


中华护理杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (11): 1330-1337.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.11.008
收稿日期:2022-11-21
出版日期:2023-06-10
发布日期:2023-06-09
通讯作者:
史崇清,E-mail:shichongqing@wust.edu.cn作者简介:马丽:女,本科(硕士在读),护士,E-mail:1132724838@qq.com
MA Li( ), SHI Chongqing(
), SHI Chongqing( ), CHEN Xiangrong
), CHEN Xiangrong
Received:2022-11-21
Online:2023-06-10
Published:2023-06-09
摘要:
目的 探究肺癌患者家庭照顾者获益感的潜在类别及其特征差异,分析相关影响因素,提出护理对策。 方法 该研究为横断面研究,采用便利抽样法选取2021年9月—2022年8月在武汉市某三级甲等医院治疗的肺癌患者及其家庭照顾者作为调查对象。使用一般资料调查表、家庭环境量表、疾病获益感量表修订版、一般自我效能感量表进行调查。使用潜在剖面分析探索肺癌患者家庭照顾者获益感的潜在类别,采用有序多分类Logistic回归分析探讨相关影响因素。 结果 共纳入261名肺癌患者家庭照顾者,其获益感分为3个类别,分别命名为“低获益-感知支持缺乏组”(n=170,65.13%)、“中等获益-接受现实组”(n=73,27.97%)和“高获益-个人成长组”(n=18,6.90%)。有序多分类Logistic回归分析结果显示,家庭照顾者有无工作、患者的疾病分期、患者是否采用联合治疗、患者确诊时长、家庭照顾者的年龄、家庭照顾者的一般自我效能感量表得分是肺癌患者家庭照顾者获益感的影响因素。 结论 肺癌患者家庭照顾者的获益感存在明显的分类特征,建议护理人员采取个性化心理干预、信息支持、正向激励等方法,着重提高其自我效能,提升其获益感。
马丽, 史崇清, 陈向荣. 肺癌患者家庭照顾者获益感的潜在剖面分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(11): 1330-1337.
MA Li, SHI Chongqing, CHEN Xiangrong. Latent profile analysis and nursing countermeasures of benefit finding in family caregivers of lung cancer patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2023, 58(11): 1330-1337.
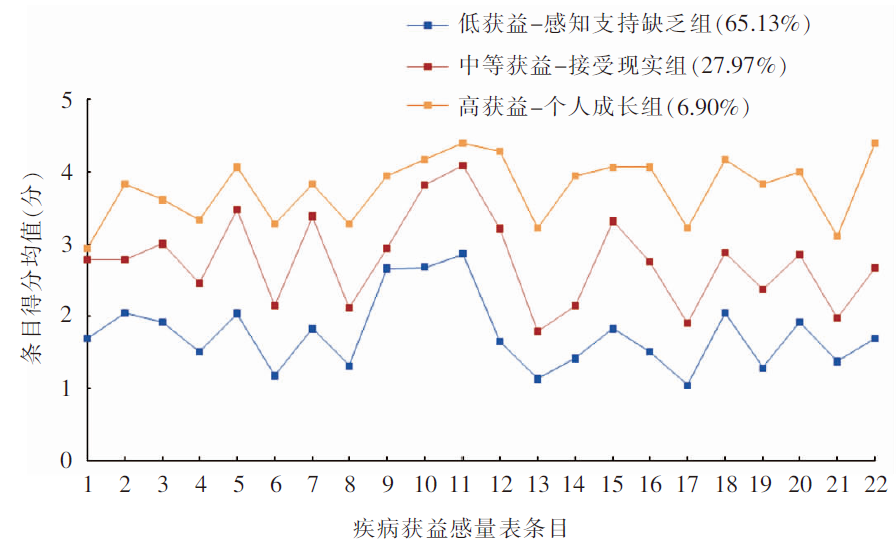
图1 肺癌患者家庭照顾者获益感3个潜在类别的特征分布
Figure 1 The characteristic distribution of 3 potential categories of benefit finding among family caregivers of lung cancer patients
 |
表2 肺癌患者家庭照顾者获益感潜在类别的单因素分析(n=261)
Table 2 Univariate analysis of potential categories of benefit finding among family caregivers of lung cancer patients(n=261)
 |
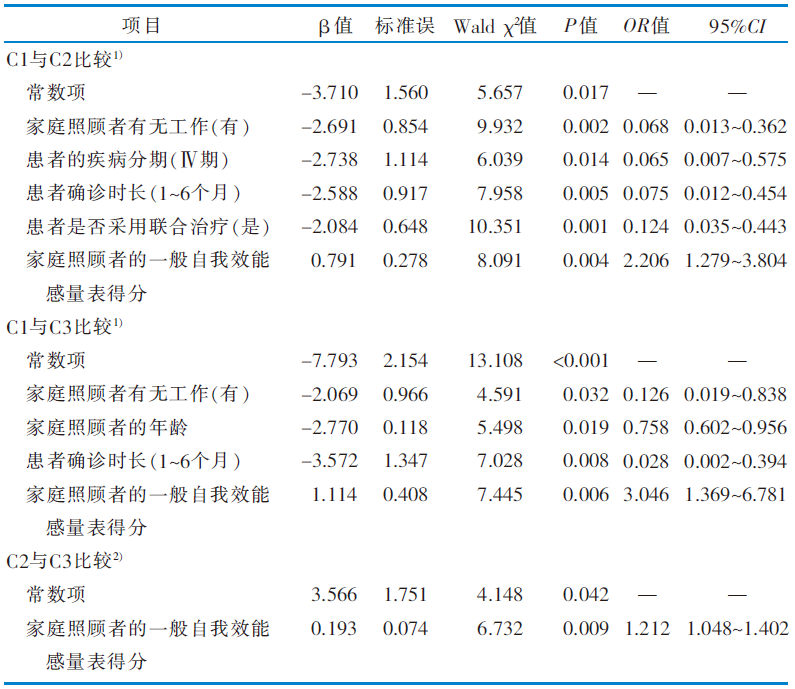 |
表3 肺癌患者家庭照顾者获益感潜在类别影响因素的有序多分类Logistic回归分析
Table 3 Results of ordered multiple logistic regression of potential category influencing factors among family caregivers of lung cancer patients
 |
| [1] |
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3):209-249.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Barello S, Castiglioni C, Bonanomi A, et al. The Caregiving Health Engagement Scale(CHE-s):development and initial validation of a new questionnaire for measuring family caregiver engagement in healthcare[J]. BMC Public Health, 2019, 19(1):1562.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
