


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (10): 1164-1170.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.10.002
李蕊( ), 宋红(
), 宋红( ), 张春艳, 耿黎明, 蔡文娟, 李一帆
), 张春艳, 耿黎明, 蔡文娟, 李一帆
收稿日期:2024-11-05
出版日期:2025-05-20
发布日期:2025-05-13
通讯作者:
宋红,E-mail:songhong197712@163.com作者简介:李蕊:女,硕士,主管护师,E-mail:vividlee2011@126.com
基金资助:
LI Rui( ), SONG Hong(
), SONG Hong( ), ZHANG Chunyan, GENG Liming, CAI Wenjuan, LI Yifan
), ZHANG Chunyan, GENG Liming, CAI Wenjuan, LI Yifan
Received:2024-11-05
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-13
摘要:
目的 探讨老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折术后邻近椎体再骨折患者(简称“老年邻近椎体再骨折患者”)运动恐惧在家庭功能及锻炼依从性间的纵向中介作用。方法 采用便利抽样法,选取2022年1月—2024年2月徐州市某三级甲等医院骨科收治的233例老年邻近椎体再骨折患者作为调查对象,采用家庭关怀度指数、功能锻炼依从性量表及运动恐惧评分量表对其进行纵向调查。采用无条件潜变量增长模型、结构方程及Bootstrap法进行统计分析。结果 回收有效问卷232份。纵向中介模型显示,老年邻近椎体再骨折患者的家庭功能的截距负向预测其运动恐惧的截距(β=-0.456,P<0.001),家庭功能的斜率负向预测运动恐惧的斜率(β=-0.962,P<0.001)。老年邻近椎体再骨折患者的运动恐惧的截距能负向预测其锻炼依从性的截距(β=-0.623,P<0.001),并负向预测锻炼依从性的斜率(β=-0.354,P=0.013)。结论 老年邻近椎体再骨折患者的运动恐惧初始水平和变化速率在家庭功能对锻炼依从性影响中起完全纵向中介作用。建议医护人员针对患者的家庭功能、运动恐惧进行评估和管理,利用其相互关系,以改善患者的锻炼依从性水平。
李蕊, 宋红, 张春艳, 耿黎明, 蔡文娟, 李一帆. 老年邻近椎体再骨折患者家庭功能与锻炼依从性的相关性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(10): 1164-1170.
LI Rui, SONG Hong, ZHANG Chunyan, GENG Liming, CAI Wenjuan, LI Yifan. The effect of family functioning on exercise adherence in elderly patients with postoperative vertebral compression fractures and adjacent vertebral re-fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(10): 1164-1170.
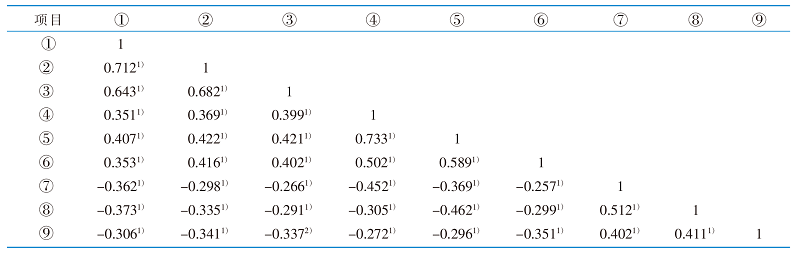 |
表2 老年邻近椎体再骨折患者3个时间点家庭功能、锻炼依从性与运动恐惧的相关性分析(r 值,n=232)
Table 2 Correlation analysis of home functioning,exercise adherence and kinesophobia in elderly patients with vertebral re-fracture adjacent after OVCF at 3 time points(r value,n=232)
 |
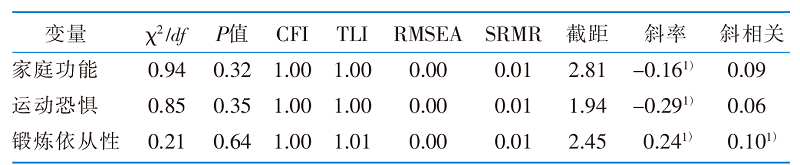 |
表3 老年邻近椎体再骨折患者家庭功能、锻炼依从性及运动恐惧线性无条件潜变量增长模型的拟合指数和系数(n=232)
Table 3 Fitting indices and coefficients of a linear unconditional potential growth model of home functioning,exercise adherence,and kinesophobia in elderly patients with vertebral re-fracture adjacent after OVCF(n=232)
 |
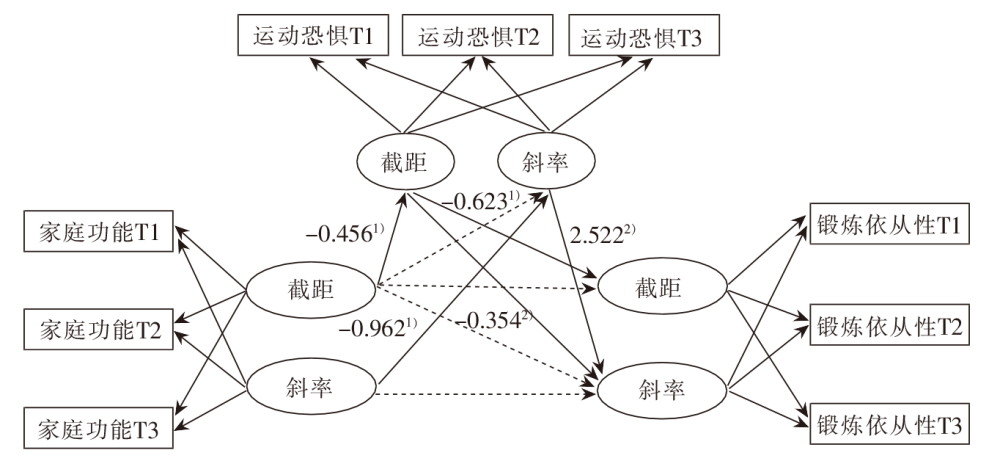
图1 运动恐惧在老年邻近椎体再骨折患者家庭功能及锻炼依从性间的纵向中介模型 注:T1为术前,T2为术后下床前,T3为术后1个月。 1)P<0.001,2)P<0.05。
