


中华护理杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (14): 1733-1741.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.14.010
收稿日期:2022-10-24
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-07-14
通讯作者:
康晓凤,E-mail:xfkangpumc@126.com作者简介:江莹:女,本科(硕士在读),护师,E-mail:jiangying_ncbi@163.com
JIANG Ying( ), YU Minhong, ZHANG Chunyan, KANG Xiaofeng(
), YU Minhong, ZHANG Chunyan, KANG Xiaofeng( )
)
Received:2022-10-24
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-07-14
摘要:
目的 调查肺动脉高压患者的主、客观经济负担现状,并探讨其与健康相关生活质量的相关性。方法 采取便利抽样法,选取2022年2月—9月在北京市某三级甲等医院就诊的肺动脉高压患者作为调查对象。使用一般资料调查表、慢性病治疗经济毒性功能评估综合评分(Comprehensive Score for Financial Toxicity Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy,COST)和肺动脉高压特异性健康相关生活质量量表等对患者进行调查,并分析其影响因素。结果 152例肺动脉高压患者中,123例(80.9%)存在经济负担,COST为(16.22±10.19)分;多元线性逐步回归结果显示,肺动脉收缩压、6 min步行距离、社会经济地位复合指数、灾难性医疗支出和经济相关服药不依从是肺动脉高压患者经济负担的影响因素,可解释总变异的42.9%。经济负担与健康相关生活质量存在相关性(P<0.05)。 结论 肺动脉高压患者主、客观经济负担普遍存在,经济负担大的患者健康相关生活质量受损严重,医护人员应重视并全面筛查患者的经济负担,防止患者在疾病管理阶段因病致贫,从而减轻经济负担对患者预后的不良影响。
江莹, 余旻虹, 张春燕, 康晓凤. 肺动脉高压患者经济负担影响因素分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(14): 1733-1741.
JIANG Ying, YU Minhong, ZHANG Chunyan, KANG Xiaofeng. Investigation and analysis of influencing factors related to financial burden among pulmonary artery hypertension patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2023, 58(14): 1733-1741.
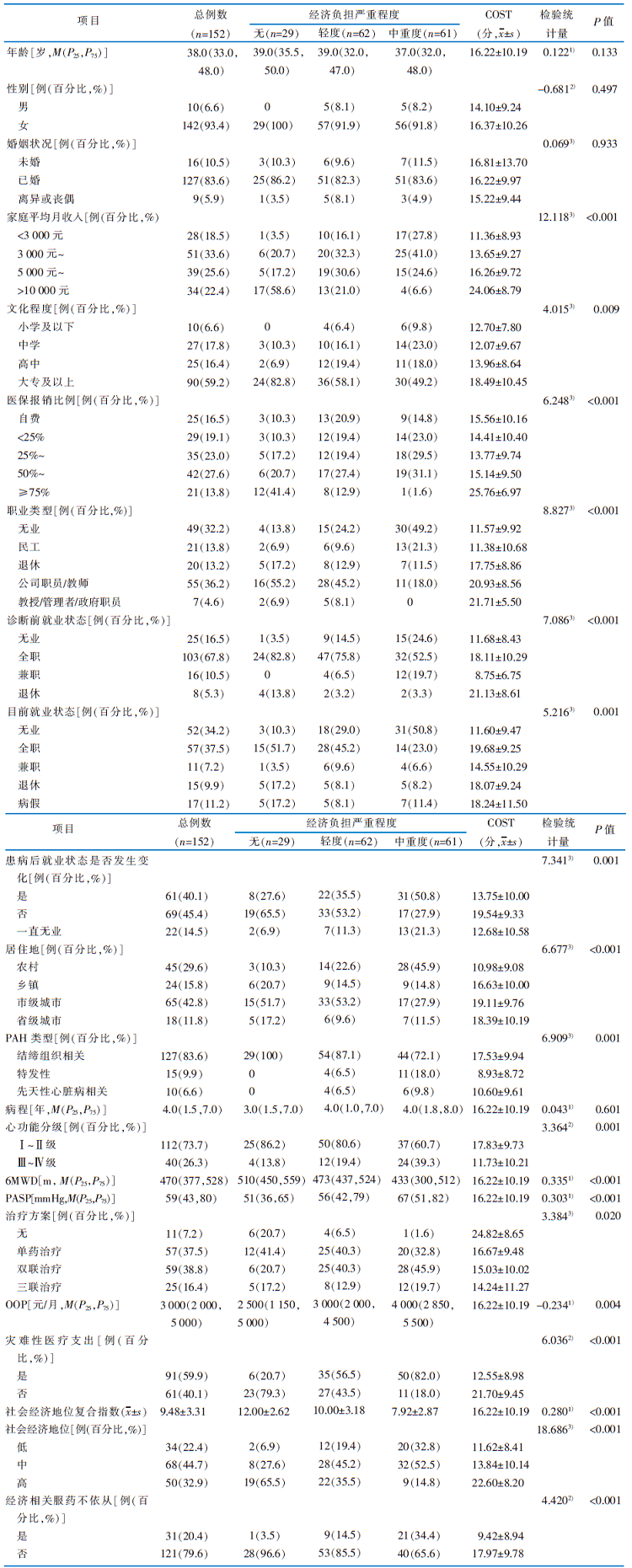 |
表1 调查对象的一般资料及经济负担的单因素分析(n=152)
Table 1 The general information of the subjects and the results of the univariate analysis on the influencing factors of financial burden(n=152)
 |
| [1] |
Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, et al. 2022 ESC/ERS gui-delines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension[J]. Eur Respir J, 2023, 61(1):2200879.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Omura J, Habbout K, Shimauchi T, et al. Identification of long noncoding RNA H19 as a new biomarker and therapeutic target in right ventricular failure in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Circulation, 2020, 142(15):1464-1484.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 中国新闻网. 《中国肺动脉高压患者生存现状白皮书》发布:揭示患者群体诊疗现状[EB/OL]. (2021-04-30)[2023-01-08]. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1698478040776411284&wfr=spider&for=pc. |
