


中华护理杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (9): 1061-1069.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2022.09.006
胡丽莎( ), 彭红华, 米元元, 曹咪, 胡敏, 祝玲, 喻红君, 彭淑华(
), 彭红华, 米元元, 曹咪, 胡敏, 祝玲, 喻红君, 彭淑华( )
)
收稿日期:2021-10-13
出版日期:2022-05-10
发布日期:2022-05-12
通讯作者:
彭淑华,E-mail: Xingqing080808@126.com作者简介:胡丽莎:女,本科(硕士在读),E-mail: 1156915358@qq.com
HU Lisha( ), PENG Honghua, MI Yuanyuan, CAO Mi, HU Min, ZHU Ling, YU Hongjun, PENG Shuhua(
), PENG Honghua, MI Yuanyuan, CAO Mi, HU Min, ZHU Ling, YU Hongjun, PENG Shuhua( )
)
Received:2021-10-13
Online:2022-05-10
Published:2022-05-12
摘要:
目的 遴选并总结肿瘤靶向治疗患者皮肤不良反应预防及管理的最佳证据,为临床决策提供参考。方法 计算机检索BMJ最佳临床实践、UpToDate临床决策系统、乔安娜布里格斯研究所循证卫生保健中心数据库、国际指南协作网、英国国家卫生与临床优化研究所、苏格兰院际指南网、医脉通指南网、美国国立临床诊疗指南数据库、美国医疗保健与研究质量局、加拿大安大略注册护士协会、世界肿瘤学网站、美国国家癌症综合网站、中国抗癌协会肺癌专业委员会、中国抗癌协会肿瘤护理专业委员协会、Cochrane Library、Embase、CHINAL、Web of Science、OVID、PubMed、SinoMed、中国知网、万方数据和维普数据库等相关网站,检索关于肿瘤靶向治疗患者皮肤不良反应预防及管理的指南、证据总结、最佳实践、专家共识、系统评价及原始研究。检索时限为2011年1月1日—2021年10月3日。由2名研究者进行文献质量评价和资料提取。 结果 共纳入15篇文献,其中3篇指南、4篇证据总结、1篇系统评价、3篇随机对照试验、1篇类实验研究和3篇专家共识,围绕皮肤评估、危险因素、药物治疗、皮肤护理、皮肤不良反应处理、健康教育等6个方面形成19条最佳证据。结论 该研究总结了肿瘤靶向治疗患者皮肤不良反应预防及管理的最佳证据,为医护人员提供循证依据,医护人员应结合临床情景,充分评估患者皮肤状况,做好皮肤方面的健康教育、检查和护理,预防皮肤不良反应的发生。
胡丽莎, 彭红华, 米元元, 曹咪, 胡敏, 祝玲, 喻红君, 彭淑华. 肿瘤靶向治疗患者皮肤不良反应预防及管理的证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1061-1069.
HU Lisha, PENG Honghua, MI Yuanyuan, CAO Mi, HU Min, ZHU Ling, YU Hongjun, PENG Shuhua. Evidence summary for prevention and management of the skin adverse reactions in patients with targeted tumor therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2022, 57(9): 1061-1069.
