


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (12): 1454-1460.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.12.007
收稿日期:2024-12-24
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-17
通讯作者:
戴莉敏,E-mail:limin1110@163.com作者简介:管婷婷:女,本科(硕士在读),主管护师,E-mail:18255386860@163.com
基金资助:
GUAN Tingting( ), DAI Limin(
), DAI Limin( ), XU Min, DU Nan
), XU Min, DU Nan
Received:2024-12-24
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-17
摘要:
目的 探讨老年糖尿病伴营养不良患者饮食管理能力的潜在类别特征,并分析不同类别的影响因素,为临床护理实践提供参考。方法 采用便利抽样法,于2023年9月—2024年9月,选取江苏省镇江市2所三级甲等医院内分泌科收治的老年糖尿病伴营养不良患者作为调查对象,采用一般资料调查表、2型糖尿病患者饮食管理量表、电子健康素养量表、简易版疾病认知问卷及领悟社会支持量表进行调查。结果 共发放问卷376份,回收有效问卷349份,有效问卷回收率为92.8%。识别出低管理-不知无畏型(24.9%)、中管理-信念支撑型(45.9%)以及高管理-能力均衡型(29.2%)3个饮食管理能力类别。病程时长、文化程度、糖化血红蛋白、白蛋白、电子健康素养、领悟社会支持及疾病认知是不同类别老年糖尿病伴营养不良患者饮食管理能力的影响因素(P<0.05)。结论 老年糖尿病伴营养不良患者饮食管理能力存在异质性,医护人员可根据不同类别特征及影响因素,制订个性化临床干预措施,提高其饮食管理能力。
管婷婷, 戴莉敏, 徐敏, 杜楠. 老年糖尿病伴营养不良患者饮食管理能力的潜在剖面及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(12): 1454-1460.
GUAN Tingting, DAI Limin, XU Min, DU Nan. Analysis of potential profile and influencing factors in elderly diabetic patients with malnutrition risk[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(12): 1454-1460.
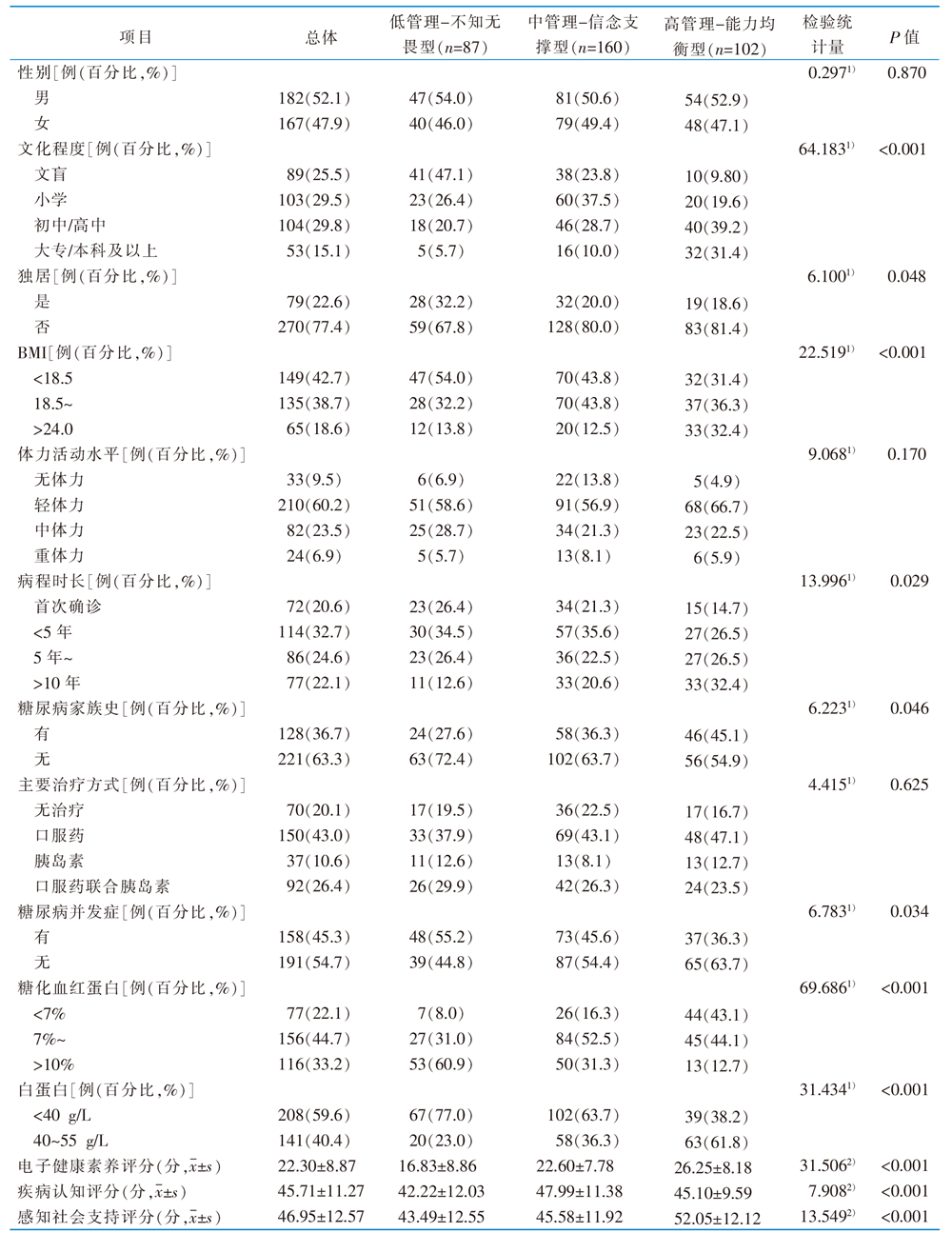 |
表1 调查对象一般资料及饮食管理能力潜在类别单因素分析(n=349)
Table 1 Univariate analysis of respondents' general information and potential categories of diet management ability(n=349)
 |
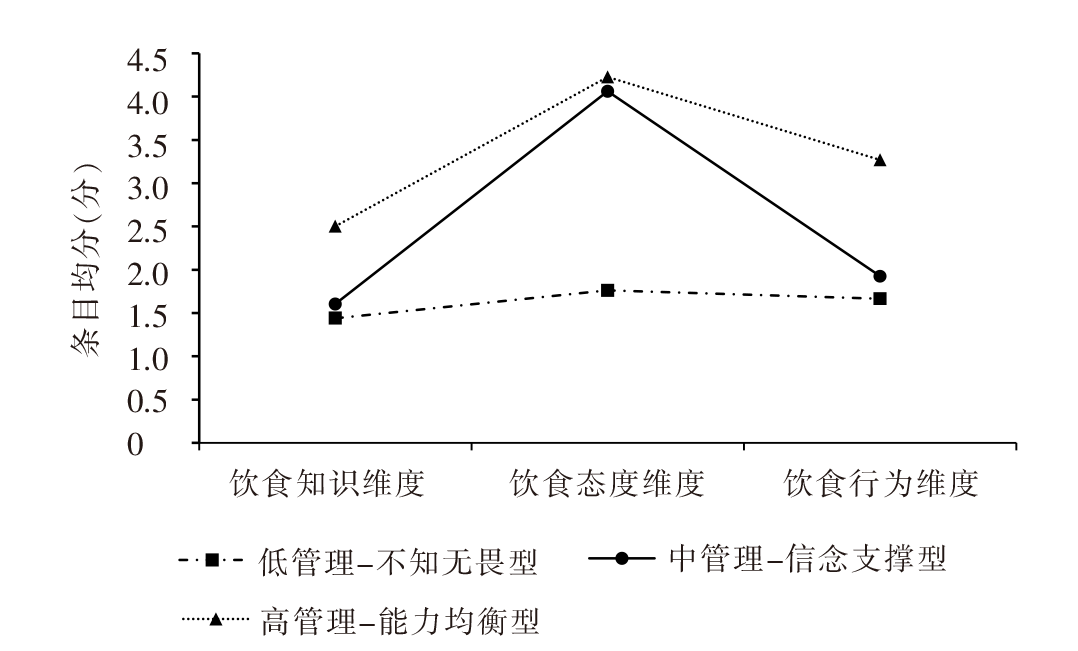
图1 老年糖尿病伴营养不良患者饮食管理能力3个潜在剖面分布特征
Figure 1 The 3 potential profiles characteristic distribution of diet management ability in elderly diabetic patients with malnutrition risk
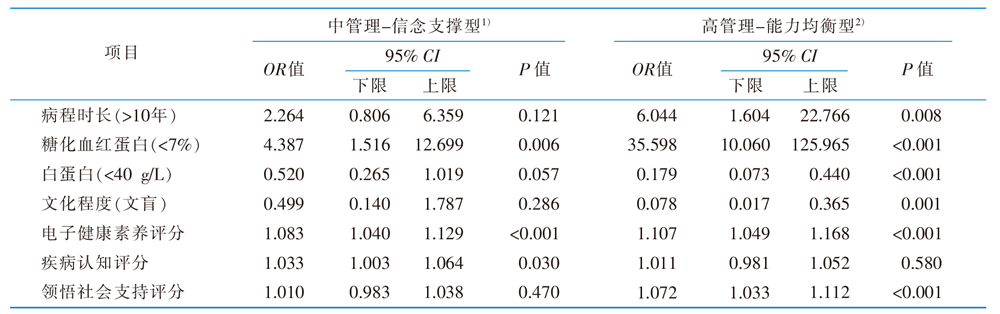 |
表3 老年糖尿病伴营养不良患者饮食管理能力的多因素分析(n=349)
Table 3 Multi-factor analysis of diet management ability in elderly diabetic patients with malnutrition risk(n=349)
 |
| [1] | Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas:global,regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2022, 183:109119. |
| [2] | Kong LL, Zhao HM, Fan JY, et al. Predictors of frailty among Chinese community-dwelling older adults with type 2 diabetes:a cross-sectional survey[J]. BMJ Open, 2021, 11(3):e041578. |
