


中华护理杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (15): 1859-1867.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2022.15.010
收稿日期:2021-10-19
出版日期:2022-08-10
发布日期:2022-08-11
通讯作者:
高欢玲,E-mail: 1723212444@qq.com作者简介:宋歌:女,本科(硕士在读),护士,E-mail: 827883181@qq.com
基金资助:
SONG Ge( ), WANG Ying, GAO Huanling(
), WANG Ying, GAO Huanling( ), QIAO Meirong, CHEN Ling, YANG Yulin
), QIAO Meirong, CHEN Ling, YANG Yulin
Received:2021-10-19
Online:2022-08-10
Published:2022-08-11
摘要:
目的 调查老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病(chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,COPD)患者认知衰弱的现状,分析相关影响因素并构建风险筛查模型。 方法 便利选取2020年5月—2021年3月山西省某三级甲等医院呼吸内科、老年科收治的386例老年COPD患者作为训练集,根据是否发生认知衰弱分为认知衰弱组(n=123)和非认知衰弱组(n=263)。通过单因素分析和Logistic回归分析筛选老年COPD患者认知衰弱的影响因素,构建风险筛查模型。于2021年4月—7月选取同一所医院住院的158例老年COPD患者作为验证集,对模型进行外部验证。 结果 训练集认知衰弱发生率为31.9%,验证集为35.4%。年龄、是否每天进行智力活动、是否多病共存、病程、肺功能分级、PaCO2是老年COPD患者认知衰弱的影响因素。风险筛查模型内部验证中,Hosmer-Lemeshow χ2检验P=0.328,受试者操作特征曲线下面积为0.813,约登指数为0.481,灵敏度为0.764,特异度为0.703。外部验证中,Hosmer-Lemeshow χ2检验P=0.468,受试者操作特征曲线下面积为0.886,灵敏度为0.732,特异度为0.824。 结论 老年COPD患者认知衰弱发生率较高,年龄≥70岁、未每天进行智力活动、多病共存、病程≥5年、肺功能分级>Ⅰ级、PaCO2>50 mmHg(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa)的老年COPD患者发生认知衰弱的风险较高。该文构建的风险筛查模型具有良好的区分度和校准度,可为临床医护人员评估老年COPD患者认知衰弱的发生风险、制订护理对策提供参考。
宋歌, 王颖, 高欢玲, 乔美荣, 陈玲, 杨玉霖. 老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者认知衰弱风险筛查模型的构建及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(15): 1859-1867.
SONG Ge, WANG Ying, GAO Huanling, QIAO Meirong, CHEN Ling, YANG Yulin. Construction and validation of a risk screening model for cognitive frailty in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2022, 57(15): 1859-1867.
 |
表1 训练集中老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者的一般资料及认知衰弱的单因素分析[例(百分比,%)]
Table 1 General information and univariate analysis of the risk of cognitive frailty in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the modeling set[cases(percentage,%)]
 |
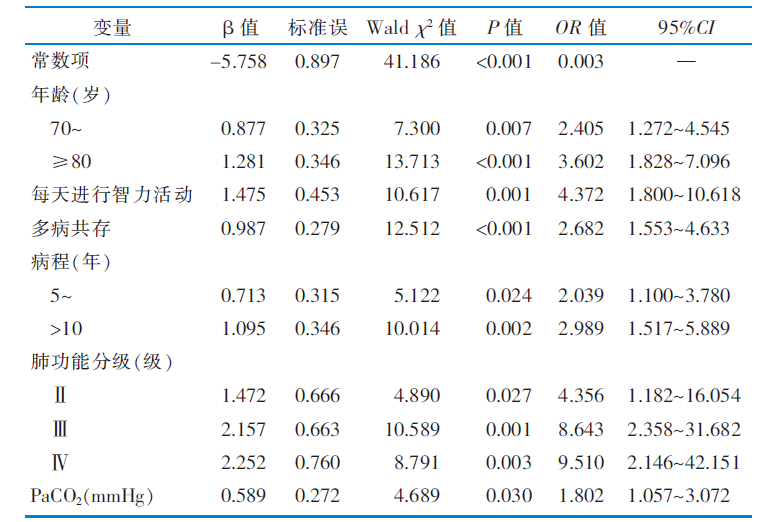 |
表2 老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者认知衰弱Logistic回归分析
Table 2 Logistic regression analysis of cognitive frailty in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 |
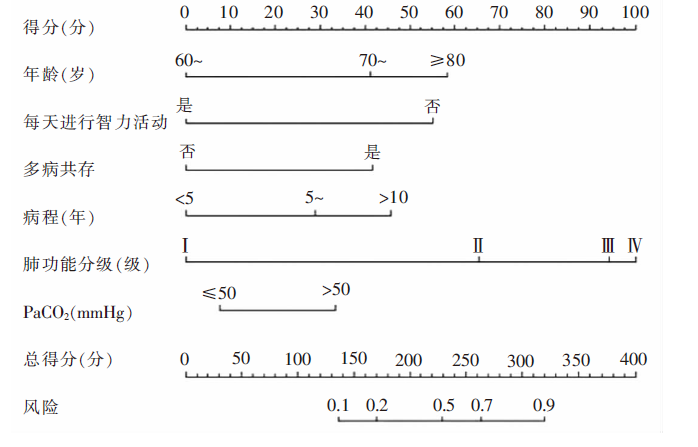
图1 老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者认知衰弱风险列线图 注:1 mmHg=0.133 kPa。
Figure 1 Nomogram of risk of cognitive frailty in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease

图2 训练集中老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者风险筛查模型的受试者操作特征曲线
Figure 2 Receiver operator characteristic curve in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease of the modeling set

图3 验证集中老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者风险筛查模型的受试者操作特征曲线
Figure 3 Receiver operator characteristic curve in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease of the validation set
| [1] | Kelaiditi E, Cesari M, Canevelli M, et al. Cognitive frailty:rational and definition from an(I.A.N.A./I.A.G.G.) international consensus group[J]. J Nutr Health Ag, 2013, 17(9):726-734. |
| [2] | Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, et al. Frailty in older adults:evidence for a phenotype[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2001, 56(3):M146-M156. |
