


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (3): 292-299.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.03.007
收稿日期:2023-07-03
出版日期:2024-02-10
发布日期:2024-02-02
通讯作者:
周雁荣,E-mail:1002406585@qq.com作者简介:吴前胜:男,硕士,副主任护师,护士长,E-mail:419059248@qq.com
基金资助:
WU Qiansheng( ), ZENG Ying, WANG Lan, WANG Xiaoxiao, ZHOU Yanrong(
), ZENG Ying, WANG Lan, WANG Xiaoxiao, ZHOU Yanrong( )
)
Received:2023-07-03
Online:2024-02-10
Published:2024-02-02
摘要:
目的 将体外循环下心脏手术患者术后谵妄管理的最佳证据应用于临床,评价应用效果。方法 筛选体外循环下心脏手术患者术后谵妄管理的最佳证据。以证据为基础制订实践方案,进行基线审查、分析障碍因素,于2022年5月—2023年4月在武汉市某三级甲等综合医院心脏大血管外科开展循证实践。比较证据应用前后护士对术后谵妄管理的知信行水平、术后谵妄与亚谵妄发生情况和审查指标执行率。结果 共纳入27篇文献,遴选23条适合临床的最佳证据,构建27条审查指标。通过循证实践,护士对术后谵妄管理的知信行得分由(100.81±13.92)分提高至(105.51±10.35)分,知识、态度、行为各维度得分均提高(P<0.05);24个审查指标的执行率高于基线审查水平(P<0.05);术后谵妄发生率由43.5%降至34.7%,差异无统计学意义(P=0.120);术后亚谵妄发生率由55.1%降至40.1%(P=0.010),术后谵妄和亚谵妄持续时间均下降,差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 构建的循证实践方案可以降低亚谵妄的发生率,减少术后谵妄及亚谵妄的持续时间,并能够提高护士对术后谵妄管理的知信行水平。
吴前胜, 曾莹, 王兰, 王萧萧, 周雁荣. 体外循环下心脏手术患者术后谵妄管理的循证实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 292-299.
WU Qiansheng, ZENG Ying, WANG Lan, WANG Xiaoxiao, ZHOU Yanrong. Evidence-based nursing practice of postoperative delirium management during cardiac surgery under cardiopulmonary bypass[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(3): 292-299.
 |
表1 体外循环下心脏手术患者术后谵妄管理的证据内容、审查指标及审查方法
Table 1 Evidence contents,review criteria,and review methods for management of postoperative delirium after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass
 |
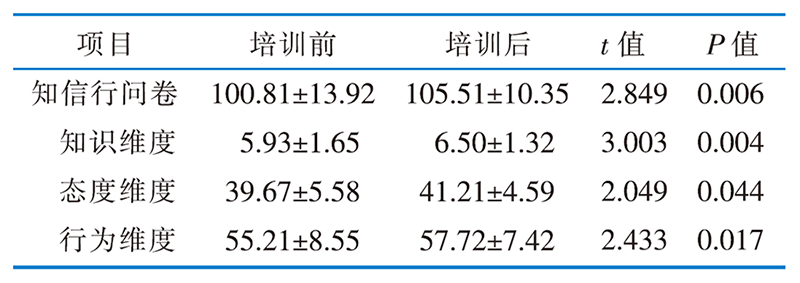 |
表3 培训前后护士对术后谵妄管理知信行问卷得分的比较 (分,$ \bar{x} \pm s$)
Table 3 Comparison of nurses’ postoperative delirium nursing KAP scores before and after training(分,$ \bar{x} \pm s$)
 |
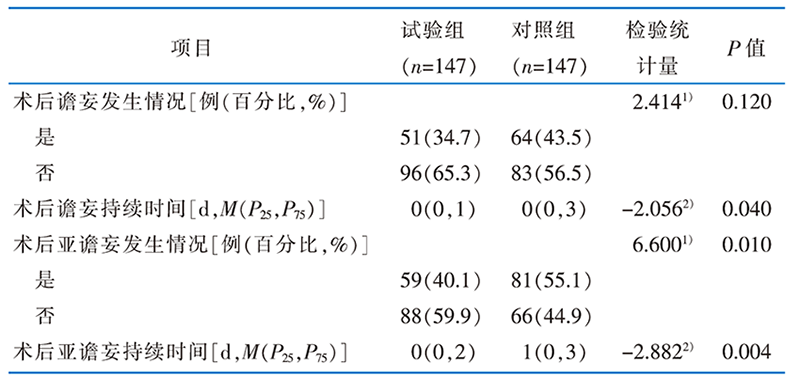 |
表4 基于倾向性评分匹配的循证实践前后术后谵妄和亚谵妄发生情况
Table 4 Incidence of postoperative delirium and subdelirium syndrome before and after implementation based on propensity score matching
 |
| [19] | Perry TE, Grant MC. Anesthetic management for enhanced reco-very after cardiac surgery(ERACS)[EB/OL].(2020-11-30)[2022-07-04]. https://www.Uptodate.Cn/Contents/Anesthetic-Manage-ment-For-Enhanced-Recovery-After-Cardiac-Surgery-Eracs?Search=Anesthetic%20management%20for%20enhanced%20recovery%20after%20cardiac%20surgery%20(Eracs)&Source=Search_Result&Selectedtitle=1-150&Usage_Type=Default&Display_Rank=1. |
