


中华护理杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 396-403.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2025.04.002
李瑞华( ), 甄莉, 朱木兰, 叶新梅, 秦芳, 张星星, 林梅燕, 李国新(
), 甄莉, 朱木兰, 叶新梅, 秦芳, 张星星, 林梅燕, 李国新( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-13
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2025-02-26
通讯作者:
李国新,E-mail:gzliguoxin@163.com作者简介:李瑞华:女,本科(硕士在读),护士,E-mail:ruihuali2000@163.com
基金资助:
LI Ruihua( ), ZHEN Li, ZHU Mulan, YE Xinmei, QIN Fang, ZHANG Xingxing, LIN Meiyan, LI Guoxin(
), ZHEN Li, ZHU Mulan, YE Xinmei, QIN Fang, ZHANG Xingxing, LIN Meiyan, LI Guoxin( )
)
Received:2024-05-13
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-02-26
摘要:
目的 了解预防性回肠造口患者的营养状况并分析其影响因素,为医护人员制订营养干预策略提供依据。 方法 采用便利抽样法,于2023年11月—2024年7月选取在广州市4所三级甲等医院复诊或住院等待还纳的239例预防性回肠造口患者为调查对象,采用一般资料调查问卷和患者主观整体营养状况评估工具进行调查,采用单因素分析和多因素有序Logistic回归分析预防性回肠造口患者营养状况的影响因素。 结果 共回收有效问卷227份,有效问卷回收率为94.98%,其中营养良好或可疑营养不良组64例(28.19%),中度营养不良组104例(45.81%),重度营养不良组59例(25.99%)。多因素有序Logistic回归分析结果显示,术前累计化疗周期、术后时间、年龄、当前饮食类型、有无摄入口服营养补充剂(oral nutritional supplements,ONS)、有无肠造口并发症和造口自我护理能力是预防性回肠造口患者营养状况的影响因素(P<0.05)。 结论 预防性回肠造口患者的中、重度营养不良发生率较高,ONS的摄入并未有效改善其营养状况。术前累计化疗周期多、术后时间较短、年龄≥65岁、流质饮食或半流质饮食、存在肠造口并发症和造口自我护理能力不足的患者营养状况较差。建议医护人员根据相关影响因素制订干预策略,以改善预防性回肠造口患者的营养状况。
李瑞华, 甄莉, 朱木兰, 叶新梅, 秦芳, 张星星, 林梅燕, 李国新. 预防性回肠造口患者营养状况及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(4): 396-403.
LI Ruihua, ZHEN Li, ZHU Mulan, YE Xinmei, QIN Fang, ZHANG Xingxing, LIN Meiyan, LI Guoxin. Nutritional status and influencing factors in patients undergoing preventive ileostomy[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2025, 60(4): 396-403.
 |
表1 调查对象的一般资料及营养状况单因素分析结果(n=227)
Table 1 General information of the respondents and results of univariate analysis on the influencing factors of nutritional status(n=227)
 |
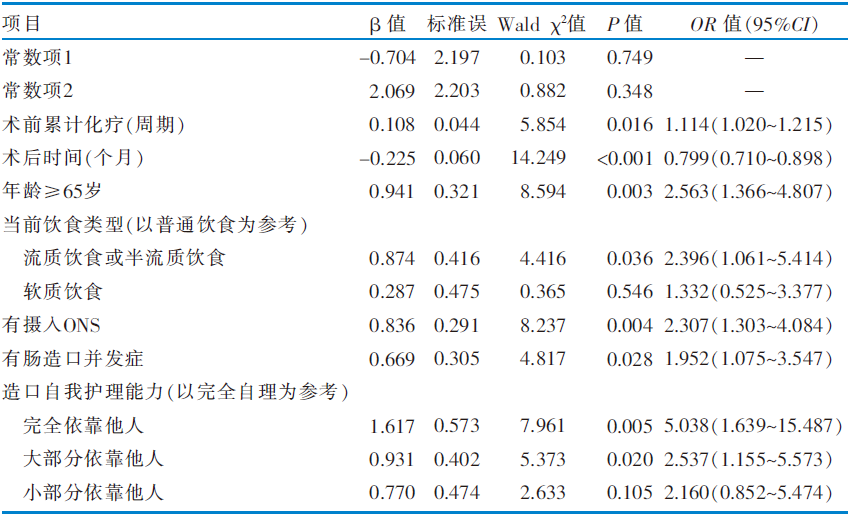 |
表3 预防性回肠造口患者营养状况影响因素的有序Logistic回归分析结果(n=227)
Table 1 Ordinal Logistic regression analysis of the influencing factors of nutritional status in patients undergoing preventive ileostomy(n=227)
 |
| [1] | 中国医师协会肛肠医师分会造口专业委员会, 中国医师协会肛肠医师分会, 中华医学会外科学分会结直肠外科学组, 等. 中低位直肠癌手术预防性肠造口中国专家共识(2022版)[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2022, 25(6):741-748. |
| Ostomy Professional Committee, Chinese Society of Coloproc-tology, Chinese Medical Doctor Association; Chinese Society of Colorectal Surgery, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association; Colorectal Tumor Professional Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association; et al. Chinese expert consensus on protective ostomy for mid-low rectal cancer(version 2022)[J]. Chin J Gastrointest Surg, 2022, 25(6):741-748. | |
| [2] |
