


中华护理杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (19): 2316-2323.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2022.19.002
高静( ), 蔡壮(
), 蔡壮( ), 李菲菲, 许冬梅, 张健一, 费琤, 张仁霞, 叶晓露
), 李菲菲, 许冬梅, 张健一, 费琤, 张仁霞, 叶晓露
收稿日期:2021-12-03
出版日期:2022-10-10
发布日期:2022-10-10
通讯作者:
蔡壮,E-mail: cai-zhuang001@163.com作者简介:高静:女,硕士,副主任护师,护士长,E-mail: dy5823415@163.com
基金资助:
GAO Jing( ), CAI Zhuang(
), CAI Zhuang( ), LI Feifei, XU Dongmei, ZHANG Jianyi, FEI Cheng, ZHANG Renxia, YE Xiaolu
), LI Feifei, XU Dongmei, ZHANG Jianyi, FEI Cheng, ZHANG Renxia, YE Xiaolu
Received:2021-12-03
Online:2022-10-10
Published:2022-10-10
摘要:
目的 构建老年住院精神障碍患者营养不良风险预测模型,为临床营养状况评估提供依据。 方法 采用便利抽样法,将2020年6月—2021年6月在北京市某精神疾病医院住院的584例老年精神障碍患者分为无营养不良组(152例)、有营养不良风险组(129例)、营养不良组(303例)3组,采用一般资料调查表、衰弱筛查量表、微型营养评估量表、简易体能状况量表、Barthel指数评定量表、家庭关怀度指数测评量表对患者进行调查,采用Logistic回归分析及Graphpad Prism软件绘制受试者操作特征曲线,检验模型拟合度及预测效果。 结果 老年住院精神障碍患者营养不良发生率为51.88%,高龄(OR=1.049)、衰弱(OR=2.578)、BMI(OR=0.629)是有营养不良风险的独立危险因素(P<0.05);高龄(OR=1.031)、诊断(OR=2.150)、衰弱(OR=2.485)、肌体功能障碍(OR=2.123)是营养不良的独立危险因素(P<0.05),衰弱是有营养不良风险转化为营养不良的最大危险因素;有营养不良风险的受试者操作特征曲线下面积为0.732,约登指数为0.388,最佳临界值为0.473,预测模型的灵敏度为0.736,特异度为0.651;营养不良的受试者操作特征曲线下面积为0.808,约登指数为0.531,最佳临界值为0.581,预测模型的灵敏度为0.865,特异度为0.667,显示两个预测模型准确可靠。 结论 该研究构建的住院老年精神障碍患者营养风险预测模型具有较高的准确性,可为老年住院精神障碍患者营养状况风险评估及防治提供依据。
高静, 蔡壮, 李菲菲, 许冬梅, 张健一, 费琤, 张仁霞, 叶晓露. 老年住院精神障碍患者营养不良风险预测模型的构建[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(19): 2316-2323.
GAO Jing, CAI Zhuang, LI Feifei, XU Dongmei, ZHANG Jianyi, FEI Cheng, ZHANG Renxia, YE Xiaolu. Nutritional risk prediction model for elderly hospitalized patients with mental disorders[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2022, 57(19): 2316-2323.
