


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (21): 2571-2578.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.21.002
收稿日期:2024-06-26
出版日期:2024-11-10
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
孙超,E-mail:sunchaobjyy@163.com作者简介:胡慧秀:女,硕士,主管护师,护理部质量控制办公室主任,E-mail:18610145247@163.com
基金资助:
HU Huixiu( ), SUN Chao(
), SUN Chao( ), ZHAO Yajie, LI Xiang, LI Lei
), ZHAO Yajie, LI Xiang, LI Lei
Received:2024-06-26
Online:2024-11-10
Published:2024-11-04
摘要:
目的 分析不同社区轻度认知障碍老年人生活行为与认知功能下降的相关性。方法 2023年3月—2024年1月,采用便利抽样法,选取北京市2所社区卫生服务中心的轻度认知障碍老年人为调查对象,对其进行6个月的追踪随访,采用一般资料调查表、生活行为调查表、中文版蒙特利尔认知评估量表、简易智能精神状态检查、日常生活活动能力量表进行问卷调查,按照是否出现可靠的临床认知功能变化分为认知功能下降组和未下降组,采用Logistic回归方法分析社区轻度认知障碍老年人认知功能短期内下降的独立影响因素。结果 该研究最终共随访385例社区轻度认知障碍老年人,有113例(29.4%)出现认知功能下降。Logistic回归分析显示,较多被动认知活动、抑郁症状、睡眠质量差是社区轻度认知降碍老年人短期内认知功能快速下降的独立危险因素(P<0.05),而较高的受教育程度和良好社交活动是保护因素(均P<0.05)。结论 社区轻度认知障碍老年人短期内认知功能下降发生率较高,应积极引导轻度认知障碍老年人建立健康生活方式,如良好社交活动、较少被动认知活动、保持良好心理状态及较好睡眠质量等,以延缓甚至逆转其认知功能下降。
胡慧秀, 孙超, 赵雅洁, 李想, 李磊. 社区轻度认知障碍老年人短期内认知功能下降与生活行为的相关性研究及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(21): 2571-2578.
HU Huixiu, SUN Chao, ZHAO Yajie, LI Xiang, LI Lei. The impact of life behaviors on the rapid cognitive decline in the short term among community-dwelling elderly with mild cognitive impairment[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(21): 2571-2578.
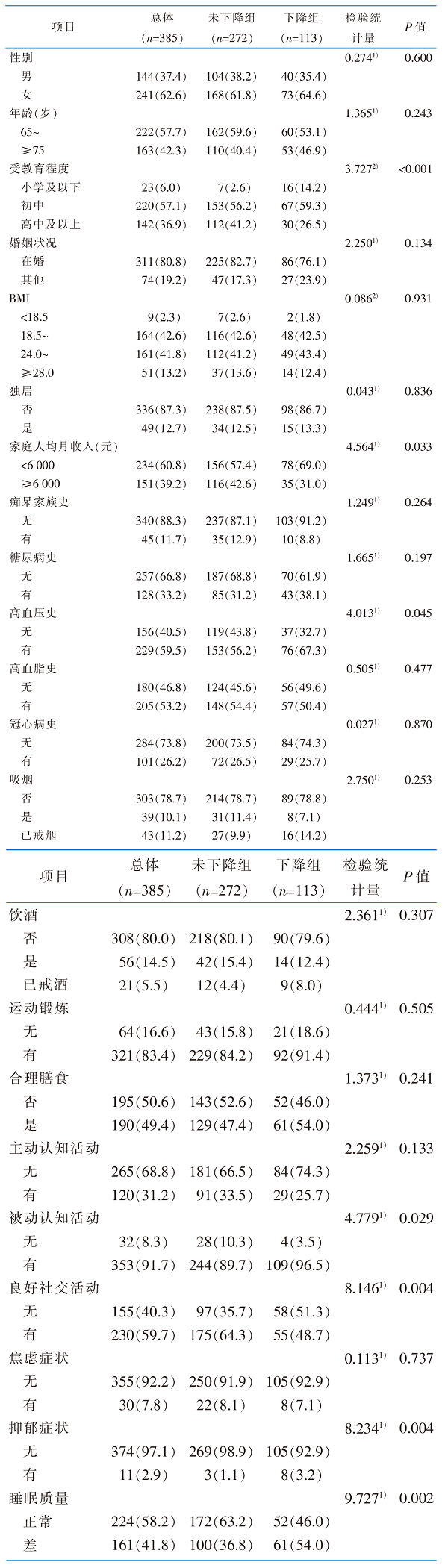 |
表1 调查对象一般资料情况及不同特征社区轻度认知障碍老年人认知功能下降的单因素分析结果[例(百分比,%)]
Table 1 The general information of survey subjects and univariate analysis of the elderly MCI with different characteristics[cases(percentage,%)]
 |
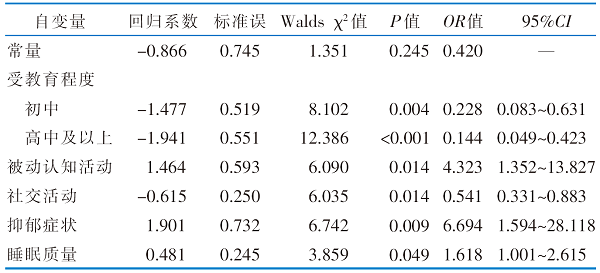 |
表3 社区轻度认知降碍老年人认知功能下降的Logistic回归分析(n=385)
Table 3 Logistic regression analysis of the impact of life behaviors on cognitive decline in the elderly with MCI(n=385)
 |
| [1] | Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC, et al. Mild cognitive impairment:clinical characterization and outcome[J]. Arch Neurol, 1999, 56(3):303-308. |
| [2] | Morris JC, Storandt M, Miller JP, et al. Mild cognitive impairment represents early-stage Alzheimer disease[J]. Arch Neurol, 2001, 58(3):397-405. |
| [3] |
Brodaty H, Connors MH, Ames D, et al. Progression from mild cognitive impairment to dementia:a 3-year longitudinal study[J]. Aust N Z J Psychiatry, 2014, 48(12):1137-1142.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Ganguli M, Dodge HH, Shen CY, et al. Mild cognitive impairment,amnestic type:an epidemiologic study[J]. Neurology, 2004, 63(1):115-121.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | 国家卫生健康委员会. 国家卫生健康委办公厅关于开展老年痴呆防治促进行动(2023—2025年)的通知[EB/OL](2023-05-26)[2024-03-20]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202306/content_6886277.htm. |
| National Health Commission. Notice of the general office of the National Health Commission on promoting the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease(2023-2025)[EB/OL]. (2023-05-26)[2024-03-20]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202306/content_6886277.htm. | |
| [6] | 郭清. 健康管理学[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2023:173. |
| Guo Q. Health management[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2023:173. | |
| [7] | 李晋磊, 金平阅, 王紫娟, 等. 城市社区老人生活方式与社交网络对认知障碍的影响[J]. 中华健康管理学杂志, 2019, 13(3):220-223. |
| Li JL, Jin PY, Wang ZJ, et al. Associations between lifestyle and social network and cognitive impairment among the elderly in three communities in China[J]. Chin J Health Manag, 2019, 13(3):220-223. | |
| [8] | 苏向妮, 化前珍, 陈建华, 等. 社区老年人认知障碍与生活方式的相关性研究[J]. 护理学报, 2016, 23(9):30-33. |
