


中华护理杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (6): 707-713.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.06.010
张舵( ), 周雁荣(
), 周雁荣( ), 刘娟, 朱利思, 胡凯利, 吴前胜, 潘友民, 郑智, 查正彪, 李碧稳, 张洁
), 刘娟, 朱利思, 胡凯利, 吴前胜, 潘友民, 郑智, 查正彪, 李碧稳, 张洁
收稿日期:2022-06-07
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2023-03-23
通讯作者:
周雁荣,E-mail:1002406585@qq.com作者简介:张舵:男,本科(硕士在读),护士,E-mail:2423750555@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Duo( ), ZHOU Yanrong(
), ZHOU Yanrong( ), LIU Juan, ZHU Lisi, HU Kaili, WU Qiansheng, PAN Youmin, ZHENG Zhi, ZHA Zhengbiao, LI Biwen, ZHANG Jie
), LIU Juan, ZHU Lisi, HU Kaili, WU Qiansheng, PAN Youmin, ZHENG Zhi, ZHA Zhengbiao, LI Biwen, ZHANG Jie
Received:2022-06-07
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-03-23
摘要:
目的 探究感知压力和不确定性忍受度在心脏大血管手术患方决策者健康素养与决策满意度间的中介效应,为提高心脏大血管手术决策满意度提供思路。 方法 2021年10月—2022年5月,采用便利抽样法,抽取武汉市某三级甲等综合医院心脏大血管外科260名手术患方决策者作为调查对象,使用全面健康素养测量量表、感知压力量表、简版无法忍受不确定性量表、决策满意度量表进行调查。 结果 最终回收有效问卷251份,有效问卷回收率为96.54%。心脏大血管手术患方决策者健康素养得分为(23.05±5.61)分,感知压力得分为(20.31±6.08)分,不确定性忍受度得分为(26.41±5.94)分,决策满意度得分为(43.86±10.54)分,4个变量均具有相关性(P<0.001)。中介模型显示,健康素养对决策满意的直接效应显著,同时,健康素养还通过3条路径间接影响决策满意,包括感知压力的独立中介作用(β=0.096,P<0.001)、不确定性忍受度的独立中介作用(β=0.093,P=0.001)、感知压力与不确定性忍受度的链式中介作用(β=0.076,P<0.001),中介效应占总效应的49.17%。 结论 感知压力与不确定性忍受度在心脏大血管手术患方决策者健康素养与决策满意间发挥中介作用,可通过提高决策者健康素养,减轻压力知觉,使其理智看待手术风险,提高决策满意度。
张舵, 周雁荣, 刘娟, 朱利思, 胡凯利, 吴前胜, 潘友民, 郑智, 查正彪, 李碧稳, 张洁. 心脏大血管手术患方决策者健康素养对决策满意度的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(6): 707-713.
ZHANG Duo, ZHOU Yanrong, LIU Juan, ZHU Lisi, HU Kaili, WU Qiansheng, PAN Youmin, ZHENG Zhi, ZHA Zhengbiao, LI Biwen, ZHANG Jie. The effects of health literacy on decision satisfaction of decision-makers in patients undergoing cardiac macrovascular surgery[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2023, 58(6): 707-713.
 |
表2 调查对象健康素养、感知压力、不确定性忍受度、决策满意度得分(n=251)
Table 2 Scores of health literacy, perceived stress, intolerance of uncertainty and decision satisfaction of respondents(n=251)
 |
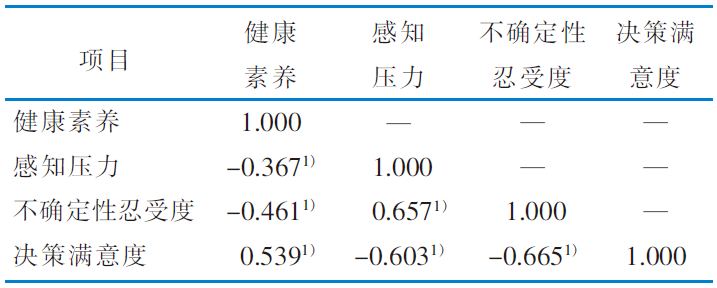 |
表3 调查对象健康素养、感知压力、不确定性忍受度、决策满意度相关性(r值,n=251)
Table 3 Correlations among health literacy, perceived stress, intolerance of uncertainty and decision satisfaction of respondents(r value,n=251)
 |

图1 感知压力和不确定性忍受度在健康素养与决策满意间的中介效应
Figure 1 The mediating effect of perceived stress and intolerance of uncertainty on health literacy and decision satisfaction
| [1] | Trimble M, Hamilton P. The thinking doctor:clinical decision making in contemporary medicine[J]. Clin Med(Lond), 2016, 16(4):343-346. |
| [2] |
Yau DKW, Underwood MJ, Joynt GM, et al. Effect of preparative rehabilitation on recovery after cardiac surgery:a systematic review[J]. Ann Phys Rehabil Med, 2021, 64(2):101391.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 张舵, 周雁荣, 刘娟, 等. 主动脉夹层术前家属代理决策现状及影响因素的研究[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2021, 38(12):53-56. |
| Zhang D, Zhou YR, Liu J, et al. Status quo of family agency decision-making before aortic dissection operations and its influencing factors[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2021, 38(12):53-56. | |
| [4] |
Zhang D, Zhou YR, Liu J, et al. Application of patient decision aids in treatment selection of cardiac surgery patients:a scoping review[J]. Heart Lung, 2022, 56:76-85.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Nibbelink CW, Brewer BB. Decision-making in nursing practice:an integrative literature review[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2018, 27(5/6):917-928.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 任慧, 张振香, 林蓓蕾, 等. 护士主导的心血管疾病高危人群发病风险沟通策略研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(04):431-436. |
|
Ren H, Zhang ZX, Lin BL, et al. Research progress on nurse-led risk communication strategies for high-risk groups of cardiovascular diseases[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(4):431-436.