王瑞博, 董诗奇, 崔盼盼, 等. 癌症患者家庭照顾者负担评估工具的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(10):1584-1588.
DOI |
| Wang RB, Dong SQ, Cui PP, et al. Research progress of assessment tools for family caregiver burden of cancer patients:a lite-rature review[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(10):1584-1588. | |
| [4] |
Saimaldaher ZH, Wazqar DY. Relationships between caregiving stress,mental health and physical health in family caregivers of adult patients with cancer:implications for nursing practice[J]. Scand J Caring Sci, 2020, 34(4):889-898.
DOI |
| [5] |
Hartnett J, Thom B, Kline N. Caregiver burden in end-stage ovarian cancer[J]. Clin J Oncol Nurs, 2016, 20(2):169-173.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Taylor SE, Kemeny ME, Reed GM, et al. Psychological resources,positive illusions,and health[J]. Am Psychol, 2000, 55(1):99-109.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Bi WY, Wang HN, Yang GT, et al. A longitudinal cohort study on benefit finding evolution in Chinese women breast cancer survivals[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1):20640.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | 王如婷, 章亚平, 吕小英, 等. 疾病获益感量表在缺血性脑卒中病人照顾者中的信效度检验[J]. 护理研究, 2020, 34(15):2655-2659. |
| Wang RT, Zhang YP, Lü XY, et al. Reliability and validity test of the Benefit Finding Scale in caregivers of ischemic stroke patients[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2020, 34(15):2655-2659. | |
| [9] | 王孟成, 毕向阳. 潜变量建模与Mplus应用:进阶篇[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2018:13-15. |
| Wang MC, Bi XY. Latent variable modeling and Mplus application-advanced chapter[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 2018:13-15. | |
| [10] | 倪平, 陈京立, 刘娜. 护理研究中量性研究的样本量估计[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010, 45(4):378-380. |
| Ni P, Chen JL, Liu N. The sample size estimation in quantitative nursing research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010, 45(4):378-380. | |
| [11] |
赵丽华, 屈欢, 李娇娇, 等. 晚期癌症患者的替代决策者姑息照护决策冲突的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(14):1683-1690.