| [3] | 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组, 中国医师协会神经内科医师分会认知障碍疾病专业委员会. 2018中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南(五):轻度认知障碍的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(17):1294-1301. |
| Chinese Guidance Group for Diagnosis and Treatment of Dementia and Cognitive Impairment,Committee of Cognitive Disorders, Neurologist Branch,Chinese Me-dical Doctor Association. 2018 Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of dementia and cognitive impairment(V):diagnosis and treatment of mild cognitive impairment[J]. Natl Med J China,2018, 98(17):1294-1301. | |
| [4] |
Lahousse L, Ziere G, Verlinden VJ, et al. Risk of frailty in elderly with COPD:a population-based study[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2016, 71(5):689-695.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Wang T, Mao LJ, Wang JH, et al. Influencing factors and exercise intervention of cognitive impairment in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2020, 15:557-566.
DOI URL |
| [6] | de Souza Dias L, Galvão Ferreira AC, et al. Prevalence of frailty and evaluation of associated variables among COPD patients[J]. Int J Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis, 2020, 15:1349-1356. |
| [7] |
Xie F, Xie LX. COPD and the risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia:a cohort study based on the Chinese longitudinal health longevity survey[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, 2019, 14:403-408.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Wang JJ, Kong DX, Yu F, et al. Cognitive deficit,physical frailty,hospitalization and emergency department visits in later life[J]. Aging Ment Health, 2021, 25(3):521-527.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Kim H, Awata S, Watanabe Y, et al. Cognitive frailty in community-dwelling older Japanese people:prevalence and its association with falls[J]. Geriatr Gerontol Int, 2019, 19(7):647-653. |
| [10] |
Liu LK, Chen CH, Lee WJ, et al. Cognitive frailty and its association with all-cause mortality among community-dwelling older adults in Taiwan:results from I-Lan longitudinal aging study[J]. Rejuvenation Res, 2018, 21(6):510-517.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Ruan QW, D’Onofrio G, Sancarlo D, et al. Emerging biomarkers and screening for cognitive frailty[J]. Aging Clin Exp Res, 2017, 29(6):1075-1086.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 中国老年医学学会呼吸病学分会慢性阻塞性肺疾病学组. 中国老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病临床诊治实践指南[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2020, 43(2):100-119. |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Group, Respiratory Branch, Chinese Geriatrics Society. Clinical guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of elderly chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China[J]. Chin J Tuberc Respir Dis, 2020, 43(2):100-119. | |
| [13] | Chen Y, Du H, Wei BH, et al. Development and validation of risk-stratification delirium prediction model for critically ill patients:a prospective,observational,single-center study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2017, 96(29):e7543. |
| [14] |
Vergouwe Y, Steyerberg EW, Eijkemans MJ, et al. Substantial effective sample sizes were required for external validation studies of predictive logistic regression models[J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 2005, 58(5):475-483.
