


中华护理杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (23): 2889-2895.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.23.010
收稿日期:2022-12-29
出版日期:2023-12-10
发布日期:2023-12-12
通讯作者:
丁炎明,E-mail:dingym60@126.com作者简介:麦智德:男,本科(硕士在读),主管护师,E-mail:maizd2909@163.com
基金资助:
MAI Zhide( ), LI Ke, YU Miao, ZHANG Jianxia, DING Yanming(
), LI Ke, YU Miao, ZHANG Jianxia, DING Yanming( )
)
Received:2022-12-29
Online:2023-12-10
Published:2023-12-12
摘要:
目的 了解伤口治疗师工作投入现状并分析其影响因素,为提高伤口治疗师的工作投入水平提供参考依据。 方法 2022年9月—2023年3月,采用方便抽样法,选取经过欧洲伤口管理协会认证时间>3个月的235名伤口治疗师作为调查对象,使用个人基本资料调查表、医院及伤口门诊开设情况调查表、个人-工作匹配量表和专科护士工作投入量表进行问卷调查。采用单因素分析及多元线性回归分析伤口治疗师工作投入的影响因素。 结果 最终纳入219名伤口治疗师。个人-工作匹配量表得分为(99.37±13.70)分,条目得分为(3.55±0.49)分;专科护士工作投入量表得分为(140.01±16.00)分,条目得分为(4.38±0.50)分。多元线性回归分析结果显示,工作认可、团队氛围、公平和价值观是伤口治疗师工作投入的影响因素(P<0.05)。 结论 伤口治疗师个人-工作匹配程度越高,工作投入水平越高。医院护理管理者应重视专科护士个人-工作匹配程度,使用科学、有效的管理方法提高个体与工作契合度,改善专科护士的工作投入,提升满意度的同时降低职业倦怠。
麦智德, 李珂, 于淼, 张建霞, 丁炎明. 伤口治疗师工作投入现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(23): 2889-2895.
MAI Zhide, LI Ke, YU Miao, ZHANG Jianxia, DING Yanming. Analysis of the current situation and influencing factors of work engagement of wound therapists[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2023, 58(23): 2889-2895.
 |
表1 调查对象的个人基本资料、医院及伤口门诊开设情况和工作投入的单因素分析(n=219)
Table 1 The general information of the respondents and opening of hospitals and wound clinics and the results of the univariate analysis of the influencing factors of work engagement(n=219)
 |
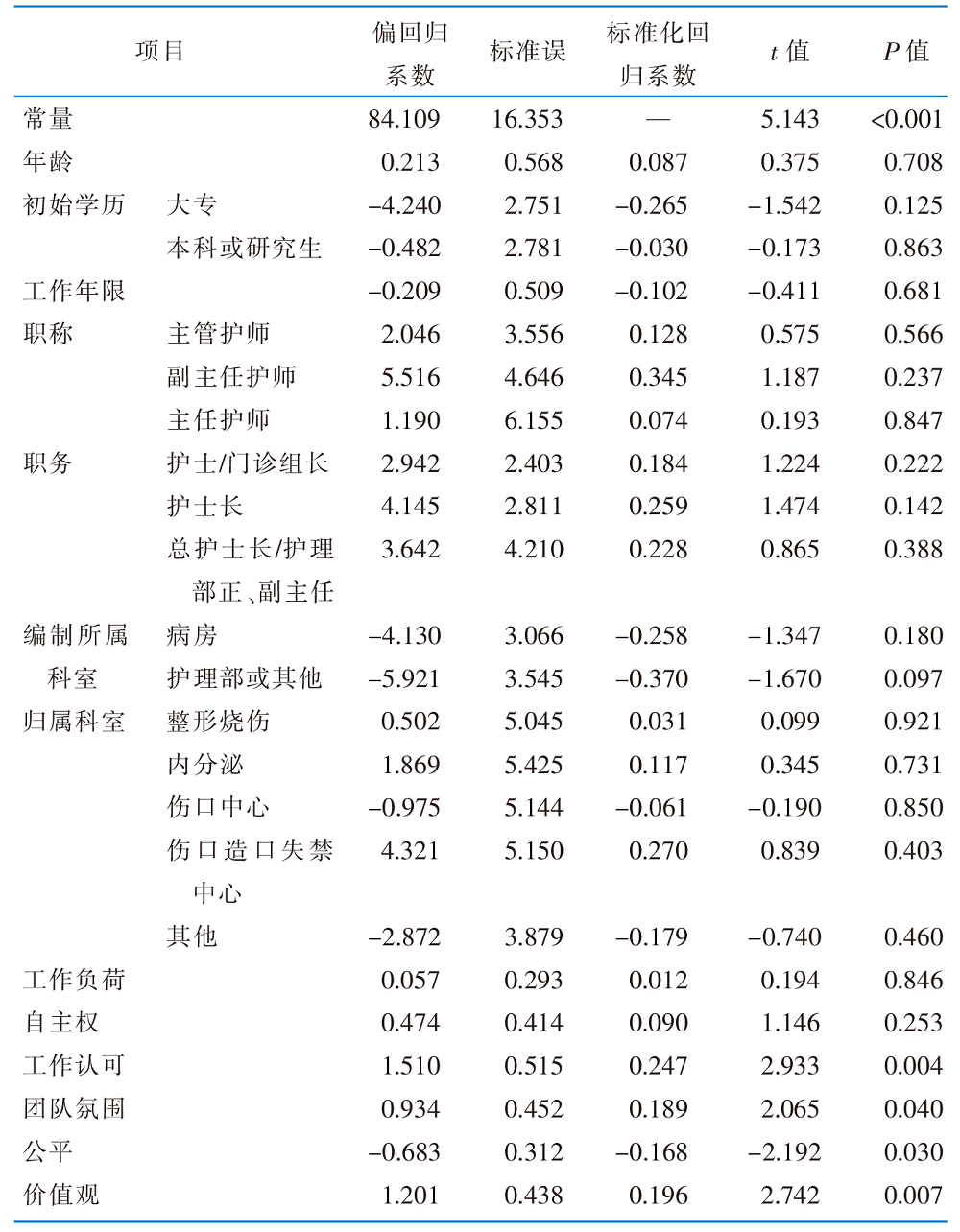 |
表3 调查对象工作投入影响因素的多元线性回归分析结果(n=219)
Table 3 Results of multiple linear regression analysis of factors influencing the work engagement of survey respondents(n=219)
 |