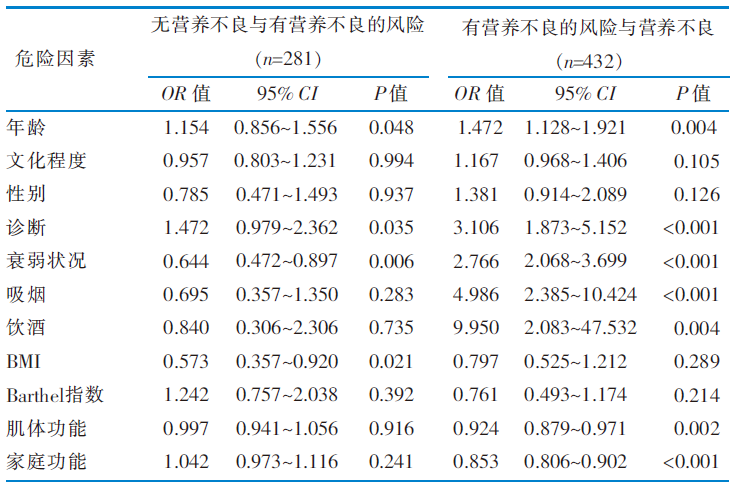 |
表2 老年住院精神障碍患者营养不良的单因素Logistic回归分析
Table 2 Univariate logistic regression analysis of malnutrition in elderly hospitalized patients with mental disorders
 |
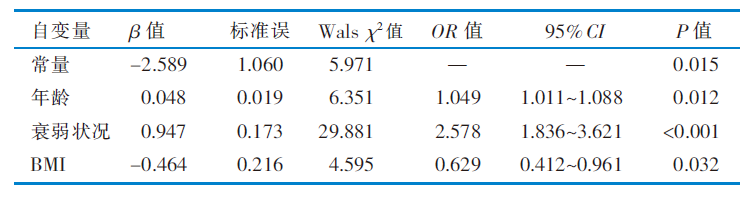 |
表3 老年住院精神障碍患者有营养不良风险的多因素Logistic回归分析(n=281)
Table 3 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of elderly hospitalized patients with mental disorders at risk of malnutrition(n=281)
 |
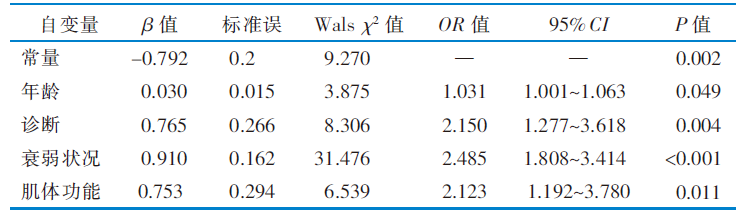 |
表4 老年住院精神障碍患者营养不良的多因素Logistic回归分析(n=432)
Table 4 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of malnutrition in elderly hospitalized patients with mental disorders(n=432)
 |
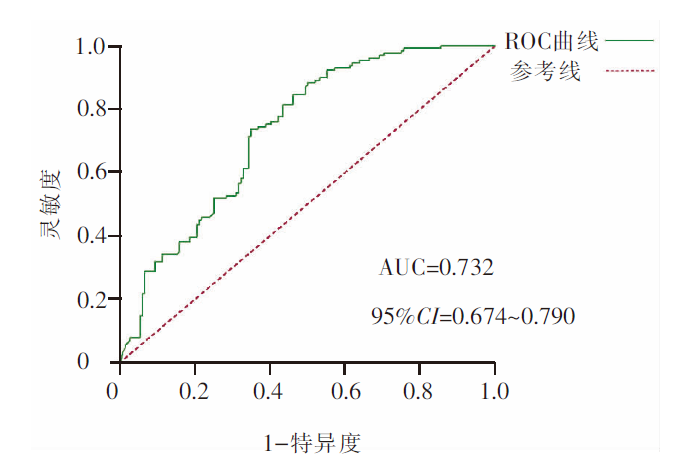
图1 老年住院精神障碍患者有营养不良风险的风险模型ROC曲线图 注:ROC为受试者工作特征曲线,AUC为曲线下面积。
Figure 1 ROC plot of the risk model with malnutrition risk of elderly hospitalized patients with mental disorders
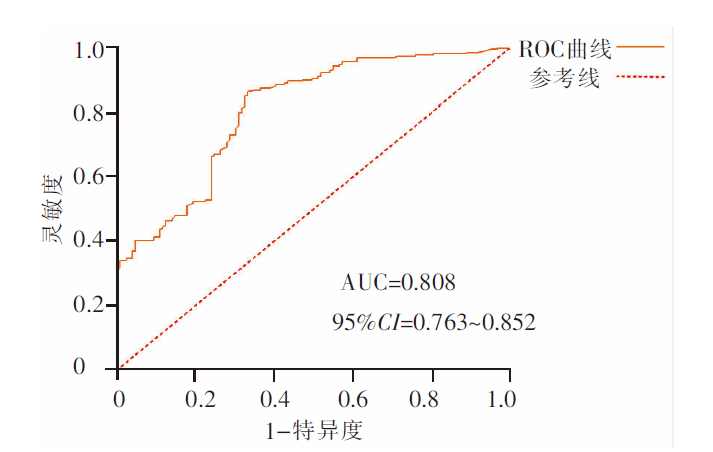
图2 老年住院精神障碍患者营养不良的风险模型ROC曲线图 注:ROC为受试者工作特征曲线,AUC为曲线下面积。
Figure 2 ROC plot of the risk model for malnutrition of elderly hospitalized patients with mental disorders
| [1] |
Vanderwee K, Clays E, Bocquaert I, et al. Malnutrition and associated factors in elderly hospital patients:a Belgian cross-sectional,multi-centre study[J]. Clin Nutr, 2010, 29(4):469-476.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Liu HP, Jiao J, Zhu C, et al. Associations between nutritional status,sociodemographic characteristics,and health-related variables and health-related quality of life among Chinese elderly patients:a multicenter prospective study[J]. Front Nutr, 2020, 7:583161.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Martínez-Reig M, Gómez-Arnedo L, Alfonso-Silguero SA, et al. Nutritional risk,nutritional status and incident disability in older adults. The FRADEA study[J]. J Nutr Health Aging, 2014, 18(3):270-276.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Pierce M, Hope HF, Kolade A, et al. Effects of parental mental illness on children’s physical health:systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Br J Psychiatry, 2020, 217(1):354-363.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Poorrezaeian M, Siassi F, Milajerdi A, et al. Depression is related to dietary diversity score in women:a cross-sectional study from a developing country[J]. Ann Gen Psychiatry, 2017, 16:39.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
惠宁, 张文杰. 慢性心力衰竭患者营养不良风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(3):325-329.
