


Chinese Journal of Nursing ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 151-157.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2022.02.004
• Special Planning—Mental Health Care • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIANG Jufang( ), LU Jiangbo, PEI Jianqin, QIAN Wei, GUO Linping, TANG Qunhua
), LU Jiangbo, PEI Jianqin, QIAN Wei, GUO Linping, TANG Qunhua
Received:2021-05-25
Online:2022-01-20
Published:2022-01-20
作者简介:蒋菊芳:女,本科,主任护师,E-mail: 908173010@qq.com
基金资助:JIANG Jufang, LU Jiangbo, PEI Jianqin, QIAN Wei, GUO Linping, TANG Qunhua. Effect of sensorimotor training in elderly patients with schizophrenia[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2022, 57(2): 151-157.
蒋菊芳, 陆江波, 裴建琴, 钱维, 郭琳萍, 唐群华. 感觉运动训练在老年精神分裂症患者中的应用效果[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(2): 151-157.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://zh.zhhlzzs.com/EN/10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2022.02.004
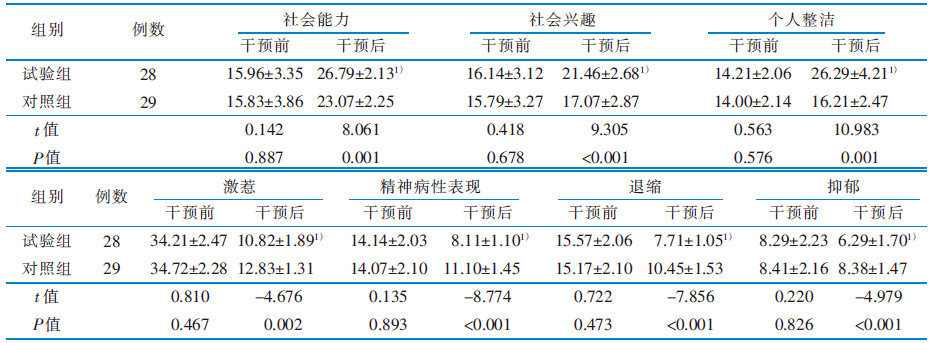 |
Table 4 Comparison of Nurses, Observation Scael for Inpatient Evaluation factor scores between two groups before and after intervention(score,$\bar{x}\pm s$)
 |
| [1] | 王华丽. 从临床研究看老年精神医学范畴[J]. 中华精神科杂志, 2017, 50(5):323-324. |
| Wang HL. View the category of geriatric psychiatry from the perspective of clinical research[J]. Chin J Psychiatry, 2017, 50(5):323-324. | |
| [2] | 阙建宇, 师乐, 刘佳佳, 等. 2002-2016年我国精神专科医院发展状况分析[J]. 中华精神科杂志, 2019, 52(2):139-144. |
| Que JY, Shi L, Liu JJ, et al. Analysis on the development of Chinese specialized psychiatric hospitals from 2002 to 2016[J]. Chin J Psychiatry, 2019, 52(2):139-144. | |
| [3] | 陈美玲, 郑玉娥, 黄婉玲, 等. 基于健康教育的生活技能训练对老年精神分裂症的康复效果分析[J]. 临床医学工程, 2019, 26(5):689-690. |
| Chen ML, Zheng YE, Huang WL, et al. Analysis on rehabilitation effect of life skill training based on health education for elderly patients with schizophrenia[J]. J Clin Med Engin, 2019, 26(5):689-690. | |
| [4] | 磨丽莉, 潘巧淑, 周芳珍, 等. 运动治疗联合心理护理对慢性精神分裂症病人康复和生活质量的影响[J]. 护理研究, 2019, 33(17):3067-3070. |
| Mo LL, Pan QS, Zhou FZ, et al. Effect of exercise therapy combined with psychological nursing on rehabilitation and quality of life of patients with chronic schizophrenia[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2019, 33(17):3067-3070. | |
| [5] | 陶宁蔚, 邓传秀. 多感官刺激训练对老年精神分裂症患者自我效能和自知力治疗态度的影响[J]. 中国校医, 2020, 34(10):735-737. |
| Tao NW, Deng CX. Effect of multi-sensory stimulation training on self-efficacy,insight and treatment attitude of elderly schizophrenics[J]. Chin J School Doctor, 2020, 34(10):735-737. | |
| [6] | 李奎, 郑海清, 李鑫, 等. 感觉运动训练对脑卒中患者家庭康复平衡和日常生活活动的影响[J]. 康复学报, 2016, 26(4):11-16. |
|
Li K, Zheng HQ, Li X, et al. Effect of sensorimotor training on balance and activity of daily living of home-based rehabilitation in patients with stroke[J]. Rehabil Med, 2016, 26(4):11-16.
