


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (23): 2872-2879.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.23.008
收稿日期:2025-07-12
出版日期:2025-12-10
发布日期:2025-12-15
通讯作者:
金学勤,E-mail:653993023@qq.com作者简介:陆沁怡:女,本科(硕士在读),护士,E-mail:2283566726@qq.com
基金资助:
LU Qinyi( ), LU Chengqian, NIE Yixuan, JIN Xueqin(
), LU Chengqian, NIE Yixuan, JIN Xueqin( )
)
Received:2025-07-12
Online:2025-12-10
Published:2025-12-15
摘要:
目的 探讨老年维持性血液透析患者习得性无助感的潜在剖面及影响因素,为临床护理实践提供参考。方法 便利选取2024年10月—2025年2月昆山市3所综合医院血液透析中心的440例老年维持性血液透析患者作为调查对象。采用一般资料调查表、习得性无助量表、国际体力活动问卷简表及透析后疲乏量表进行调查,通过潜在剖面分析和Logistic回归分析老年维持性血液透析患者习得性无助感潜在剖面的影响因素。结果 回收有效问卷432份,有效问卷回收率为98.18%。432例老年维持性血液透析患者习得性无助得分为(37.34±12.76)分,可分为3个潜在剖面,分别是低无助-低绝望组(59.72%)、高无助-低绝望组(25.92%)、高无助-高绝望组(14.35%)。Logistic回归分析显示,年龄、原发疾病、久坐行为、透析后疲乏是老年维持性血液透析患者习得性无助感潜在剖面的影响因素(P<0.05)。结论 老年维持性血液透析患者习得性无助感存在异质性,医护人员可根据不同的潜在剖面影响因素进行个体化干预,以降低其无助感。
