


中华护理杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (14): 1683-1690.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.14.003
收稿日期:2023-02-08
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-07-14
通讯作者:
刘欣梅,E-mail:xinmei@jlu.edu.cn作者简介:杨雯雯:女,硕士,护师,E-mail:1617159790@qq.com
YANG Wenwen( ), ZHOU Xue, DU Yifei, YONG Jun, LIU Xinmei(
), ZHOU Xue, DU Yifei, YONG Jun, LIU Xinmei( )
)
Received:2023-02-08
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-07-14
摘要:
目的 探讨预防性吞咽干预模式在喉部分切除术患者中的应用效果。方法 采用便利抽样法,选取2020年8月—2022年2月长春市某三级甲等医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科首次行喉部分切除术的患者80例,按入院顺序分为试验组和对照组各40例。试验组在对照组干预措施的基础上进行院内与家庭康复,实施为期1个月的联合下颌抗阻与呼吸-吞咽协调训练模式的预防性吞咽干预;对照组给予常规护理及基础吞咽训练。比较入组前1 d,术后14 d及1个月两组吞咽安全性、吞咽-经口摄食功能以及生活质量的差异。结果 试验组38例,对照组37例完成研究。两组吞咽安全性、吞咽-经口摄食功能及生活质量的时间、组间及交互效应均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),术后14 d和1个月试验组各指标均优于对照组(P<0.05)。结论 预防性下颌抗阻与呼吸-吞咽协调训练模式联合干预能够提高喉部分切除患者吞咽的安全性,改善吞咽功能,恢复功能性经口摄食,提升生活质量,促进早期康复。
杨雯雯, 周雪, 杜羿霏, 勇君, 刘欣梅. 预防性吞咽干预在喉部分切除术患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(14): 1683-1690.
YANG Wenwen, ZHOU Xue, DU Yifei, YONG Jun, LIU Xinmei. Effectiveness of prophylactic swallowing interventions in patients with partial laryngectomy[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2023, 58(14): 1683-1690.
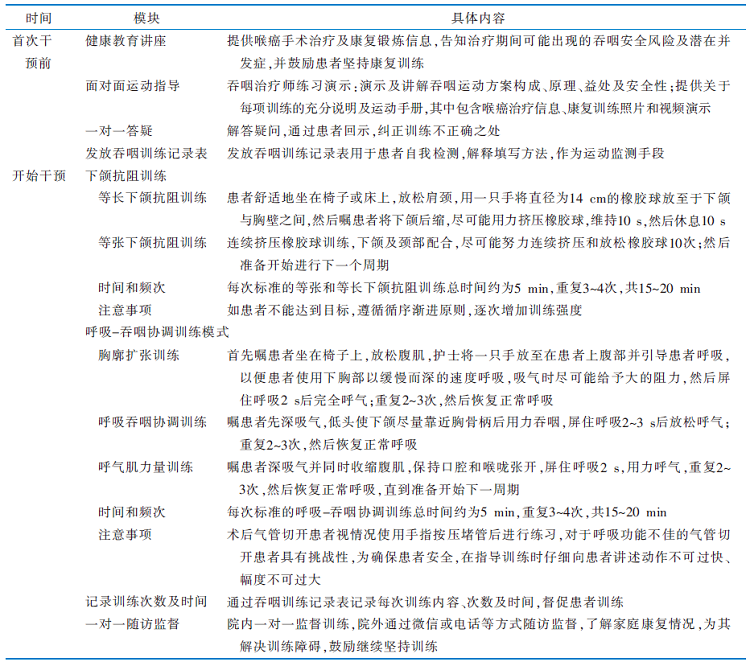 |
表1 下颌抗阻与呼吸-吞咽协调训练模式联合干预方案
Table 1 Implementation programmes of combined intervention of Chin tuck against resistance and respiratory-swallowing coordination model
 |
| [1] |
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3):209-249.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 黄师菊, 蔡有弟, 李晓玲, 等. 护士主导的高危科室吞咽障碍患者筛查及分级干预效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(11):1303-1308. |
| Huang SJ, Cai YD, Li XL, et al. The effectiveness of screening and grading intervention for dysphagia in high-risk departments in all hospitals led by nurses[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(11):1303-1308. | |
| [3] |
Hajdú SF, Wessel I, Dalton SO, et al. Swallowing exercise during head and neck cancer treatment:results of a randomized trial[J]. Dysphagia, 2022, 37(4):749-762.
