


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (20): 2499-2506.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.20.010
杨晓霞1( ), 于子夫2, 王芳1, 侯亚丽1, 朱礼敬1, 吕利明3(
), 于子夫2, 王芳1, 侯亚丽1, 朱礼敬1, 吕利明3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-17
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-10-11
通讯作者:
吕利明,E-mail:liminglv1@163.com作者简介:杨晓霞:女,硕士,护师,E-mail:yangxiaoxia_0611@163.com
YANG Xiaoxia1( ), YU Zifu2, WANG Fang1, HOU Yali1, ZHU Lijing1, LÜ Liming3(
), YU Zifu2, WANG Fang1, HOU Yali1, ZHU Lijing1, LÜ Liming3( )
)
Received:2025-02-17
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-11
摘要:
目的 分析结直肠癌患者社会疏离的潜在类别,并探讨不同类别的影响因素及风险因素的累积效应,以期为实施个体化干预提供参考。 方法 采用便利抽样法,选取2023年1—6月在山东省3所三级甲等医院胃肠外科、肿瘤科住院的结直肠癌患者作为调查对象。使用一般资料调查表、社交回避量表、社交焦虑量表、加利福尼亚洛杉矶分校孤独感量表、心理一致感量表、家庭亲密度量表、社会支持评定量表进行问卷调查。采用潜在剖面分析、多元Logistic回归分析进行分析。 结果 发放问卷292份,回收有效问卷270份,有效问卷回收率为92.47%。结直肠癌患者社会疏离可分为3个潜在类别:低疏离组(42.59%)、高疏离-高社交回避组(14.08%)、中等疏离-高社交焦虑组(43.33%)。Logistic回归分析结果显示,工作状况、造口情况、是否转移、心理一致感、家庭亲密度、社会支持是不同潜在类别的影响因素,且心理一致感、家庭亲密度和社会支持对不同类别的影响存在累积效应(P<0.05)。 结论 结直肠癌患者社会疏离存在群体异质性,医护人员应识别不同患者的特征差异,重点关注存在多个风险因素的患者,以制订针对性的干预措施,帮助其更好地融入社会。
杨晓霞, 于子夫, 王芳, 侯亚丽, 朱礼敬, 吕利明. 结直肠癌患者社会疏离的潜在剖面分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(20): 2499-2506.
YANG Xiaoxia, YU Zifu, WANG Fang, HOU Yali, ZHU Lijing, LÜ Liming. Latent profile analysis and nursing implications of social alienation in colorectal cancer patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(20): 2499-2506.
 |
表3 结直肠癌患者社会疏离潜在类别的多元Logistic回归分析(n=270)
Table 3 Multiple Logistic regression analysis of potential categories of social alienation in patients with colorectal cancer(n=270)
 |
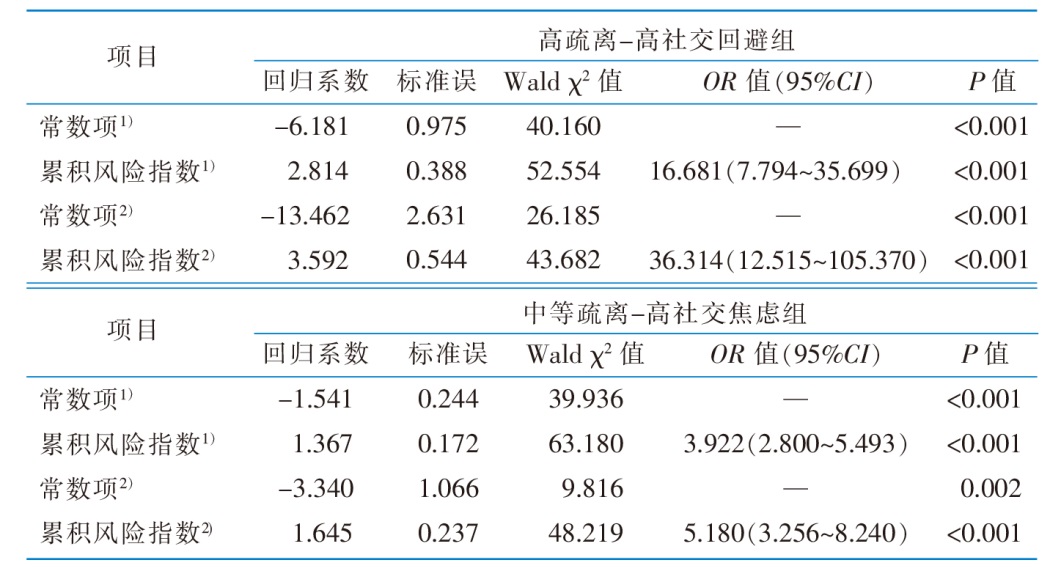 |
表4 社会疏离潜在类别累积风险的多元Logistic回归分析(n=270)
Table 4 Multiple Logistic regression analyses of cumulative risk of potential categories of social alienation(n=270)
 |
| [1] | Morgan E, Arnold M, Gini A, et al. Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040:incidence and mortality estimates from GLO-BOCAN[J]. Gut, 2023, 72(2):338-344. |
| [2] | Vlaski T, Slavic M, Caspari R, et al. From a clustering of adverse symptoms after colorectal cancer therapy to chronic fatigue and low ability to work:a cohort study analysis with 3 months of follow-up[J]. Cancers, 2024, 16(1):202. |
| [3] | Fujita Y, Hida K, Sakamoto T, et al. Employment status of patients with colorectal cancer after surgery:a multicenter prospective cohort study in Japan[J]. Dis Colon Rectum, 2023, 66(12):e1207-e1216. |
| [4] |
董朝晖, 卢惠娟, 陆箴琦, 等. 癌症患者社会疏离体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(6):670-675.
DOI |
