


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (10): 1212-1217.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.10.009
收稿日期:2023-05-11
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-05-11
通讯作者:
许磊波,E-mail:xuleibo3@mial.sysu.edu.cn作者简介:周惠玲:女,本科,主管护师,护士长,E-mail:zhouhling3@mial.sysu.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHOU Huiling( ), YANG Zhiyu, YAN Jingwen, XU Leibo(
), YANG Zhiyu, YAN Jingwen, XU Leibo( )
)
Received:2023-05-11
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-05-11
摘要:
目的 调查肝移植患者的体力活动状况,探讨相关影响因素,为制订针对性的体力活动管理方案提供依据。方法 采用方便抽样法,2023年1月—5月采用一般情况调查表、国际体力活动问卷、坦帕运动恐惧量表、器官移植患者症状和幸福感量表对广州市某三级甲等医院肝移植科住院的250例肝移植患者进行调查,采用有序多分类Logistic回归分析肝移植患者体力活动的相关影响因素。结果 回收有效问卷240份,肝移植患者的体力活动总代谢当量为2 433(506,30 263) MET-min/周;Logistic回归分析显示,BMI、移植时间、术后随访频次、运动恐惧及生活质量是肝移植患者体力活动的主要影响因素(P<0.05)。结论 肝移植患者体力活动强度较低,以步行等轻活动强度为主。医护人员需注重对肝移植患者体力活动的管理,尤其是对于肥胖、生活质量较低的患者,应加强术后随访,改善患者的运动恐惧,以促进患者早期规律开展活动锻炼。
周惠玲, 杨志玉, 严靖雯, 许磊波. 肝移植患者体力活动现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(10): 1212-1217.
ZHOU Huiling, YANG Zhiyu, YAN Jingwen, XU Leibo. Status and influencing factors of physical activity among liver transplant patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(10): 1212-1217.
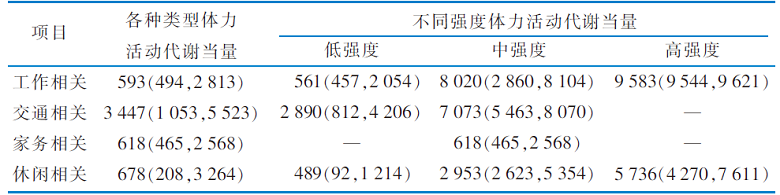 |
表3 肝移植患者的各种类型体力活动总代谢当量[MET-min/周,M(P25,P75)]
Table 3 Total metabolic equivalent of physical activity and characteristics of liver transplant patients[MET-min/weekly,M(P25,P75)]
 |
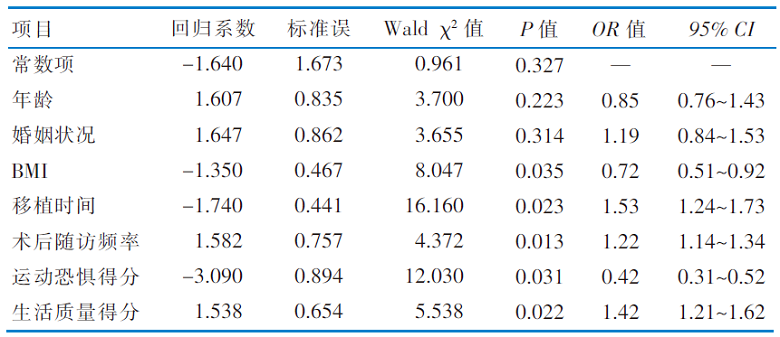 |
表5 肝移植患者体力活动影响因素的有序多分类Logistic回归分析结果(n=240)
Table 5 Ordinal logistic regression analysis results of factors affecting physical activity in liver transplant patients(n=240)
 |
| [1] | Guo HJ, Wang K, Chen KC, et al. Middle hepatic vein recons-truction in adult right lobe living donor liver transplantation improves recipient survival[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2019, 18:125-131. |
| [2] | Dunn MA, Rogal SS, Duarte-Rojo A, et al. Physical function,physical activity,and quality of life after liver transplantation[J]. Liver Transpl, 2020, 26(5):702-708. |
| [3] | Tanaka S, Fujita K, Kanaoka M, et al. Prospective study of objective physical activity and quality of life in living donor liver transplant recipients[J]. Jpn J Nurs Sci, 2020, 17(4):e12362. |
| [4] | 俞静娴, 张玉侠, 陈潇, 等. 肝移植术后患者不同时期运动方案的构建[J]. 中国护理管理, 2021, 21(8):1147-1152. |
| Yu JX, Zhang YX, Chen X, et al. The development of exercise programs for liver transplantation recipients in different periods after operation[J]. Chin Nurs Man, 2021, 21(8):1147-1152. | |
| [5] |
郭利敏, 孟萌, 关玉珠, 等. 肝移植受者衰弱的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(8):1265-1270.