| [1] | 国家卫生健康委. 全国护理事业发展规划(2021-2025年)[EB/OL]. (2022-05-07)[2022-12-25]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653pd/202205/441f75ad347b4ed68a7d2f2972f78e67.shtml. |
| National Health Commission. National nursing development plan(2021-2025)[EB/OL].(2022-05-07)[2022-12-25]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653pd/202205/441f75ad347b4ed68a7d2f2972-f78e67.shtml. | |
| [2] | Bowers S, Franco E. Chronic wounds:evaluation and management[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2020, 101(3):159-166. |
| [3] | 刘欢, 宁宁, 何凌霄, 等. 伤口治疗师工作环境及职业发展情况的调查[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2014, 49(11):1374-1377. |
| Liu H, Ning N, He LX, et al. The current work environment and career development of certificated wound specialists in China[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2014, 49(11):1374-1377. | |
| [4] |
Seaton PCJ, Cant RP, Trip HT. Quality indicators for a community-based wound care centre:an integrative review[J]. Int Wound J, 2020, 17(3):587-600.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Gethin G, Probst S, Stryja J, et al. Evidence for person-centred care in chronic wound care:a systematic review and recommendations for practice[J]. J Wound Care, 2020, 29(Sup9):S1-S22. |
| [6] | 罗家音, 孙超, 许政曦, 等. 伤口治疗师主导的护理管理模式在癌性伤口围手术期的应用[J]. 中国护理管理, 2022, 22(8):1131-1135. |
| Luo JY, Sun C, Xu ZX, et al. Clinical application of wound therapist-led perioperative nursing management of malignant fungating wounds[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2022, 22(8):1131-1135. | |
| [7] |
丁炎明, 吴欣娟, 肖艳艳, 等. 我国53316名专科护士职业发展情况调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(2):182-186.
DOI |
|
Ding YM, Wu XJ, Xiao YY, et al. Investigation on career development of 53,316 specialist nurses in China[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(2):182-186.