| [20] | Francis J. Delirium and acute confusional states:prevention,treatment,and prognosis[EB/OL].(2019-05-22)[2022-07-04]. https://www.Uptodate.Cn/Contents/Delirium-And-Acute-Confusio-nal-States-Prevention-Treatment-And-Prognosis?Search=%E8%B0%B5%E5%A6%84&Source=Out%20of%20date%20-%20zh-Hans&Selectedtitle=2-150. |
| [21] | Healthcare Improvement Scotland. Delirium:a booklet for people who have experienced delirium,and for their carers[EB/OL].[2023-10-19]. https://www.Sign.Ac.Uk/Assets/Pat157.Pdf. |
| [22] | Devlin JW, Skrobik Y, Gélinas C, et al. Clinical practice gui-delines for the prevention and management of pain,agitation/sedation,delirium,immobility,and sleep disruption in adult patients in the ICU[J]. Crit Care Med, 2018, 46(9):e825-e873. |
| [23] | Healthcare Improvement Scotland. Risk reduction and mana-gement of delirium:a national clinical guideline[EB/OL].[2023-10-19]. https://www.sign.ac.uk/media/1423/sign157.pdf. |
| [24] | Bush SH, Lawlor PG, Ryan K, et al. Delirium in adult cancer patients:ESMO clinical practice guidelines[J]. Ann Oncol, 2018, 29:iv143-iv165. |
| [25] | 汤铂, 王小亭, 陈文劲, 等. 重症患者谵妄管理专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2019, 58(2):108-118. |
| Tang B, Wang XT, Chen WJ, et al. Experts consensus on the management of delirium in critically ill patients[J]. Chin J Internal Med, 2019, 58(2):108-118. | |
| [26] | 中华医学会神经病学分会神经心理与行为神经病学学组. 综合医院谵妄诊治中国专家共识(2021)[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2021, 10:1226-1233. |
| Neuropsychology and Behavioral Medical Section of Neurology Credit Association of Chinese Medical Association. Chinese experts consensus on diagnosis and treatment of delirium in general hospital(2021)[J]. Chin J Geriat, 2021, 10:1226-1233. | |
| [1] |
Aldecoa C, Bettelli G, Bilotta F, et al. European society of anaesthesiology evidence-based and consensus-based guideline on postoperative delirium[J]. Eur J Anaesthesiol, 2017, 34(4):192-214.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
高燕, 甘秀妮, 杨睿琦, 等. 亚谵妄综合征的概念内涵及研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(12):1883-1888.
DOI |
| Gao Y, Gan XN, Yang RQ, et al. Con-ceptual connotation and research pro-gress of subsyndromal delirium[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(12):1883-1888. | |
| [3] | 王华英, 由春梅, 谢涛, 等. 术后谵妄患者的临床特点及危险因素[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2019, 39(22):5538-5540. |
| Wang HY, You CM, Xie T, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of postoperative delirium[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2019, 39(22):5538-5540. | |
| [4] |
李真, 李奇, 李尊柱, 等. ICU患者亚谵妄综合征患病率及危险因素的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(2):288-293.