陆沁怡, 陆程倩, 聂奕轩, 金学勤. 老年维持性血液透析患者习得性无助感潜在剖面及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(23): 2872-2879.
LU Qinyi, LU Chengqian, NIE Yixuan, JIN Xueqin. Latent profiles of learned helplessness and its influencing factors in elderly patients on maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(23): 2872-2879.
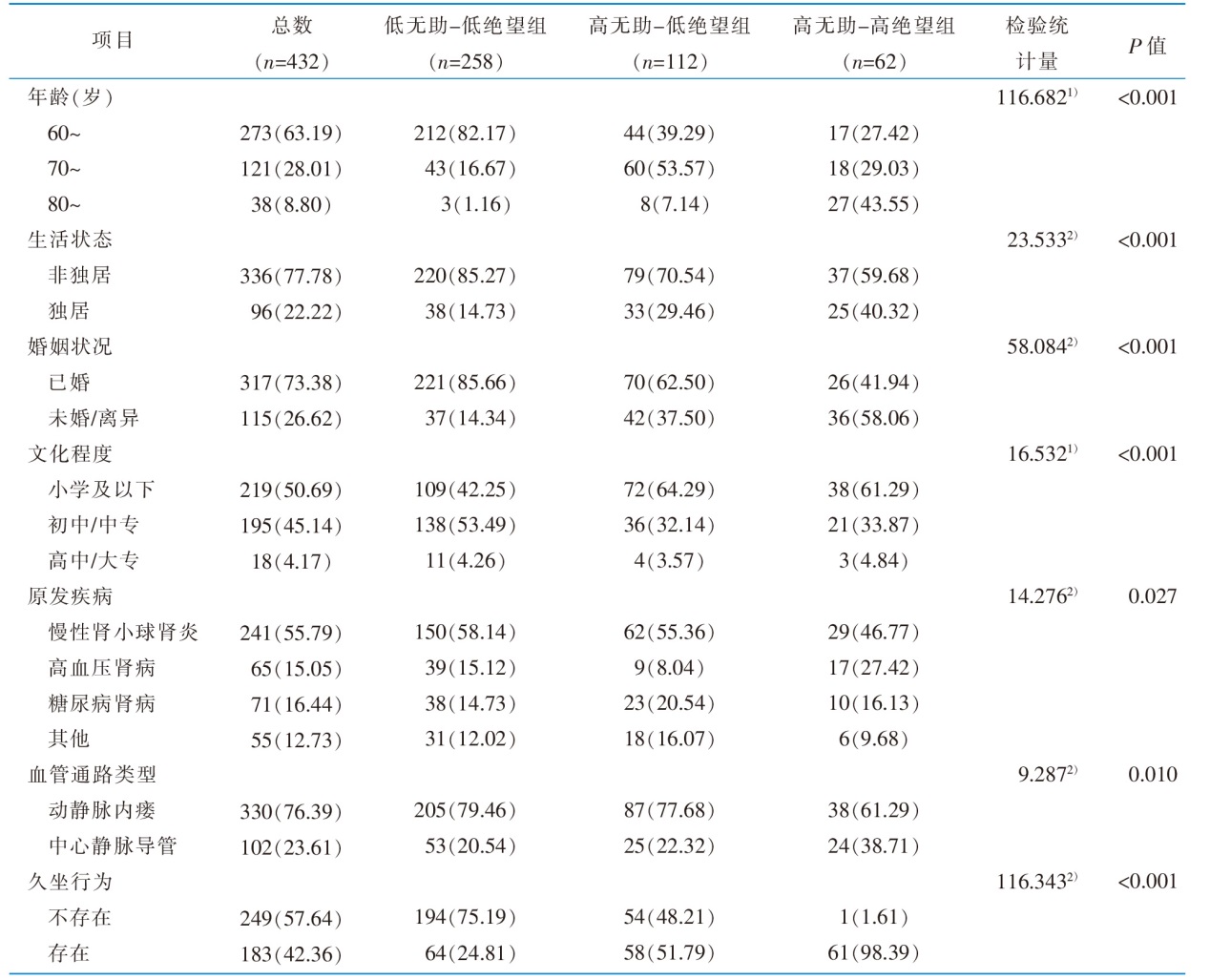 |
表1 老年维持性血液透析患者的一般资料及习得性无助感潜在剖面的单因素分析[例(百分比,%)]
Table 1 Univariate analysis of general information and latent profiles of learned helplessness among elderly patients on maintenance hemodialysis[cases(percentage,%)]
 |
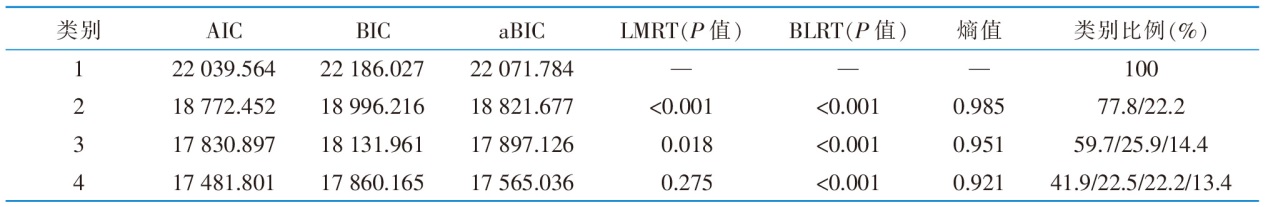 |
表2 老年维持性血液透析患者习得性无助感潜在剖面分析模型拟合结果(n=432)