DOI |
|
| [8] | 张怡妮. 工作—个人资源关系建设及其对护士工作投入的影响研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. |
| Zhang YN. Study on the relationship between work and personal resources and its influence on nurses’ job engagement[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019. | |
| [9] | Chan S. Burnout,engagement & leadership[J]. Rev Assoc Med Bras(1992), 2021, 67(9):1217-1220. |
| [10] |
Hetzel-Riggin MD, Swords BA, Tuang HL, et al. Work engagement and resiliency impact the relationship between nursing stress and burnout[J]. Psychol Rep, 2020, 123(5):1835-1853.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | 覃慧, 吴金凤, 王婷, 等. 江苏省专科护士工作投入现状及影响因素调查分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(11):53-56. |
| Qin H, Wu JF, Wang T, et al. The level and determinants of work engagement among nurse specialists in Jiangsu Province[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(11):53-56. | |
| [12] | Leiter MP, Maslach C. Areas of worklife:a structured approa-ch to organizational predictors of job burnout[M]// Research in Occupational Stress and Well-being. Bingley: Emerald(MCB UP), 2004:91-134. |
| [13] | 李姗姗, 卜晓佳, 刘曼, 等. 护士个人—工作匹配量表的汉化及信度效度检验[J]. 中国护理管理, 2020, 20(5):681-686. |
| Li SS, Bu XJ, Liu M, et al. Adaptation and psychometric properties of the Chinese version of Areas of Worklife Scale among nurses[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2020, 20(5):681-686. | |
| [14] | 覃慧, 吴金凤, 王婷, 等. 专科护士工作投入量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(1):56-59. |
| Qin H, Wu JF, Wang T, et al. Development and psychometric testing of the Specialty Nurse Work Engagement Scale[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(1):56-59. | |
| [15] | 王丽敏, 万巧琴, 谷水, 等. 临床护士感知的工作负荷水平及其对工作投入的影响[J]. 护理学杂志, 2020, 35(17):57-61. |
| Wang LM, Wan QQ, Gu S, et al. The level of self-rated workload among clinical nurses and its impact on work engagement[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2020, 35(17):57-61. | |
| [16] | 邬燕平, 徐凤霞, 刘小玮, 等. 我国护士职业发展现况及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国护理管理, 2021, 21(1):80-84. |
| Wu YP, Xu FX, Liu XW, et al. Analysis on the status of nurses’ career development and influencing factors in China[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2021, 21(1):80-84. | |
| [17] | 潘小康, 李冬英, 李欣, 等. 护士工作投入的研究进展[J]. 中国护理管理, 2017, 17(7):951-955. |
| Pan XK, Li DY, Li X, et al. The research progress of nurses’ work engagement[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2017, 17(7):951-955. | |
| [18] | 李姗姗. 护士感知真实型领导水平现状调查及相关因素研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2020. |
| Li SS. Investigation on the current situation of nurses’ perceived authentic leadership level and related factors[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2020. | |
| [19] | 张嘉, 王月华, 朱可蓉. 株洲市综合医院儿科护士个人-工作匹配与工作投入相关性研究[J]. 中华护理教育, 2022, 19(4):360-363. |
| Zhang J, Wang YH, Zhu KR. The correlation between areas of worklife and work engagement of pediatric nurses in Zhuzhou[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2022, 19(4):360-363. | |
| [20] |
Chatman JA. Matching people and organizations:selection and socialization in public accounting firms[J]. Adm Sci Q, 1991, 36(3):459.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 贾秀丽, 王艳, 王欢. 护理人员个人-组织匹配的影响因素[J]. 解放军医院管理杂志, 2021, 28(2):187-190,194. |
| Jia XL, Wang Y, Wang H. Influencing factors of person-organization fitness of nurses[J]. Hosp Adm J Chin PLA, 2021, 28(2):187-190,194. | |
| [22] | 史妍萍, 张红梅, 洪成伟. 全国三级甲等医院青年护士职业成长现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中国护理管理, 2021, 21(9):1381-1386. |
| Shi YP, Zhang HM, Hong CW. The status quo of young nurses’ professional growth and the influencing factors in tertiary grade A hospitals in China[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2021, 21(9):1381-1386. | |
| [23] |
聂圣肖, 赵瑾, 孙红. 我国226所二三级医院专科护士使用情况的调查[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(11):1677-1682.
