


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (19): 2362-2368.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.19.008
收稿日期:2023-12-04
出版日期:2024-10-10
发布日期:2024-10-14
通讯作者:
裔雅萍,E-mail:93915336@qq.com作者简介:李芬:女,本科,主任护师,E-mail:2647532537@qq.com
基金资助:
LI Fen( ), GENG Yaqin, ZHANG Yi, SHEN Biyu, GAO Bo, YI Yaping(
), GENG Yaqin, ZHANG Yi, SHEN Biyu, GAO Bo, YI Yaping( )
)
Received:2023-12-04
Online:2024-10-10
Published:2024-10-14
摘要:
目的 探索类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)患者自我效能潜在类别,分析其影响因素,为制订个性化护理措施提供参考。 方法 便利选取2022年3月—2023年3月就诊于常州市某三级甲等综合医院风湿免疫科门诊的RA患者,采用一般资料调查表、中文版类风湿关节炎自我效能感量表,风湿病治疗依从性问卷对RA患者进行调查,采用潜在类别分析对自我效能进行分类,通过多元Logistic回归分析探索自我效能的影响因素。 结果 共纳入RA患者219例,中文版类风湿关节炎自我效能感量表得分为(100.68±12.64)分,RA患者自我效能分为高效能-低支持组(105.18±10.18)分,中效能-多样需求组(93.21±4.16)分,低效能-高疲劳组(84.07±13.96)分。Logistic回归分析显示,病程(OR=1.062,P=0.024)、学历(OR=5.405,P=0.036;OR=12.347,P=0.021)、红细胞沉降率(OR=1.019,P=0.020;OR=1.019,P=0.027)是RA患者自我效能的影响因素。RA患者自我效能3个潜在类别的治疗依从性得分(F=10.902,P<0.001)、治疗依从性良好率(χ2=16.053,P<0.001)比较,差异具有统计学意义。 结论 RA患者自我效能水平具有明显的异质性,不同自我效能类别的患者治疗依从性存在差异。护士应重点关注中效能-多样需求组和低效能-高疲劳组人群,对患者实施认知行为等干预手段,协助其设定明确的目标,并提供具体的规划和指导,以改善其健康结局。
李芬, 耿亚琴, 张艺, 沈碧玉, 高波, 裔雅萍. 类风湿关节炎患者自我效能潜在类别及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(19): 2362-2368.
LI Fen, GENG Yaqin, ZHANG Yi, SHEN Biyu, GAO Bo, YI Yaping. Analysis of potential categories and influencing factors of self-efficacy among patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(19): 2362-2368.
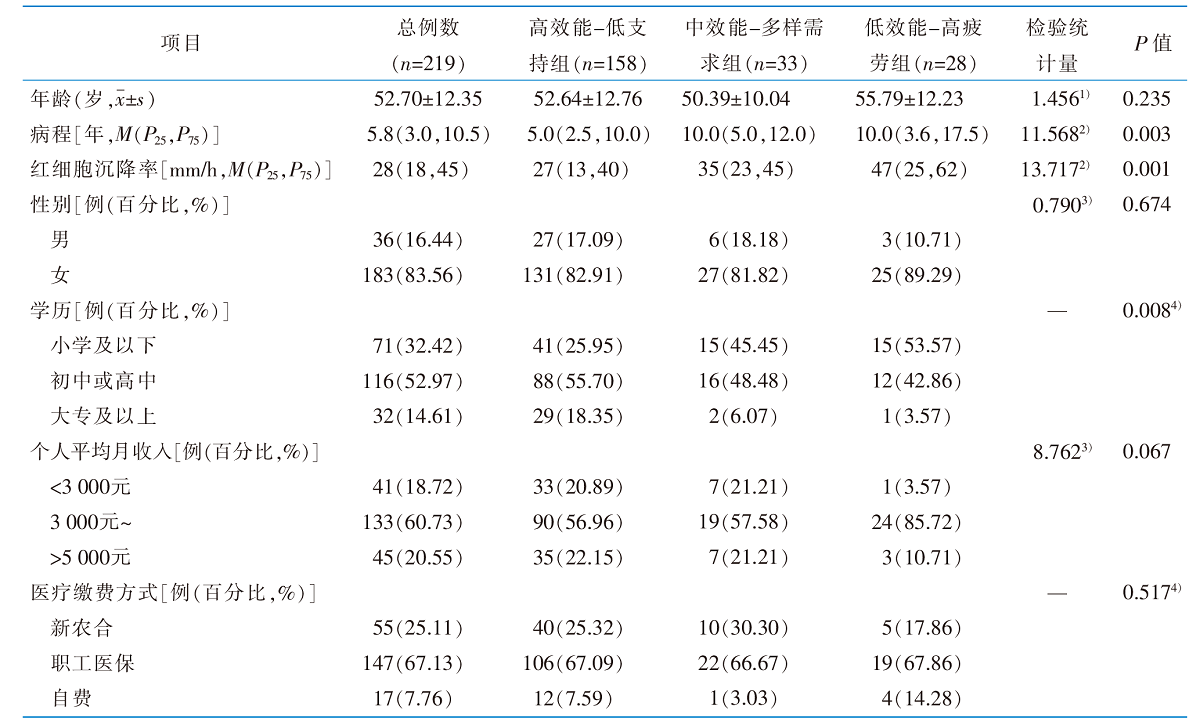 |
表1 类风湿关节炎患者一般资料及自我效能潜在类别的单因素分析(n=219)
Table 1 Demographic characteristics and univariate analysis of latent classes of self-efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis patients(n=219)
 |
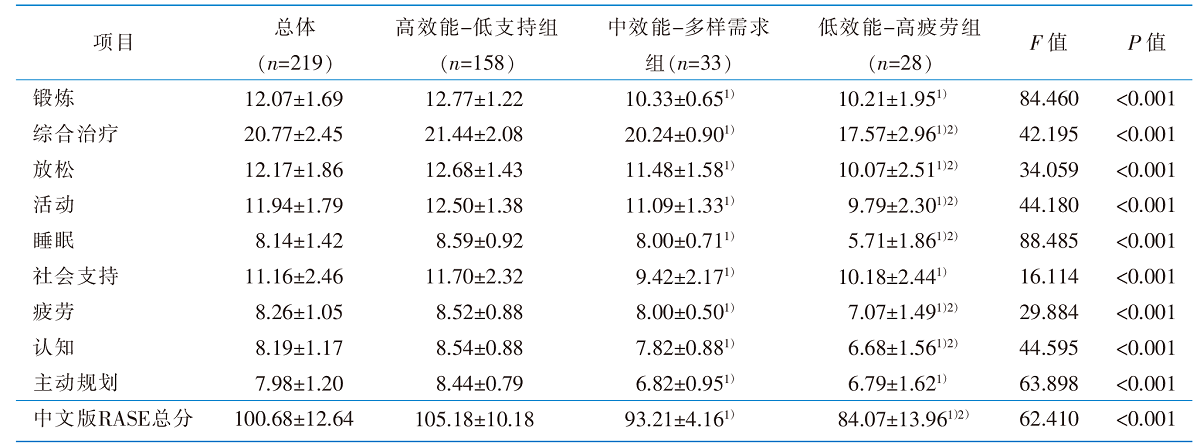 |
表3 类风湿关节炎患者自我效能感量表在不同潜在类别间的比较(n=219,分,$\bar{x}±s$)