Table 2 Model fit results of latent profile analysis for learned helplessness in elderly patients on maintenance hemodialysis(n=432)
 |

图1 老年维持性血液透析患者习得性无助感3个潜在剖面的特征分布
Figure 1 Characteristics and distribution of 3 potential profiles of learned helplessness among elderly patients on maintenance hemodialysis
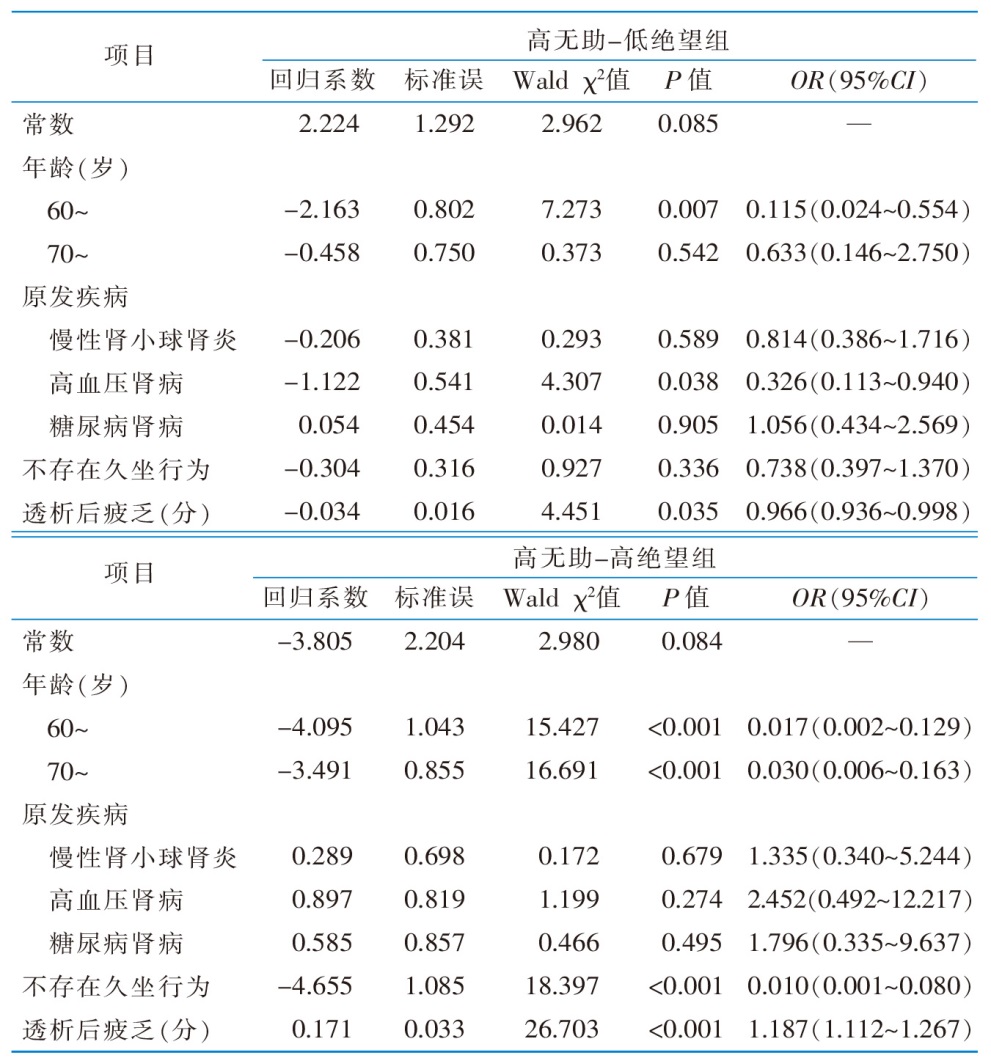 |
表5 老年维持性血液透析患者习得性无助感潜在剖面的多因素Logistic回归分析(n=432)
Table 5 Multivariate logistic regression analysis of latent profiles of learned helplessness in elderly patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis(n=432)
 |
| [1] |
曾豪洁, 赵莉, 张陈, 等. 维持性血液透析患者自我调节疲劳的影响因素及路径分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(2):156-164.
DOI |
|
Zeng HJ, Zhao L, Zhang C, et al. Analysis of influencing factors and pathway of self-regulatory fatigue in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(2):156-164.