DOI |
|
Nie SX, Zhao J, Sun H. A survey of current working situation of specialist nurses in 226 secondary and tertiary hospitals in mainland China[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(11):1677-1682.
DOI |
|
| [24] | 王念念. 员工个人-组织契合度、工作投入、工作满意度与工匠心理的关系研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. |
| Wang NN. Research on the relationship among employee’s personal-organizational fit,job engagement,job satisfaction and craftsman’s psychology[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020. | |
| [25] | 武蕊, 林梅. 护士组织气氛与护士职业认同的相关性研究[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2017, 32(16):1446-1448. |
| Wu R, Lin M. The correlation study on the nursing organizational climate and nurses’ professional identity[J]. J Nurses Train, 2017, 32(16):1446-1448. | |
| [26] | 苏方国. 高绩效人力资源实践与情感承诺:个人与组织匹配和个人与工作匹配的调节效应[J]. 商业研究, 2017(4):105-114. |
| Su FG. High performance human resource practices and affec-tive commitment: moderated by person-organization fit and person-job fit[J]. Commer Res, 2017(4):105-114. | |
| [27] |
El-Gazar HE, Abdelhafez S, Zoromba MA. Effects of the areas of worklife on job embeddedness:a national cross-sectional study among Egyptian nurses[J]. BMC Nurs, 2022, 21(1):353.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 姜珊, 郭彩霞, 郭立华, 赵媛媛, 肖蒙, 杨依玲, 魏春艳, 李硕, 刘殿媛, 尚志丽. 外周静脉留置针并发症风险管理系统的开发与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 908-913. |
| [2] | 明爱红, 龙秀红, 梁志金, 李砺, 黎凤民, 林思慧, 杨云帆, 王智慧, 冯甜. 国内医疗护理员培训和管理省级政策的文本分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 960-967. |
| [3] | 黄婵, 池艳宇, 闵玉娣, 曹培叶, 刘君, 郑镕昕, 张海燕. 基于信息交互需求的护理会诊信息系统的开发及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 645-651. |
| [4] | 田君叶, 张霞, 苏莉, 孙路路, 赵瑾, 丁炎明. 专科护士培训信息管理平台的建设与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 652-658. |
| [5] | 江燕, 谭莉, 邹明君, 冉懋君, 李文苑, 马佳钦. 护士主导的智能化医疗废物暂存设备的研发及实用性评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 659-665. |
| [6] | 朱雨涵, 李文佳, 祝雪花. 国内长期照护护理队伍建设现行政策分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 729-735. |
| [7] | 魏永婷, 田书梅, 杨娇, 余良欢, 倪福, 范雨晴, 肖瑶, 席祖洋, 沙菊艳, 刘聪. 护士循证决策能力量表的汉化及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 736-742. |
| [8] | 李燕, 吴雪, 庞建美, 强万敏, 杨川川, 孙盛楠, 李静. 24个省份胸外科护士围手术期肺康复知信行的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 569-574. |
| [9] | 施金丽, 莫军军, 鲁玲玲, 陈叶. 442所消毒供应中心应对新发突发传染病应急处置管理现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 589-595. |
| [10] | 崔钰震, 姚卓娅, 耿军辉, 李漫春, 詹朦, 丁丽娜, 蒋恩社. 河南省348所医疗机构口腔器械清洗消毒灭菌管理现状及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 596-602. |
| [11] | 杜洁, 余强, 李亚敏. 轮班制护士睡眠质量非药物干预的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(5): 629-634. |
| [12] | 徐娉, 王华芬, 封亚萍, 徐婷, 许涛, 陶月仙. 安宁疗护中护士的死亡态度对悲伤情绪影响的路径分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 319-324. |
| [13] | 蒲江锋, 王婉儿, 李格格, 谢章浩, 许怡璇, 詹宁静, 黄惠根. 护士组织支持感现状及潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 340-346. |
| [14] | 赵蕊, 范文琪, 刘晓夏, 葛莉娜. 基于机器学习的3种妇产科护士共情疲劳风险预测模型的构建与比较[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 347-354. |
| [15] | 柏新蕊, 张红燕, 安宁, 韩琳. 价值共创视角下数字赋能护理质量管理的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(3): 379-384. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||