DOI URL |
|
Hui N, Zhang WJ. Construction and evaluation of a model for predicting malnutrition risk in patients with chronic heart failure[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(3):325-329.
DOI URL |
|
| [7] |
王湾湾, 李园园, 石小天, 等. 老年住院患者衰弱的影响因素分析及其与营养不良的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(6):678-684.
DOI |
| Wang WW, Li YY, Shi XT, et al. Frailty-related factors and degree of association of frailty with malnutrition in elderly inpatients[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2021, 24(6):678-684. | |
| [8] | 朱丹, 付萍, 王晓芳, 等. 养老机构老年人营养不良风险及影响因素[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(12):2657-2662. |
| Zhu D, Fu P, Wang XF, et al. The risk and influencing factors of malnutrition in the elderly in nursing homes[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2021, 41(12):2657-2662. | |
| [9] | 武冬冬, 张华, 侯世芳. 强直性肌营养不良的心血管表现及其临床管理策略[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志, 2021, 28(5):415-418. |
| Wu DD, Zhang H, Hou SF. Cardiovascular manifestations and clinical management strategies of myotonic dystrophy[J]. Chin J Neuroimmunol Neurol, 2021, 28(5):415-418. | |
| [10] |
Sandvik D, Bade P, Dunham A, et al. A hospital-to-nursing home transfer process associated with low hospital readmission rates while targeting quality of care,patient safety,and convenience:a 20-year perspective[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2013, 14(5):367-374.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | 许丽娟, 张丽虹, 叶丽娜, 等. 社区老年衰弱危险因素及风险预测模型构建[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(1):170-173. |
| Xu LJ, Zhang LH, Ye LN, et al. Construction of risk factors and risk prediction models for the elderly in the community[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2021, 41(1):170-173. | |
| [12] | Fabre C, Pauly V, Baumstarck K, et al. Pregnancy,delivery and neonatal complications in women with schizophrenia:a national population-based cohort study[J]. Lancet Reg Health Eur, 2021, 10:100209. |
| [13] |
Chern CJH, Lee SD. Malnutrition in hospitalized Asian seniors:an issue that calls for action[J]. J Clin Gerontol Geriatr, 2015, 6(3):73-77.