England C, Mitchell A, Atkinson C. Diet after ileostomy study:an observational study describing dietary intake and stoma-related symptoms in people with an ileostomy[J]. J Hum Nutr Diet, 2023, 36(4):1600-1612.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Santamaría MM, Villafranca JJA, Abilés J, et al. Impact of a nutrition consultation on the rate of high output stoma-related readmission:an ambispective cohort study[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1):16620.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Martellucci J, Balestri R, Brusciano L, et al. Ileostomy versus colostomy:impact on functional outcomes after total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer[J]. Colorectal Dis, 2023, 25(8):1686-1693.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Shiraishi T, Ogawa H, Katayama C, et al. The presurgical controlling nutritional status(CONUT) score is independently associated with severe peristomal skin disorders:a single-center retrospective cohort study[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1):18857.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Abe S, Nozawa H, Sasaki K, et al. Nutritional status indicators predict tolerability to adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with stage Ⅱ/Ⅲ rectal cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy[J/OL]. Digestion, 2024,105:345-358. |
| [7] | 杜茜茜, 邹其云, 霍明科, 等. 结直肠癌回肠造口患者营养状况与社会心理适应的关系研究[J]. 护理管理杂志, 2019, 19(12):845-848. |
| Du XX, Zou QY, Huo MK, et al. Correlation between nutritional status and psychosocial adaptation in colorectal cancer patients with ileostomy[J]. J Nurs Adm, 2019, 19(12):845-848. | |
| [8] | 林鸿缘, 陈璟, 刘颖洁, 等. 直肠癌预防性回肠造口患者的营养教育[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(10):10-14. |
| Lin HY, Chen J, Liu YJ, et al. Nutrition education for patients with rectal cancer undergoing prophylactic ileostomy[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2022, 37(10):10-14. | |
| [9] | 李乐之, 路潜. 外科护理学[M]. 7版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2021:422. |
| Li LZ, Lu Q. Surgical nursing[M]. 7th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House,2021:422. | |
| [10] | 倪平, 陈京立, 刘娜. 护理研究中量性研究的样本量估计[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010, 45(4):378-380. |
| Ni P, Chen JL, Liu N. The sample size estimation in quantitative nursing research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010, 45(4):378-380. | |
| [11] | 中国造口管理协作组, 中华护理学会伤口造口失禁护理专业委员会, 中国医师协会外科医师分会结直肠医师专业委员会, 等. 肠造口并发症的分型与分级标准(2023版)[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2023, 26(10):915-921. |
| The Chinese Ostomy Collaboration Group; Wound, Ostomy,and Continence Nursing Committee of Chinese Nursing Association; Colon and Rectal Surgeon Committee of Surgeon Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, et al. Criteria of enterostomy complications:classification and grading(2023 edition)[J]. Chin J Gastrointest Surg, 2023, 26(10):915-921. | |
| [12] |
Ottery FD. Rethinking nutritional support of the cancer patient:the new field of nutritional oncology[J]. Semin Oncol, 1994, 21(6):770-778.