Table 3 Distribution of potential categories of the scores of RASE in rheumatoid arthritis patients(n=219,scores,$\bar{x}±s$)
 |
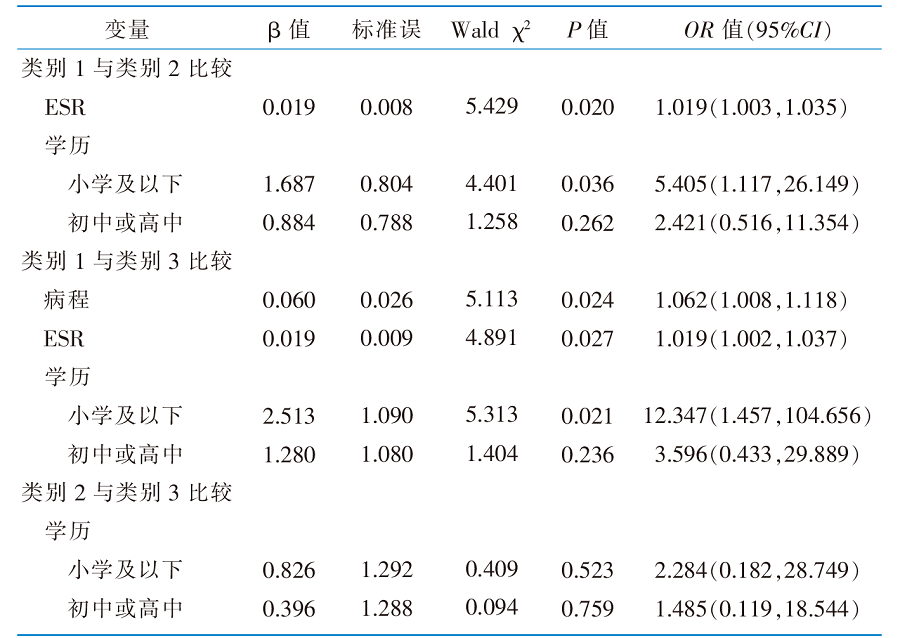 |
表4 类风湿关节炎患者自我效能潜在类别的多元Logistic回归分析结果(n=219)
Table 4 Results of multiple Logistic regression of self-efficacy category in rheumatoid arthritis patients(n=219)
 |
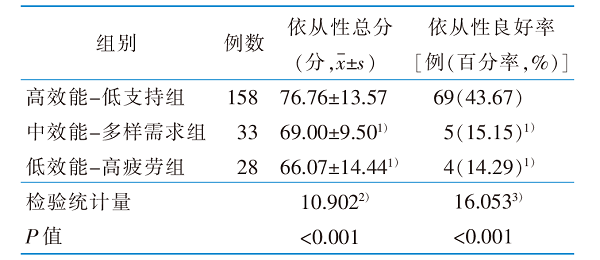 |
表5 不同自我效能潜在类别类风湿关节炎患者风湿治疗依从性比较(n=219)
Table 5 Comparison oftreatment compliance in different classes of self-efficacy of patients with rheumatoid arthritis(n=219)
 |
| [1] | Cao F, Liu YC, Ni QY, et al. Temporal trends in the prevalence of autoimmune diseases from 1990 to 2019[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2023, 22(8):103359. |
| [2] |
田新平, 李梦涛, 曾小峰. 我国类风湿关节炎诊治现状与挑战:来自中国类风湿关节炎2019年年度报告[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2021, 60(7):593-598.
PMID |
|
Tian XP, Li MT, Zeng XF. The challenges and opportunities for the management of rheumatoid arthritis in China:an annual report of 2019[J]. Chin J Intern Med, 2021, 60(7):593-598.
DOI PMID |
|
| [3] | 周云杉, 王秀茹, 安媛, 等. 全国多中心类风湿关节炎患者残疾及功能受限情况的调查[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2013, 17(8):526-532. |
| Zhou YS, Wang XR, An Y, et al. A multicenter study of deformity and disability in rheumatoid arthritis patients in China[J]. Chin J Rheumatol, 2013, 17(8):526-532. | |
| [4] | 张晓翠, 高蕾, 李苗苗, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者自我效能感影响因素的研究[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2016, 20(11):734-738. |
| Zhang XC, Gao L, Li MM, et al. Study on the influencing factors of self-assessed efficacy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chin J Rheumatol, 2016, 20(11):734-738. | |
| [5] | Farley H. Promoting self-efficacy in patients with chronic disease beyond traditional education:a literature review[J]. Nurs Open, 2020, 7(1):30-41. |
