


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (21): 2611-2619.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.21.008
收稿日期:2024-01-23
出版日期:2024-11-10
发布日期:2024-11-04
作者简介:吕桂兰:女,硕士,主任护师,科护士长,E-mail:2271500539@qq.com
基金资助:
LÜ Guilan( ), CAO Hunan, WANG Hao, FAN Rui
), CAO Hunan, WANG Hao, FAN Rui
Received:2024-01-23
Online:2024-11-10
Published:2024-11-04
摘要:
目的 基于Meta建模构建维持性血液透析中低血压(intradialytic hypotension,IDH)风险预测模型并进行验证。方法 检索Cochrane Library、PubMed、Web of Science、EBSCO、Scopus、CINAHL、中国知网、万方数据库自建库至2023年3月31日报告IDH危险因素的文献。使用随机效应模型合并OR值,筛选P<0.05的因素并通过其β系数建立模型,选择286例血液透析患者作为验证集评估模型的区分度、校准度和临床实用度。结果 共纳入39篇文献,涉及25 546例患者,选取14个影响因素用于构建风险预测模型。IDH发生风险得分=-0.301 × 男性+0.015 × 年龄+0.004 × 透析龄+0.988 × 合并糖尿病+0.730 × 合并心血管疾病-0.042 × 透析前舒张压+0.666 × 采用血液透析滤过模式+0.076 × 加热温度+0.159 × 超滤率+0.476 × 超滤量+1.024 × 透析间期体重增加+0.053 × 血清磷+0.023 × 血尿素氮+0.040 × β2微球蛋白,选择肾脏病预后质量倡议、透析中最低收缩压<90 mmHg(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa)、透析中收缩压下降≥20 mmHg及英国肾脏病协会指南定义的透析中低血压作为4种结局指标。IDH预测模型在4种结局指标的曲线下面积分别为0.830、0.648、0.647和0.763。校准曲线显示模型在前2种结局下预测与实际大致相符(χ2=14.824,P=0.064;χ2=12.016,P=0.149)。决策分析显示在所有定义下模型整体上比全部干预和全部不干预的策略有更好的净获益。结论 该研究利用Meta建模开发的IDH风险预测模型预测性能良好,具有一定的临床应用价值。
吕桂兰, 曹虎男, 王浩, 樊蕊. 维持性血液透析中低血压风险预测的Meta建模及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(21): 2611-2619.
LÜ Guilan, CAO Hunan, WANG Hao, FAN Rui. Meta-modeling and validation of a risk prediction model for intradialytic hypotension in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(21): 2611-2619.
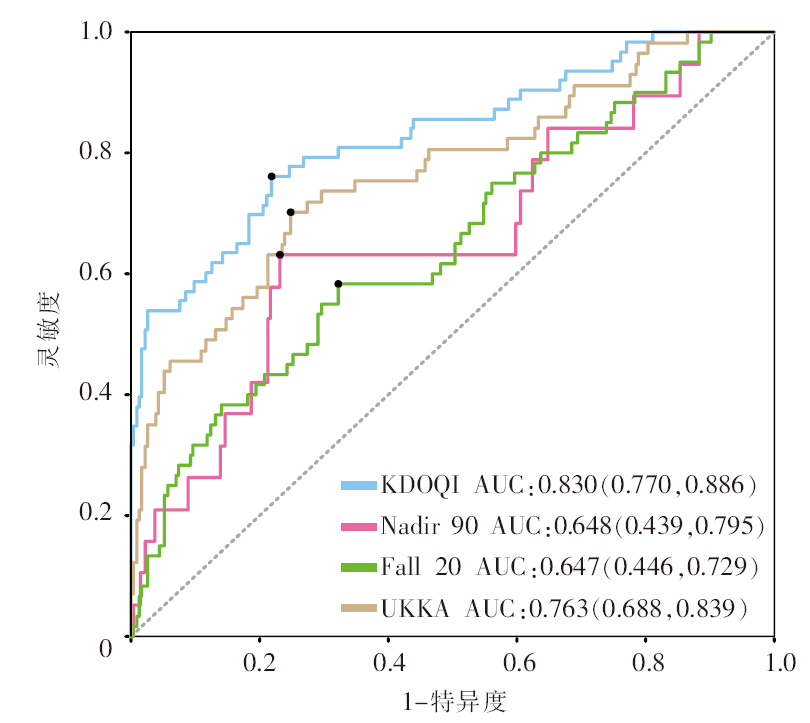
图2 4种定义下透析中低血压发生风险预测模型的受试者操作特征曲线 注:KDOQI为以肾脏病预后质量倡议的透析中低血压定义为结局指标;Nadir 90为以透析中最低收缩压<90 mmHg(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa)为结局指标;Fall 20为以透析中收缩压下降≥20 mmHg为结局指标;UKKA为以英国肾脏病协会指南的透析中低血压定义为结局指标;AUC为曲线下面积。
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curves for the risk prediction model of intradialytic hypotension under 4 definitions
| [1] | Kanbay M, Ertuglu LA, Afsar B, et al. An update review of intradialytic hypotension:concept,risk factors,clinical implications and management[J]. Clin Kidney J, 2020, 13(6):981-993. |
| [2] |
朱东阁, 王菊子, 赵倩, 等. 维持性血液透析患者透析中低血压风险预测模型的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(2):174-183.