DOI URL |
|
| [7] | 范肖冬. ICD-10精神与行为障碍分类[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1993:72-89. |
| Fan XD. ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioral disorders[M]. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 1993:72-89. | |
| [8] | 宋岳涛. CGA老年综合评估[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国协和医科大学出版社, 2019,227-229. |
| Song YT. CGA comprehensive geriatric assessment[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press, 2019,227-229. | |
| [9] | 王才康, 胡中锋, 刘勇. 一般自我效能感量表的信度和效度研究[J]. 应用心理学, 2001, 7(1):37-41. |
| Wang CK, Hu ZF, Liu Y. Evidences for reliability and validity of the Chinese version of General Self Efficacy Scale[J]. Chin J App Psycho, 2001, 7(1):37-41. | |
| [10] | 张明园. 精神科量表评定手册[M]. 2版. 长沙: 湖南科学技术出版社, 1998:215-217. |
| Zhang MY. Manual of psychiatric rating scales[M]. 2nd ed. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 1998:215-217. | |
| [11] | 谭晓林, 文丽, 杨冰香, 等. 团体自我肯定训练对精神分裂症患者病耻感的干预效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(10):1168-1173. |
| Tan XL, Wen L, Yang BX, et al. Effects of a group self-assertiveness training intervention on stigma of patients with schizophrenia[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(10)1168-1173. | |
| [12] | 赵莹, 田丽, 王晓萍, 等. 感觉统合训练对卒中后轻度认知障碍患者认知功能及生活自理能力的影响[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2020, 36(34):2655-2659. |
| Zhao Y, Tian L, Wang XP, et al. Effects of sensory integration therapy on cognitive function and self-care ability in patients with mild cognitive impairment after stroke[J]. Chin J Prac Nurs, 2020, 36(34):2655-2659. | |
| [13] | 葛高琪, 王晶晶, 齐冲, 等. 多感官刺激疗法的临床研究进展[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2018, 35(6):51-55. |
| Ge GQ, Wang JJ, Qi C, et al. Clinical research progress of snoezelen[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2018, 35(6):51-55. | |
| [14] |
Martorell AJ, Paulson AL, Suk HJ, et al. Multi-sensory gamma stimulation ameliorates Alzheimer’s-associated pathology and improves cognition[J]. Cell, 2019, 177(2):256-271.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | 赵海容. 本体感觉康复训练在脑卒中后下肢Brunnstrom Ⅳ期膝骨性关节炎病人中的应用[J]. 护理研究, 2016, 30(2):758-759. |
| Zhao HR. Application of proprioceptive rehabilitation training in patients with Brunnstro Ⅳstage knee osteoarthritis after stroke[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2016, 30(2):758-759. |
| [1] | YAN Yinzhi, WEN Fang, WANG Min, ZHOU Xuemei, MA Jinling, WU Huifang, YAO Wenying. Construction and application of a graded nursing program for exercise rehabilitation in children with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [2] | YAN Xueqin, CAO Songmei, ZHOU Fangfang, ZHU Liqun, CHEN Cheng, ZHU Mengxue, ZHANG Yanhong, LIANG Yiqing, BAI Suping. Summary of best evidence for early rehabilitation management of hand function in patients with hand burns [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(8): 998-1004. |
| [3] | ZHANG Hao, XU Guanxue, WANG Man, JIA Yuyang, LEI Fang, YANG Ming. Advances in digital health technology in home-based cardiac rehabilitation for patients with acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(3): 373-378. |