| [3] |
Rajamanickam A, Munisankar S, Dolla CK, et al. Impact of malnutrition on systemic immune and metabolic profiles in type 2 diabetes[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2020, 20(1):168.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Tamura Y, Omura T, Toyoshima K, et al. Nutrition management in older adults with diabetes:a review on the importance of shifting prevention strategies from metabolic syndrome to frailty[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(11):3367. |
| [5] | Sanz-Cánovas J, López-Sampalo A, Cobos-Palacios L, et al. Management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in elderly patients with frailty and/or sarcopenia[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(14):8677. |
| [6] | 国家老年医学中心, 中华医学会老年医学分会, 中国老年保健协会糖尿病专业委员会. 中国老年糖尿病诊疗指南(2024版)[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2024, 15(4):771-800. |
| National Center of Gerontology, Chinese Society of Geriatrics of Chinese Medical Association, Diabetes Professional Committee of Chinese Aging Well Association. Guideline for the management of diabetes mellitus in the elderly in China(2024 edition)[J]. Med J Peking Union Med Coll Hosp, 2024, 15(4):771-800. | |
| [7] | 李冬静, 邢凤梅, 董春艳, 等. 基于自我效能理论的护理干预对老年糖尿病病人饮食自我管理行为的长期影响[J]. 护理研究, 2020, 34(5):897-899. |
| Li DJ, Xing FM, Dong CY, et al. Long-term effects of nursing intervention based on self-efficacy theory on dietary self-management behavior of elderly diabetic patients[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2020, 34(5):897-899. | |
| [8] | 宿冰, 范桂红, 吴林雪, 等. 回授法健康教育对2型糖尿病患者自我管理能力及生活质量的影响[J]. 中国健康教育, 2023, 39(3):283-287. |
| Su B, Fan GH, Wu LX, et al. Effect of feedback health educa-tion on self-management ability and quality of life among pa-tients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin J Health Educ, 2023, 39(3):283-287. | |
| [9] | 张丽芹, 张丽华, 陈霞, 等. 社区老年2型糖尿病患者饮食自我管理现状及影响因素[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2016, 36(22):5725-5726. |
