


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (20): 2455-2462.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.20.004
收稿日期:2024-01-05
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-10-28
通讯作者:
答秀维,E-mail:182181335@qq.com作者简介:张阳阳:女,本科,主管护师,护士长,E-mail:wt2018121987@163.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Yangyang( ), ZHANG Hongxin, ZHANG Na, HE Hua, DA Xiuwei(
), ZHANG Hongxin, ZHANG Na, HE Hua, DA Xiuwei( )
)
Received:2024-01-05
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-10-28
摘要:
目的 分析肝癌化疗患者完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管的现状及影响因素,建立风险预测模型,并对模型进行内部验证。方法 该研究为前瞻性巢式病例对照研究,选取2021年10月—2023年9月在陕西省某三级甲等医院进行完全植入式静脉输液港维护的肝癌化疗患者作为调查对象,将其中因并发症拔管的患者纳入因并发症拔管组,按照1 ∶ 10的比例进行匹配,随机选取该时间段内计划性拔管患者作为计划性拔管组。分析肝癌化疗患者完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管的原因,同时采用单因素分析和Logistic回归分析探究因并发症拔管的影响因素,建立风险预测模型及列线图,采用受试者操作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线、校准曲线和Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验对预测模型进行内部验证。结果 肝癌化疗患者完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管的发生率为7.0%,感染(36.7%)和血栓(30.0%)是因并发症拔管的主要原因。BMI、TNM分期、是否合并糖尿病、输液港管腔数量、化疗次数是肝癌化疗患者完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管的主要影响因素(P<0.05)。预测模型的ROC曲线下面积为0.871,最佳截断值为0.106,灵敏度为0.800,特异度为0.820;校准曲线的实际值与预测值间的平均绝对误差为0.011,且校准曲线接近理想曲线;Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验中,χ2=2.913(P=0.940)。结论 肝癌化疗患者完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管的发生率较低,感染、血栓是其主要原因,BMI≥24、TNM分期为Ⅲ或Ⅳ期、合并糖尿病、置入双腔完全植入式静脉输液港、化疗次数>5次的患者,容易因并发症拔管。该研究构建的风险预测模型的预测效果良好,可为医护人员早期识别因并发症拔管的高风险患者提供参考。
张阳阳, 张洪新, 张娜, 何华, 答秀维. 完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管风险预测模型的建立及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(20): 2455-2462.
ZHANG Yangyang, ZHANG Hongxin, ZHANG Na, HE Hua, DA Xiuwei. Construction and validation of a risk prediction model for extubation due to complications of totally implantable access port[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(20): 2455-2462.
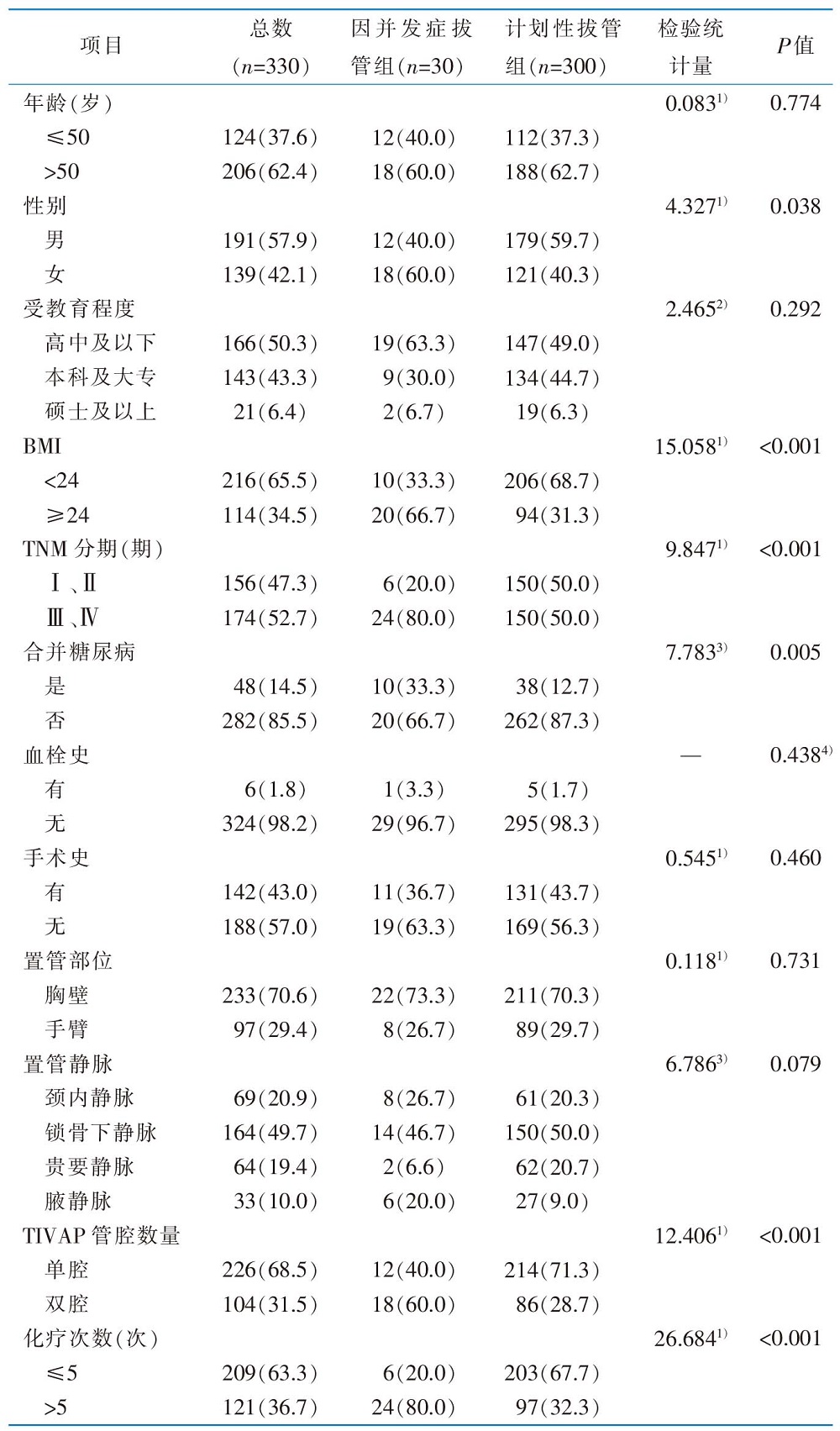 |
表1 肝癌化疗患者完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管影响因素的单因素分析结果[例(百分比,%)]