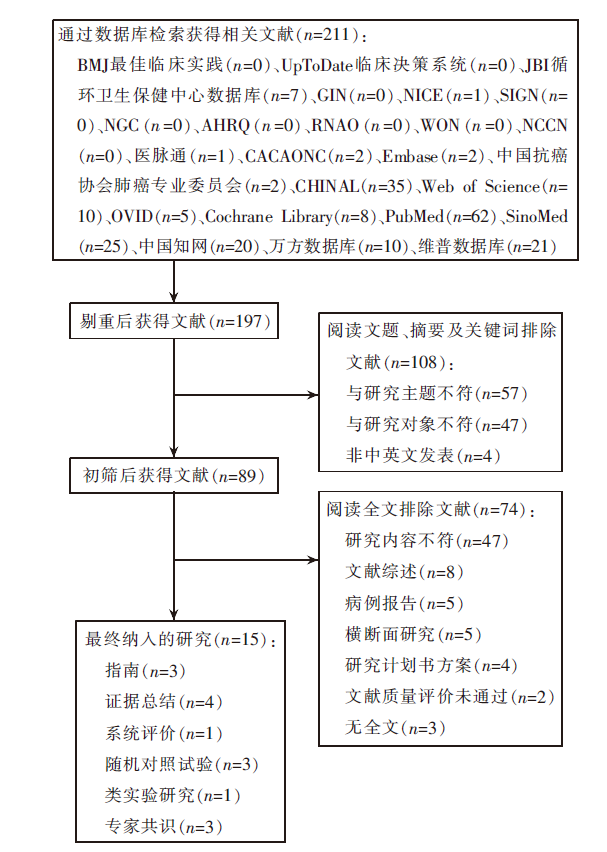
图2 文献筛选流程图 注:BMJ为最佳临床实践、JBI为乔安娜布里格斯研究所、GIN为国际指南协作网、NICE为英国国家卫生与临床优化研究所、SIGN为苏格兰院际指南网、NGC为美国国立临床诊疗指南数据库、AHRQ为美国医疗保健与研究质量局、RNAO为加拿大安大略注册护士协会、WON为世界肿瘤学网站、NCCN为美国国家癌症综合网站、CACAONC为中国抗癌协会肿瘤护理专业委员协会。
Figure 2 Flow chart of literature screening
 |
表3 肿瘤靶向治疗患者皮肤不良反应预防及管理的最佳证据总结
Table 3 Evidence summary for the best prevention and management of the skin adverse reactions in patients with targeted tumor therapy
 |
| [1] |
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3):209-249.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 肿瘤医学论坛. 2020年全球癌症最新数据解读[J]. 中国肿瘤临床与康复, 2021, 28(3):301. |
| Cancer Medicine Forum. Interpretation of the latest global cancer data in 2020[J]. Chin J Clin Oncol Rehabilitation, 2021, 28(3):301. | |
| [3] |
Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer(OAK):a phase 3,open-label,multicentre randomised controlled trial[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10066):255-265.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Motoi F, Kosuge T, Ueno H, et al. Randomized phase II/III trial of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine and S-1 versus upfront surgery for resectable pancreatic cancer(Prep-02/JSAP05)[J]. Jpn J Clin Oncol, 2019, 49(2):190-194.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Ding JY, Farah MH, Nayfeh T, et al. Targeted therapy-and chemotherapy-associated skin toxicities:systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Oncol Nurs Forum, 2020, 47(5):E149-E160. |
| [6] |
Lacouture ME, Anadkat M, Jatoi A, et al. Dermatologic toxicity occurring during anti-EGFR monoclonal inhibitor therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer:a systematic review[J]. Clin Colorectal Cancer, 2018, 17(2):85-96.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 笪美红, 史美祺, 严翘, 等. 阿法替尼皮肤不良反应及其与疗效的相关性分析[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志, 2021, 54(1):64-67. |
| Da MH, Shi MQ, Yan Q, et al. Skin adverse reactions to afatinib and their correlation with anti-lung cancer efficacy[J]. Chin J Dermatol, 2021, 54(1):64-67. | |
| [8] | 笪美红. 表皮生长因子受体抑制剂相关皮肤不良反应临床研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018. |
| Da MH. Clinical research of dermatologic adverse events induced by epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2018. | |
| [9] |
Agirgol S, aytemel C, Pilanci KN. Dermatological side effects of targeted antineoplastic therapies:a prospective study[J]. Cutan Ocul Toxicol, 2020, 39(4):380-384.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Lacouture ME, Sibaud V, Gerber PA, et al. Prevention and management of dermatological toxicities related to anticancer agents:ESMO clinical practice guidelines[J]. Ann Oncol, 2021, 32(2):157-170.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Lacouture ME, Anadkat MJ, Bensadoun RJ, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of EGFR inhibitor-associated dermatologic toxicities[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2011, 19(8):1079-1095.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Melosky B, Leighl NB, Rothenstein J, et al. Management of egfr- tki-induced dermatologic adverse events[J]. Curr Oncol, 2015, 22(2):123-132.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | 张方圆, 吕苏梅, 杨玄, 等. 中国癌症症状管理实践指南:皮肤反应[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2019, 34(22):2017-2024. |
| Zhang FY, Lü SM, Yang X, et al. China cancer symptom management practice guideline:skin reaction[J]. J Nurses Train, 2019, 34(22):2017-2024. | |
| [14] | 朱政, 胡雁, 邢唯杰, 等. 不同类型循证问题的构成[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2017, 32(21):1991-1994. |
| Zhu Z, Hu Y, Xing WJ, et al. The composition of different types of evidence based problems[J]. J Nurses Train, 2017, 32(21):1991-1994. | |
| [15] | 谢利民, 王文岳. 《临床指南研究与评价系统Ⅱ》简介[J]. 中西医结合学报, 2012, 10(2):160-165. |
|
Xie LM, Wang WY. A brief introduction to appraisal of guidelines for research and evaluation Ⅱ[J]. J Chin Integr Med, 2012, 10(2):160-165.