DOI |
|
Zhao LH, Qu H, Li JJ, et al. Analysis on status and influencing factors of palliative care decisions conflict among substitutive decision-makers of advanced cancer patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(14):1683-1690.
DOI |
|
| [12] |
Liu W, Unick J, Galik E, et al. Barthel Index of activities of daily living:item response theory analysis of ratings for long-term care residents[J]. Nurs Res, 2015, 64(2):88-99.
DOI URL |
| [13] | 费立鹏, 沈其杰, 郑延平, 等. “家庭亲密度和适应性量表”和“家庭环境量表”的初步评价:正常家庭与精神分裂症家庭成员对照研究[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 1991, 5(5):198-202,238. |
| Fei LP, Shen QJ, Zheng YP, et al. Preliminary evaluation of Chinese version of FACES Ⅱ and FES:comparison of normal families and families of schizophrenic patients[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 1991, 5(5):198-202,238. | |
| [14] |
Antoni MH, Lehman JM, Kilbourn KM, et al. Cognitive-behavioral stress management intervention decreases the prevalence of depression and enhances benefit finding among women under treatment for early-stage breast cancer[J]. Health Psychol, 2001, 20(1):20-32.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
边静, 张兰凤, 刘谆谆, 等. 疾病获益感量表修订版在癌症家庭照顾者中应用的信效度检验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21(17):2091-2096.
DOI |
| Bian J, Zhang LF, Liu ZZ, et al. Reliability and validity of the revised Chinese version of Benefit Finding Scale in family caregivers of cancer patients[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2018, 21(17):2091-2096. | |
| [16] | Schwarzer R, Born A, Iwawaki S, et al. The assessment of optimistic self-beliefs:comparison of the Chinese,Indonesian,Japanese,and Korean versions of the General Self-Efficacy Scale[J]. Psychologia, 1997, 40(1):1-13. |
| [17] | 王才康, 胡中锋, 刘勇. 一般自我效能感量表的信度和效度研究[J]. 应用心理学, 2001, 7(1):37-40. |
| Wang CK, Hu ZF, Liu Y. Evidences for reliability and validity of the Chinese version of General Self Efficacy Scale[J]. Chin J Appl Psychol, 2001, 7(1):37-40. | |
| [18] |
周丹, 蒋小平, 陈澜, 等. 恶性肿瘤患儿家庭管理特征的潜在剖面分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(20):2493-2501.
DOI |
|
Zhou D, Jiang XP, Chen L, et al. Latent profile analysis of family management characteristics in children with malignant tumor[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(20):2493-2501.
DOI |
|
| [19] |
Jiang Y, Liu C, Li JY, et al. Different attitudes of Chinese patients and their families toward truth telling of different stages of cancer[J]. Psychooncology, 2007, 16(10):928-936.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Barakat LP, Madden RE, Vega G, et al. Longitudinal predictors of caregiver resilience outcomes at the end of childhood cancer treatment[J]. Psychooncology, 2021, 30(5):747-755.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | 张青月, 肖珊, 魏婷婷, 等. 癌症患者照顾者益处发现现状及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2017, 33(8):598-602. |
| Zhang QY, Xiao S, Wei TT, et al. Benefit finding and its influencing factors for caregivers of patients with cancer[J]. Chin J Pract Nurs, 2017, 33(8):598-602. | |
| [22] |
柯丹丹, 罗洁, 洪轶颖, 等. 膀胱全切术后行腹壁造口患者照顾者创伤后成长体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(3):294-300.
