


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (13): 1588-1594.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.13.009
陈阳( ), 王诗瑜, 高川, 蔡文清, 苏雅静, 张雨萌, 李庆印(
), 王诗瑜, 高川, 蔡文清, 苏雅静, 张雨萌, 李庆印( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-09
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-07-03
通讯作者:
李庆印,E-mail:fuwainursing@163.com作者简介:陈阳:女,本科(硕士在读),护师,E-mail:vivianchan8622@163.com
基金资助:
CHEN Yang( ), WANG Shiyu, GAO Chuan, CAI Wenqing, SU Yajing, ZHANG Yumeng, LI Qingyin(
), WANG Shiyu, GAO Chuan, CAI Wenqing, SU Yajing, ZHANG Yumeng, LI Qingyin( )
)
Received:2024-10-09
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-07-03
摘要:
目的 评估75岁以上行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(percutaneous coronary intervention,PCI)术后患者的衰弱现状及危险因素,为改善、延缓其衰弱状态提供参考。方法 于2024年3月—8月,采用便利抽样法,选取北京市某三级甲等心血管病专科医院行PCI治疗的75岁以上患者作为调查对象,采用自行设计的一般资料调查表收集患者相关信息,于术后至出院前分别使用Fried衰弱表型、katz指数、工具性日常生活活动能力量表、Charlson共病指数、Morse跌倒评估量表、微型营养评定简表、简版老年抑郁量表进行综合评估。采用单因素及多因素Logistic回归分析PCI术后患者合并衰弱的影响因素。结果 最终纳入患者278例,PCI术后衰弱发生率为52.16%,按照Fried衰弱表型评分分为非衰弱组和衰弱组,单因素分析显示,两组年龄、性别、血红蛋白、N末端脑钠肽前体、左心室射血分数、工具性日常生活活动能力量表得分、是否独居、营养状况、跌倒风险、抑郁程度等方面的比较,差异具有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析显示,年龄、工具性日常生活活动能力量表得分、跌倒风险、营养状况、抑郁程度是衰弱的影响因素,OR值分别为1.167、0.575、1.597、0.399、3.610(均P<0.05)。结论 75岁以上PCI术后患者衰弱发生率较高,其影响因素较多,临床医护人员要重视对这类患者的长期管理,结合老年人生理、心理及社会情况等进行综合干预。
陈阳, 王诗瑜, 高川, 蔡文清, 苏雅静, 张雨萌, 李庆印. 75岁以上经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者衰弱现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(13): 1588-1594.
CHEN Yang, WANG Shiyu, GAO Chuan, CAI Wenqing, SU Yajing, ZHANG Yumeng, LI Qingyin. Analysis of the current status and influencing factors of frailty in patients aged 75 and above after percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(13): 1588-1594.
 |
表1 研究对象的一般资料及衰弱单因素分析
Table 1 General characteristics and univariate analysis results of the influencing factors of frailty in elderly patients with coronary heart disease after PCI
 |
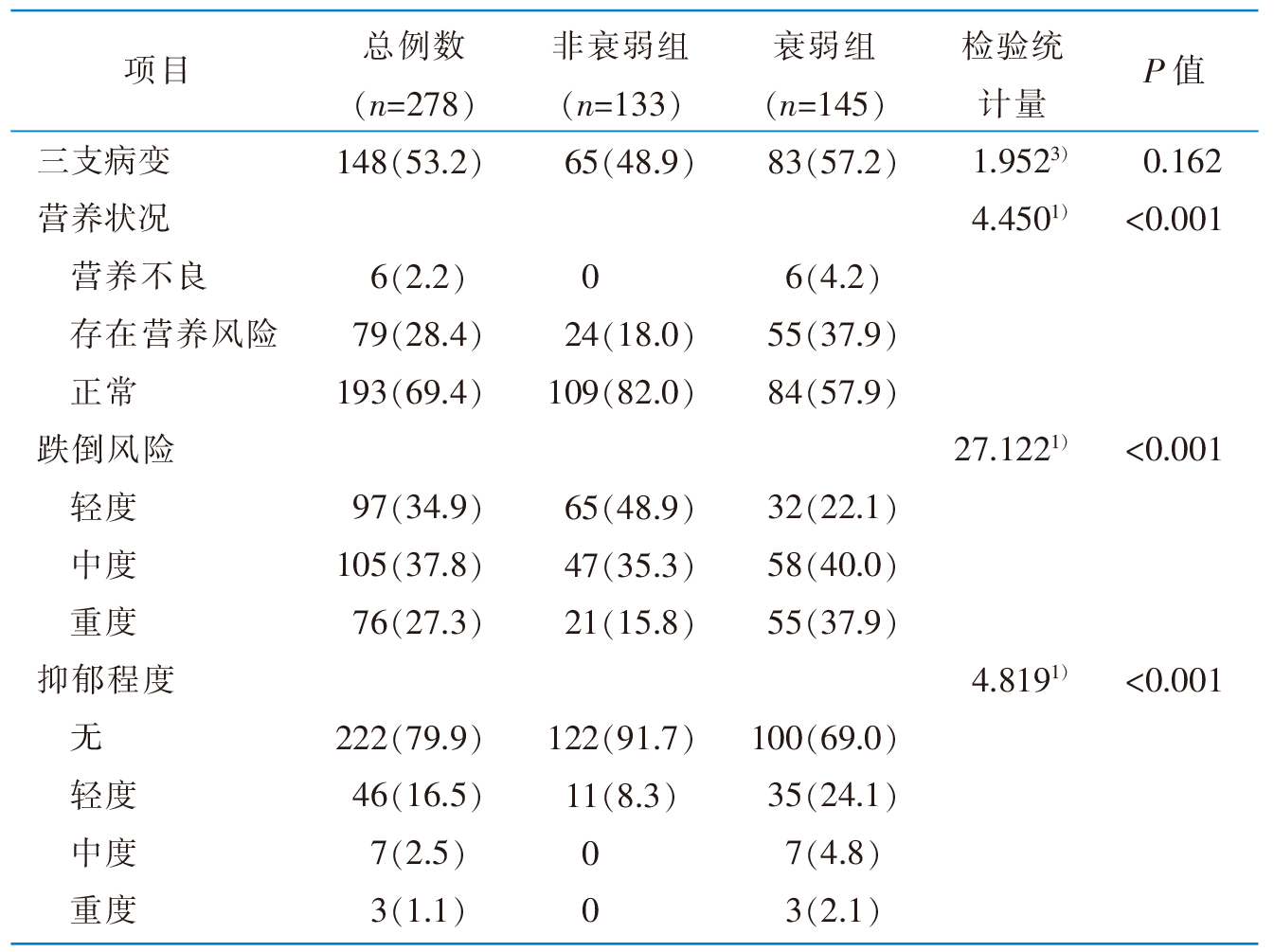 |
续表1 研究对象的一般资料及衰弱单因素分析
Table 1(Continued) General characteristics and univariate analysis results of the influencing factors of frailty in elderly patients with coronary heart disease after PCI
 |
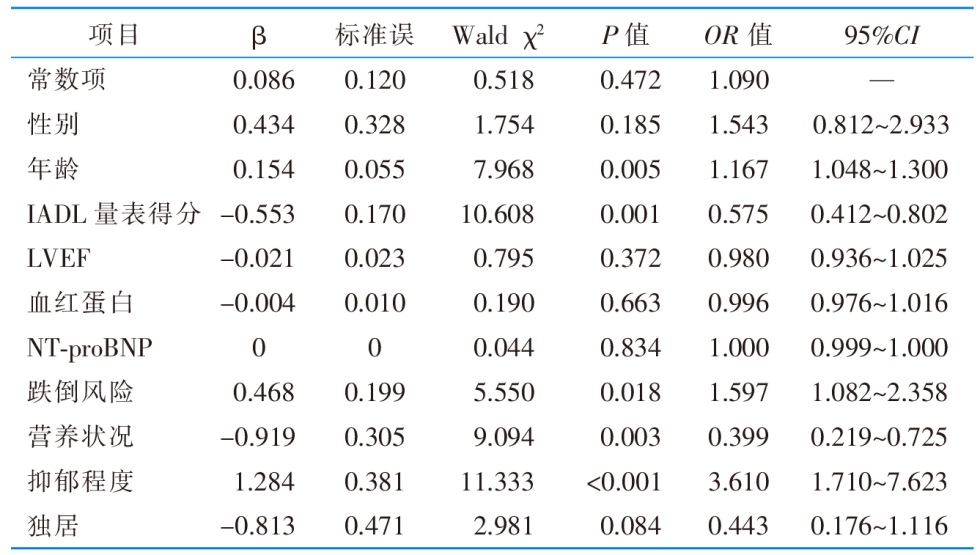 |
表3 75岁以上经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者衰弱多因素Logistic回归分析(n=278)
Table 3 Binary logistic regression analysis of the influencing factors of frailty in patients aged 75 and above after PCI(n=278)
 |
| [1] | 刘明波, 何新叶, 杨晓红, 等. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2023》要点解读[J]. 中国心血管杂志, 2024, 29(4):305-324. |
| Liu MB, He XY, Yang XH, et al. Interpretation of report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2023[J]. Chin J Cardiovasc Med, 2024, 29(4):305-324. | |
