


中华护理杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (23): 2873-2879.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.23.008
郑煜琳( ), 孔令玲, 张明名, 郭京, 刘雪敏, 王欣然(
), 孔令玲, 张明名, 郭京, 刘雪敏, 王欣然( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-27
出版日期:2023-12-10
发布日期:2023-12-12
通讯作者:
王欣然,E-mail:xwsicu2011@163.com作者简介:郑煜琳:女,硕士,护师,E-mail:496732457@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHENG Yulin( ), KONG Lingling, ZHANG Mingming, GUO Jing, LIU Xuemin, WANG Xinran(
), KONG Lingling, ZHANG Mingming, GUO Jing, LIU Xuemin, WANG Xinran( )
)
Received:2023-03-27
Online:2023-12-10
Published:2023-12-12
摘要:
目的 调查经腹腔镜胃底折叠术后患者的生活质量现状,并分析其影响因素。 方法 采用便利抽样法,选取2021年3月—2022年12月在北京市某三级甲等医院胃食管反流病外科诊疗中心住院治疗的223例患者为调查对象,利用一般资料调查表、健康状况问卷、匹兹堡睡眠质量指数、综合医院焦虑抑郁情绪测量表、领悟社会支持量表等进行调查。 结果 回收有效问卷207份,有效问卷回收率为92.8%。术后3个月时,患者的躯体方面生活质量、心理方面生活质量较术前相比均有明显提高(P<0.05),但低于我国健康人群常模水平(P<0.05)。多元线性回归分析显示,年龄、BMI、家庭人均月收入、焦虑、抑郁、术后并发症个数是患者躯体方面生活质量的影响因素(P<0.05),BMI、焦虑、抑郁是患者心理方面生活质量的影响因素(P<0.05)。 结论 经腹腔镜胃底折叠术后3个月时,患者的生活质量较术前有明显提升,但未恢复至正常水平。术后护理人员应重点关注老年、BMI<18.5、家庭人均月收入低、术后并发症多、焦虑、抑郁的患者,及早采取干预措施,促进患者早日回归社会。
郑煜琳, 孔令玲, 张明名, 郭京, 刘雪敏, 王欣然. 经腹腔镜胃底折叠术后患者生活质量现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(23): 2873-2879.
ZHENG Yulin, KONG Lingling, ZHANG Mingming, GUO Jing, LIU Xuemin, WANG Xinran. Quality of life of patients after laparoscopic fundoplication and influencing factors analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2023, 58(23): 2873-2879.
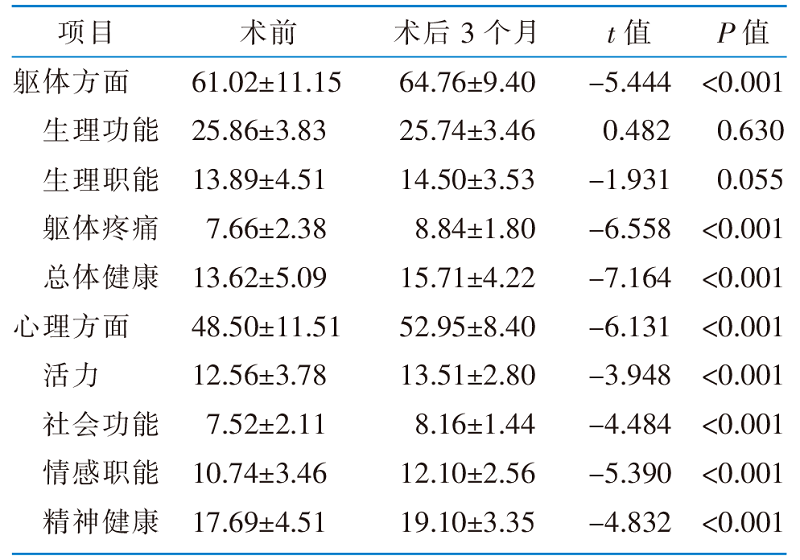 |
表1 经腹腔镜胃底折叠术患者术后3个月生活质量与术前比较(n=207,分,$\bar{x}±s$)
Table 1 Comparison of the quality of life of patients at 3 months after operation and before operation(n=207,score,$\bar{x}±s$)
 |
 |
表2 经腹腔镜胃底折叠术患者术后3个月生活质量子维度标准分与国内常模得分比较(分,$\bar{x}±s$)
Table 2 Comparison of standard score of quality of life and domestic norm score at 3 months after operation(score,$\bar{x}±s$)
 |
| [1] | 汪忠镐, 吴继敏, 胡志伟, 等. 中国胃食管反流病多学科诊疗共识[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2019, 11(9):30-56. |
| Wang ZG, Wu JM, Hu ZW, et al. Consensus on multidisci-plinary diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux di-sease in China[J]. Chin J Gastroesophagol Reflux Dis(electro-nic edition), 2019, 11(9):30-56. | |
| [2] |
周景海, 谭群友. 传统外科手术治疗胃食管反流病不容忽视[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2020, 58(9):672-676.