DOI |
|
Zhu DG, Wang JZ, Zhao Q, et al. Systematic review of risk prediction models for intradialytic hypotension in patients with maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(2):174-183.
DOI |
|
| [3] |
卜黎静, 程飞儿, 张爱琴, 等. 危重症患者肠内营养喂养不耐受风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(15):1877-1883.
DOI |
|
Bu LJ, Cheng FE, Zhang AQ, et al. Development and validation of a prediction model for enteral feeding intolerance in critically ill patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2024, 59(15):1877-1883.
DOI |
|
| [4] |
Jiang WH, Wang JY, Shen XF, et al. Establishment and validation of a risk prediction model for early diabetic kidney disease based on a systematic review and meta-analysis of 20 cohorts[J]. Diabetes Care, 2020, 43(4):925-933.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale(NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses[J]. Ottawa:Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, 2011, 2(1):1-12. |
| [6] |
Sullivan LM, Massaro JM, D’Agostino RB Sr. Presentation of multivariate data for clinical use:the Framingham study risk score functions[J]. Stat Med, 2004, 23(10):1631-1660.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | K/DOQI Workgroup. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2005, 45:16-153. |
| [8] | Cho A, Lee YK, Oh J, et al. The relationship between intradialytic hypotension and vascular calcification in hemodialysis patients[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(10):e0185846. |
| [9] | Mangoni AA, Hewitson CL, Woodman RJ, et al. Symmetric di-methylarginine is an independent predictor of intradialytic hypotension[J]. Am J Hypertens, 2008, 21(8):955-959. |
| [10] | Mactier R, Hoenich N, Breen C. Renal association clinical practice guideline on haemodialysis[J]. Nephron Clin Pract, 2011, 118(Suppl 1):c241-c286. |
| [11] | Allinovi M, Palazzini G, Lugli G, et al. Pre-dialysis B-line quantification at lung ultrasound is a useful method for evaluating the dry weight and predicting the risk of intradialytic hypotension[J]. Diagnostics, 2022, 12(12):2990. |
| [12] | Assayag M, Levy D, Seris P, et al. Relative change of protidemia level predicts intradialytic hypotension[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2020, 9(1):e014264. |
| [13] |
Bossola M, Laudisio A, Antocicco M, et al. Intradialytic hypotension is associated with dialytic age in patients on chronic hemodialysis[J]. Ren Fail, 2013, 35(9):1260-1263.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Chang YM, Shiao CC, Chang KC, et al. Heart rate variability is an indicator for intradialytic hypotension among chronic hemo-dialysis patients[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2016, 20(4):650-659. |
| [15] |
Correa S, Pena-Esparragoza JK, Scovner KM, et al. Predictors of intradialytic symptoms:an analysis of data from the hemo-dialysis study[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2020, 76(3):331-339.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Deng F, Di WJ, Ma YX, et al. The relationship between prescription of ultrafiltration and intradialytic hypotension in Chinese hemodialysis patients[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2021, 10(5):5316-5321. |
| [17] |
Geng XM, Yu JB, Xu JR, et al. Role of magnesium in the risk of intradialytic hypotension among maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Hemodial Int, 2020, 24(3):351-358.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Kuipers J, Oosterhuis JK, Krijnen WP, et al. Prevalence of intradialytic hypotension,clinical symptoms and nursing interventions:a three-months,prospective study of 3818 haemodialysis sessions[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2016, 17:21. |
| [19] | Locatelli F, Altieri P, Andrulli S, et al. Hemofiltration and hemo-diafiltration reduce intradialytic hypotension in ESRD[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010, 21(10):1798-1807. |
| [20] |