| Dong ZH, Lu HJ, Lu ZQ, et al. Experiences of social isolation in cancer patients:a qualitative research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(6):670-675. | |
| [5] | Liu X, Wen S, Wu DD. The mediating roles of family care and self-efficacy between stigma and social alienation among colorectal cancer survivors[J]. Sci Rep, 2025, 15(1):15312. |
| [6] | 王芬, 于海燕, 张淑娟, 等. 肠造口患者社会疏离感现状及影响因素研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(14):40-43. |
| Wang F, Yu HY, Zhang SJ, et al. Social isolation and influencing factors among colorectal cancer patients with an ostomy[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(14):40-43. | |
| [7] | 倪平, 陈京立, 刘娜. 护理研究中量性研究的样本量估计[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010, 45(4):378-380. |
| Ni P, Chen JL, Liu N. The sample size estimation in quantita-tive nursing research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010, 45(4):378-380. | |
| [8] | 王硕. 乳腺癌幸存者社会疏离与病耻感、应对方式的关系研究[D]. 济南: 山东中医药大学, 2020. |
| Wang S. Study on the relationship between social alienation,stigma and coping style of breast cancer survivors[D]. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020. | |
| [9] | 汪向东, 王希林, 马弘. 心理卫生评定量表手册(增订版)[M]. 北京: 中国心理卫生杂志社,1999. |
| Wang XD, Wang XL, Ma H. Rating scales for mental health (updated edition)[M]. Beijing: Chinese Mental Health Journal, 1999. | |
| [10] | 包蕾萍, 刘俊升, 周颖. 心理一致感量表(SOC-13)的信、效度初步研究[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2006, 20(5):299-301. |
| Bao LP, Liu JS, Zhou Y. Reliability and validity of Sense of Coherence-13(SOC-13)[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 2006, 20(5):299-301. | |
| [11] | 费立鹏, 沈其杰, 郑延平, 等. “家庭亲密度和适应性量表”和“家庭环境量表”的初步评价:正常家庭与精神分裂症家庭成员对照研究[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 1991, 5(5):198-202,238. |
| Fei LP, Shen QJ, Zheng YP, et al. Preliminary evaluation of Chinese version of FACES Ⅱ and FES:comparison of normal families and families of schizophrenic patients[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 1991, 5(5):198-202,238. | |
| [12] | 肖水源. 《社会支持评定量表》的理论基础与研究应用[J]. 临床精神医学杂志, 1994, 4(2):98-100. |
| Xiao SY. Theoretical basis and research application of Social Support Rating Scale[J]. J Clin Psychiatry, 1994, 4(2):98-100. | |
| [13] |
Marco JH, Llombart P, Romero R, et al. Meaning-centered psychotherapy versus cognitive behavioral therapy for cancer survivors:a randomized controlled trial[J]. Behav Ther, 2024, 55(5):1071-1083.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
秦晓红, 张连杰, 殷晴, 等. 结直肠癌患者运动干预方案的构建及应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8):901-907.