| Zhang LQ, Zhang LH, Chen X, et al. Dietary self-management status and influencing factors of elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in community[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2016, 36(22):5725-5726. | |
| [10] | 韩明月, 张福莲, 张华, 等. 疾病感知对2型糖尿病患者自我管理行为的影响[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制, 2021, 29(12):934-938. |
| Han MY, Zhang FL, Zhang H, et al. Effect of disease perception on self-management behavior of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin J Prev Contr Chronic Dis, 2021, 29(12):934-938. | |
| [11] | Tominaga H, Hamaguchi M, Ando S, et al. Individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus tend to select low-carbohydrate,low-calorie food menus at home on diet application[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(20):4290. |
| [12] |
Sanz-París A, Gómez-Candela C, Martín-Palmero Á, et al. Application of the new ESPEN definition of malnutrition in geriatric diabetic patients during hospitalization:a multicentric study[J]. Clin Nutr, 2016, 35(6):1564-1567.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | 倪平, 陈京立, 刘娜. 护理研究中量性研究的样本量估计[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010, 45(4):378-380. |
| Ni P, Chen JL, Liu N. The sample size estimation in quantitative nursing research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010, 45(4):378-380. | |
| [14] | 马珊珊. 2型糖尿病患者饮食管理量表的编制[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2016. |
| Ma SS. Development of Diet Management Scale for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2016. | |
| [15] | 郭帅军, 余小鸣, 孙玉颖, 等. eHEALS健康素养量表的汉化及适用性探索[J]. 中国健康教育, 2013, 29(2):106-108,123. |
| Guo SJ, Yu XM, Sun YY, et al. Adaptation and evaluation of Chinese version of eHEALS and its usage among senior high school students[J]. Chin J Health Educ, 2013, 29(2):106-108,123. | |
| [16] | 孙伟铭, 楼青, 袁也丰, 等. 简易版疾病认知问卷中文版在躯体化障碍患者中的应用[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2015, 40(8):1138-1142. |
| Sun WM, Lou Q, Yuan YF, et al. Application of the Chinese version of brief illness perception questionnaire in patients with somatoform disorder[J]. J Chongqing Med Univ, 2015, 40(8):1138-1142. | |