| China News. 《White Book on Pulmonary Artery Hypertension Patients》released:to reveal the status of diagnosis and treatment in patient groups[EB/OL].(2021-04-30)[2023-01-08]. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1698478040776411284&wfr=spider&for=pc. | |
| [4] |
Piette JD, Heisler M, Horne R, et al. A conceptually based approach to understanding chronically ill patients’ responses to medication cost pressures[J]. Soc Sci Med, 2006, 62(4):846-857.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | 吴文汇. 中国肺动脉高压患者社会经济地位与其疾病严重程度和生存的相关性研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2012. |
| Wu WH. Correlation between socio-economic status and disease severity and survival of patients with pulmonary hypertension in China[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2012. | |
| [6] | 中华医学会呼吸病学分会肺栓塞与肺血管病学组, 中国医师协会呼吸医师分会肺栓塞与肺血管病工作委员会, 全国肺栓塞与肺血管病防治协作组, 等. 中国肺动脉高压诊断与治疗指南(2021版)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2021, 101(1):11-51. |
| Pulmonary Embolism and Pulmonary Vascular Disease Group of Respiratory Medicine Branch of Chinese Medical Association,Pulmonary Embolism and Pulmonary Vascular Disease Working Committee of Respiratory Physician Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, National Cooperative Group for Prevention and Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism and Pulmonary Vascular Disease, et al. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension in China(2021 edition)[J]. Natl Med J China, 2021, 101(1):11-51. | |
| [7] | 姚静静, 王海鹏, 孙强. 山东省2型糖尿病患者自付医疗费用和疾病经济风险现状分析[J]. 中国卫生政策研究, 2019, 12(7):75-80. |
| Yao JJ, Wang HP, Sun Q. Analysis of the status of self-paid medical expenses and disease economic risks among T2MD patients in Shandong province[J]. Chin J Health Policy, 2019, 12(7):75-80. | |
| [8] |
Rijal A, Adhikari TB, Khan JAM, et al. The economic impact of non-communicable diseases among households in South Asia and their coping strategy:a systematic review[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(11):e0205745.