PMID |
| [13] |
Bauer J, Capra S, Ferguson M. Use of the scored Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment(PG-SGA) as a nutrition assessment tool in patients with cancer[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2002, 56(8):779-785.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 肿瘤患者主观整体营养评估(WS/T 555-2017)[S/OL]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017:1-7[2023-08-23]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/yingyang/201708/fb23588e8ea64da7ae93c8d81b1fa663.shtml. |
| National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Subjective nutrition assessment for cancer patients(WS/T 555-2017)[S/OL]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2017:1-7[2023-08-23]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/yingyang/201708/fb23588e8ea64da7ae93c8d81b1fa663.shtml. | |
| [15] | 中华护理学会伤口、造口、失禁护理专业委员会. 成人肠造口护理标准[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(增刊):15-19. |
| Wound, Ostomy,and Continence Nursing Committee of Chinese Nursing Association. Nursing care for adult stoma patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(Suppl):15-19. | |
| [16] | Daly LE, Ní Bhuachalla éB, Power DG, et al. Loss of skeletal muscle during systemic chemotherapy is prognostic of poor survival in patients with foregut cancer[J]. J Cachexia Sar-copenia Muscle, 2018, 9(2):315-325. |
| [17] | Willett CG. Neoadjuvant therapy for rectal adenocarcinoma[EB/OL]. (2024-03-08)[2024-08-07]. https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/neoadjuvant-therapy-for-rectal-adenocarcinoma. |
| [18] | Rowe KM, Schiller LR. Ileostomy diarrhea:pathophysiology and management[J]. Proc(Bayl Univ Med Cent), 2020, 33(2):218-226. |
| [19] |
Whiteley I, Randall S, Fetheny J, et al. Comparison of adjustment to a temporary or permanent ostomy using the OAI-23[J]. Colorectal Dis, 2024, 26(6):1231-1238.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | 汤玉梅, 张桂菊, 马静. 老年肠造口患者症状群与生活质量的相关性[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2022, 42(2):477-480. |
| Tang YM, Zhang GJ, Ma J. Correlation between symptom groups and quality of life in elderly patients with enterostomy[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2022, 42(2):477-480. | |
| [21] | Ritchie C. Geriatric nutrition:nutritional issues in older adults[EB/OL]. (2023-03-23)[2024-07-11]. https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/zh-Hans/geriatric-nutrition-nutritional-issues-in-older-adults?search=Geriatric%20nutrition%3A%20nutritional%20issues%20in%20older%20adults&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1%7E150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1. |
| [22] |
Weimann A, Braga M, Carli F, et al. ESPEN practical guide-line:clinical nutrition in surgery[J]. Clin Nutr, 2021, 40(7):4745-4761.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
刘莺歌, 吴燕, 曹秋君, 等. 肠造口周围潮湿相关性皮肤损伤风险预测模型的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(11):1612-1617.
DOI URL |
|
Liu YG, Wu Y, Cao QJ, et al. The development and validation of a risk prediction model for peristomal moisture-associated skin damage[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(11):1612-1617.
DOI URL |
|
| [24] | Wu XS, Miles A, Braakhuis AJ. Texture-modified diets,nutritional status and mealtime satisfaction:a systematic review[J]. Healthcare, 2021, 9(6):624. |
| [25] |
熊照玉, 柯卉, 李素云, 等. 围手术期患者口服营养补充的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(2):283-288.
DOI URL |
|
Xiong ZY, Ke H, Li SY, et al. Evidence summary of oral nutritional supplements in perioperative patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(2):283-288.
DOI URL |
|
| [26] | 中华医学会肠外肠内营养学分会. 中国成人患者肠外肠内营养临床应用指南(2023版)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2023, 103(13):946-974. |
| Chinese Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. Guideline for clinical application of parenteral and enteral nutrition in adults patients in China(2023 edition)[J]. Natl Med J China, 2023, 103(13):946-974. | |
| [27] | 中华医学会外科学分会胃肠外科学组, 中华医学会外科学分会结直肠外科学组,中国医师协会外科医师分会上消化道外科医师委员会. 胃肠外科病人围手术期全程营养管理中国专家共识(2021版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2021, 41(10):1111-1125. |
| Chinese Society of Gastrointestinal Surgery,Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Colorectal Surgery,Chinese Society of Surgery,Chinese Medical Association; Association of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons,Chinese College of Surgeons,Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Chinese expert consensus on perioperative whole-course nutrition management for gastrointestinal surgery(2021 edition)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2021, 41(10):1111-1125. | |
| [28] | 王方, 戴晓冬, 蒋秀敏, 等. 直肠癌永久性肠造口患者的营养状况现状[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2022, 28(31):4426-4429. |
| Wang F, Dai XD, Jiang XM, et al. Nutritional status of rectal cancer patients with permanent enterostomy[J]. Chin J Mod Nurs, 2022, 28(31):4426-4429. |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||