DOI |
| Li Z, Li Q, Li ZZ, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of subsyn-dromal delirium among adult intensive care unit patients:a systematic review[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(2):288-293. | |
| [5] |
Engelman DT, Ben Ali W, Williams JB, et al. Guidelines for perioperative care in cardiac surgery:enhanced recovery after surgery society recommendations[J]. JAMA Surg, 2019, 154(8):755-766.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Hughes CG, Boncyk CS, Culley DJ, et al. American society for enhanced recovery and perioperative quality initiative joint consensus statement on postoperative delirium prevention[J]. Anesth Analg, 2020, 130(6):1572-1590.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | 韩劲松, 张爽, 马超, 等. 成人心脏外科术后脑损伤诊治的中国专家共识[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(32):5203-5212. |
| Han JS, Zhang S, Ma C, et al. Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of postoperative brain injury in adult cardiac surgery[J]. Chin J Tissue Eng Res, 2020, 24(32):5203-5212. | |
| [8] | 戴航令. 认知功能训练在预防心外科ICU患者谵妄的应用研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2021. |
| Dai HL. Study on the application of cognitive function training in preventing delirium in ICU patients of cardiac surgery[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2021. | |
| [9] | Marin, Tania, Overall, Bronwyn. Delirium:prevention and manage-ment in postoperative care[EB/OL].[2023-10-19]. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=jbi&NEWS=N&AN=JBI3727. |
| [10] | Pamaiahgari, Priyanka. Delirium:screening and assessment in critical care[EB/OL].[2023-10-19]. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovi-dweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=jbi&NEWS=N&AN=JBI5419. |
| [11] | Bayuo, Jonathan. Delirium:screening and assessment in acute care[EB/OL].[2023-10-19]. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=jbi&NEWS=N&AN=JBI21433. |
| [12] | Pamaiahgari, Priyanka. Delirium:prevention and management in acute care[EB/OL].[2023-10-19]. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovid-web.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=jbi&NEWS=N&AN=JBI-14502 |
| [13] | Bayuo, Jonathan. Delirium:occupational therapy[EB/OL].[2023-10-19]. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=referen-ce&D=jbi&NEWS=N&AN=JBI1756. |
| [14] | Postoperative delirium(geriatrics):surgical strategies[EB/OL]. [2023-10-19]. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=jbi&NEWS=N&AN=JBI3728. |
| [15] | Pamaiahgari, Priyanka. Delirium:pharmacological management[EB/OL].[2023-10-19]. http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=jbi&NEWS=N&AN=JBI14501. |
| [16] | Mahanna-Gabrielli E, Eckenhoff RG. Perioperative neurocog-nitive disorders in adults:risk factors and mitigation strate-gies[EB/OL].(2022-01-26)[2022-07-04]. https://www.Uptodate.Cn/Contents/Perioperative-Neurocognitive-Disorders-In-Adults-Ri-sk-Factors-And-Mitigation-Strategies?Search=Perioperative%20ne-urocognitive%20disorders%20in%20adults%Ef%Bc%9arisk%20factors%20and%20mitigation%20stra. |
| [17] | Cheung AT, Stafford-Smith M, Heath M. Management of cardio-pulmonary bypass[EB/OL].(2021-10-15)[2022-07-04]. https://www.Uptodate.Cn/Contents/Management-Of-Cardiopulmonary-By-pass?Search=%E4%Bd%93%E5%A4%96%E5%Be%Aa%E7%8e%Af%E6%9c%Af%E5%90%8e%E8%B0%B5%E5%A6%84&Source=Out%20of%20date%20-%20zh-Hans&Selectedtitle=1-150. |
| [18] | Barbeito A, Johnbull EA. Anesthesia for cardiac surgery:gene-ral principles[EB/OL].(2021-06-10)[2022-07-04]. https://www.Uptodate.Cn/Contents/Anesthesia-For-Cardiac-Surgery-General-Principles?Search=Anesthesia%20for%20cardiac%20surgery:%20general%20principles&Source=Search_Result&Selectedtitle=1-150&Usage_Type=Default&Display_Rank=1. |
| [27] | 万小健, 王东信, 方向明, 等. 成人术后谵妄防治的专家共识(2020版)[EB/OL].(2021-08-13)[2023-10-19]. https://www.cn-healthcare.com/articlewm/20210812/content-1252408.html. |
| Wan XJ, Wang DX, Fang XM, et al. Expert consensus on the prevention and treatment of postoperative delirium in adults (2020 Edition)[EB/OL].(2021-08-13)[2023-10-19]. https://www.cn-healthcare.com/articlewm/20210812/content-1252408.html. | |
| [28] | Hall Kk, Shoemaker Hs, Hoffman L, et al. Making healthcare safer iii:a critical analysis of existing and emerging patient safety practices[M]. Rockville(Md):Agency For Healthcare Research And Quality (Us),2020. |
| [29] |
Chen TJ, Traynor V, Wang AY, et al. Comparative effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions for preventing delirium in critically ill adults:a systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Int J Nurs Stud, 2022, 131:104239.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Haley MN, Casey P, Kane RY, et al. Delirium management:let’s get physical?A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Austra las J Ageing, 2019, 38(4):231-241. |
| [31] |
Ezinne O,Igwe,PhD, et al. Multi-disciplinary and pharmacologi -cal interventions to reduce post-operative delirium in elderly patients:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Anesth, 2020, 67:110004.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | 张爱琴, 陈俊杉, 余金甜. ICU患者谵妄非药物管理相关指南的系统评价[J]. 护理学报, 2020, 27(11):26-32. |
| Zhang AQ, Chen JS, Yu JT. Guidelines on non-pharmacologi-cal management of delirium in ICU patients:a systematic review[J]. J Nurs, 2020, 27(11):26-32. | |
| [33] | 胡雁, 郝玉芳. 循证护理学[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017:31. |
| Hu Y, Hao YF. Evidence based nursing[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: People’s Health Publishing House, 2017:31. | |
| [34] | Zhou C, Qu X, Wang L, et al. Knowledge,attitude,and practice regarding postoperative delirium among cardiac surgery nurses:a cross-sectional multi-centre study[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2023. |
| [35] |
Gaudreau JD, Gagnon P, Harel F, et al. Fast,systematic,and continuous delirium assessment in hospitalized patients:the nursing delirium screening scale[J]. J Pain Symptom Manage, 2005, 29(4):368-375.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Chen HY, Mo L, Hu HJ, et al. Risk factors of postoperative delirium after cardiac surgery:a meta-analysis[J]. J Cardiotho-rac Surg, 2021, 16(1):113. |
| [37] |
吴明珑, 周雁荣, 詹雪, 等. 颈椎手术患者气道梗阻预防及管理的最佳证据应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(2):133-140.
