


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (18): 2223-2230.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.18.008
收稿日期:2025-01-09
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-12
通讯作者:
许凤琴,E-mail:75775125@qq.com作者简介:陈瑛:女,硕士,副主任护师,护士长,E-mail:760020220042@xzhmu.edu.cn
基金资助:
CHEN Ying( ), YIN Yuanyuan, XU Fengqin(
), YIN Yuanyuan, XU Fengqin( )
)
Received:2025-01-09
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-12
摘要:
目的 调查老年单侧全髋关节置换患者术后康复期参与生产性活动现状并分析其影响因素,旨在为临床护理实践提供借鉴。 方法 采用便利抽样方法,选取2024年5—11月连云港市某三级甲等医院关节外科收治的242例老年单侧全髋关节置换患者作为调查对象,于其术后首次下床接受康复训练1周后采用一般资料调查问卷、生产性参与量表、改良Barthel指数评定量表、焦虑自评量表、抑郁自评量表、社区老年人跌倒风险感知量表、恐动症Tampa评分量表17条目版、领悟社会支持量表、老年人社会隔离量表进行调查。 结果 回收有效问卷230份,老年单侧全髋关节置换患者术后康复期生产性参与量表得分为(31.13±3.69)分,多元线性回归分析显示,年龄、文化程度、居住地、BMI是否正常、合并慢性疾病数量、距离手术时间、生活是否能自理、跌倒风险感知、有无恐动症、领悟社会支持和社会隔离是老年单侧全髋关节置换患者术后康复期参与生产性活动的影响因素(P<0.05)。 结论 老年单侧全髋关节置换患者术后康复期参与生产性活动水平较低,并受到多种因素影响,医护人员应根据以上影响因素制订针对性的干预方案,提升其参与生产性活动水平。
陈瑛, 殷媛媛, 许凤琴. 老年单侧全髋关节置换患者康复期参与生产性活动的现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(18): 2223-2230.
CHEN Ying, YIN Yuanyuan, XU Fengqin. Investigation of current status and influencing factors of productive engagement of elderly patients undergoing unilateral total hip arthroplasty in postoperative rehabilitation period[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(18): 2223-2230.
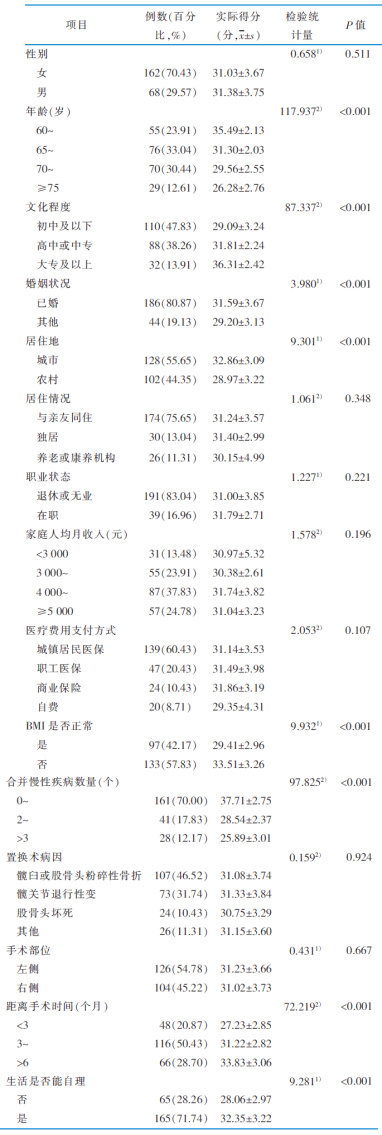 |
表1 老年单侧全髋关节置换患者的一般资料及术后康复期生产性参与量表得分的单因素分析(n=230)
Table 1 Single factor comparison of productive engagement of elderly patients undergoing unilateral total hip arthroplasty in postoperative rehabilitation period(n=230)
 |
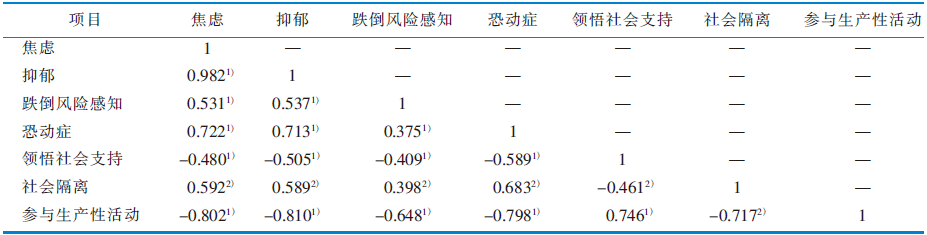 |
表2 老年单侧全髋关节置换患者术后康复期焦虑、抑郁、跌倒风险感知、恐动症、领悟社会支持、社会隔离和参与生产性活动的相关性分析(n=230,r 值)
Table 2 Correlation analysis among anxiety,depression,fall risk perception,tampa, perceived social support,social isolation and productive engagement(n=230,r value)
 |
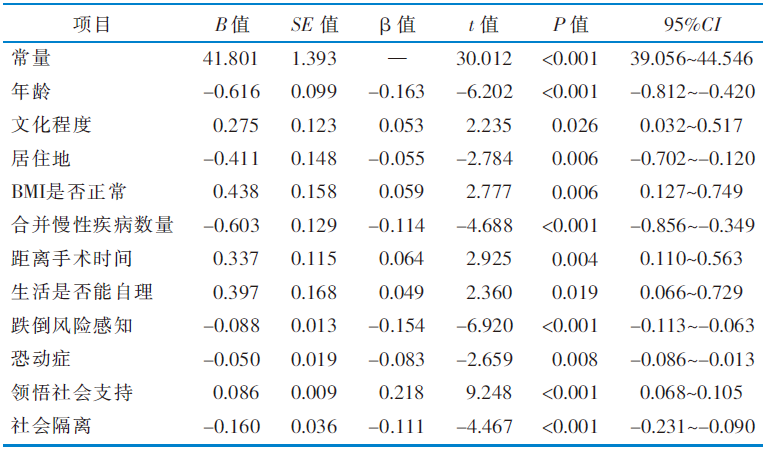 |
表4 老年单侧全髋关节置换患者术后康复期参与生产性活动影响因素的多元线性回归分析结果(n=230)
Table 4 Results of linear regression analysis of influencing factors of elderly patients undergoing unilateral total hip arthroplasty in postoperative rehabilitation period(n=230)
 |
| [1] | Kamp T, Brouwer S, Hylkema TH, et al. Psychosocial working conditions play an important role in the return-to-work process after total knee and hip arthroplasty[J]. J Occup Rehabil, 2022, 32(2):295-305. |
| [2] | 宋靓珺, 吕明阳, 汤衡. 基于分层线性模型的老年人“生产性参与”影响因素研究[J]. 人口与发展, 2020, 26(6):25-39. |
| Song LJ, Lü MY, Tang H. A quantitative study of associated factors for productive engagement in later life based on the hierarchical linear model[J]. Popul Dev, 2020, 26(6):25-39. | |
| [3] |
Shen YJ, Zhao ML, Zhao WY, et al. Development and validation of a questionnaire to evaluate the productive engagement of Chinese older adults in the community[J]. BMC Public Health, 2024, 24(1):3074.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Reissmann M, Storms A, Woopen C. Individual values and spirituality and their meaning for affective well-being and engagement with life in very old age[J]. Z Gerontol Geriatr, 2021, 54(Suppl 2):85-92.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Hill AM, Ross-Adjie G, McPhail SM, et al. Incidence and associated risk factors for falls in older adults postdischarge who undergo elective total hip replacement surgery:a prospective cohort study[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2021, 76(10):1814-1820. |
