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | 毛细花, 滕荣建, 陈敏华, 等. 负压封闭引流技术联合局部加氧治疗糖尿病足慢性创面的临床研究[J]. 中国现代医生, 2020, 58(24):96-99. |
| Mao XH, Teng RJ, Chen MH, et al. Clinical study of negative pressure closed drainage technology combined with local oxygenation in the treatment of chronic wounds of diabetic foot[J]. Chin Mod Doctor, 2020, 58(24):96-99. | |
| [24] | Jonker L, Smith D, Mark E, et al. A pragmatic,single-center,prospective,randomized controlled trial of adjunct hemoglobin-mediated granulox topical oxygen therapy twice weekly for foot ulcers[J]. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc, 2021, 111(5). |
| [25] |
Schlingemann RO, van Noorden CJ, Diekman MJ, et al. VEGF levels in plasma in relation to platelet activation,glycemic control,and microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Care, 2013, 36(6):1629-1634.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | 陈梦越, 李乐之. 慢性伤口细菌生物膜相关微环境的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2016, 51(12):1483-1486. |
| Chen MY, Li YZ. Advances in the microenvironment associat-ed with bacterial biofilms in chronic wounds[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2016, 51(12):1483-1486. | |
| [27] | 谭谦, 徐晔. 慢性创面治疗的理论和策略[J]. 中华烧伤杂志, 2020, 36(9):798-802. |
| Tan Q, Xu Y. Theories and strategies of chronic wound treatment[J]. Chin J Burns, 2020, 36(9):798-802. | |
| [28] | Wei X, Li M, Zheng Z, et al. Senescence in chronic wounds and potential targeted therapies[J]. Burns Trauma, 2022, 10:b45. |
| [29] |
Sun XK, Li R, Yang XL, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical oxygen therapy for diabetic foot ulcers:an updated systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int Wound J, 2022, 19(8):2200-2209.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Kaufman H, Gurevich M, Tamir E, et al. Topical oxygen therapy stimulates healing in difficult,chronic wounds:a tertiary centre experience[J]. J Wound Care, 2018, 27(7):426-433.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 刘晓熠, 王红, 周智聪, 孙旭, 王意茹, 仝紫薇, 刘晓莹. 沉浸式虚拟现实技术对外周性前庭功能障碍患者康复效果的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1140-1145. |
| [2] | 梁元元, 高兴莲, 戴张章, 周荣超, 胡娟娟, 王曾妍, 沈剑辉. 医院手术器械管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 1005-1011. |
| [3] | 王婷, 王佳婷, 金爱云, 朱霞明, 方云, 汪靖, 田菲, 濮益琴, 万滢, 贺瑾, 颜霞. 自体造血干细胞移植术后患者护理随访清单的构建及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 914-920. |
| [4] | 盛婉婷, 王蕊, 赵玉晓, 戚鹏菲, 高祀龙, 冯娟, 吕伯瀚, 牛群, 王刚. 中等长度静脉导管不同尖端位置应用效果的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 990-997. |
| [5] | 严雪芹, 曹松梅, 周芳芳, 朱丽群, 陈成, 朱梦雪, 张艳红, 梁怡青, 柏素萍. 手部烧伤患者手功能早期康复管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 998-1004. |
| [6] | 魏永婷, 田书梅, 杨娇, 余良欢, 倪福, 范雨晴, 肖瑶, 席祖洋, 沙菊艳, 刘聪. 护士循证决策能力量表的汉化及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 736-742. |
| [7] | 王雯静, 郝妩媚, 台靖宇, 董倩, 郭爱敏. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者吸入药物治疗体验的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 545-551. |
| [8] | 唐佳怡, 唐桂清, 张娜, 李晓波. 慢加急性肝衰竭患者营养管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 581-588. |
| [9] | 刘婷婷, 牛巧红, 焦雪萍, 卫嘉玮, 段少铭, 胡聪丽, 苏芮. 直肠癌保肛术后患者肠道症状体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 603-610. |
| [10] | 蒋思珊, 成琴琴, 罗听薇, 张娜, 郭俊晨, 李东雅, 李丹丹, 朱丽辉. 儿童安宁疗护质量评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 611-618. |
| [11] | 中华护理学会老年护理专业委员会, 北京医院 国家老年医学中心, 中国医学科学院老年医学研究院, 北京大学护理学院(执笔:刘文静 王志稳 余跃琳 任欣 琚慧 陈宏 王君鑫 陈闪闪 周佳 伊默 王文霞 张玲娟 陈思烨 杨宇帆 王小萌 孙红). 老年人内在能力评估与维护指南[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 261-265. |
| [12] | 段煜, 郭张慧, 张洁, 焦萌, 屈简妮, 刘桂英, 赵丹, 陈颖宇, 郭红. 衰弱老年人运动锻炼促进与阻碍因素的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 288-296. |
| [13] | 宗小燕, 李红燕, 韩小云, 景新华. 胃癌患者围手术期口服营养补充管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 355-363. |
| [14] | 力晶, 毛秋婷, 黄毅, 曾凡, 熊沫, 李倩倩, 周双红. 癌症化疗患者味觉改变发生率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(14): 1778-1785. |
| [15] | 杨舒, 林伊慧, 韩知浩, 唐林霞, 裘云霞, 马小琴. 乳腺癌患者身体意象体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(14): 1786-1792. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||