Figure 1 A longitudinal mediation model of kinesophobia between family functioning and exercise adherence in elderly patients with vertebral re-fracture adjacent after OVCF
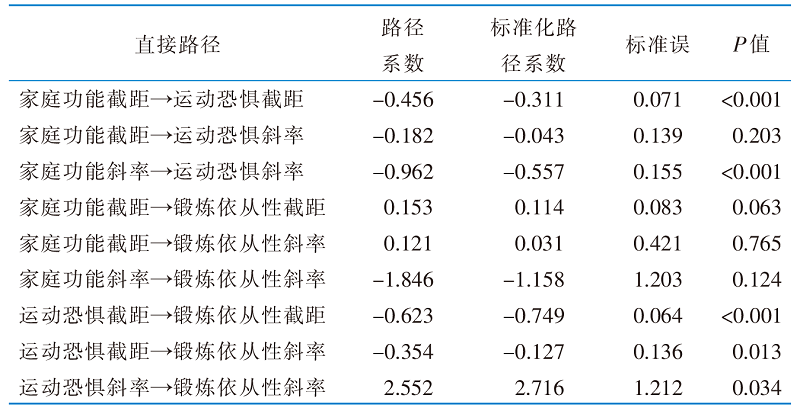 |
表4 运动恐惧在老年邻近椎体再骨折患者家庭功能及锻炼依从性间的纵向中介模型中的直接路径(n=232)
Table 4 Direct pathways of kinesophobia in a longitudinal mediation model between family functioning and exercise adherence in elderly patients with vertebral re-fracture adjacent after OVCF(n=232)
 |
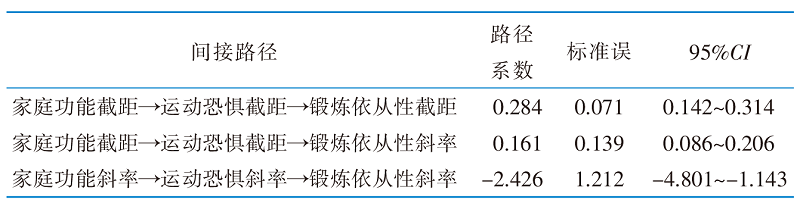 |
表5 运动恐惧在老年邻近椎体再骨折患者家庭功能及锻炼依从性间的纵向中介模型中的间接路径(n=232)
Table 5 Indirect pathways of kinesophobia in a longitudinal mediation model between family functioning and exercise adherence in elderly patients with vertebral re-fracture adjacent after OVCF(n=232)
 |
| [1] |
Ling X, Cummings SR, Mingwei Q, et al. Vertebral fractures in Beijing,China:the Beijing osteoporosis project[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2000, 15(10):2019-2025.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Liang DW, Pei J, Pei RY, et al. Clinical efficacy of percutaneous vertebroplasty versus percutaneous kyphoplasty treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with kyphosis[J]. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg, 2024, 50(3):1043-1049. |
| [3] |
Liu DH, Xu J, Wang Q, et al. Timing of percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures[J]. Pain Physician, 2023, 26(3):231-243.
PMID |
| [4] | Ko BS, Cho KJ, Park JW. Early adjacent vertebral fractures after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures[J]. Asian Spine J, 2019, 13(2):210-215. |
| [5] |
Hwang SH, Cho PG, Kim KT, et al. What are the risk factors for a second osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture?[J]. Spine J, 2023, 23(11):1586-1592.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Zhang AQ, Lin YC, Kong MX, et al. A nomogram for predicting the risk of new vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous kyphoplasty[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2023, 28(1):280.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
徐榕璟, 贺旭妍, 贾守梅. 骨科老年患者术后运动恐惧的范围综述[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(5):626-633.