DOI URL |
| [9] | WHO. Designing health financing systems to reduce catastro-phic health expenditure[EB/OL].[2023-01-08]. https://www.who.int/health_financing/documents/pb_e_05_2-cata_sys.pdf. |
| [10] |
Piette JD, Heisler M, Wagner TH. Cost-related medication underuse among chronically ill adults:the treatments people forgo,how often,and who is at risk[J]. Am J Public Health, 2004, 94(10):1782-1787.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Pierre-Jacques M, Safran DG, Zhang F, et al. Reliability of new measures of cost-related medication nonadherence[J]. Med Care, 2008, 46(4):444-448.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
de Souza JA, Yap BJ, Hlubocky FJ, et al. The development of a financial toxicity patient-reported outcome in cancer:the COST measure[J]. Cancer, 2014, 120(20):3245-3253.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
于慧会, 毕雪, 刘运泳. 中文版癌症患者报告结局的经济毒性量表信度和效度研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(8):1118-1120.
PMID |
|
Yu HH, Bi X, Liu YY. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version on Comprehensive Scores for Financial Toxicity based on the patient-reported outcome measures[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(8):1118-1120.
DOI PMID |
|
| [14] |
Yorke J, Corris P, Gaine S, et al. EmPHasis-10:development of a health-related quality of life measure in pulmonary hypertension[J]. Eur Respir J, 2014, 43(4):1106-1113.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 陈月香, 孙国珍. 中文版肺高压疾病特异性量表的心理测量学特征评价[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2017, 32(5):396-399. |
| Chen YX, Sun GZ. Evaluation of psychometric characteristics of Chinese Version Scale for Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension[J]. J Nurses Train, 2017, 32(5):396-399. | |
| [16] |
Shi Y, Dong XB, Hu XY, et al. Cross-cultural validation of the Chinese version of the EmPHasis-10 questionnaire in connective tissue disease patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension and its relationship with risk stratification[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2022, 22(1):264.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | 袁潇逸, 孙艳玲, 况艺, 等. 乳腺癌生存者经济毒性现状与影响因素分析[J]. 中国护理管理, 2022, 22(6):830-835. |
| Yuan XY, Sun YL, Kuang Y, et al. Status and influencing factors of cancer-related financial toxicity of breast cancer survivors[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2022, 22(6):830-835. | |
| [18] |
袁方, 林梦月, 刘永珍, 等. 前列腺癌患者经济负担现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(8):918-925.
DOI URL |
|
Yuan F, Lin MY, Liu YZ, et al. The analysis of the financial toxicity and its influencing factors in prostate cancer patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(8):918-925.