| Su XN, Hua QZ, Chen JH, et al. Correlation between lifestyle and mild cognitive impairment among community-dwelling seniors[J]. J Nurs(China), 2016, 23(9):30-33. | |
| [9] | 陶雪琴. 老年轻度认知功能障碍人群的阿尔茨海默病发病预测模型及风险评估研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2016. |
| Tao XQ. Study on prediction model and risk assessment of Alzheimer’s disease in elderly people with mild cognitive impairment[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2016. | |
| [10] |
Skolariki K, Terrera GM, Danso S. Multivariate data analysis and machine learning for prediction of MCI-to-AD conversion[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2020, 1194:81-103.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组, 中国医师协会神经内科医师分会认知障碍疾病专业委员会. 2018中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南(五):轻度认知障碍的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(17):1294-1301. |
| Chinese Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Dementia and Cognitive Disorders,Cognitive Disorders Professional Committee,Neurology Branch,Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of dementia and cognitive impairment in China in 2018(V):diagnosis and treatment of mild cognitive impairment[J]. Natl Med J China, 2018, 98(17):1294-1301. | |
| [12] | 侯继文. 轻度认知障碍影响因素分析及决策树模型研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2020. |
| Hou JW. Analysis of influencing factors of mild cognitive impairment and research on decision tree model[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2020. | |
| [13] | 石宇. 轻度认知障碍影响因素预测模型研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2018. |
| Shi Y. Study on prediction model of influencing factors of mild cognitive impairment[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2018. | |
| [14] | Raichlen DA, Klimentidis YC, Sayre MK, et al. Leisure-time sedentary behaviors are differentially associated with all-cause dementia regardless of engagement in physical activity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2022, 119(35):e2206931119. |
| [15] | 王瑜龙. 中国老年人社交活动及其影响研究[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学, 2023. |
| Wang YL. A study on the social activities of the elderly in china and their influence[D]. Jilin:Jilin University, 2023. | |
| [16] | 郑颖. 规律性运动大学生的睡眠质量实证研究:以安徽师范大学为例[D]. 芜湖: 安徽师范大学, 2020. |
| Zheng Y. An empirical study on the sleep quality of regular exercise college students:taking Anhui Normal University as an example[D]. Wuhu: Anhui Normal University, 2020. | |
| [17] | 何筱衍, 李春波, 钱洁, 等. 广泛性焦虑量表在综合性医院的信度和效度研究[J]. 上海精神医学, 2010, 22(4):200-203. |
| He XY, Li CB, Qian J, et al. Reliability and validity of a Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale in general hospital outpatients[J]. Shanghai Arch Psychiatr, 2010, 22(4):200-203. | |
| [18] | 侯晓琳, 高静, 吴晨曦, 等. 养老机构老年人衰弱现状及分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(1):88-93. |
| Hou XL, Gao J, Wu CX, et al. Prevalence and factors associated with frailty among institutional older adults[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(1):88-93. | |
| [19] | 潘惠英, 王君俏, 周标, 等. 老年轻度认知障碍患者抑郁水平的调查与分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2012, 47(1):17-19. |
| Pan HY, Wang JQ, Zhou B, et al. A cross-sectional survey of depression in the elderly people with mild cognitive impairment[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2012, 47(1):17-19. | |
| [20] | 王征宇, 张明园, 瞿光亚, 等. 中文版简易智能状态检查(MMSE)的应用[J]. 上海精神医学, 1989, 7(3):108-111. |