PMID |
| [15] |
张义静, 李娟, 孙丽, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者早期简易肺康复方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(5):690-695.
DOI |
| Zhang YJ, Li J, Sun L, et al. Construction of an early simple pulmonary rehabilitation programme for patients with COPD and its evaluation of effectiveness[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(5):690-695. | |
| [16] | 周巧学, 周建荣, 库敏, 等. 养老机构老年人认知衰弱现状及影响因素分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2020, 35(9):88-92. |
| Zhou QX, Zhou JR, Ku M, et al. The prevalence and determinants of cognitive frailty among institutionalized older adults[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2020, 35(9):88-92. | |
| [17] | 靳真真. 社区老年人群睡眠时间与认知功能的相关性研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学,2019. |
| Jin ZZ. Association between sleep duration and cognitive impairment in community elderly adults[D]. Jinan: University of Jinan,2019. | |
| [18] | 王燕秋, 韩斌如, 李非. 胃肠道疾病老年住院患者衰弱现况及影响因素研究[J]. 护理学报, 2016, 23(6):7-11. |
| Wang YQ, Han BR, Li F. Current status of frailty of elderly inpatients with gastrointestinal diseases and its influence factors[J]. J Nurs China, 2016, 23(6):7-11. | |
| [19] |
Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment,MoCA:a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2005, 53(4):695-699.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | 张立秀, 刘雪琴. 蒙特利尔认知评估量表中文版的信效度研究[J]. 护理研究, 2007, 21(31):2906-2907. |
| Zhang LX, Liu XQ. A study on reliability and validity of MOCA scale of Chinese version[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2007, 21(31):2906-2907. | |
| [21] |
Hughes CP, Berg L, Danziger WL, et al. A new clinical scale for the staging of dementia[J]. Br J Psychiatry, 1982, 140:566-572.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Sheikh J, Yesavage J. Geriatric Depression Scale(GDS):recent evidence and development of a shorter version[J]. Clin Gerontol, 1986, 5:165-173.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 唐丹. 简版老年抑郁量表(GDS-15)在中国老年人中的使用[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2013, 21(3):402-405. |
| Tang D. Application of short form Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS-15) in Chinese elderly[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2013, 21(3):402-405. | |
| [24] |
Rubenstein LZ, Harker JO, Salvà A, et al. Screening for undernutrition in geriatric practice:developing the short-form Mini-Nutritional Assessment(MNA-SF)[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2001, 56(6):M366-M372.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 何扬利, 蹇在金. 简易营养评价法及简易营养评价精法对老年人营养不良的评价[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2005(4):278-281. |
| He YL, Jian ZJ. The application and evaluation of the elderly malnutrition assessment methods[J]. Chin J Geriatr, 2005(4):278-281. | |
| [26] | 潘利妞, 张伟宏, 余珍, 等. 郑州市社区老年人认知衰弱患病现状及影响因素[J]. 护理学杂志, 2019, 34(11):79-82. |
| Pan LN, Zhang WH, Yu Z, et al. The current status and influencing factors of cognitive frailty among elderly community residents in Zhengzhou City,China[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2019, 34(11):79-82. | |
| [27] |
Fujiwara Y, Chaves PH, Yoshida H, et al. Intellectual activity and likelihood of subsequently improving or maintaining instrumental activities of daily living functioning in community-dwelling older Japanese:a longitudinal study[J]. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry, 2009, 24(6):547-555.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
潘晶雪, 陈利群, 王敬丽, 等. 社区老年慢性病患者认知功能的现状调查[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(1):109-115.