| [2] | 中国医师协会心血管内科医师分会预防与康复专业委员会. 经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后运动康复专家共识[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2016, 24(7):361-369. |
| Prevention and Rehabilitation Professional Committee of the Cardiovascular Physician Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Expert consensus on sports rehabilitation after percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Chin J Interv Cardiol, 2016, 24(7):361-369. | |
| [3] | 中华医学会老年医学分会, 高龄老年冠心病诊治中国专家共识写作组. 高龄老年冠心病诊治中国专家共识[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2016, 35(7):683-691. |
| Geriatrics Medicine Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Writing Group of China Expert Consensus of Diagnosis and Treatment of Senile Coronary Heart Disease. China expert consensus of diagnosis and treatment of senile coronary heart diseasee[J]. Chin J Geriatr, 2016, 35(7):683-691. | |
| [4] | Camici GG, Liberale L. Aging:the next cardiovascular disease?[J]. Eur Heart J, 2017, 38(21):1621-1623. |
| [5] | 刘淼, 何耀, 吴蕾, 等. 老年综合征的定义、评估工具及应用[J]. 中华保健医学杂志, 2015, 17(6):513-515. |
| Liu M, He Y, Wu L, et al. Definition,evaluation tool and application of senile syndrome[J]. Chin J Health Care Med, 2015, 17(6):513-515. | |
| [6] | James K, Jamil Y, Kumar M, et al. Frailty and cardiovascular health[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2024, 13(15):e031736. |
| [7] | 顾莹珍, 党爱民. 衰弱与动脉粥样硬化[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2021, 23(9):997-999. |
| Gu YZ, Dang AM. Frailty and atherosclerosis[J]. Chin J Geriatr Heart Brain Vessel Dis, 2021, 23(9):997-999. | |
| [8] | Yoshioka N, Takagi K, Morishima I, et al. Influence of preadmission frailty on short-and mid-term prognoses in octogenarians with ST-elevation myocardial infarction[J]. Circ J, 2019, 84(1):109-118. |
| [9] | Zong M, Guan XN, Huang W, et al. Effect of frailty on the long-term prognosis of elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2023, 18:2021-2029. |
| [10] | van Wyk GW, Berkovsky S, Fraile Navarro D, et al. Comparing health outcomes between coronary interventions in frail patients aged 75 years or older with acute coronary syndrome:a systematic review[J]. Eur Geriatr Med, 2022, 13(5):1057-1069. |
| [11] | Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, et al. Frailty in older adults:evidence for a phenotype[J]. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2001, 56(3):M146-M156. |
| [12] | 吴珍珍, 张瑞, 常艳, 等. 衰弱表型和衰弱筛查量表在老年住院患者中的应用比较[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(5):673-679. |