DOI URL |
|
| [19] |
Zhai ZG, Zhou X, Zhang S, et al. The impact and financial burden of pulmonary arterial hypertension on patients and caregivers:results from a national survey[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2017, 96(39):e6783.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Housten-Harris T. The nurse specialist and practical issues in the care of pulmonary arterial hypertension patients[J]. Int J Clin Pract Suppl, 2007(158):10-18. |
| [21] | 阮君怡, 刘城, 况艺, 等. 年轻女性乳腺癌生存者经济毒性应对策略的质性研究[J]. 军事护理, 2022, 39(8):29-33. |
| Ruan JY, Liu C, Kuang Y, et al. Coping strategies for financial toxicity in young female breast cancer survivors:a qualitative study[J]. Mil Nurs, 2022, 39(8):29-33. | |
| [22] |
Carrera PM, Kantarjian HM, Blinder VS. The financial burden and distress of patients with cancer:understanding and stepping-up action on the financial toxicity of cancer treatment[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(2):153-165.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Chan RJ, Gordon LG, Tan CJ, et al. Relationships between financial toxicity and symptom burden in cancer survivors:a systematic review[J]. J Pain Symptom Manage, 2019, 57(3):646-660.e1.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Zafar SY, Peppercorn JM, Schrag D, et al. The financial toxicity of cancer treatment:a pilot study assessing out-of-pocket expenses and the insured cancer patient’s experience[J]. Oncologist, 2013, 18(4):381-390.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Bouberhan S, Shea M, Kennedy A, et al. Financial toxicity in gynecologic oncology[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2019, 154(1):8-12.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Ting CY, Teh GC, Yu KL, et al. Financial toxicity and its associations with health-related quality of life among urologic cancer patients in an upper middle-income country[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2020, 28(4):1703-1715.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | 焦延超, 刘化侠, 石红伟, 等. 癌症患者自我感受负担相关因素的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2012, 47(5):473-475. |
| Jiao YC, Liu HX, Shi HW, et al. The related factors of self-perceived burden in cancer patients:a literature review[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2012, 47(5):473-475. |
| [1] | 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 梁江淑渊, 王衍蝶, 蔡凌云. 儿童双肺移植术后肺康复护理方案的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1029-1035. |
| [2] | 阎寅至, 闻芳, 王敏, 周雪梅, 马金玲, 吴惠芳, 姚文英. 造血干细胞移植患儿运动康复分级护理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1036-1042. |
| [3] | 刘曦璇, 刘玉琳, 刘莎, 杨帆, 谢晓虹, 王紫娟, 刘丽芳, 魏红雨. 学龄期支气管哮喘患儿呼吸康复操的研制及效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 黄盼盼, 李丽玲, 胡晓静. 先天性心脏病婴儿早期运动康复的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | 陈丽鸥, 张文婷, 刘俊其, 王允琮, 王振霖, 齐赛, 杨娜. 肺叶体表投影定位结合肺段引流排痰技术对吸入性肺炎患者气道廓清的效果研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1056-1061. |
| [6] | 杨娜娜, 程传丽, 曾慧, 符丹丹, 王燕, 陈悦, 冉宏敏, 范红静, 龙霞. 分级运动康复对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的效果评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1062-1067. |
| [7] | 曹云, 孙国珍, 陈凤, 季学丽, 闫梦婉, 敬雷, 钱堃. 改良式踝泵运动在脑卒中患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1068-1074. |
| [8] | 谢敏, 漆文凯, 殷玲, 张旋, 赵如琴. 腹膜透析患者恐动症潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1080-1086. |
| [9] | 陈冰倩, 赵彬, 孙佳蓉, 郝四芳, 侯晓丽. 慢性牙周炎种植义齿患者口腔健康管理困境的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1087-1092. |
| [10] | 秦春兰, 吴振云, 钱红英, 赵茜, 孙锦庭. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疾病自我控制体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1093-1098. |
| [11] | 李子崴, 冯丽娟, 陈旭升, 黄毅, 杨洁. PICC置管患者运动恐惧评估量表的编制及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1099-1106. |
| [12] | 程志强, 张宝珍, 汤利萍, 李静, 夏娇云, 魏雪岩, 龚智娴, 张美珍, 黎露思. 尿失禁患者疾病认知与态度量表的汉化及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | 杨静, 王华芬, 卢芳燕, 鲍瑞洁, 朱莉. 肝移植患儿术后营养状况变化的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | 石美琴, 吴建芳, 张铎, 吴春萍, 陈玲, 陶磊. 1例全喉切除辅助发音管Ⅰ期植入患者术后喉功能康复的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1120-1123. |
| [15] | 谷茜, 黄玺, 施伟雄, 吴静, 谭若铭, 王枫. 1例T细胞免疫治疗后并发细胞因子释放综合征患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2025, 60(9): 1124-1127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||