DOI |
|
| [7] |
Nutbeam D. The evolving concept of health literacy[J]. Soc Sci Med, 2008, 67(12):2072-2078.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | 王振辉, 王永杰, 胡培, 等. 医患信任脆弱性:理论框架与反脆弱发展体系[J]. 甘肃行政学院学报, 2019, 136(6):105-113,127. |
| Wang ZH, Wang YJ, Hu P, et al. Vulnerability of trust between doctors and patients:theoretical framework and antifragile development system[J]. J Gansu Adm Inst, 2019, 136(6):105-113, 127. | |
| [9] |
Xu RH, Zhou LM, Wong EL, et al. The association between patients’ eHealth literacy and satisfaction with shared decision-making and well-being:multicenter cross-sectional study[J]. J Med Internet Res, 2021, 23(9):e26721.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Buhr K, Dugas MJ. The Intolerance of Uncertainty Scale:psychometric properties of the English version[J]. Behav Res Ther, 2002, 40(8):931-945.
PMID |
| [11] |
Chen YW, Liang Y, Zhang W, et al. Perceived stress and cognitive decline in Chinese-American older adults[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2019, 67(S3):S519-S524.
DOI |
| [12] |
Chinn D, McCarthy C. All Aspects of Health Literacy Scale (AAHLS):developing a tool to measure functional,communicative and critical health literacy in primary healthcare settings[J]. Patient Educ Couns, 2013, 90(2):247-253.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
吴清, 叶旭春, 巫雅萍, 等. 全面健康素养测量量表的汉化及信效度分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2017, 20(10):1229-1233.
DOI |
| Wu Q, Ye XC, Wu YP, et al. The chinesization of All Aspects of Health Literacy Scale and its reliability and validity[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2017, 20(10):1229-1233. | |
| [14] |
Cohen S, Kamarck T, Mermelstein R. A global measure of perceived stress[J]. J Health Soc Behav, 1983, 24(4):385-396.
PMID |
| [15] |
Leung DY, Lam TH, Chan SS. Three versions of Perceived Stress Scale:validation in a sample of Chinese cardiac patients who smoke[J]. BMC Public Health, 2010, 10:513.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Carleton RN, Norton MA, Asmundson GJ. Fearing the unknown:a short version of the Intolerance of Uncertainty Scale[J]. J Anxiety Disord, 2007, 21(1):105-117.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 吴莉娟, 王佳宁, 齐晓栋. 简版无法忍受不确定性量表在中学生中应用的效度和信度[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2016, 30(9):700-705. |
| Wu LJ, Wang JN, Qi XD. Validity and reliability of the Intolerance of Uncertainty Scale-12 in middle school students[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 2016, 30(9):700-705. | |
| [18] | 徐小琳. 患者对医疗决策参与的满意度量表的编制及信效度考评[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010. |
| Xu XL. The patients satisfaction with participation in medical decision-making scale:development,reliability and validity[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010. | |
| [19] | 邓音韵, 张子辰, 张晚霞, 等. 外科病人健康素养现状及其影响因素研究[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2022, 47(1):109-113. |
| Deng YY, Zhang ZC, Zhang WX, et al. Study on the status quo of health literacy of surgical patients and its influencing factors[J]. J Bengbu Med Coll, 2022, 47(1):109-113. | |
| [20] |
Baker S, Malone E, Graham L, et al. Patient-reported health literacy scores are associated with readmissions following surgery[J]. Am J Surg, 2020, 220(5):1138-1144.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
林琪, 曾莉, 任君红, 等. ICU患者家属沟通管理的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(2):294-298.