| Wu ZZ, Zhang R, Chang Y, et al. Application comparison of Frailty Phenotype and FRAIL Scale in frailty risk screening of elderly inpatients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(5):673-679. | |
| [13] | Katz S, Downs TD, Cash HR, et al. Progress in development of the index of ADL[J]. Gerontologist, 1970, 10(1):20-30. |
| [14] | Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people:self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living[J]. Gerontologist, 1969, 9(3):179-186. |
| [15] | Rubenstein LZ, Harker JO, Salvà A, et al. Screening for undernutrition in geriatric practice:developing the short-form Mini-Nutritional Assessment(MNA-SF)[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2001, 56(6):M366-M372. |
| [16] | 罗芳, 范华霞, 张芹飞, 等. 三种方法对住院老年稳定性冠心病患者的营养风险状况筛查分析[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2023, 25(9):945-948. |
| Luo F, Fan HX, Zhang QF, et al. Analysis of three screening tools of nutritional risk of elderly inpatients with stable coronary heart disease[J]. Chin J Geriatr Heart Brain Vessel Dis, 2023, 25(9):945-948. | |
| [17] | Bannay A, Chaignot C, Blotière PO, et al. The best use of the charlson comorbidity index with electronic health care data-base to predict mortality[J]. Med Care, 2016, 54(2):188-194. |
| [18] | Sheng S, Xu FQ, Zhang YH, et al. Charlson Comorbidity Index is correlated with all-cause readmission within six months in patients with heart failure:a retrospective cohort study in China[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2023, 23(1):111. |
| [19] | Morse JM, Black C, Oberle K, et al. A prospective study to identify the fall-prone patient[J]. Soc Sci Med, 1989, 28(1):81-86. |
| [20] | 周君桂. 中文版Morse跌倒评估量表用于住院老年患者跌倒风险评估的初步研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2010. |
| Zhou JG. A preliminary study on the Chinese version of Morse Fall Assessment Scale for the fall risk assessment of hospitalized elderly patients[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2010. | |
| [21] | 唐玮, 甘秀妮, 刘章会, 等. 汉化Morse跌倒评估量表在中国临床护理中应用的可行性[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2010, 39(11):943-946. |
| Tang W, Gan XN, Liu ZH, et al. Feasibility of the Chinesized Morse Fall Scale in clinical nursing[J]. J China Med Univ, 2010, 39(11):943-946. | |
| [22] | Sheikh J, Yesavage J. Geriatric Depression Scale(GDS):recent evidence and development of a shorter version[J]. Clin Gerontol, 2016,5:165-173. |
| [23] | 唐丹. 简版老年抑郁量表(GDS-15)在中国老年人中的使用[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2013, 21(3):402-405. |
| Tang D. Application of Short Form Geriatric Depression Scale(GDS-15) in Chinese elderly[J]. Chin J Clin Psych, 2013, 21(3):402-405. | |
| [24] | 李娟利, 王小芹, 肖懿慧, 等. 75岁以上女性冠心病PCI术后衰弱风险预测模型的构建[J]. 中国妇幼健康研究, 2021, 32(10):1469-1475. |