| [6] |
徐延卉, 潘婕, 陈家应, 等. 门诊类风湿关节炎患者关节炎自我效能感的特征及相关因素分析[J]. 新医学, 2023, 54(11):832-836.
DOI |
| Xu YH, Pan J, Chen JY, et al. Characteristics and associated factors of arthritis self-efficacy in outpatients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. J Natl Prosec Coll, 2023, 54(11):832-836. | |
| [7] | 王方, 刘健, 梁华, 等. 老年类风湿关节炎患者躯体功能与自我效能及心理弹性的相关性[J]. 国际老年医学杂志, 2023, 44(1):57-61. |
| Wang F, Liu J, Liang H, et al. Correlation of physical function with self-efficacy and psychological resilience in older patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Int J Dig Dis, 2023, 44(1):57-61. | |
| [8] |
Vergara F, Rosa J, Orozco C, et al. Evaluation of learned helplessness,self-efficacy and disease activity,functional capacity and pain in Argentinian patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2017, 46(1):17-21.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Sarhan SA, Kamal DE, Hamed MS, et al. Validity and reliability of the Arabic version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease scale in rheumatoid arthritis patients[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2022, 41(10):2967-2975.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | 高蕾, 史宝欣. 类风湿关节炎患者自我效能感的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2016, 51(7):848-852. |
| Gao L, Shi BX. Research progress on self-efficacy of patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2016, 51(7):848-852. | |
| [11] |
Sugiharto F, Nuraeni A, Trisyani Y, et al. A scoping review of predictors associated with self-efficacy among patients with coronary heart disease[J]. Vasc Health Risk Manag, 2023, 19:719-731.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Wasserman AM. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2011, 84(11):1245-1252.