| [4] | ZHAI Zhongchang, YANG Linjie, WANG Huihua, ZENG Zhu, HU Yuting, WANG Jing, YANG Sai. Experiences of home-based rehabilitation of individuals with fully magnetically levitated left ventricular assist device:a qualitative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(2): 149-153. |
| [5] | LU Keying, QIN Caiping, QIAN Huilizhu, SONG Yuexia. Rehabilitation nursing of a patient with scrotal hematoma caused by emergency treatment of coronary vasospasm after cardiac radiofrequency ablation [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(2): 158-161. |
| [6] | HUANG Jinyan, ZHAI Huimin, WANG Xiwen, ZHAO Xinyu, WU Waner, MAI Shunxin, LUO Yuan-yuan, LAN Yandan, LEI Ruqi. Study on the effect of a horticultural therapy on the elderly with mild cognitive impairment in nursing homes [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(14): 1749-1756. |
| [7] | ZHANG Lin, ZHENG Yaxing, XIONG Tao, LONG Jun, CHEN Changrong. A scoping review of application of non-invasive brain computer interface technology in upper limb functional rehabilitation of stroke patients and nursing implications [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(13): 1658-1664. |
| [8] | LUO Yanfang, ZHANG Leilei, ZHU Lingyun, YU Xiaoyan, LU Bingyuan, LIU Ying, LIU Tianhao, SUN Renjuan, SU Zhenzhen. Influencing factors and nursing enlightenment of exercise self-efficacy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(11): 1315-1322. |
| [9] | SI Qianqian, WANG Ying, ZHAO Fuyun, MA Xiaoxiao, LIU June. Construction and application of early phase Ⅰ cardiopulmonary rehabilitation program for patients with Type A aortic dissection [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(9): 1037-1042. |
| [10] | WANG Xuan, WEN Xianxiu, GOU Li, ZHOU Lijuan, CHEN Fuli, WU Haiyan, WANG Liang. The cardiac rehabilitation adherence assessment tools:a systematic review of psychometric properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(6): 736-743. |
| [11] | LI Li, SHEN Yawen, LI Delong, CHENG Fangfang, YU Xifeng, PAN Linlin, ZHUANG Shuyuan, DONG Sihong, WU Jiao, LIANG Yan, ZANG Yuantong. Analysis of influencing factors and pathways of postoperative self-efficacy in patients with fragility fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(24): 3003-3008. |
| [12] | DAI Yaqin, SHAO Ting, YAO Lifeng, HU Fei, JIA Qin. Construction and application of a spinal cord injury rehabilitation care platform based on patient portrait [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(22): 2693-2699. |
| [13] | TAN Yuting, ZHANG Zhixia, YANG Zhen, QIAO Linru, CHENG Rong, CHEN Qiuxia, CHEN Lanjiao, XIAO Qin, JIANG Fang. A qualitative study of the influencing factors of ecological momentary assessment of rehabilitation exercise in middle-aged stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(21): 2620-2626. |
| [14] | LI Fen, GENG Yaqin, ZHANG Yi, SHEN Biyu, GAO Bo, YI Yaping. Analysis of potential categories and influencing factors of self-efficacy among patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(19): 2362-2368. |
| [15] | LÜ Dan, ZHAO Ying, HE Yan, LIU Qing, SONG Fujuan, LI Meng, ZHANG Xinyue, WANG Xiaoping. Construction and application of an advanced pulmonary rehabilitation programme for patients undergoing high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(17): 2053-2061. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||