DOI |
| Pan JX, Chen LQ, Wang JL, et al. Study on the status of cognitive function in community elderly adults with chronic diseases[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(1):109-115. | |
| [29] | 侯晓琳, 高静, 吴晨曦, 等. 养老机构老年人衰弱现状及分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(1):88-93. |
| Hou XL, Gao J, Wu CX, et al. Prevalence and factors associated with frailty among institutional older adults[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(1):88-93. | |
| [30] |
赵妹, 张强, 聂立婷, 等. 衰弱对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者不良健康结局影响的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(5):703-708.
DOI |
| Zhao M, Zhang Q, Nie LT, et al. The effects of frailty on adverse health outcomes in patients with COPD:a systematic review[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(5):703-708. | |
| [31] |
Nishiguchi S, Yamada M, Fukutani N, et al. Differential association of frailty with cognitive decline and sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2015, 16(2):120-124.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Jaitovich A, Angulo M, Lecuona E, et al. High CO2 levels cause skeletal muscle atrophy via AMP-activated kinase (AMPK),FoxO3a protein,and muscle-specific ring finger pro-tein 1(MuRF1)[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290(14):9183-9194.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 韩冬芳, 田甜, 高畅, 张婧珺, 李小妹. 肺结核患者健康促进行为与健康心理控制源关系的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1029-1036. |
| [2] | 司茜茜, 王莹, 赵福云, 马晓骁, 刘均娥. A型主动脉夹层患者Ⅰ期心肺康复护理方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1037-1042. |
| [3] | 沈支佳, 陈新宇, 钱志杰, 殷丽梅. 反复低血糖患者血糖管理行为退化特征的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1043-1050. |
| [4] | 王丽梅, 李露, 李玉霞, 喻鹏, 罗倩, 张翀旎. 糖尿病周围神经病理性疼痛患者运动恐惧现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1051-1056. |
| [5] | 丁慧敏, 戴莉敏, 蔡冬青, 杨群. 糖尿病前期患者自我管理潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1057-1064. |
| [6] | 刘海婷, 王咏梅, 郑贝贝, 蔡丽丽, 叶林斌, 吴佳芸, 宁丽, 李益民, 陈为霞. 冠心病合并糖尿病患者药物素养自评量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1065-1071. |
| [7] | 陈丽霞, 施慧, 朱德政, 曾莹. 成人低血糖恐惧评估工具的质量评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1072-1079. |
| [8] | 中国研究型医院学会过敏医学专业委员会, 中华医学会变态反应分会过敏性疾病护理学组(筹), 中华预防医学会过敏病预防与控制专业委员会, (执笔:王青 刘君 支凡 万文锦 田丰英 霍晓鹏 周文华 杨永仕 王田田 孙劲旅). 变应原特异性免疫治疗皮下注射护理的专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1080-1083. |
| [9] | 李琪, 苏晴晴, 张瑶瑶, 王田田, 吕静, 李亚可, 李海燕. 全膝关节置换患者关节遗忘变化轨迹及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1084-1090. |
| [10] | 刘娅, 刘晓晴, 杨雪凝, 王平, 刘学奎, 罗丹. 结肠镜检查患者肠道准备失败风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1091-1098. |
| [11] | 孙晓晴, 张爱霞, 朱珠, 樊雪梅, 梅士娟, 黄欣欣, 丛胜楠, 谢红燕. 分娩心理创伤评估量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1099-1105. |
| [12] | 谢玉生, 黄蓉蓉, 赵雪, 马蕾, 胡雁, 杨倩, 王乾沙, 明玥. 成人重度烧伤患者肠内肠外营养的证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1106-1113. |
| [13] | 李旭琴, 冯洁惠, 黄昉芳, 俞超, 梁诗雨, 王晓, 李旭芳, 朱含. 1例行机械循环辅助桥接心脏移植患者的术前护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1114-1117. |
| [14] | 贾晓静, 陈一竹, 许志英, 和霞, 耿超. 1例尿黑酸尿症双膝关节置换术后患者并发急性心肌梗死的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1118-1121. |
| [15] | 顾培培, 曾妃, 兰美娟, 梁江淑渊, 郭璐瑶, 蔡凌云, 朱岩, 郭鸽. 肺移植患者衰弱影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1122-1129. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||