DOI |
|
| [2] | Xie CY, Li L, Li YM. Learned helplessness in renal dialysis patients:concept analysis with an evolutionary approach[J]. Pa-tient Prefer Adherence, 2022, 16:2301-2312. |
| [3] |
Xie CY, Li L, Li YM. “Alive day is the day”:a qualitative study of experiences of learned helplessness in maintenance haemodialysis patients[J]. Risk Manag Healthc Policy, 2023, 16:231-245.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
尹奎, 彭坚, 张君. 潜在剖面分析在组织行为领域中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7):1056-1070.
DOI |
|
Yin K, Peng J, Zhang J. The application of latent profile analysis in organizational behavior research[J]. Adv Psychol Sci, 2020, 28(7):1056-1070.
DOI |
|
| [5] | 中华预防医学会肾脏病预防与控制专业委员会, 张路霞, 赵明辉. 中国慢性肾脏病早期评价与管理指南[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2023, 62(8):902-930. |
| Chinese Preventive Medicine Association,Kidney Disease Prevention and Control Professional Committee, Zhang LX, Zhao MH. Guidelines for the early evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease in China[J]. Chin J Intern Med, 2023, 62(8):902-930. | |
| [6] | 倪平, 陈京立, 刘娜. 护理研究中量性研究的样本量估计[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010, 45(4):378-380. |
| Ni P, Chen JL, Liu N. The sample size estimation in quantitative nursing research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010, 45(4):378-380. | |
| [7] | 武晓艳, 曾红, 马绍斌, 等. 习得性无助量表研制及其与人格相关研究[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2009, 30(3):357-361. |
| Wu XY, Zeng H, Ma SB, et al. Development of learned helplessness scale and its relationship with personality[J]. J Sun Yat Sen Univ Med Sci, 2009, 30(3):357-361. | |
| [8] | 屈宁宁, 李可基. 国际体力活动问卷中文版的信度和效度研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2004, 25(3):265-268. |
| Qu NN, Li KJ. Study on the reliability and validity of International Physical Activity Questionnaire(Chinese Version,IPAQ)[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2004, 25(3):265-268. | |
| [9] | 曹提, 陈辉, 秦金雪, 等. 老年维持性血液透析患者久坐行为现状及影响因素分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2023, 38(9):35-39. |
| Cao T, Chen H, Qin JX, et al. Sedentary behavior and determinants in elderly patients on maintenance hemodialysis[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2023, 38(9):35-39. | |
| [10] |
Kodama H, Togari T, Konno Y, et al. A new assessment scale for post-dialysis fatigue in hemodialysis patients[J]. Ren Replace Ther, 2020, 6(1):1.
DOI |
| [11] | 张帆, 杨雪, 李杰, 等. 维持性血液透析患者透析后疲乏评估量表汉化及信效度检验[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2024, 39(22):2416-2420. |
| Zhang F, Yang X, Li J, et al. The Chinesization of the Fatigue Assessment Scale for Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients and its test of reliability and validity[J]. J Nurses Train, 2024, 39(22):2416-2420. | |
| [12] | 李春玉, 周丽, 张书溢. 慢性伤口老年患者习得性无助感与成功老龄化的关系研究[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2021, 38(4):1-4. |
| Li CY, Zhou L, Zhang SY. Relationship between learned helplessness and successful aging in elderly patients with chronic wounds[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2021, 38(4):1-4. | |
| [13] | 梁莉. 老年糖尿病病人习得性无助感现状调查及影响因素分析[J]. 全科护理, 2022, 20(13):1862-1865. |
| Liang L. Investigation and analysis of learned helplessness’s feeling in elderly diabetic patients and its influencing factors[J]. Chin Gen Pract Nurs, 2022, 20(13):1862-1865. | |
| [14] | 阎佳蓉, 霍明姝, 于倩, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病病人习得性无助感现状及影响因素分析[J]. 全科护理, 2024, 22(12):2226-2229. |
| Yan JR, Huo MS, Yu Q, et al. Analysis of learned helplessness’s feeling and its influencing factors in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chin Gen Pract Nurs, 2024, 22(12):2226-2229. | |
| [15] |
刘芮, 吴敏, 赵云凤, 等. 参与生产性活动对老年慢性病患者失志综合征的影响及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(13):1610-1616.
