


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (19): 2309-2318.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.19.001
• 论著 • 下一篇
王彦艳( ), 姚梁怡, 陈鑫, 李汝情, 曹梦迪, 钱学珂, 刘延锦, 李星, 陈阳, 赵情
), 姚梁怡, 陈鑫, 李汝情, 曹梦迪, 钱学珂, 刘延锦, 李星, 陈阳, 赵情
收稿日期:2023-10-25
出版日期:2024-10-10
发布日期:2024-10-14
作者简介:王彦艳:女,硕士,副主任护师,学部护士长,E-mail:271103918@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Yanyan( ), YAO Liangyi, CHEN Xin, LI Ruqing, CAO Mengdi, QIAN Xueke, LIU Yanjin, LI Xing, CHEN Yang, ZHAO Qing
), YAO Liangyi, CHEN Xin, LI Ruqing, CAO Mengdi, QIAN Xueke, LIU Yanjin, LI Xing, CHEN Yang, ZHAO Qing
Received:2023-10-25
Online:2024-10-10
Published:2024-10-14
摘要:
目的 构建乳腺癌术后患者上肢淋巴水肿预防方案并评价其效果。 方法 在证据总结和半结构式访谈的基础上,构建乳腺癌术后患者上肢淋巴水肿预防方案初稿,于2022年12月进行2轮专家函询。采用便利抽样法,选取郑州市某三级甲等医院乳腺外科恶性肿瘤手术患者为研究对象,根据首次就诊时间,将2023年1月—3月收治的58例患者纳入试验组,实施乳腺癌术后患者上肢淋巴水肿预防方案。将2022年7月—12月收治的57例患者纳入对照组,予以常规护理。比较两组出院后1、3、6个月淋巴水肿发生率、上肢功能得分、淋巴水肿预防行为依从性得分。 结果 2轮函询问卷的有效回收率分别为92.59%、100%,专家权威系数分别为0.940、0.950,肯德尔和谐系数分别为0.228、0.254(均P<0.001)。第2轮函询的变异系数为0.07~0.24。方案终稿包括一级指标5项、二级指标12项、三级指标32项。方案应用过程中,共脱落5例,试验组和对照组各纳入55例。重复测量方差分析结果显示,两组干预前和出院后1、3、6个月的上肢功能得分、淋巴水肿预防行为依从性得分的时间与组间存在交互效应(P<0.05);简单效应分析显示,出院后1、3、6个月,试验组的上肢功能得分、淋巴水肿预防行为依从性得分均优于对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。出院后6个月,两组淋巴水肿发生率比较,差异有统计学意义(P=0.032)。两组均未发生皮下淤血、跌倒等不良事件。 结果 该研究构建的乳腺癌术后患者上肢淋巴水肿预防方案具有科学性、可行性及安全性,可有效降低患者淋巴水肿的发生率,提高患者的生活质量。
王彦艳, 姚梁怡, 陈鑫, 李汝情, 曹梦迪, 钱学珂, 刘延锦, 李星, 陈阳, 赵情. 乳腺癌术后患者上肢淋巴水肿预防方案的构建及应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(19): 2309-2318.
WANG Yanyan, YAO Liangyi, CHEN Xin, LI Ruqing, CAO Mengdi, QIAN Xueke, LIU Yanjin, LI Xing, CHEN Yang, ZHAO Qing. Construction and application of a management program for arm lymphedema prevention in postoperative breast cancer patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(19): 2309-2318.