PMID |
|
Zhou JH, Tan QY. The role of the traditional surgical proce-dures for gastroesophageal reflux disease cannot be ignored[J]. Chin J Surg, 2020, 58(9):672-676.
DOI PMID |
|
| [3] |
Kobiela J, Kaska L, Pindel M, et al. Dynamics of quality of life improvement after floppy Nissen fundoplication for gastroeso-phageal reflux disease[J]. Videosurgery Miniinv, 2015, 10(3):389-397.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Statz AK, Stroud AM, Jolles SA, et al. Psychosocial factors are associated with quality of life after laparoscopic antireflux surgery[J]. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A, 2017, 27(8):755-760.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Holcomb CN, Switzer NJ, Jalilvand A, et al. Impact of psychia-tric disorders on patient satisfaction after Nissen fundoplication[J]. Surg Endosc, 2020, 34(4):1829-1834.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Kamolz T, Granderath FA, Bammer T, et al. Psychological inter-vention influences the outcome of laparoscopic antireflux surgery in patients with stress-related symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2001, 36(8):800-805.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 刘雅静, 刘娟. 瑞巴派特胶囊联合清胃抑反汤对腹腔镜Nissen胃底折叠术后吞咽困难、抗反酸效果及生活质量的影响[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2019, 28(36):4021-4025,4093. |
| Liu YJ, Liu J. Effects of rebamipide capsule combined with decoction of clearing stomach and inhibiting acid regurgitation on dysphagia,anti-acid regurgitation and quality of life after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication[J]. Mod J Inte Trad Chin Western Med, 2019, 28(36):4021-4025,4093. | |
| [8] | 孙燕, 郑明伟, 戴其利, 等. 腹腔镜Nissen胃底折叠术及术后健康管理在改善老年重度胃食管反流病患者生活质量中的作用[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2019, 34(10):895-897. |
| Sun Y, Zheng MW, Dai QL, et al. The role of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication and postoperative health management in improving the quality of life of elderly patients with severe gastroesophageal reflux disease[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2019, 34(10):895-897. | |
| [9] | 吴圣贤, 王成祥. 临床研究样本含量估算[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008:24. |
| Wu SX, Wang CX. Estimation of sample content in clinical research[M]. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2008:24. | |
| [10] | 官小莉, 汪晖. 胃食管反流病患者生存质量测评量表的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2015, 50(1):97-101. |
| Guan XL, Wang H. The measurement tools for the quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease:a review[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2015, 50(1):97-101. | |
| [11] |
Ware JJ, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey(SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection[J]. Med Care, 1992, 30(6):473-483.