DOI |
| [4] | 王剑锋, 孙庆佳, 宗敏茹. 吞咽训练结合营养干预对喉癌患者术后放疗后营养状态和生活质量的影响[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2018, 40(12):910-912. |
| Wang JF, Sun QJ, Zong MR. Effect of swallowing training combined with nutritional intervention on nutritional status and quality of life of laryngeal cancer patients after postoperative radiotherapy[J]. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil, 2018, 40(12):910-912. | |
| [5] |
Mortensen HR, Jensen K, Aksglæde K, et al. Prophylactic swallowing exercises in head and neck cancer radiotherapy[J]. Dysphagia, 2015, 30(3):304-314.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Messing BP, Ward EC, Lazarus CL, et al. Prophylactic swallow therapy for patients with head and neck cancer undergoing chemoradiotherapy:a randomized trial[J]. Dysphagia, 2017, 32(4):487-500.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Yang WW, Nie WB, Zhou X, et al. Review of prophylactic swallowing interventions for head and neck cancer[J]. Int J Nurs Stud, 2021, 123:104074.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Yoon WL, Khoo JKP, Rickard Liow SJ. Chin tuck against resistance(CTAR):new method for enhancing suprahyoid muscle activity using a Shaker-type exercise[J]. Dysphagia, 2014, 29(2):243-248.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology CSCO Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines for Colorectal Cancer Working Group. Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology(CSCO) diagnosis and treatment guidelines for colorectal cancer 2018(English version)[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2019, 31(1):117-134.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 中国吞咽障碍康复评估与治疗专家共识组. 中国吞咽障碍评估与治疗专家共识(2017年版)第二部分治疗与康复管理篇[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2018, 40(1):1-10. |
| Expert Consensus group on rehabilitation assessment and treatment of swallowing disorders in China. Chinese expert consensus on the evaluation and treat-ment of dysphagia(2017 edition),part Ⅱ,treatment and reha-bilitation management[J]. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil, 2018, 40(1):1-10. | |
| [11] |
Shaker R, Easterling C, Kern M, et al. Rehabilitation of swallowing by exercise in tube-fed patients with pharyngeal dysphagia secondary to abnormal UES opening[J]. Gastroenterology, 2002, 122(5):1314-1321.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Uysal H, Kızılay F, Ünal A, et al. The interaction between breathing and swallowing in healthy individuals[J]. J Electromyogr Kinesiol, 2013, 23(3):659-663.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Martin-Harris B, McFarland D, Hill EG, et al. Respiratory-swallow training in patients with head and neck cancer[J]. Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 2015, 96(5):885-893.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Langmore S, Kenneth SMA, Olsen N. Fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing safety:a new procedure[J]. Dysphagia, 1988, 2(4):216-219.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, et al. A Penetration-Aspiration Scale[J]. Dysphagia, 1996, 11(2):93-98.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Neubauer PD, Rademaker AW, Leder SB. The Yale Pharyngeal Residue Severity Rating Scale:an anatomically defined and image-based tool[J]. Dysphagia, 2015, 30(5):521-528.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Yoshimatsu Y, Tobino K, Sueyasu T, et al. Repetitive Saliva swallowing test and water swallowing test may identify a COPD phenotype at high risk of exacerbation[J]. Clin Respir J, 2019, 13(5):321-327.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Hamzic S, Braun T, Juenemann M, et al. Validation of the German version of Functional Oral Intake Scale(FOIS-G) for flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing(FEES)[J]. Dysphagia, 2021, 36(1):130-139.
DOI |
| [19] |
张咏梅, 彭峥嵘, 吴沛霞, 等. 喉切除术后吞咽结局量表的汉化和信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(7):1115-1120.
DOI URL |
|
Zhang YM, Peng ZR, Wu PX, et al. Translation and reliability and validity testing of Chinese version of Swallowing Outcome after Total Laryngectomy Scale[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(7):1115-1120.