DOI |
|
Xu RJ, He XY, Jia SM. A scoping review of kinesiophobia research in elderly orthopedic postoperative patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(5):626-633.
DOI |
|
| [8] |
罗屹惟, 程悦, 罗如珍, 等. 骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折患者术后居家康复体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(10):1165-1171.
DOI |
| Luo YW, Cheng Y, Luo RZ, et al. Experiences of home-based rehabilitation continuity care after osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture:a qualitative study[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(10):1165-1171. | |
| [9] | Bäck M, Caldenius V, Svensson L, et al. Perceptions of kinesiophobia in relation to physical activity and exercise after myocardial infarction:a qualitative study[J]. Phys Ther, 2020, 100(12):2110-2119. |
| [10] | Yu L, Guo YL, Che T. The effect of Pilates exercise nursing combined with communication standard-reaching theory nursing and pelvic floor muscle training on bladder function and family function of patients after cervical cancer surgery[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2022, 2022:6444462. |
| [11] |
Camacho PM, Petak SM, Binkley N, et al. American association of clinical endocrinologists/American college of endocrinology clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis-2020 update[J]. Endocr Pract, 2020, 26(Suppl 1):1-46.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | 陈楠, 刘红云. 基于增长模型的非随机缺失数据处理:选择模型和极大似然方法[J]. 心理科学, 2015, 38(2):446-451. |
| Chen N, Liu HY. Comparison of methods addressing MNAR missing data when fitting a latent growth model:selection model and ML[J]. J Psychol Sci, 2015, 38(2):446-451. | |
| [13] | Smilkstein G. The family APGAR:a proposal for a family function test and its use by physicians[J]. J Fam Pract, 1978, 6(6):1231-1239. |
| [14] | 吕繁, 曾光, 刘松暖, 等. 家庭关怀度指数问卷测量脑血管病病人家庭功能的信度和效度研究[J]. 中国公共卫生, 1999, 15(11):987-988. |
| Lü F, Zeng G, Liu SN, et al. Reliability and validity of the Family Care Index Questionnaire for measuring family functioning in patients with cerebrovascular disease[J]. Chin J Public Health, 1999, 15(11):987-988. | |
| [15] | 谭媛媛, 和晖, 杨秀贤, 等. 骨科患者功能锻炼依从性量表的编制及信度效度检验[J]. 中国护理管理, 2019, 19(11):1626-1631. |
| Tan YY, He H, Yang XX, et al. Development and reliability and validity test of the Compliance Scale of Functional Exercise for Orthopedic Patients[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2019, 19(11):1626-1631. | |
| [16] | 胡文. 简体中文版TSK和FABQ量表的文化调适及其在退行性腰腿痛中的应用研究[D]. 上海: 第二军医大学, 2012. |
| Hu W. Cultural adjustment of simplified Chinese TSK and FABQ Scale and its application in degenerative lumbago and leg pain[D]. Shanghai: Second Military Medical University, 2012. | |
| [17] | 汤丹丹, 温忠麟. 共同方法偏差检验:问题与建议[J]. 心理科学, 2020, 43(1):215-223. |
| Tang DD, Wen ZL. Statistical approaches for testing common method bias:problems and suggestions[J]. J Psychol Sci, 2020, 43(1):215-223. | |
| [18] | 钟梅艳, 莫忠贵, 唐海军, 等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折二级预防依从性现状及其影响因素的统计分析[J]. 解放军预防医学杂志, 2020, 38(5):69-72. |
| Zhong MY, Mo ZG, Tang HJ, et al. Statistical analysis of compliance status and influencing factors of secondary prevention of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture[J]. J Prev Med Chin PLA, 2020, 38(5):69-72. | |
| [19] | Gawulayo S, Erasmus CJ, Rhoda AJ. Family functioning and stroke:family members’ perspectives[J]. Afr J Disabil, 2021, 10:801. |
| [20] | Chang LX, Zhang SJ, Yan ZP, et al. Symptom burden,family resilience,and functional exercise adherence among postoperative breast cancer patients[J]. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs, 2022, 9(11):100129. |
| [21] |
Zakiei A, Vafapoor H, Alikhani M, et al. The relationship between family function and personality traits with general self-efficacy(parallel samples studies)[J]. BMC Psychol, 2020, 8(1):88.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Rosenblatt A, Greenberg J, Solomon S, et al. Evidence for terror management theory:I. the effects of mortality salience on reactions to those who violate or uphold cultural values[J]. J Pers Soc Psychol, 1989, 57(4):681-690.
PMID |
| [23] | Wang Q, Du N. Relationship between kinesiophobia and quality of life among patients with breast cancer-related lymphedema:chain-mediating effect of self-care and functional exercise compliance[J]. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs, 2024, 11(1):100346. |
| [24] |
梁琪, 胡三莲, 韦小梅, 等. 前交叉韧带重建术后患者运动恐惧的研究进展及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(24):3049-3054.
DOI |
|
Liang Q, Hu SL, Wei XM, et al. Research progress on kinesiophobia in patients after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and nursing enlightenment[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(24):3049-3054.
DOI |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||