Table 1 Univariate analysis of extubation due to complications of totally implantable access port in patients with liver cancer undergoing chemotherapy[case(percentage,%)]
 |
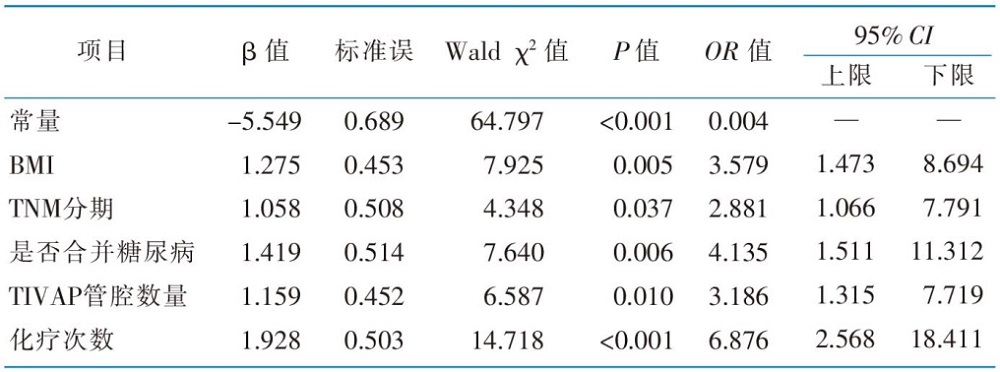 |
表2 肝癌化疗患者完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管风险的Logistic回归分析结果
Table 2 Logistic regression of the risk for extubation due to complications of totally implantable access port in patients with liver cancer undergoing chemotherapy
 |
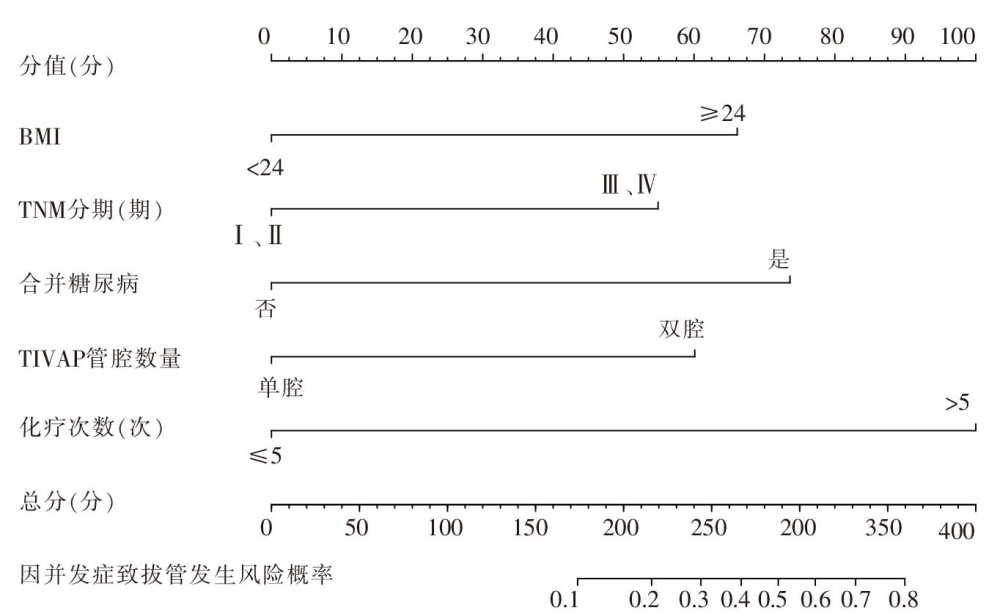
图1 肝癌化疗患者完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管风险预测模型列线图 注:TIVAP为完全植入式静脉输液港。
Figure 1 Predictive nomogram for extubation due to complications of totally implantable access port in patients with liver cancer undergoing chemotherapy
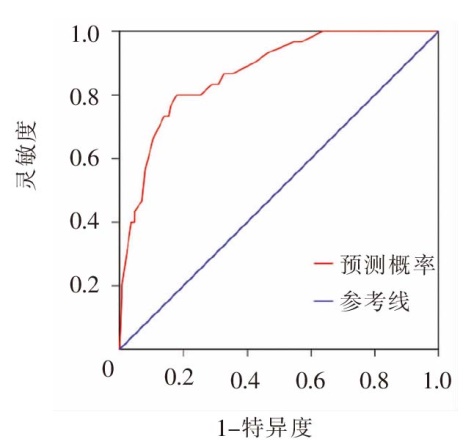
图2 肝癌化疗患者完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管风险预测模型的受试者操作特征曲线
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curve of the prediction model for extubation due to complications of totally implantable access port in patients with liver cancer undergoing chemotherapy
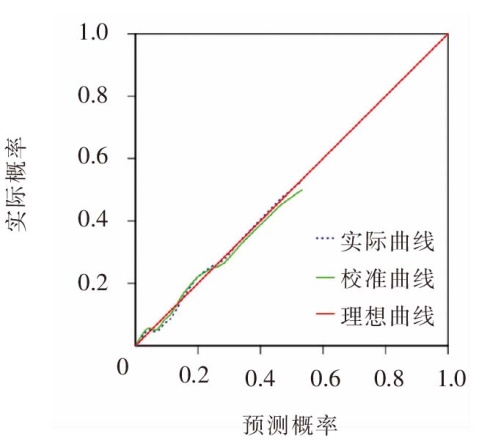
图3 肝癌化疗患者完全植入式静脉输液港因并发症拔管风险预测模型的校准曲线
Figure 3 Calibration curve of the prediction model for extubation due to complications of totally implantable access port in patients with liver cancer undergoing chemotherapy
| [1] | 国家卫生健康委办公厅. 原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2022, 60(4):273-309. |
| General Office of National Health Commission. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition)[J]. Chin J Surg, 2022, 60(4):273-309. | |
| [2] | 国家重大疑难疾病(原发性肝癌)中西医临床协作组. 原发性肝癌中西医结合诊疗专家共识[J]. 中医药导报, 2021, 27(9):101-107. |
| National Clinical Collaboration Group of Chinese and Western Medicine for Major Difficult Diseases(Primary Liver Cancer). Consensus on diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer with integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine[J]. Guid J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2021, 27(9):101-107. | |
| [3] | Moss JG, Wu O, Bodenham AR, et al. Central venous access devices for the delivery of systemic anticancer therapy(CAVA):a randomised controlled trial[J]. Lancet, 2021, 398(10298):403-415. |
| [4] |
王凯蓉, 周英凤, 张晓菊, 等. 两种中心静脉输液技术的成本效果分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(4):574-581.