PMID |
| [13] | Hewlett S, Cockshott Z, Kirwan J, et al. Development and validation of a Self-Efficacy Scale for use in British patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis(RASE)[J]. Rheumatology, 2001, 40(11):1221-1230. |
| [14] | 李现文, 杭琤, 孙露, 等. 中文版类风湿关节炎自我效能感量表的信效度初步分析[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2019, 23(4):228-232. |
| Li XW, Hang C, Sun L, et al. Reliability and validity analysis of Chinese version of Rheumatoid Arthritis Self-Efficacy Scale[J]. Chin J Rheumatol, 2019, 23(4):228-232. | |
| [15] |
de Klerk E, van der Heijde D, van der Tempel H, et al. Development of a questionnaire to investigate patient compliance with antirheumatic drug therapy[J]. J Rheumatol, 1999, 26(12):2635-2641.
PMID |
| [16] | 朱桂华, 王永志, 童宗武, 等. 中文版风湿病治疗依从性问卷的信度和效度研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2013, 16(24):2803-2805. |
| Zhu GH, Wang YZ, Tong ZW, et al. Reliability and validity of Chinese Compliance Questionnaire for Rheumatology[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2013, 16(24):2803-2805. | |
| [17] | 周蕾, 史娜, 姚辉, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者自我调节疲劳现状及其影响因素[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2022, 39(6):44-47,80. |
| Zhou L, Shi N, Yao H, et al. Status quo of self-regulation fatigue among patients with rheumatoid arthritis and its influencing factors[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2022, 39(6):44-47,80. | |
| [18] | Yang J, Zhang HL. Efficacy of comprehensive nursing in pa-tients with pneumoconiosis and its influence on quality of life[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2022, 14(7):5178-5186. |
| [19] |
Primdahl J, Wagner L, Hørslev-Petersen K. Self-efficacy in rheu-matoid arthritis:translation and test of validity,reliability and sensitivity of the Danish version of the Rheumatoid Arthritis Self-Efficacy Questionnaire(RASE)[J]. Musculoskeletal Care, 2010, 8(3):123-135.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
朱宇倩, 高亚南, 贾俊婉, 等. 炎症性肠病患者饮食限制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(1):50-56.
DOI URL |
| Zhu YQ, Gao YN, Jia JW, et al. Experience of dietary restriction in patients with inflammatory bowel disease:a qualitative study[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(1):50-56. | |
| [21] | Cantero-Téllez R, Martin Mateos A, Cuesta García C, et al. The predictive value of self-efficacy in the evolution of rheumatoid arthritis and its relationship with pain and function[J]. Reu-matol Clin(Engl Ed), 2023, 19(10):549-554. |
| [22] |
Jiao XN, Yu XY, Wang SY, et al. Are effect sizes in self-efficacy field changing over time? A meta-meta analysis[J]. Int J Psychol, 2021, 56(5):801-811.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Yeom HE, Lee J. The association of education level with autonomy support,self-efficacy and health behaviour in patients with cardiovascular risk factors[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2022, 31(11/12):1547-1556. |
| [24] |
赵露, 李俊玲, 王俊锋, 等. 中青年2型糖尿病患者二元应对现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(5):576-581.
DOI URL |
|
Zhao L, Li JL, Wang JF, et al. Investigation and analysis of factors related to dyadic coping among young and middle-aged patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(5):576-581.
DOI URL |
|
| [25] | Náfrádi L, Nakamoto K, Schulz PJ. Is patient empowerment the key to promote adherence? A systematic review of the relationship between self-efficacy,health locus of control and medication adherence[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(10):e0186458. |
| [26] | 王敏, 谭江红, 贺晓元, 等. 类风湿关节炎病人疾病管理积极度对长期服药执行意向的影响[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(24):4399-4403. |
| Wang M, Tan JH, He XY, et al. Influence of active degree of disease management on long term medication implementation intention in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2022, 36(24):4399-4403. | |
| [27] | Liu HQ, Yao ZQ, Shi SJ, et al. The mediating effect of self-efficacy on the relationship between medication literacy and medication adherence among patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Patient Prefer Adherence, 2023, 17:1657-1670. |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||