Mc Causland FR, Waikar SS. Association of predialysis calcu-lated plasma osmolarity with intradialytic blood pressure de-cline[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2015, 66(3):499-506.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | McIntyre D, Havas K, Bonner A. Monitoring for intradialytic hypotension:an audit of nursing practice[J]. J Ren Care, 2021, 47(1):27-33. |
| [22] | Mizuiri S, Nishizawa Y, Doi T,et al. Coronary artery calcification is a risk factor for intradialytic hypotension in patients undergoing hemodialysis[J]. Hemodial Int,2022,26(3):335-344. |
| [23] | Ravi KS, Reeves PB, Correa S, et al. Predialysis serum phosphate and intradialytic hypotension[J]. Hemodial Int, 2022, 26(1):38-47. |
| [24] | Rocha A, Sousa C, Teles P, et al. Effect of dialysis day on intradialytic hypotension risk[J]. Kidney Blood Press Res, 2016, 41(2):168-174. |
| [25] | Sands JJ, Usvyat LA, Sullivan T, et al. Intradialytic hypotension:frequency,sources of variation and correlation with clinical outcome[J]. Hemodial Int, 2014, 18(2):415-422. |
| [26] |
Son HE, Ryu JY, Lee K, et al. The importance of muscle mass in predicting intradialytic hypotension in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Kidney Res Clin Pract, 2022, 41(5):611-622.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Takeda A, Toda T, Fujii T, et al. Can predialysis hypertension prevent intradialytic hypotension in hemodialysis patients?[J]. Nephron Clin Pract, 2006, 103(4):c137-c143.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Thongdee C, Phinyo P, Patumanond J, et al. Ultrafiltration rates and intradialytic hypotension:a case-control sampling of pooled haemodialysis data[J]. J Ren Care, 2021, 47(1):34-42. |
| [29] | Yang KH, Cho S, Kim SR, et al. Serum phosphorus levels are associated with intradialytic hypotension in hemodialysis patients[J]. Nephron, 2021, 145(3):238-244. |
| [30] | Yu JB, Liu ZH, Shen B, et al. Intradialytic hypotension as an independent risk factor for long-term mortality in maintaining hemodialysis patients:a 5-year follow-up cohort study[J]. Blood Purif, 2018, 45(4):320-326. |
| [31] | Zoccali C, Tripepi G, Neri L, et al. Effectiveness of cold HD for the prevention of HD hypotension and mortality in the general HD population[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2023, 38(7):1700-1706. |
| [32] |
曹虎男, 刘玉秀, 樊蕊, 等. 老年维持性血液透析患者透析中低血压的危险因素分析[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志, 2023, 39(2):101-111.
DOI |
|
Cao HN, Liu YX, Fan R, et al. Analysis of risk factors for intradialytic hypotension in elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Nephrol, 2023, 39(2):101-111.
DOI |
|
| [33] | 陈雪兰, 丘余良. 维持性血液透析患者频发透析中低血压的相关因素分析[J]. 中国现代医生, 2020, 58(23):110-112,117. |
| Chen XL, Qiu YL. Analysis of related factors of frequent intradialytic hypotension in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. China Mod Dr, 2020, 58(23):110-112,117. | |
| [34] | 郭雪梅, 朱朕男, 罗佳懿, 等. 维持性血液透析患者透析中低血压风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中国血液净化, 2022, 21(6):408-412. |
| Guo XM, Zhu ZN, Luo JY, et al. Construction and validation of a prediction model for the risk of intradialytic hypotension in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2022, 21(6):408-412. | |
| [35] | 何鑫, 詹亚, 张红, 等. 列线图模型对3906名血液透析患者透析中低血压发生风险的预测及评估[J]. 中国血液净化, 2022, 21(5):350-355. |
| He X, Zhan Y, Zhang H, et al. Prediction and evaluation of intradialytic hypotension risk in 3,906 hemodialysis patients by a nomogram model[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2022, 21(5):350-355. | |
| [36] | 李鹏举, 刘凤菊. 维持性血液透析患者合并透析相关低血压的危险因素[J]. 国际移植与血液净化杂志, 2022, 20(5):9-12. |
| Li PJ, Liu FJ. Risk factors for dialysis-related hypotension in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Int J Transplant Hemo-purification, 2022, 20(5):9-12. | |
| [37] |
林丽桑, 何丽芳, 应秀红. 维持性血液透析患者透析中低血压风险预测模型的构建[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(10):1466-1471.