DOI URL |
|
Wang KR, Zhou YF, Zhang XJ, et al. A cost-effectiveness analysis of peripherally inserted central catheter versus totally implanted venous port[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(4):574-581.
DOI URL |
|
| [5] | 马力, 刘运江, 刘荫华. 中国乳腺癌中心静脉血管通路临床实践指南(2022版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2022, 42(2):151-158. |
| Ma L, Liu YJ, Liu YH. Clinical practice China guidelines on central venous vascular access for breast cancer(2022 edition)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2022, 42(2):151-158. | |
| [6] | Zhang JH, Ma GY, Peng S, et al. Risk factors and predictive models for peripherally inserted central catheter unplanned extubation in patients with cancer:prospective,machine learning study[J]. J Med Internet Res, 2023,25:e49016. |
| [7] | Sun XW, Bai XM, Zhang Y, et al. Perioperative and postoperative complications of ultrasound-guided totally implantable venous access ports via the brachiocephalic vein in patients with cancer:a prospective study[J]. J Cancer, 2021, 12(5):1379-1385. |
| [8] | 叶冬青. 巢式病例对照研究的设计及分析[J]. 疾病控制杂志, 2001, 5(1):65-68. |
| Ye DQ. Design and analysis of nested case-control study[J]. Chin J Dis Contr Prev, 2001, 5(1):65-68. | |
| [9] | 中心静脉通路上海协作组, 上海市抗癌协会实体肿瘤聚焦诊疗专委会血管通路专家委员会. 完全植入式输液港上海专家共识(2019)[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2019, 28(12):1123-1128. |
| Shanghai Collaborative Group on Central Venous Access,Expert Committee on Vascular Access of Solid Tumor Focus Committee of Shanghai Anti-Cancer Association. Consensus of Shanghai experts on totally implantable access port(2019)[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2019, 28(12):1123-1128. | |
| [10] | Chinese Research Hospital Association Digestive Tumor Committee, Chinese Association of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons,Chinese Gastric Cancer Association and Gastrointestinal Surgical Group of Chinese Surgical Society Affiliated to the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese expert consensus and practice guideline of totally implantable access port for digestive tract carcinomas[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26(25):3517-3527. |