DOI URL |
| [14] | American Psychiatric Association Autism Spectrum Disorder. Diagnostic and Statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th edition(DMS-5)[M]. M1.Arlington,VA: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013. |
| [15] |
Kaehr E, Visvanathan R, Malmstrom TK, et al. Frailty in nursing homes:the FRAIL-NH scale[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2015, 16(2):87-89.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Liau SJ, Lalic S, Visvanathan R, et al. The FRAIL-NH Scale:systematic review of the use,validity and adaptations for frailty screening in nursing homes[J]. J Nutr Health Aging, 2021, 25(10):1205-1216.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Guigoz Y, Vellas B, Garry PJ. Assessing the nutritional status of the elderly:the Mini Nutritional Assessment as part of the geriatric evaluation[J]. Nutr Rev, 1996, 54(1 Pt 2):S59-S65.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Valentini A, Federici M, Cianfarani MA, et al. Frailty and nutritional status in older people:the Mini Nutritional Assessment as a screening tool for the identification of frail subjects[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2018, 13:1237-1244.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Rogowski Ł, Kusztal M, Gołębiowski T, et al. Nutritional assessment of patients with end-stage renal disease using the MNA scale[J]. Adv Clin Exp Med, 2018, 27(8):1117-1123.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function:association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission[J]. J Gerontol, 1994, 49(2):M85-M94.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Rogan S, Radlinger L, Schmidtbleicher D, et al. Preliminary inconclusive results of a randomised double blinded cross-over pilot trial in long-term-care dwelling elderly assessing the feasibility of stochastic resonance whole-body vibration[J]. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act, 2015, 12:5.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Mahoney FI, Barthel DW. Funcitional evaluation:the barthel index[J]. Md State Med J, 1965, 14:61-65. |
| [23] | 张作记. 行为医学量表手册[M]. 北京: 中华医学电子音像出版社, 2005:156. |
| Zhang ZJ. Handbook of behavioral medicine scale[M]. Beijing: China medical electronic audio visual publishing house, 2005:156. | |
| [24] | 黄心仪, 王华斌, 范希景, 等. SF、CA125、CA15-3在恶性淋巴瘤骨髓受累中的诊断价值[J]. 中国现代医生, 2021, 59(1):20-23,193. |
| Huang XY, Wang HB, Fan XJ, et al. Diagnostic value of SF,CA125 and CA15-3 in bone marrow involvement in malignant lymphoma[J]. China Mod Dr, 2021, 59(1):20-23,193. | |
| [25] | 邢焕民, 吕冬梅, 王晓慧, 等. 术后谵妄风险预测模型的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(1):8-13. |
| Xing HM, Lü DM, Wang XH, et al. The development and application of a risk prediction model for postoperative delirium in ICU patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(1):8-13. | |
| [26] | 杨振, 张会君. 社区老年慢性病患者认知衰弱风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 护理学杂志, 2021, 36(12):86-89. |
| Yang Z, Zhang HJ. A nomogram for predicting the risk of cognitive frailty in community-dwelling elderly people with chronic diseases[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2021, 36(12):86-89. | |
| [27] | 杨宏军, 王晓斌, 师燕. 老年普外科住院患者发生营养风险的危险因素及接受营养支持情况分析[J]. 中国医药, 2021, 16(4):588-591. |
| Yang HJ, Wang XB, Shi Y, et al. The risk factors of nutritional risk and receiving nutritional support in elderly inpatients of department of geriatric general surgery[J]. China Med, 2021, 16(4):588-591. | |
| [28] |
Jie B, Jiang ZM, Nolan MT, et al. Impact of nutritional support on clinical outcome in patients at nutritional risk:a multicenter,prospective cohort study in Baltimore and Beijing teaching hospitals[J]. Nutrition, 2010, 26(11/12):1088-1093.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Schuetz P, Fehr R, Baechli V, et al. Individualised nutritional support in medical inpatients at nutritional risk:a randomised clinical trial[J]. Lancet, 2019, 393(10188):2312-2321.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
McWhirter JP, Pennington CR. Incidence and recognition of malnutrition in hospital[J]. BMJ, 1994, 308(6934):945-948.
PMID |
| [31] | 张宏强, 邓小豆, 周玉红, 等. 老年精神障碍患者营养状况调查[J]. 中国现代医生, 2016, 54(26):142-144. |
| Zhang HQ, Deng XD, Zhou YH, et al. Investigation of nutritional conditions of elderly patients with mental disorders[J]. China Mod Dr, 2016, 54(26):142-144. | |
| [32] | Hao RX, Qi XM, Xia XS, et al. Malnutrition on admission increases the in-hospital mortality and length of stay in elder adults with acute ischemic stroke[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2022, 36(1):e24132. |
| [33] | 何福培. 衰弱与营养不良的相关性研究进展[J]. 全科护理, 2021, 19(19):2637-2640. |
| He FP. Research progress on the correlation between weakness and malnutrition[J]. Chin Gen Pract Nurs, 2021, 19(19):2637-2640. | |
| [34] |
Verlaan S, Ligthart-Melis GC, Wijers SLJ, et al. High prevalence of physical frailty among community-dwelling malnourished older adults-a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2017, 18(5):374-382.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | 刘枫, 束敏, 陈志美, 等. 老年人衰弱与营养状况关系的研究进展[J]. 中西医结合护理(中英文), 2019, 5(10):216-218. |
| Liu F, Shu M, Chen ZM, et al. Research progress of the relationship between frailty and nutrition in the elderly[J]. Nurs Integr Tradit Chin West Med, 2019, 5(10):216-218. | |
| [36] |
Volkert D, Chourdakis M, Faxen-Irving G, et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutrition in dementia[J]. Clin Nutr, 2015, 34(6):1052-1073.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Agarwal E, Miller M, Yaxley A, et al. Malnutrition in the elderly:a narrative review[J]. Maturitas, 2013, 76(4):296-302.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Chapman IM. Weight loss in older persons[J]. Med Clin North Am, 2011, 95(3):579-593,xi.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 陈颖勇, 张正敏, 左倩倩, 等. 社区老年人认知衰弱风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(2):197-203. |
| Chen YY, Zhang ZM, Zuo QQ, et al. Construction and validation of a prediction model for the risk of cognitive frailty among the elderly in a community[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(2):197-203. | |
| [40] | 王丽娜, 赵岳. 轻度认知障碍的早期识别及相关理论模型的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(5):612-617. |
| Wang LL, Zhao Y. Research progress on early recognition of mild cognitive impairment and related theoretical models[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(5):612-617. | |
| [41] |
郭琳, 丁焱, 张铮, 等. 分娩时会阴切开决策影响因素预测模型的构建[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(10):1469-1474.