DOI |
|
Liu R, Wu M, Zhao YF, et al. Impact of productive engagement on demoralization syndrome and its threshold effect in elderly patients with chronic diseases and nursing enlightenment[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(13):1610-1616.
DOI |
|
| [16] | 郑志贵, 何东元, 陈宜方, 等. 高龄老年血液透析患者的生存分析[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2020, 39(5):559-563. |
| Zheng ZG, He DY, Chen YF, et al. Survival analysis of hemodialysis patients aged 80 years and over[J]. Chin J Geriatr, 2020, 39(5):559-563. | |
| [17] |
Wang L, Wang JY, Zhang YM, et al. Current perspectives and trends of the research on hypertensive nephropathy:a bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2023[J]. Ren Fail, 2024, 46(1):2310122.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 庞慧, 程焕焕, 李燕, 等. 社区高血压老年人积极度现状及影响因素研究[J]. 护理管理杂志, 2025, 25(5):449-454. |
| Pang H, Cheng HH, Li Y, et al. A study on the status and influencing factors on the patient activation levels of elderly people with hypertension in the community[J]. J Nurs Adm, 2025, 25(5):449-454. | |
| [19] | 邹伟能, 王旸, 朱珍珍, 等. 与健康相关的互联网使用行为对中老年高血压患者自我管理行为的影响[J]. 中华高血压杂志(中英文), 2025, 33(8):766-772. |
| Zou WN, Wang Y, Zhu ZZ, et al. Effectiveness of health-related Internet use on self-management behavior in middle-aged and elderly patients with hypertension[J]. Chin J Hypertens, 2025, 33(8):766-772. | |
| [20] | 曾维玲, 栾中佼, 吴私, 等. 维持性血液透析患者透析后疲劳的影响因素分析[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2020, 49(10):943-948. |
| Zeng WL, Luan ZJ, Wu S, et al. Influencing factors of post-dialysis fatigue in patients under maintenance hemodialysis[J]. J China Med Univ, 2020, 49(10):943-948. | |
| [21] | 张颖, 刘晓辉. 血液透析后疲乏的概念分析[J]. 护理研究, 2023, 37(19):3423-3427. |
| Zhang Y, Liu XH. Concept analysis of post-dialysis fatigue[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2023, 37(19):3423-3427. | |
| [22] |
尹艳茹, 周洪昌, 刘梦如, 等. 老年维持性血液透析患者社会隔离现状的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(7):822-829.
DOI |
|
Yin YR, Zhou HC, Liu MR, et al. Status and influencing factors of social isolation in elderly patients with maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(7):822-829.
DOI |
|
| [23] |
Ju A, Teixeira-Pinto A, Tong A, et al. Validation of a core patient-reported outcome measure for fatigue in patients receiving hemodialysis:the SONG-HD fatigue instrument[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2020, 15(11):1614-1621.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 王慧敏, 孙建萍, 吴红霞. 老年慢性病病人久坐行为的研究进展[J]. 护理研究, 2021, 35(1):110-114. |
| Wang HM, Sun JP, Wu HX. Research progress on sedentary behavior in elderly patients with chronic disease[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2021, 35(1):110-114. | |
| [25] | 李珂, 常颖. 维持性血液透析病人习得性无助感的研究进展[J]. 护理研究, 2025, 39(11):1935-1940. |
| Li K, Chang Y. Research progress on learned helplessness in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2025, 39(11):1935-1940. | |
| [26] | 李东泽, 李芳卉, 刘怡, 等. 《2020年世界卫生组织运动和久坐行为指南》解读[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2021, 28(4):376-383. |
| Li DZ, Li FH, Liu Y, et al. Interpretation of the World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour[J]. Chin J Clin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2021, 28(4):376-383. |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||