DOI |
|
Qin XH, Zhang LJ, Yin Q, et al. Construction and application of an exercise intervention scheme for patients with colorectal cancer[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(8):901-907.
DOI |
|
| [15] | 美华慈心关怀联盟. 安心茶话屋[EB/OL]. (2014-06-29)[2024-12-28]. http://www.caccc-usa.org/ch/activities/heart2heart.html. |
| Chinese American Coalition for Compassionate Care. Heart to heart café[EB/OL].(2014-06-29)[2024-12-28]. http://www.cac-cc-usa.org/ch/activities/heart2heart.html. | |
| [16] |
杨阳, 刘美, 熊沫, 等. 中青年肠造口患者及其主要照护者护理依赖二元应对体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4):389-395.
DOI |
|
Yang Y, Liu M, Xiong M, et al. A qualitative study on the dual coping experience of nursing dependence among middle-aged and young patients with enterostomy and their primary caregivers[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2025, 60(4):389-395.
DOI |
|
| [17] | Denti FC, Guerra E, Caroppo F, et al. Exploring the impact of a structured educational approach on peristomal skin complications:an interim analysis[J]. Healthcare, 2024, 12(18):1805. |
| [18] |
Liu Q, Ge R, Zhu Y, et al. The potential characteristics of the sense of coherence in cancer radiotherapy patients and its correlation with coping strategies[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2024, 32(11):755.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Gu ZH, Li B, OuYang L, et al. A study on improving cancer-related fatigue and disease-related psychological variables in patients with cervical cancer based on online mindfulness-based stress reduction:a randomized controlled trial[J]. BMC Womens Health, 2024, 24(1):525. |
| [20] | 何丽芳, 李倩倩, 甘香. 病耻感对中青年维持性血液透析患者心理痛苦的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(21):2585-2591. |
| He LF, Li QQ, Gan X. Influence of stigma on psychological distress among young and middle-aged maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(21):2585-2591. | |
| [21] | Saleem S, Baig A, Sajun SN, et al. A mixed methods exploration of the role of multi-family groups in community treatment of patients with depression and anxiety in Pakistan[J]. Int J Ment Health Syst, 2021, 15(1):78. |
| [22] | Gao ZR, Li SY, Bai XH. Social alienation and related factors in patients with head and neck tumors undergoing radiotherapy:a cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Nurs, 2025, 24(1):275. |
| [23] | 王林凤, 周小红, 金淑芳. 社区多元群体抗癌模式对康复期癌症患者心理及生活质量的影响[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2018, 35(10):41-44. |
| Wang LF, Zhou XH, Jin SF. Effect of community multi-group anticancer model on the psychological status and quality of life of cancer patients in rehabilitation stage[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2018, 35(10):41-44. | |
| [24] |
Evans GW, Li DP, Whipple SS. Cumulative risk and child de-velopment[J]. Psychol Bull, 2013, 139(6):1342-1396.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Bronfenbrenner U. The ecology of human development:experi-ments by nature and design[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge Univer-sity Press, 1979. |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||