| [11] |
Bertoglio S, Cafiero F, Meszaros P, et al. PICC-PORT totally implantable vascular access device in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy[J]. J Vasc Access, 2020, 21(4):460-466.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Tsuruta S, Goto Y, Miyake H, et al. Late complications associated with totally implantable venous access port implantation via the internal jugular vein[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2020, 28(6):2761-2768.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | 中国中西医结合学会外周血管疾病委员会中心静脉通路专家组. 静脉输液港植入与管理多学科专家共识(2023版)[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2023, 32(6):799-814. |
| Expert Group of Central Venous Pathway,Committee of Peripheral Vascular Diseases, Chinese Society of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. Multidisciplinary expert consensus on implantation and management of venous infusion port(2023 edition)[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2023, 32(6):799-814. | |
| [14] | 季学闻, 马利兵, 肉斯太木江·依马木, 等. 肝癌切除术后感染性并发症的危险因素及其预测模型的建立[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2023, 33(4):542-546. |
| Ji XW, Ma LB, Rousitaimujiang YMM, et al. Risk factors of infectious complications after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma and the construction of its predictive model[J]. Chin J Nosocomiology, 2023, 33(4):542-546. | |
| [15] | 黄晓钰, 吴丽红. 肿瘤患者输液港相关性血流感染危险因素的研究进展[J]. 四川医学, 2022, 43(7):717-721. |
| Huang XY, Wu LH. Research progress on risk factors of transfusion port-related bloodstream infection in tumor patients[J]. Sichuan Med J, 2022, 43(7):717-721. | |
| [16] | 刘运江, 屈翔, 葛智成, 等. 乳腺癌植入式静脉输液港临床应用专家共识及技术操作指南(2017版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2017, 37(12):1377-1382. |
| Liu YJ, Qu X, Ge ZC, et al. Expert consensus and technical operation guide for clinical application of implantable intravenous infusion port for breast cancer(2017 edition)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2017, 37(12):1377-1382. | |
| [17] |