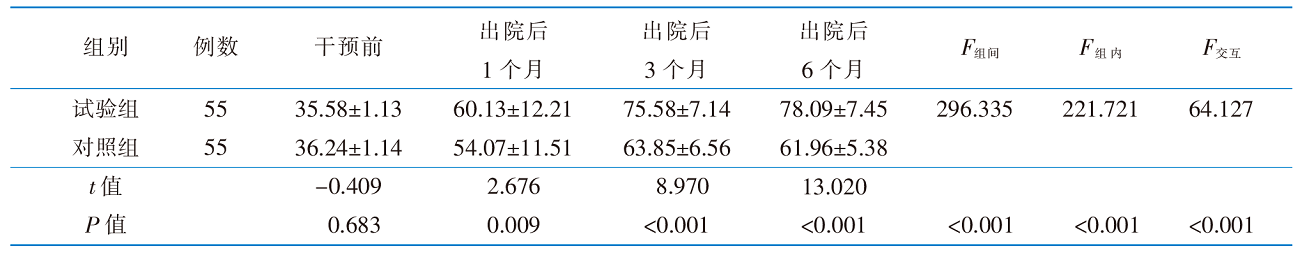 |
表4 两组淋巴水肿预防行为依从性得分的比较(分,$\bar{x}±s$)
Table 4 Comparison of lymphoedema prevention behavioural adherence scores between the 2 groups of patients(score,$\bar{x}±s$)
 |
| [1] | Geller BM, Vacek PM, O’Brien P, et al. Factors associated with arm swelling after breast cancer surgery[J]. J Womens Health (Larchmt), 2003, 12(9):921-930. |
| [2] |
Jorgensen MG, Toyserkani NM, Hansen FG, et al. The impact of lymphedema on health-related quality of life up to 10 years after breast cancer treatment[J]. NPJ Breast Cancer, 2021, 7(1):70.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Executive Committee of the International Society of Lymphology. The diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema:2020 Consensus Document of the International Society of Lymphology[J]. Lymphology, 2020, 53(1):3-19. |
| [4] | Ridner SH, Dietrich MS, Stewart BR, et al. Body mass index and breast cancer treatment related lymphedema[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2011, 19(6):853-857. |
| [5] | Hayes SC, Janda M, Cornish B, et al. Lymphedema after breast cancer:incidence,risk factors,and effect on upper body function[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2008, 26(21):3536-3542. |
| [6] | 中华护理学会. 护理团体标准解读:乳腺癌术后淋巴水肿预防和护理[EB/OL]. (2021-03-13)[2022-12-29]. http://www.zhhlxh.org.cn/cnaWebcn/article/3245. |
| Chinese Nursing Association. Prevention and nursing of lymphedema after breast cancer surgery[EB/OL]. (2021-03-13)[2022-12-29]. http://www.zhhlxh.org.cn/cnaWebcn/article/3245. | |
| [7] |
郭员志, 张红梅, 赵培, 等. 乳腺癌术后淋巴水肿预防与护理的循证实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(7):773-781.
DOI URL |
|
Guo YZ, Zhang HM, Zhao P, et al. Evidence-based practice of lymphedema prevention and nursing care after breast cancer surgery[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(7):773-781.
DOI URL |
|
| [8] | 王惠雪. 乳腺癌术后淋巴水肿预防行为临床实践指南初步构建[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2017. |
| Wang HX. Primary establishment of clinical practice guideline for preventive behavior of breast cancer-related lymphedema[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2017. | |
| [9] |
Gebruers N, Verbelen H, De Vrieze T, et al. Current and future perspectives on the evaluation,prevention and conservative management of breast cancer related lymphoedema:a best practice guideline[J]. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 2017, 216:245-253.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会. 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌诊治指南与规范(2021年版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2021, 31(10):954-1040. |
| Breast Cancer Professional Committee of the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association. Chinese Anti-Cancer Association breast cancer diagnosis and treatment guidelines and standards(2021 edition)[J]. Chin Oncol, 2021, 31(10):954-1040. | |
| [11] | Australasian Lymphology Association. Lymphoedema management[EB/OL]. (2015-03-01)[2022-12-27]. https://www.lymphoedema.org.au/aboutlymphoedema/lymphoedema-management/. |
| [12] | American Cancer Society. Lymphedema[EB/OL]. (2021-05-21)[2022-12-27]. https://www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects.html. |
| [13] |
Armer JM, Hulett JM, Bernas M, et al. Best practice guidelines in assessment,risk reduction,management,and surveillance for post-breast cancer lymphedema[J]. Curr Breast Cancer Rep, 2013, 5(2):134-144.
PMID |
| [14] | 中华整形外科学分会淋巴水肿学组. 外周淋巴水肿诊疗的中国专家共识[J]. 中华外科整形外科杂志, 2020, 36(4):355-360. |
| The Chinese Society of Plastic Surgery Lymphedema Group. The Chinese consensus of the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema[J]. Chin J Plast Surg, 2020, 36(4):355-360. | |
| [15] | 河南省肿瘤医院乳腺癌诊疗共识专家团队, 刘真真, 焦得闯, 等. 河南省肿瘤医院乳腺癌相关继发性淋巴水肿诊疗专家共识[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2019, 26(24):1855-1858. |
| Breast Cancer Treatment Consensus Expert Team of Henan Cancer Hospital, Liu ZZ, Jiao DC, et al. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer-associated secondary lymphoedema in Henan Provincial Cancer Hospital[J]. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat, 2019, 26(24):1855-1858. | |
| [16] |
McLaughlin SA, DeSnyder SM, Klimberg S, et al. Considerations for clinicians in the diagnosis,prevention,and treatment of breast cancer-related lymphedema,recommendations from an expert panel:part 2:preventive and therapeutic options[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2017, 24(10):2827-2835.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | 徐洁慧, 胡一惠, 陈花, 等. 乳腺癌相关淋巴水肿非手术预防的证据整合[J]. 中国护理管理, 2021, 21(5):720-727. |
| Xu JH, Hu YH, Chen H, et al. Evidence integration of non-surgical prevention strategies for lymphedema related to breast cancer[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2021, 21(5):720-727. | |
| [18] | 蒋文婷, 陈丽君. 乳腺癌患者乳腺癌相关淋巴水肿发生风险及其与发病情况的关联效应分析[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(18):3338-3343. |
| Jiang WT, Chen LJ. Risk of breast cancer-related lymphedema of patients with breast cancer and its correlation with incidence[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2022, 36(18):3338-3343. | |
| [19] |
李思雨, 袁媛, 安然, 等. 肝硬化老年衰弱患者综合运动康复护理方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(20):2437-2445.