DOI |
|
Ke DD, Luo J, Hong YY, et al. A qualitative research on post-traumatic growth experience of family members in patients with abdominal wall stoma after radical cystectomy[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(3):294-300.
DOI |
|
| [23] |
Longacre ML, Valdmanis VG, Handorf EA, et al. Work impact and emotional stress among informal caregivers for older adults[J]. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci, 2017, 72(3):522-531.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Akpan-Idiok PA, Anarado AN. Perceptions of burden of caregiving by informal caregivers of cancer patients attending University of Calabar Teaching Hospital,Calabar,Nigeria[J]. Pan Afr Med J, 2014, 18:159.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Peng XC, Su YL, Huang WX, et al. Status and factors related to posttraumatic growth in patients with lung cancer:a STROBE-compliant article[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2019, 98(7):e14314. |
| [26] |
Kangas M, McDonald S, Williams JR, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy program for distressed adults with a primary brain tumor:a case series study[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2015, 23(10):2855-2859.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Cassidy T, Giles M, McLaughlin M. Benefit finding and resi-lience in child caregivers[J]. Br J Health Psychol, 2014, 19(3):606-618.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | 谭琳, 罗珊, 佘秋群, 等. 老年脑卒中患者照顾者自我效能感与益处发现的相关性[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2020, 40(19):4213-4216. |
| Tan L, Luo S, She QQ, et al. Correlation between self-efficacy and benefit discovery of caregivers of elderly stroke patients[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2020, 40(19):4213-4216. |
| [1] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [2] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [3] | 刘方, 刘云访, 德宗, 皮蓉, 何子涵, 李素云. 肝硬化患者口渴感现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 934-939. |
| [4] | 章子怡, 杜冰, 张荩之, 尹敏. 青少年心境障碍患者心理求助体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(8): 947-952. |
| [5] | 周柯冰, 黄晓娇, 闫凤侠. 首发脑卒中恢复期患者症状负担及其影响因素的网络分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 792-798. |
| [6] | 王奕, 王小惠, 王娟, 王晓峰, 葛静玲. 卵巢癌术后患者自我管理问题清单的构建及应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 806-812. |
| [7] | 张程, 王霄一, 杨文娟, 刘梦如, 贺飞. 双向社会支持在老年维持性血液透析患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 813-818. |
| [8] | 李红颐, 李雪, 范宇莹, 赵一莎, 李京淑. ICU患者创伤心理反应的潜在剖面及影响因素的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 842-848. |
| [9] | 陈丽花, 黄瑶, 盛青青, 谭玉凤, 张书琴, 黄小群, 徐蒙蒙. 肺移植术后肠内营养患者喂养不耐受的现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 849-855. |
| [10] | 周楠, 智诗涵, 王萌, 张惠, 张丽红, 罗茂语, 何瑛, 顾炜. 性功能障碍干预在宫颈癌患者中应用的范围综述及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(7): 890-897. |
| [11] | 王衍蝶, 曾妃, 梁江淑渊, 顾培培. 肺移植患者骨代谢异常影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 703-709. |
| [12] | 唐楠, 高远, 苏清清, 宋咪, 邱晨, 邵梦琪. 老年骨质疏松患者再骨折影响因素分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(6): 710-716. |
| [13] | 李瑞华, 甄莉, 朱木兰, 叶新梅, 秦芳, 张星星, 林梅燕, 李国新. 预防性回肠造口患者营养状况及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4): 396-403. |
| [14] | 李卫珍, 周子怡, 王飞霞, 潘喆, 应玲玲, 倪晓波, 朱米娜, 李璐, 李霞, 李思若. 造口患者居家沐浴知信行现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4): 404-410. |
| [15] | 韩娜菲, 贺红, 袁华娣, 兰美娟, 吴小燕, 曹俊华, 高丽燕, 辛鼎杰. 日间肺癌手术患者出院后症状纵向变化及护理对策研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4): 432-438. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||