| [17] | 姜乾金. 领悟社会支持量表[J]. 中国行为医学科学, 2001, 10(10):41-43. |
| Jiang QJ. Perceived Social Support Scale[J]. Chin J Behav Med Sci, 2001, 10(10):41-43. | |
| [18] |
Abdulah DM, Hassan AB, Saadi FS, et al. Impacts of self-management education on glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr, 2018, 12(6):969-975.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
颜钰, 龚姝, 段棣飞, 等. 知识图谱在慢性病患者饮食管理中的应用进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(6):753-757.
DOI URL |
|
Yan Y, Gong S, Duan DF, et al. Application and progress of knowledge graphs in dietary management of patients with chronic diseases[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(6):753-757.
DOI URL |
|
| [20] | 李萍, 韩梅. 糖尿病病人电子健康素养研究进展[J]. 护理研究, 2023, 37(19):3528-3532. |
| Li P, Han M. Research progress of ehealth literacy in diabetic patients[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2023, 37(19):3528-3532. | |
| [21] | 张霞, 冯世平, 曾书萍, 等. 2型糖尿病患者电子健康素养与自我效能感及自我管理行为的现状及相关性分析[J]. 现代临床医学, 2022, 48(3):170-174. |
| Zhang X, Feng SP, Zeng SP, et al. Status quo and correlation analysis of electronic health literacy,self-efficacy and self-management behavior in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. J Mod Clin Med, 2022, 48(3):170-174. | |
| [22] | 张茜, 熊引, 饶婷, 等. 老年糖尿病患者自我管理知信行水平现状及影响因素分析[J]. 当代护士(上旬刊), 2023, 30(3):24-26. |
| Zhang Q, Xiong Y, Rao T, et al. Analysis on the present situation and influencing factors of self-management knowledge,attitude and practice of elderly diabetic patients[J]. Mod Nurse, 2023, 30(3):24-26. | |
| [23] | Dural G, Kavak Budak F, Özdemir AA, et al. Effect of perceived social support on self-care agency and loneliness among elderly muslim people[J]. J Religion Health, 2022, 61(2):1505-1513. |
| [24] |
Baiardini I, Braido F, Menoni S, et al. Wellbeing,illness perception and coping strategies in Italian Celiac patients[J]. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2012, 25(4):1175-1182.
PMID |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||