DOI URL |
|
| [16] | 张方圆, 沈傲梅, 曾宪涛, 等. 系统评价方法学质量评价工具AMSTAR 2解读[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2018, 10(1):14-18. |
| Zhang FY, Shen AM, Zeng XT, et al. An introduction to AMSTAR 2:a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews[J]. Chin J Evid Based Cardiovasc Med, 2018, 10(1):14-18. | |
| [17] | 胡雁, 郝玉芳. 循证护理学[M]. 2版 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017:31. |
| Hu Y, Hao YF. Evidence based nursing[M]. 2 nd ed. Beijing: People’s Health Publishing House, 2017:31. | |
| [18] | 米元元, 黄培培, 董江, 等. 危重症患者肠内营养不耐受预防及管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(12):1868-1876. |
| Mi YY, Huang PP, Dong J, et al. Best evidence summary for prevention and management of enteral feeding intolerance in critically ill patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(12):1868-1876. | |
| [19] | 马婷婷, 吴琼, 欧阳静, 等. 中国癌症症状管理实践指南:口腔黏膜炎[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2020, 35(20):1871-1878. |
| Ma TT, Wu Q, Ouyang J, et al. Construction of Chinese management practice guideline for oral mucositis for cancer patients[J]. J Nurses Train, 2020, 35(20):1871-1878. | |
| [20] | Fong E. Targeted therapy:treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor(EGFRI) induced paronychia[EB/OL].(2019-07-01)[2021-10-03]. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=jbi&NEWS=N&AN=JBI17014. |
| [21] | Fong E. Targeted therapy:epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor(EGFRI) assocliated skin rash prevedntion and treatment[EB/OL].(2018-05-10)[2021-10-03]. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=jbi&NEWS=N&AN=JBI16060. |
| [22] | Sydor A. Targeted therapy:epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor(EGFRI) assocliated dermatitis[EB/OL].(2019-01-10)[2021-10-03]. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=jbi&NEWS=N&AN=JBI16059. |
| [23] | 郭小璐, 陈凤珍, 张晓菊, 等. 表皮生长因子受体抑制剂所致皮肤毒性症状管理的最佳证据应用[J]. 中国护理管理, 2018, 18(2):282-287. |
| Guo XL, Chen FZ, Zhang XJ, et al. The application of best evidence-informed practice of skin toxicity caused by EGFRIs[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2018, 18(2):282-287. | |
| [24] |
Ensslin CJ, Rosen AC, Wu SH, et al. Pruritus in patients treated with targeted cancer therapies:systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2013, 69(5):708-720.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Si XY, Zhang L, Wang HP, et al. Management of anlotinib-related adverse events in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer:experiences in ALTER-0303[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2019, 10(3):551-556.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Clabbers JMK, Boers-Doets CB, Gelderblom H, et al. Xerosis and pruritus as major EGFRI-associated adverse events[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2016, 24(2):513-521.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | 于然, 贾立群, 裴育莹, 等. 中药复方LC09颗粒泡洗联合尿素软膏治疗抗肿瘤靶向药物多激酶抑制剂致手足皮肤反应的随机对照双盲临床研究[J]. 中医杂志, 2020, 61(23):2078-2081. |
| Yu R, Jia LQ, Pei YY, et al. Study on traditional Chinese medicine compound LC09 granule soaking combined with urea ointment in the treatment of hand-foot skin reactions caused by anti-tumor targeted drug multikinase inhibitors:a randomized-controlled double-blind clinical trial[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 61(23):2078-2081. | |
| [28] |
Dika E, Patrizi A, Ribero S, et al. Hair and nail adverse events during treatment with targeted therapies for metastatic melanoma[J]. Eur J Dermatol, 2016, 26(3):232-239.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
王碧芸, 葛睿, 江泽飞, 等. 乳腺癌靶向人表皮生长因子受体2酪氨酸激酶抑制剂不良反应管理共识[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2020, 42(10):798-806.