DOI |
|
Lin LS, He LF, Ying XH. Development of a risk prediction model for intradialytic hypotension in patients with maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(10):1466-1471.
DOI |
|
| [38] | 罗平平, 张红梅. 透析前血浆渗透压对血液透析患者频发性透析中低血压的预测价值[J]. 中国血液净化, 2022, 21(2):103-106. |
| Luo PP, Zhang HM. Predialysis plasma osmolality for the prediction of frequent-intradialytic hypotension in hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2022, 21(2):103-106. | |
| [39] | 马国婷, 马欣, 徐文彬, 等. 维持性血液透析患者透析中低血压风险预测模型研究[J]. 成都医学院学报, 2023, 18(1):122-127,136. |
| Ma GT, Ma X, Xu WB, et al. Study on risk prediction models for intradialytic hypotension in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. J Chengdu Med Coll, 2023, 18(1):122-127,136. | |
| [40] | 潘璐璐, 何颖雪, 邵国建. 维持性血液透析患者发生透析中低血压的相关危险因素分析[J]. 浙江医学, 2019, 41(22):2421-2423,2437. |
| Pan LL, He YX, Shao GJ. A study on the related risk factors for intradialytic hypotension in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Zhejiang Med J, 2019, 41(22):2421-2423,2437. | |
| [41] | 秦明明, 张洪旭, 章超群, 等. 平均红细胞体积、红细胞分布宽度与血液透析患者透析中低血压的相关性分析[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志, 2022, 22(7):553-559. |
| Qin MM, Zhang HX, Zhang CQ, et al. Relationships between mean red blood cell volume,red blood cell distribution width and intradialytic hypotension in hemodialysis patients[J]. J Clin Nephrol, 2022, 22(7):553-559. | |
| [42] | 任永强, 何光伦, 于桂巧, 等. 维持性血液透析诱发低血压的危险因素[J]. 武警医学, 2022, 33(10):869-872. |
| Ren YQ, He GL, Yu GQ, et al. Risk factors of hypotension caused by maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Med J Chin People’s Armed Police Force, 2022, 33(10):869-872. | |
| [43] | 王仁伴, 胡文雯, 邵国建. 维持性血液透析患者透析中低血压发生的列线图预测模型构建与评估[J]. 现代实用医学, 2022, 34(4):439-441,473. |
| Wang RB, Hu WW, Shao GJ. Construction and evaluation of a nomogram prediction model for the occurrence of intradialysis hypotension in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Mod Pract Med, 2022, 34(4):439-441,473. | |
| [44] | 王欣, 曹艳佩, 杨晓莉, 等. 血液透析患者频发性透析中低血压发生情况和影响因素分析[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2019, 35(8):599-603. |
| Wang X, Cao YP, Yang XL, et al. Analysis on the occurrence and influencing factors of frequent intradialytic hypotension in hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Pract Nurs, 2019, 35(8):599-603. | |
| [45] | 姚为华, 刁宗礼, 李霞, 等. 糖尿病患者血液透析中低血压的影响因素分析[J]. 中国血液净化, 2022, 21(5):346-349. |
| Yao WH, Diao ZL, Li X, et al. The influencing factors for intradialytic hypotension in diabetic patients with maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2022, 21(5):346-349. | |
| [46] | 张红, 周培一, 党毅, 等. 透析间期体质量增长情况与透析性低血压的相关性分析[J]. 中国血液净化, 2020, 19(8):513-516. |
| Zhang H, Zhou PY, Dang Y, et al. Correlation between interdialytic weight gain and intradialytic hypotension[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2020, 19(8):513-516. | |
| [47] | 祖源, 喻倩, 李寒, 等. 维持性血液透析患者高频透析相关低血压与透析后乳酸水平相关性研究[J]. 中国血液净化, 2019, 18(10):669-672. |
| Zu Y, Yu Q, Li H, et al. The relationship between high frequency dialysis related intradialytic hypotension and post-dialysis lactic acid level in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Chin J Blood Purif, 2019, 18(10):669-672. | |
| [48] | Drury ER, Wu J, Gigliotti JC, et al. Sex differences in blood pressure regulation and hypertension:renal,hemodynamic,and hormonal mechanisms[J]. Physiol Rev, 2024, 104(1):199-251. |
| [49] | Nitta K, Masakane I, Hanafusa N, et al. Annual dialysis data report 2017,JSDT Renal Data Registry[J]. Ren Replace Ther, 2019, 5(1):53. |
| [50] | Flint AC, Conell C, Ren XS, et al. Effect of systolic and diastolic blood pressure on cardiovascular outcomes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 381(3):243-251. |
| [51] |
赵洁, 常红, 王晓娟, 等. 脑卒中患者静脉溶栓24小时内血压与出血的相关性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(7):981-984.