Tiegs G, Horst AK. TNF in the liver:targeting a central player in inflammation[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2022, 44(4):445-459.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Hassan SA, Palaskas N, Kim P, et al. Chemotherapeutic agents and the risk of ischemia and arterial thrombosis[J]. Curr Atheroscler Rep, 2018, 20(2):10.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | 陈志波, 陈钦昌, 李勇辉, 等. 身体质量指数与深静脉血栓形成因果关系的孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 中华血管外科杂志, 2019, 4(4):247-251. |
| Chen ZB, Chen QC, Li YH, et al. Mendelian randomization study on the causal relationship between body mass index and deep vein thrombosis[J]. Chin J Vasc Surg, 2019, 4(4):247-251. | |
| [20] |
温萌, 豆欣蔓, 苗晓琦, 等. 肿瘤患者完全植入式静脉输液港导管相关性血栓形成危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(23):2825-2833.
DOI URL |
| Wen M, Dou XM, Miao XQ, et al. Risk factors for catheter-related thrombosis in cancer patients with totally implantable venous access ports:a Meta-analysis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(23):2825-2833. | |
| [21] | Salim S, Zarrouk M, Elf J, et al. Clinical implications of different risk factor profiles in patients with mesenteric venous thrombosis and systemic venous thromboembolism:a population-based study[J]. J Thromb Thrombolysis, 2019, 47(4):572-577. |
| [22] |
Song X, Chen SY, Dai Y, et al. A novel incision technique of a totally implanted venous access port in the upper arm for patients with breast cancer[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2023, 21(1):162.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Santacruz E, Mateo-Lobo R, Riveiro J, et al. Infectious complications in home parenteral nutrition:a long-term study with peripherally inserted central catheters,tunneled catheters,and ports[J]. Nutrition, 2019,58:89-93. |
| [24] | Chang TC, Yen MH, Kiu KT. Incidence and risk factor for infection of totally implantable venous access port[J]. Langenbecks Arch Surg, 2022, 407(1):343-351. |
| [25] |
鲁佳, 谢开红, 陈文思, 等. 肿瘤患者输液港相关性血栓预防及管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(5):544-551.
DOI URL |
|
Lu J, Xie KH, Chen WS, et al. Evidence summary for the prevention and management of port-related venous thromboembolism in cancer patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(5):544-551.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||