PMID |
|
Wang BY, Ge R, Jiang ZF, et al. Expert consensus on the management of adverse events of ErbB family tyrosine kinase inhibitors in breast cancer[J]. Chin J Oncol, 2020, 42(10):798-806.
DOI PMID |
|
| [30] | 王刚, 项蕾红, 袁瑛, 等. 抗EGFR单抗治疗相关皮肤不良反应临床处理专家共识[J]. 实用肿瘤杂志, 2021, 36(3):195-201. |
| Wang G, Xiang LH, Yuan Y, et al. Expert consensus on management of skin toxicities induced by anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody[J]. J Pract Oncol, 2021, 36(3):195-201. | |
| [31] | 胡洁, 林丽珠, 骆肖群, 等. EGFR-TKI不良反应管理专家共识[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2019, 22(2):57-81. |
| Hu J, Lin LZ, Luo XQ, et al. EGFR-TKI ADR management Chinese expert consensus[J]. Chin J Lung Cancer, 2019, 22(2):57-81. | |
| [32] |
Brown J, Su Y, Nelleson D, et al. Management of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-associated rash:a systematic review[J]. J Community Support Oncol, 2016, 14(1):21-28.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Wagner LI, Berg SR, Gandhi M, et al. The development of a Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy(FACT) questionnaire to assess dermatologic symptoms associated with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors(FACT-EGFRI-18)[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2013, 21(4):1033-1041.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | 张仲昭. 简体中文版Skindex-29和Skindex-16的建立和文化调适及信效度评价[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2013. |
| Zhang ZZ. Establishment,cultural adaptation,reliability and validity evaluation of simplified Chinese versions of skindex-29 and skindex-16[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2013. | |
| [35] |
Du RF, Wang X, Ma LX, et al. Adverse reactions of targeted therapy in cancer patients:a retrospective study of hospital medical data in China[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1):206.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Barton-Burke M, Ciccolini K, Mekas M, et al. Dermatologic reactions to targeted therapy:a focus on epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors and nursing care[J]. Nurs Clin North Am, 2017, 52(1):83-113.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 王芳, 唐旭华, 周晖. 分子靶向抗肿瘤药物的皮肤不良反应及处理[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志, 2016, 49(7):519-523. |
| Wang F, Tang XH, Zhou H. Cutaneous adverse reactions to molecular targeted antitumor drugs and their management[J]. Chin J Dermatol, 2016, 49(7):519-523. | |
| [38] | 杨剑霞, 孙丽凯. 复方金银花煎液湿热敷联合夫西地酸乳膏外用治疗分子靶向药物所致皮疹的效果观察[J]. 护理学报, 2015, 22(2):61-62. |
| Yang JX, Sun LK. Observation on the effect of compound honeysuckle decoction wet and hot compress combined with fuxidi acid cream on skin rash caused by molecular targeted drugs[J]. J Nurs China, 2015, 22(2):61-62. | |
| [39] | 杨泽佩, 田桢, 鲍伟倩, 等. 益元通络法针刺治疗手足综合征的临床经验[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2020, 35(6):2932-2935. |
| Yang ZP, Tian Z, Bao WQ, et al. Clinical experience of Yiyuan Tongluo method in treating hand-foot syndrome with acupuncture[J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2020, 35(6):2932-2935. | |
| [40] | 张誉华, 沈洋, 龙麟, 等. 养肺消疹方治疗肺癌靶向药物相关性皮疹的临床观察[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2016, 31(1):100-103. |
| Zhang YH, Shen Y, Long L, et al. Clinical observation of treating rash induced by lung cancer targeted drug with Yangfei Xiaozhen Formula[J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2016, 31(1):100-103. | |
| [41] | 钟香玉, 何晓华, 柯熹. 2型糖尿病口服EGFRI靶向药物致痤疮样皮疹的观察与护理[J]. 护理实践与研究, 2017, 14(18):35-36. |
| Zhong XY, He XH, Ke X. Observation and nursing of acne-like rash induced by oral targeted medicine of EGFRI in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Nurs Pract Res, 2017, 14(18):35-36. | |