DOI |
|
Zhao J, Chang H, Wang XJ, et al. Association between 24-hour blood pressure and bleeding complications in patients underwent intravenous thrombolysis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(7):981-984.
DOI |
|
| [52] |
Buchanan C, Mohammed A, Cox E, et al. Intradialytic cardiac magnetic resonance imaging to assess cardiovascular responses in a short-term trial of hemodiafiltration and hemodialysis[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017, 28(4):1269-1277.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | Zhou C, Shi ZY, Ouyang N, et al. Hyperphosphatemia and cardiovascular disease[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9:644363. |
| [54] | Hong CL, Zhu HP, Zhou XD, et al. Association of blood urea nitrogen with cardiovascular diseases and all-cause mortality in USA adults:results from NHANES 1999-2006[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15(2):461. |
| [55] | Huang YX, Lin YF, Zhai XB, et al. Association of beta-2-microglobulin with coronary heart disease and all-cause mortality in the United States general population[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9:834150. |
| [1] | 韩冬芳, 田甜, 高畅, 张婧珺, 李小妹. 肺结核患者健康促进行为与健康心理控制源关系的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1029-1036. |
| [2] | 司茜茜, 王莹, 赵福云, 马晓骁, 刘均娥. A型主动脉夹层患者Ⅰ期心肺康复护理方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1037-1042. |
| [3] | 沈支佳, 陈新宇, 钱志杰, 殷丽梅. 反复低血糖患者血糖管理行为退化特征的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1043-1050. |
| [4] | 王丽梅, 李露, 李玉霞, 喻鹏, 罗倩, 张翀旎. 糖尿病周围神经病理性疼痛患者运动恐惧现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1051-1056. |
| [5] | 丁慧敏, 戴莉敏, 蔡冬青, 杨群. 糖尿病前期患者自我管理潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1057-1064. |
| [6] | 刘海婷, 王咏梅, 郑贝贝, 蔡丽丽, 叶林斌, 吴佳芸, 宁丽, 李益民, 陈为霞. 冠心病合并糖尿病患者药物素养自评量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1065-1071. |
| [7] | 陈丽霞, 施慧, 朱德政, 曾莹. 成人低血糖恐惧评估工具的质量评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1072-1079. |
| [8] | 中国研究型医院学会过敏医学专业委员会, 中华医学会变态反应分会过敏性疾病护理学组(筹), 中华预防医学会过敏病预防与控制专业委员会, (执笔:王青 刘君 支凡 万文锦 田丰英 霍晓鹏 周文华 杨永仕 王田田 孙劲旅). 变应原特异性免疫治疗皮下注射护理的专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1080-1083. |
| [9] | 李琪, 苏晴晴, 张瑶瑶, 王田田, 吕静, 李亚可, 李海燕. 全膝关节置换患者关节遗忘变化轨迹及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1084-1090. |
| [10] | 刘娅, 刘晓晴, 杨雪凝, 王平, 刘学奎, 罗丹. 结肠镜检查患者肠道准备失败风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1091-1098. |
| [11] | 孙晓晴, 张爱霞, 朱珠, 樊雪梅, 梅士娟, 黄欣欣, 丛胜楠, 谢红燕. 分娩心理创伤评估量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1099-1105. |
| [12] | 谢玉生, 黄蓉蓉, 赵雪, 马蕾, 胡雁, 杨倩, 王乾沙, 明玥. 成人重度烧伤患者肠内肠外营养的证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1106-1113. |
| [13] | 李旭琴, 冯洁惠, 黄昉芳, 俞超, 梁诗雨, 王晓, 李旭芳, 朱含. 1例行机械循环辅助桥接心脏移植患者的术前护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1114-1117. |
| [14] | 贾晓静, 陈一竹, 许志英, 和霞, 耿超. 1例尿黑酸尿症双膝关节置换术后患者并发急性心肌梗死的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1118-1121. |
| [15] | 顾培培, 曾妃, 兰美娟, 梁江淑渊, 郭璐瑶, 蔡凌云, 朱岩, 郭鸽. 肺移植患者衰弱影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1122-1129. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||