| Li JL, Wang XQ, Xiao YH, et al. Development of a risk prediction model on frailty after PCI for female coronary heart disease patients over 75 years old[J]. Chin J Woman and Child Health Res, 2021, 32(10):1469-1475. | |
| [25] | Halvorsen S, Mehilli J, Cassese S, et al. 2022 ESC guidelines on cardiovascular assessment and management of patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery[J]. Eur Heart J, 2022, 43(39):3826-3924. |
| [26] | Murali-Krishnan R, Iqbal J, Rowe R, et al. Impact of frailty on outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention:a prospective cohort study[J]. Open Heart, 2015, 2(1):e000294. |
| [27] | 王洪梅, 李娜, 王红, 等. 住院老年眩晕患者衰弱现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(2):205-210. |
| Wang HM, Li N, Wang H, et al. The current situation and influential factors of frailty in elderly patient with vertigo[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(2):205-210. | |
| [28] | 姚丽, 马慧, 张康宁. 老年冠状动脉内支架植入患者衰弱现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 当代护士, 2024, 31(6):127-131. |
| Yao L, Ma H, Zhang KN. Analysis of weakness and its influencing factors in elderly patients with coronary stent implantation[J]. Mod Nurse, 2024, 31(6):127-131. | |
| [29] | Cacciatore S, Spadafora L, Bernardi M, et al. Management of coronary artery disease in older adults:recent advan-ces and gaps in evidence[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(16):5233. |
| [30] | 王英杰, 刘薇, 朱宏伟, 等. 老年衰弱患者肌力训练干预方案的构建及应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(14):1669-1677. |
| Wang YJ, Liu W, Zhu HW, et al. Construction and application of muscle strength training program for the elderly frail patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(14):1669-1677. | |
| [31] | Rawashdeh SI, Ibdah R, Kheirallah KA, et al. Prevalence estimates,severity,and risk factors of depressive symptoms among coronary artery disease patients after ten days of percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health, 2021, 17:103-113. |
| [32] | 梁倩, 汪晓丽, 刘梦琪, 等. 多组分运动护理干预在老年慢性心力衰竭合并衰弱患者中的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(23):2821-2828. |
| Liang Q, Wang XL, Liu MQ, et al. Effects of multi-component exercise nursing intervention on frailty in elderly patients with chronic heart failure[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(23):2821-2828. | |
| [33] | Mangalesh S, Daniel KV, Dudani S, et al. Combined nutritional and frailty screening improves assessment of short-term prognosis in older adults following percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Coron Artery Dis, 2023, 34(3):185-194. |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||