| Wang ZY, Zhang MY, Qu GY, et al. Chinese version of Simple Intelligent Status Check(MMSE) application[J]. Shanghai Arch Psychiatr, 1989, 7(3):108-111. | |
| [21] | 宋岳涛. 老年综合评估[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国协和医科大学出版社, 2019:152-153. |
| Song YT. Comprehensive geriatric assessment[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press, 2019:152-153. | |
| [22] | Kopecek M, Bezdicek O, Sulc Z, et al. Montreal Cognitive Assessment and Mini-Mental State Examination reliable change indices in healthy older adults[J]. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry, 2017, 32(8):868-875. |
| [23] |
Krishnan K, Rossetti H, Hynan LS, et al. Changes in Montreal cognitive assessment scores over time[J]. Assessment, 2017, 24(6):772-777.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Wada M, Noda Y, Shinagawa S, et al. Effect of education on Alzheimer’s disease-related neuroimaging biomarkers in healthy controls,and participants with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease:a cross-sectional study[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2018, 63(2):861-869. |
| [25] | Xue HP, Hou P, Li YN, et al. Factors for predicting reversion from mild cognitive impairment to normal cognition:a meta-analysis[J]. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry, 2019, 34(10):1361-1368. |
| [26] | Cai XY, Qian GP, Wang F, et al. Association between sedentary behavior and risk of cognitive decline or mild cognitive impairment among the elderly:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Neurosci, 2023, 17:1221990. |
| [27] |
Bakrania K, Edwardson CL, Khunti K, et al. Associations between sedentary behaviors and cognitive function:cross-sectional and prospective findings from the UK biobank[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2018, 187(3):441-454.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Hughes TF, Flatt JD, Fu B, et al. Engagement in social activities and progression from mild to severe cognitive impairment:the MYHAT study[J]. Int Psychogeriatr, 2013, 25(4):587-595. |
| [29] | Wang HX, Karp A, Winblad B, et al. Late-life engagement in social and leisure activities is associated with a decreased risk of dementia:a longitudinal study from the Kungsholmen Project[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2002, 155(12):1081-1087. |
| [30] | Caetano I, Ferreira S, Coelho A, et al. Perceived stress modulates the activity between the amygdala and the cortex[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2022, 27(12):4939-4947. |
| [31] | McHugh Power J, Tang JJ, Lawlor B, et al. Mediators of the relationship between social activities and cognitive function among older Irish adults:results from the Irish longitudinal study on ageing[J]. Aging Ment Health, 2018, 22(1):129-134. |
| [32] | Zacková L, Jáni M, Brázdil M, et al. Cognitive impairment and depression:Meta-analysis of structural magnetic resonance imaging studies[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2021, 32:102830. |
| [33] | 李树亚, 李峥. 轻度认知障碍老年人精神行为症状及影响因素的调查研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(10):1192-1198. |
| Li SY, Li Z. Incidence and its influencing factors of psychological and behavioral symptoms among older adults with mild cognitive impairment[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(10):1192-1198. | |
| [34] | Ju YE, McLeland JS, Toedebusch CD, et al. Sleep quality and preclinical Alzheimer disease[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2013, 70(5):587-593. |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||