DOI |
|
Wu ML, Zhou YR, Zhan X, et al. Evidence-based nursing practice of airway obstruction prevention and management in patients undergoing cervical spinal surgery[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(2):133-140.
DOI |
|
| [38] |
李加敏, 庞冬, 路潜, 等. 尿路造口周围刺激性皮炎患者的循证护理实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(11):1624-1629.
DOI |
|
Li JM, Pang D, Lu Q, et al. Evidence-based nursing practice of peristomal irritant dermatitis in patients with urostomies[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(11):1624-1629.
DOI |
| [1] | 张若萱, 赵健, 牟利宁. 钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制剂导致酮症酸中毒的Meta分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 353-361. |
| [2] | 冯琦凡, 涂发妹, 吴季敏, 刘萍萍, 刘佳晨, 张思易, 张鑫. 烧伤患者身体意象体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 362-370. |
| [3] | 朱东阁, 王菊子, 赵倩, 何亚鹏, 张转转, 杨雨桐. 维持性血液透析患者透析中低血压风险预测模型的系统评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(2): 174-183. |
| [4] | 季谋芳, 李若冰, 胡廷进, 陈静怡. 不同非药物干预方式对产后抑郁症患者影响的网状Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(2): 228-235. |
| [5] | 台瑞, 方芳, 杨富, 余倩. 择期胃肠道手术患者预康复的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(2): 236-243. |
| [6] | 尹佳宁, 管晓敏, 贾登帅, 徐玲, 陈兰. ICU机械通气患者撤机后呼吸肌训练的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(1): 33-41. |
| [7] | 韩娜菲, 冯华丽, 贺红, 李茜, 徐剑锋, 金尧娟, 沈孟雅, 孙佳烨, 黄天海. 肺癌合并慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者术后肺康复管理的证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(1): 42-49. |
| [8] | 许志玮, 王娴, 穆文方, 王燕, 王安子. 下肢静脉溃疡患者体力活动的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(1): 100-107. |
| [9] | 常可意, 吴杨峰, 单锶楷, 韩舒羽, 全晓丽, 韩佳凝, 吴冬霞, 张莉莉. HIV感染者/AIDS患者参与同伴支持体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(1): 108-116. |
| [10] | 雒晓燕, 崔仁善, 许秀梅, 崔苗苗, 郭玲茹, 周丹. 基于“互联网+”的护理干预对癌症患者疼痛影响的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(9): 1056-1062. |
| [11] | 张琦, 陈丽艳, 李媛媛, 张爱华, 杨丽娟. 非创伤性下肢截肢患者生活体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(9): 1112-1119. |
| [12] | 王利秀, 李建芳, 程红霞, 罗彦, 杨冰香, 刘茜. 造血干细胞移植并发移植物抗宿主病患者皮肤护理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(9): 1120-1126. |
| [13] | 张若林, 楼妍, 吴婉英, 王春兰, 傅丽英, 周瑶, 洪美容, 徐毓露, 冯欣悦. 癌症患者照顾者角色过渡体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(9): 1127-1134. |
| [14] | 董永泽, 许秀君, 沈华娟, 周美玲, 贾艳清. 维持性血液透析患者动静脉血管通路穿刺管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(9): 1135-1141. |
| [15] | 赵宝生, 李振香, 马超群, 王艳艳, 范桂敏, 李涵, 郑晓丽. 青少年自杀未遂患者心理体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(8): 979-985. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||