DOI |
| Lin Q, Zeng L, Ren JH, et a1. Research progress on communication management of family members of patients in ICU[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(2):294-298. | |
| [22] |
Niburski K, Guadagno E, Abbasgholizadeh-Rahimi S, et al. Shared decision making in surgery:a meta-analysis of existing literature[J]. Patient, 2020, 13(6):667-681.
DOI |
| [23] |
李学靖, 赵俊强, 张小艳, 等. 渥太华决策支持框架内涵及其临床应用的范围综述[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(6):756-762.
DOI |
| Li XJ, Zhao JQ, Zhang XY, et al. The concept and clinical implementation status of Ottawa Decision Support Framework:a scoping review[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(6):756-762. | |
| [24] |
Maher DI, Serpell JW, Ayton D, et al. Patient reported experience on consenting for surgery-elective versus emergency patients[J]. J Surg Res, 2021, 265:114-121.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Wisgalla A, Hasford J. Four reasons why too many informed consents to clinical research are invalid:a critical analysis of current practices[J]. BMJ Open, 2022, 12(3):e050543.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 贾冠华, 桑文凤, 申文佳, 等. 稳定性冠心病患者健康素养对血循环重建决策冲突的影响[J]. 护理学杂志, 2019, 34(24):4-7. |
| Jia GH, Sang WF, Shen WJ, et al. Impact of health literacy on revascularization decision conflict among patients with stable coronary artery disease[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2019, 34(24):4-7. | |
| [27] |
罗曦, 邹萍. 胆道闭锁患儿家长治疗决策困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(11):1630-1633.
DOI |
|
Luo X, Zou P. Medical decision-making difficulties among parents of children with biliary atresia[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(11):1630-1633.
DOI |
|
| [28] |
Conard S. Best practices in digital health literacy[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2019, 292:277-279.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 韩冬芳, 田甜, 高畅, 张婧珺, 李小妹. 肺结核患者健康促进行为与健康心理控制源关系的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1029-1036. |
| [2] | 司茜茜, 王莹, 赵福云, 马晓骁, 刘均娥. A型主动脉夹层患者Ⅰ期心肺康复护理方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1037-1042. |
| [3] | 沈支佳, 陈新宇, 钱志杰, 殷丽梅. 反复低血糖患者血糖管理行为退化特征的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1043-1050. |
| [4] | 王丽梅, 李露, 李玉霞, 喻鹏, 罗倩, 张翀旎. 糖尿病周围神经病理性疼痛患者运动恐惧现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1051-1056. |
| [5] | 丁慧敏, 戴莉敏, 蔡冬青, 杨群. 糖尿病前期患者自我管理潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1057-1064. |
| [6] | 刘海婷, 王咏梅, 郑贝贝, 蔡丽丽, 叶林斌, 吴佳芸, 宁丽, 李益民, 陈为霞. 冠心病合并糖尿病患者药物素养自评量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1065-1071. |
| [7] | 陈丽霞, 施慧, 朱德政, 曾莹. 成人低血糖恐惧评估工具的质量评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1072-1079. |
| [8] | 中国研究型医院学会过敏医学专业委员会, 中华医学会变态反应分会过敏性疾病护理学组(筹), 中华预防医学会过敏病预防与控制专业委员会, (执笔:王青 刘君 支凡 万文锦 田丰英 霍晓鹏 周文华 杨永仕 王田田 孙劲旅). 变应原特异性免疫治疗皮下注射护理的专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1080-1083. |
| [9] | 李琪, 苏晴晴, 张瑶瑶, 王田田, 吕静, 李亚可, 李海燕. 全膝关节置换患者关节遗忘变化轨迹及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1084-1090. |
| [10] | 刘娅, 刘晓晴, 杨雪凝, 王平, 刘学奎, 罗丹. 结肠镜检查患者肠道准备失败风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1091-1098. |
| [11] | 孙晓晴, 张爱霞, 朱珠, 樊雪梅, 梅士娟, 黄欣欣, 丛胜楠, 谢红燕. 分娩心理创伤评估量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1099-1105. |
| [12] | 谢玉生, 黄蓉蓉, 赵雪, 马蕾, 胡雁, 杨倩, 王乾沙, 明玥. 成人重度烧伤患者肠内肠外营养的证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1106-1113. |
| [13] | 李旭琴, 冯洁惠, 黄昉芳, 俞超, 梁诗雨, 王晓, 李旭芳, 朱含. 1例行机械循环辅助桥接心脏移植患者的术前护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1114-1117. |
| [14] | 贾晓静, 陈一竹, 许志英, 和霞, 耿超. 1例尿黑酸尿症双膝关节置换术后患者并发急性心肌梗死的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1118-1121. |
| [15] | 顾培培, 曾妃, 兰美娟, 梁江淑渊, 郭璐瑶, 蔡凌云, 朱岩, 郭鸽. 肺移植患者衰弱影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1122-1129. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 9
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 596
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||