| [42] |
Kozuki T. Skin problems and EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor[J]. Jpn J Clin Oncol, 2016, 46(4):291-298.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 陈晨, 刘凌云, 薄婧. 基于中国乳腺癌靶向治疗药物安全性管理专家共识的护理措施临床效果观察[J]. 护理实践与研究, 2021, 18(4):580-582. |
| Chen C, Liu LY, Bo J. Clinical observation of nursing measures based on consensus of experts on safety management of breast cancer targeted therapy in China[J]. Nurs Pract Res, 2021, 18(4):580-582. | |
| [44] | 何雪瑜, 曾小芳. 1例利妥昔单抗治疗重症天疱疮患者并发皮下血肿的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(6):917-920. |
| He XY, Zeng XF. Nursing care of a severe pemphigus complicated patient with subcutaneous hematoma treated with Rituximab[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(6):917-920. | |
| [45] | 王慧琳, 韩红, 朱慧瑛. 晚期非小细胞肺癌分子靶向药物治疗的不良反应及护理[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2017, 32(8):744-746. |
| Wang HL, Han H, Zhu HY. Adverse reactions and nursing of molecular targeted drug therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Nurses Train, 2017, 32(8):744-746. | |
| [46] | 赵云, 羊波, 孟爱凤, 等. 多学科协作干预在居家晚期肾癌靶向治疗患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(4):394-398. |
| Zhao Y, Yang B, Meng AF, et al. Application of multidisciplinary teamwork continuity of care for advanced renal cell carcinoma community dwelling patients treated with targeted drugs[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(4):394-398. | |
| [47] | 李静, 黄李华, 俞瑛. 肺癌患者靶向治疗期间健康教育内容需求的调查[J]. 上海护理, 2016, 16(6):5-8. |
| Li J, Huang LH, Yu Y. Health education demands of patients with non-small cell lung cancer during targeted therapy[J]. Shanghai Nurs, 2016, 16(6):5-8. |
| [1] | 孙艳霞, 李莹, 刘明月, 郭丹丹, 李敏. 宫颈癌患者性健康护理培训方案的构建[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1054-1060. |
| [2] | 孙倩倩, 叶红芳, 杨莉. 接纳与承诺疗法对乳腺癌患者干预效果的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1070-1078. |
| [3] | 张晓梅, 秦毅, 陈瑜, 王伶俐, 李静逸, 王娅. 经中心静脉通路装置采血的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1134-1140. |
| [4] | 岳岚, 许妍, 李珍, 杨长永, 古钰君, 王梦, 李蕾蕾. 肿瘤患者医用粘胶相关性皮肤损伤风险评估量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(8): 964-969. |
| [5] | 任宣霖, 樊落, 田金徽, 朱伟, 郝雅茹. ICU气管插管患者拔管指南的质量评价与内容分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(8): 1001-1007. |
| [6] | 尹晓彤, 朱蓝玉, 王幽, 李雪, 温娜, 朱亚飞. 中青年癌症患者预立医疗照护计划接受度现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(7): 834-840. |
| [7] | 古钰君, 张国增, 冯宪凌, 白杨, 岳岚, 王梦. 癌症患者化疗所致脱发心理体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(7): 872-879. |
| [8] | 罗桢蓝, 胡三莲, 朱凌燕, 徐梦琦, 阮甜甜. 慢性心力衰竭患者自我容量管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(7): 880-886. |
| [9] | 施若霖, 张丽青, 孙捷豪, 翁成杰, 郭城楠, 孙彩霞, 潘贻飞, 谢作流, 王明山, 卢中秋. 间歇充气加压装置不同使用模式对预防直肠癌腹腔镜术中患者静脉血栓的效果[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(6): 695-702. |
| [10] | 穆文方, 王娴, 肖星婷, 王燕, 许志玮. 下肢静脉溃疡患者自我管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(6): 740-747. |
| [11] | 鲁佳, 谢开红, 陈文思, 陈肖敏. 肿瘤患者输液港相关性血栓预防及管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(5): 544-550. |
| [12] | 毛越, 徐剑锋, 李梅, 朱蓓蓓, 杨丹燕, 莫权峰, 何杰. 经导管主动脉瓣置换术患者Ⅰ期心脏康复的最佳证据应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(5): 563-568. |
| [13] | 孙闽闽, 吴娟, 李文霞, 王逸楠, 王莉. 心肌梗死患者出院后重返社会体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(4): 415-423. |
| [14] | 林楠, 诸纪华, 徐红贞, 周红琴. 早产儿体位管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(4): 486-492. |
| [15] | 包磊, 朱丽群, 唐为定, 陈吉祥, 周英凤, 韩小云, 舒芳芳, 曹松梅, 庄若, 殷婷. 非药物管理对成人择期手术术前焦虑影响的系统评价再评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(4): 493-501. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||