DOI URL |
|
Li SY, Yuan Y, An R, et al. Construction and application of a comprehensive exercise rehabilitation program in elderly patients with cirrhosis and frailty[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(20):2437-2445.
DOI URL |
|
| [20] | 方积乾. 生物医学研究的统计方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007. |
| Fang JQ. Statistical Methods of biomedical research[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007. | |
| [21] |
Gillespie TC, Sayegh HE, Brunelle CL, et al. Breast cancer-related lymphedema: risk factors,precautionary measures,and treatments[J]. Gland Surg, 2018, 7(4):379-403.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Fu MR, McDaniel RW, Rhodes VA. Measuring symptom occurrence and symptom distress:development of the symptom experience index[J]. J Adv Nurs, 2007, 59(6):623-634. |
| [23] | Shi S, Lu Q, Fu MR, et al. Psychometric properties of the Breast Cancer and Lymphedema Symptom Experience Index:the Chinese version[J]. Eur J Oncol Nurs, 2016, 20:10-16. |
| [24] |
Beaton DE, Katz JN, Fossel AH el al. Measuring the whole or the parts? Validity,reliability,and responsiveness of the disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand outcome measure in different regions of the upper extremity[J]. J Hand Ther, 2001, 14:128-142.
PMID |
| [25] | 廖春丽, 王聪, 周欣, 等. DASH简式评分表中文版应用于乳腺癌患者上肢功能障碍评价研究的信效度检验[J]. 护理研究, 2014, 28(28):3581-3583. |
| Liao CL, Wang C, Zhou X, et al. Reliability and validity of Chinese version of DASH Short Form Scale applied in upper limb dysfunction evaluation research of breast cancer patients[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2014, 28(28):3581-3583. | |
| [26] |
尤渺宁, 万巧琴. 乳腺癌相关淋巴水肿患者自我护理的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(3):464-468.
DOI URL |
|
You MN, Wan QQ. Research progress of self-care in patients with breast cancer-related lymphedema[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(3):464-468.
DOI URL |
|
| [27] |
童静韬, 王颖, 倪平, 等. 乳腺癌患者术后肢体功能康复行为的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(6):711-717.
DOI URL |
| Tong JT, Wang Y, Ni P, et al. Rehabilitation behavior of limb function in postoperative breast cancer patients based on the theory of planned behavior:a qualitative research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(6):711-717. | |
| [28] | Alzubaidi H, Mc NK, Kilmartin GM, et al. The relationships between illness and treatment perceptions with adherence to diabetes self-care:a comparison between Arabic-speaking migrants and Caucasian English-speaking patients[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2015, 110(2):208-217. |
| [29] | Levy EW, Pfalzer LA, Danoff J, et al. Predictors of functional shoulder recovery at 1 and 12 months after breast cancer surgery[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2012, 134:315-324. |
| [30] | 韩娜, 刘延锦, 栗英, 等. 乳腺癌患者改良根治术后上肢功能康复手机应用软件的设计及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2017, 52(3):267-270. |
| Han N, Liu YJ, Li Y, et al. Effect of the application on improving postoperative upper extremity function rehabilitation in patients with breast cancer[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2017, 52(3):267-270. | |
| [31] | 廖妍妍, 王蓓, 王莉莉, 等. 上肢运动操改善乳腺癌淋巴水肿患者上肢功能的效果观察[J]. 中华护理教育, 2018, 15(3):223-226. |
| Liao YY, Wang B, Wang LL, et al. The effects of an upper extremity exercise on improving the function of upper extremity in postoperative patients with breast cancer-related lymphedema[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2018, 15(3):223-226. |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||