DOI URL |
| Guo L, Ding Y, Zhang Z, et al. Establishment of predictive model of midwives’ decision on episiotomy during childbirth[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(10):1469-1474. |
| [1] | 吴月红, 梁红霞, 席芳, 李成, 李莹莹, 贾育萌, 郑云云, 冯珍珍. 体外膈肌起搏预防无创机械通气患者膈肌功能障碍的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1029-1034. |
| [2] | 王子安, 刘欣, 张茜, 俞梦盈, 郑贝贝, 陆骏, 陈婷婷. 经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者恐动症水平变化轨迹研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1035-1041. |
| [3] | 邓雁, 余琼, 武福姣, 方亮. 基于自我效能理论的护理干预对食管癌根治术后患者的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1042-1047. |
| [4] | 成磊, 钱佳艺, 段明霞, 黄海英, 王颖雯. 专业照护者感知的癌症患儿向成人过渡影响因素的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1048-1053. |
| [5] | 孙艳霞, 李莹, 刘明月, 郭丹丹, 李敏. 宫颈癌患者性健康护理培训方案的构建[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1054-1060. |
| [6] | 胡丽莎, 彭红华, 米元元, 曹咪, 胡敏, 祝玲, 喻红君, 彭淑华. 肿瘤靶向治疗患者皮肤不良反应预防及管理的证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1061-1069. |
| [7] | 孙倩倩, 叶红芳, 杨莉. 接纳与承诺疗法对乳腺癌患者干预效果的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1070-1078. |
| [8] | 李静, 侯云霞, 强万敏. 癌症患者非计划性再入院风险预测模型的范围综述[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1079-1087. |
| [9] | 孟祥敏, 王倩, 闫荣, 林雨婷, 丁敏. 结直肠癌患者报告结局评估工具及临床应用的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1094-1099. |
| [10] | 周红琴, 陈秀萍, 诸纪华, 夏姗姗, 金陈娣, 盛美君, 罗飞翔, 谢王芳, 左泽兰, 胡静, 刘丽丽, 浦凯. 儿科ICU护士对每日唤醒患儿的知信行现状调查[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1100-1104. |
| [11] | 蒋琪霞, 唐永利, 洪艳燕, 匡丹, 王静, 展颖颖, 潘迎春, 高艳红, 郝景平, 陈锐, 刘海燕, 俞萍, 蔡蕴敏, 黄玲, 王祖晶. 50所医院老年患者皮肤损伤现状及危险因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1105-1112. |
| [12] | 贾红红, 刘丽, 罗小茜, 周郁秋. 认知-预警干预对农村糖尿病治疗延误患者的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1113-1119. |
| [13] | 张毅, 汪健健, 邓艳红, 陈章群, 罗姜, 彭德珍, 赵丽萍. 护士人文素养自评量表的研制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1120-1128. |
| [14] | 吴海燕, 王淑芹, 郭琪, 张春艳, 贾燕瑞, 孙兵. 1例肾病综合征合并肺孢子菌及巨细胞病毒肺炎患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1129-1133. |
| [15] | 张晓梅, 秦毅, 陈瑜, 王伶俐, 李静逸, 王娅. 经中心静脉通路装置采血的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1134-1140. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||