PMID |
| [12] | 姜敏敏. SF-36 v2量表在中国人群的性能测试、常模制定及慢性病应用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2008. |
| Jiang MM. Study on performance test,norm formulation and chronic disease application of SF-36 V2 scale in Chinese population[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2008. | |
| [13] | 朱清, 裴小红, 黄重发, 等. SF-36量表在胃食管反流病患者生存质量评价中的应用[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2010, 9(3):188-190. |
| Zhu Q, Pei XH, Huang CF, et al. Application SF-36 scale to evaluate the quality of life in gastroesophageal reflux disease[J]. Chin J Diffic Compl Cas, 2010, 9(3):188-190. | |
| [14] |
Buysse DJ, Reynolds CR, Monk TH, et al. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index:a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research[J]. Psychiatry Res, 1989, 28(2):193-213.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 刘贤臣, 唐茂芹. 匹慈堡睡眠质量指数的信度和效度研究[J]. 中华精神科杂志, 1996, 28(2):103-107. |
| Liu XC, Tang MQ. Reliability and validity of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index[J]. Chin J Psychiatry, 1996, 28(2):103-107. | |
| [16] |
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale[J]. Acta Psychiatr Scand, 1983, 67(6):361-370.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 孙振晓, 刘化学, 焦林瑛, 等. 医院焦虑抑郁量表的信度及效度研究[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2017, 11(2):198-201. |
| Sun ZX, Liu HX, Jiao LY, et al. Reliability and validity of Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale[J]. Chin J Clinicians(electronic edition), 2017, 11(2):198-201. | |
| [18] |
Blumenthal JA, Burg MM, Barefoot J, et al. Social support,type A behavior,and coronary artery disease[J]. Psychosom Med, 1987, 49(4):331-340.
PMID |
| [19] | 姜乾金. 领悟社会支持量表(PSSS).心理卫生评定手册(增订)[M]. 北京: 中国心理卫生杂志社, 1999:131-133. |
| Jiang QJ. Perceived Social Support Scale(PSSS). Mental Health Assessment Manual(Updated)[M]. Beijing: Chin J Mental Health, 1999:131-133. | |
| [20] |
Koetje JH, Nieuwenhuijs VB, Irvine T, et al. Measuring outco-mes of laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery:quality of life versus symptom scores?[J]. World J Surg, 2016, 40(5):1137-1144.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | 史海霞, 王智凤, 孙晓红. 不同年龄组胃食管反流病患者食管动力及临床特点[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2021, 101(14):1015-1019. |
| Shi HX, Wang ZF, Sun XH. Characteristics of esophageal mo-tility and clinical presentation in gastroesophageal reflux di-sease patients of different age groups[J]. Natl Med J Chin, 2021, 101(14):1015-1019. | |
| [22] |
Ranson ME, Danielson A, Maxwell JG, et al. Prospective study of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in a community hospital and its effect on typical,atypical,and nonspecific gastrointes-tinal symptoms[J]. JSLS, 2007, 11(1):66.
PMID |
| [23] |
Gee DW, Andreoli MT, Rattner DW. Measuring the effective-ness of laparoscopic antireflux surgery:long-term results[J]. Arch Surg, 2008, 143(5):482-487.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Sanford Z, Jayaraman S, Weltz AS, et al. The role of body mass index in determining clinical and quality of life out-comes after laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery[J]. Surg Endosc, 2020, 34:646-657.
DOI |
| [25] |
Neumayer C, Ciovica R, Gadenst Tter M, et al. Significant weight loss after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication[J]. Surg Endosc, 2005, 19(1):15-20.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Park SK, Lee T, Yang HJ, et al. Weight loss and waist reduction is associated with improvement in gastroesophageal disease reflux symptoms:a longitudinal study of 15 295 subjects un-dergoing health checkups[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2017, 29(5):e13009.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
顾芳臣, 王美峰, 林征, 等. 腹式深呼吸训练在胃食管反流病患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2019, 54(4):501-505.
DOI URL |
|
Gu FC, Wang MF, Lin Z, et al. Effect of abdominal deep breathing exercises on gastrointestinal and psychological symptom clusters in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2019, 54(4):501-505.
DOI URL |
|
| [28] |
白铁娟, 秦璐, 董建秀, 等. 基于微信直播的正念训练对经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者阈下抑郁症状的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(11):1304-1309.
DOI URL |
|
Bai TJ, Qin L, Dong JX, et al. Effects of mindfulness training based on WeChat live broadcast on subthreshold depressive symptoms after PCI[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(11):1304-1309.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||