DOI URL |
|
| [20] | 邹敏, 席淑新, 吴沛霞, 等. 中文版安德森吞咽困难量表的信效度研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2013, 48(11):1003-1007. |
| Zou M, Xi SX, Wu PX, et al. Reliability and validity of Chinese version of Anderson Dysphagia Scale[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2013, 48(11):1003-1007. | |
| [21] | 张雯. 基于康复前移理念的综合康复护理对喉癌术后患者负性情绪及生活质量的影响[J]. 国际护理学杂志, 2021, 40(16):2925-2928. |
| Zhang W. Effects of comprehensive rehabilitation nursing based on the concept of rehabilitation forward on negative emotions and quality of life of patients with laryngeal cancer after surgery[J]. Int J Nurs Sci, 2021, 40(16):2925-2928. | |
| [22] |
Karsten RT, van der Molen L, Hamming-Vrieze O, et al. Long-term swallowing,trismus,and speech outcomes after combined chemoradiotherapy and preventive rehabilitation for head and neck cancer;10-year plus update[J]. Head Neck, 2020, 42(8):1907-1918.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Ning Y, Wang Q, Ding YX, et al. Barriers and facilitators to physical activity participation in patients with head and neck cancer:a scoping review[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2022, 30(6):4591-4601.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 司茜茜, 王莹, 赵福云, 马晓骁, 刘均娥. A型主动脉夹层患者Ⅰ期心肺康复护理方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1037-1042. |
| [2] | 王旋, 温贤秀, 苟莉, 周丽娟, 陈付利, 吴海燕, 王良. 心脏康复依从性评估工具测量学属性的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(6): 736-743. |
| [3] | 吕丹, 赵莹, 贺艳, 刘青, 宋福娟, 李萌, 张馨月, 王晓萍. 进阶式肺康复在经鼻高流量氧疗患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(17): 2053-2061. |
| [4] | 胡树菁, 孙菁, 王奕, 高宝, 朱虹, 齐星宇. 肺移植受者居家肺康复锻炼促进与障碍因素的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(17): 2070-2076. |
| [5] | 陈玉娥, 高远, 孔丹, 谷思琪, 康珊珊, 解涛. 静态牵伸在单髁置换术患者围手术期康复护理中的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(12): 1462-1467. |
| [6] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 杨琦, 吴惠芳, 张一铭. 运动干预在造血干细胞移植患儿中应用的范围综述[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(11): 1331-1339. |
| [7] | 朱虹宣, 庞建美, 孙盛楠, 李燕. 老年肺癌患者术后过渡期肺康复行为影响因素的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(1): 15-21. |
| [8] | 林琦, 刘玉荣, 杨慧, 杨凤娟, 王丹, 陈瑞云. 肺癌患者运动训练行为感知量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(1): 22-28. |
| [9] | 黄彬彬, 王辉. 1例肺巨大肿瘤老年偏瘫患者术后肺复张的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(1): 29-32. |
| [10] | 顾婕, 马倩云, 高旭, 李惠珍, 孟晓红, 谢双怡, 樊帆, 周意, 曹洁. 前列腺癌术后尿失禁患者康复护理方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(9): 1029-1036. |
| [11] | 梁江淑渊, 曾妃, 顾培培, 郭璐瑶. 肺移植术后患者匹配式运动训练方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(8): 901-906. |
| [12] | 沈利凤, 朱慧, 孙美蓉, 钱雅芬, 李英, 郭海巍, 金艾香. 体感运动协同经皮穴位电刺激康复护理方案在甲状腺癌术后患者中的应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(8): 963-970. |
| [13] | 马喜宁, 白艳娟, 孔思铭, 黄蓉, 张静, 姚辉. 强直性脊柱炎患者运动指导方案的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(7): 864-870. |
| [14] | 张雪茹, 郝习君, 陈长香. 言语听觉反馈认知训练在脑外伤认知障碍患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(5): 552-557. |
| [15] | 夏瑶瑶, 李颐, 熊晓云, 周亮, 王艳慧, 马兰英. 经皮冠状动脉介入治疗患者心脏康复信息需求和自我管理的研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 398-405. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 21
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 568
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||