| [6] | Lenguerrand E, Ben-Shlomo Y, Rangan A, et al. Inequalities in provision of hip and knee replacement surgery for osteoarthritis by age,sex,and social deprivation in England between 2007-2017:a population-based cohort study of the National Joint Registry[J]. PLoS Med, 2023, 20(4):e1004210. |
| [7] | 中华中医药学会骨伤科分会髋关节功能障碍诊疗指南制定工作组. 中医骨伤科临床诊疗指南·人工髋关节置换围手术期康复专家共识[J]. 康复学报, 2017, 27(4):1-6. |
| Dysfunction by the Orthopedics Branch of the Chinese Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Expert consensus for rehabilitation of traditional Chinese medicine in perioperative period of total hip replacement[J]. Rehabil Med, 2017, 27(4):1-6. | |
| [8] | 潘岳松, 金奥铭, 王梦星. 临床研究样本量的估计方法和常见错误[J]. 中国卒中杂志, 2022, 17(1):31-35. |
| Pan YS, Jin AM, Wang MX. Methods and common pitfalls of sample size estimation in clinical studies[J]. Chin J Stroke, 2022, 17(1):31-35. | |
| [9] | Matz-Costa C, James JB, Ludlow L, et al. The meaning and measurement of productive engagement in later life[J]. Soc Indic Res, 2014, 118(3):1293-1314. |
| [10] | 代霜霜, 赵明利, 王雪, 等. 生产性参与量表的汉化及信效度检验[J]. 军事护理, 2024, 41(5):81-84. |
| Dai SS, Zhao ML, Wang X, et al. Chinese version of Productive Engagement Scale:reliability and validity[J]. Mil Nurs, 2024, 41(5):81-84. | |
| [11] | 李小峰, 陈敏. 改良Barthel指数评定量表的设计与应用[J]. 护理研究, 2015, 29(13):1657-1658. |
| Li XF, Chen M. Design and application of improved Barthel Index Rating Scale[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2015, 29(13):1657-1658. | |
| [12] | Zung WW. A Self-rating Depression Scale[J]. Arch Gen Psychiatry, 1965,12:63-70. |
| [13] |
Zung WW. A rating instrument for anxiety disorders[J]. Psychosomatics, 1971, 12(6):371-379.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | 段泉泉, 胜利. 焦虑及抑郁自评量表的临床效度[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2012, 26(9):676-679. |
| Duan QQ, Sheng L. Differential validity of SAS and SDS among psychiatric non-psychotic outpatients and their partners[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 2012, 26(9):676-679. | |
| [15] | 鲍冠君, 罗烨, 刘苑菲, 等. 社区老年人跌倒风险感知量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(24):9-13. |
| Bao GJ, Luo Y, Liu YF, et al. Development of Fall Risk Perception Scale for Community-Dwelling Older Adults:reliability and validity testing[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(24):9-13. | |
| [16] | 胡文. 简体中文版TSK和FABQ量表的文化调适及其在退行性腰腿痛中的应用研究[D]. 上海: 第二军医大学, 2012. |
| Hu W. Cultural adjustment of simplified Chinese TSK and FABQ scale and its application in degenerative lumbago and leg pain[D]. Shanghai: Second Military Medical University, 2012. | |
| [17] | Zimet GD, Powell SS, Farley GK, et al. Psychometric characteristics of the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support[J]. J Pers Assess, 1990, 55(3/4):610-617. |
| [18] | 姜乾金. 领悟社会支持量表[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志, 2001, 10(10):41-43. |
| Jiang QJ. Perceived Social Support Scale[J]. Chin J Behav Med Brain Sci, 2001, 10(10):41-43. | |
| [19] | Nicholson NR, Feinn R, Casey EA, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the Social Isolation Scale in older adults[J]. Gerontologist, 2020, 60(7):e491-e501. |
| [20] | 庞慧. 老年人社会隔离量表(SIS)的汉化及初步应用研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古医科大学, 2021. |
| Pang H. Study on sinicization and preliminary application of Social Isolation Scale for the Elderly(SIS)[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Medical University, 2021. | |
| [21] |
Min K, Beom J, Kim BR, et al. Clinical practice guideline for postoperative rehabilitation in older patients with hip fractures[J]. Ann Rehabil Med, 2021, 45(3):225-259.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Sagherian K, Rose K, Zhu SJ, et al. Productive activities but not paid work relate to well-being in older adults[J]. Res Gerontol Nurs, 2021, 14(1):24-32.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Sia BK, Tey NP, Goh KL, et al. Productive engagement of older adults in China:a multilevel analysis[J]. Geriatr Gerontol Int, 2021, 21(12):1138-1146. |
| [24] | 韦玮, 李剑, 黄林海, 等. 全膝或全髋关节置换后老年人首次活动时跌倒恐惧的影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9):1351-1355. |
| Wei W, Li J, Huang LH, et al. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty[J]. Chin J Tissue Eng Res, 2021, 25(9):1351-1355. | |
| [25] | 黄莉, 杨旭, 李芳芳, 等. 髋、膝关节置换术后患者恐动症发生现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2023, 16(11):1001-1007. |
| Huang L, Yang X, Li FF, et al. Current status and influencing factors of kinesiophobia in patients after hip arthroplasty or knee arthroplasty[J]. Chin J Bone Jt Surg, 2023, 16(11):1001-1007. | |
| [26] |
张亚琴, 李艳婷, 单丹丹, 等. 协同护理模式在全髋关节置换术后恐动症患者中的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(4):515-520.
DOI |
|
Zhang YQ, Li YT, Shan DD, et al. The effect of a collaborative nursing model on patients with kinesiophobia after total hip replacement[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(4):515-520.
DOI |
|
| [27] |
谷斌, 陈绪娜, 张千坤, 等. 全髋关节置换术后患者渐进式平衡训练方案的制订与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(10):1458-1464.
DOI |
|
Gu B, Chen XN, Zhang QK, et al. Formulation and application of a progressive balance training program after total hip arthroplasty[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(10):1458-1464.
DOI |
|
| [28] | 刘珊, 张先庚, 杨玲娜, 等. 社会支持在老年全髋关节置换术患者疾病不确定感与出院准备度间的中介效应[J]. 成都医学院学报, 2023, 18(1):87-90. |
| Liu S, Zhang XG, Yang LN, et al. Mediating effect of social support between disease uncertainty and discharge readiness in elderly patients after total hip replacement[J]. J Chengdu Med Coll, 2023, 18(1):87-90. | |
| [29] | Luo H, Wong GHY, Tang JYM, et al. Perceived life expectancy predicts time investment in productive aging activities:an ecological momentary assessment study[J]. Res Aging, 2022, 44(1):73-82. |
| [30] |
尹艳茹, 周洪昌, 刘梦如, 等. 老年维持性血液透析患者社会隔离现状的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(7):822-828.
DOI |
|
Yin YR, Zhou HC, Liu MR, et al. Status and influencing factors of social isolation in elderly patients with maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(7):822-828.
DOI |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||