DOI |
| Guo LM, Meng M, Guan YZ, et al. Research progress on frailty in liver transplant recipients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(8):1265-1270. | |
| [6] | Williams FR, Berzigotti A, Lord JM, et al. Review article:impact of exercise on physical frailty in patients with chronic liver disease[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 50(9):988-1000. |
| [7] | 陈红, 余婷, 吴慧青, 等. 肾移植受者体力活动现状及影响因素研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2020, 35(15):39-42. |
| Chen H, Yu T, Wu HQ, et al. Physical activity and its influen-cing factors among kindney transplantation recipients[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2020, 35(15):39-42. | |
| [8] | 屈宁宁, 李可基. 国际体力活动问卷中文版的信度和效度研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2004, 25(3):87-90. |
| Qu NN, Li KJ. Study on the reliability and validity of Inter-national Physical Activity Questionnaire[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2004, 25(3):87-90. | |
| [9] | Miller RP, Kori SH, Todd DD. The Tampa Scale[J]. Clin J Pain, 1991, 7(1):51. |
| [10] | 胡阅. 肾移植受者运动锻炼的现状及影响因素研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2019. |
| Hu Y. A study on the current status and factors influencing exercise in renal transplant recipients[D]. Beijing: Beijing Uni-versity of Chinese Medicine, 2019. | |
| [11] |
Forsberg A, Persson LO, Nilsson M, et al. The organ transplant symptom and well-being instrument-psychometric evaluation[J]. Open Nurs J, 2012, 6:30-40.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | 石英. 器官移植患者症状和幸福感量表汉化及应用[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2022. |
| Shi Y. Chinese translation and application of Organ Trans-plant Symptom and Well-being Instrument[D]. Shenyang: China Medical University, 2022. | |
| [13] | 罗富健, 曹杰, 董忠, 等. 2011年北京市成年居民身体活动与经常锻炼现状调查[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2018, 33(1):73-78. |
| Luo FJ, Cao J, Dong Z, et al. 2011 Status survey for physical activity and regular exercise in adult residents of Beijing[J]. Chin Circul J,2018, 33(1):73-78. | |
| [14] | Farrugia MA, Le Garf S, Chierici A, et al. Therapeutic physical exercise programs in the context of NASH cirrhosis and liver transplantation:a systematic review[J]. Metabolites, 2023, 13(3):330. |
| [15] | 沃琪, 任咪, 张金彦, 等. 肥胖与肝病:肝移植的新时代[J]. 肝脏, 2019, 24(11):1227-1228. |
| Wo Q, Ren M, Zhang JY, et al. Obesity and liver disease:a new era of liver transplantation[J]. Liver, 2019, 24(11):1227-1228. | |
| [16] | Burra P, Becchetti C, Germani G. NAFLD and liver transplan-tation:disease burden,current management and future chal-lenges[J]. JHEP Rep, 2020, 2(6):100192. |
| [17] | Barnett A, Campbell KL, Mayr HL, et al. Liver transplant reci-pients’ experiences and perspectives of a telehealth-delivered lifestyle programme:a qualitative study[J]. J Telemed Telecare, 2021, 27(9):590-598. |
| [18] | Suarez M, Boque N, Del Bas JM, et al. Mediterranean diet and multi-ingredient-based interventions for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nutrients, 2017, 9(10):1052. |
| [19] |
Spillman LN, Melville-Claxton A, Gatiss GA, et al. Diet and physical activity after liver transplant:a qualitative study of barriers and facilitators to following advice[J]. J Hum Nutr Diet, 2021, 34(5):910-919.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Zhong L, Jin Y, Gu Y, et al. Clinically ill patients’ experiences of early mobilisation after liver transplantation:a qualitative study using Pender’s health promotion model[J]. Int J Rehabil Res, 2023, 46(1):92-97. |
| [21] |
孟盈彤, 诸葛炜, 郑清如, 等. 慢性心力衰竭患者体力活动体验的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(12):1789-1795.
DOI |
| Meng YT, Zhuge W, Zheng QR, et al. The experience of physical activities in chronic heart failure patients:a meta-synthesis of qualitative[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(12):1789-1795. | |
| [22] |
Wiltshire G, Clarke NJ, Phoenix C, et al. Organ transplant reci-pients’ experiences of physical activity:health,self-care,and transliminality[J]. Qual Health Res, 2021, 31(2):385-398.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Totti V, Tamè M, Burra P, et al. Physical condition,glycemia,liver function,and quality of life in liver transplant recipients after a 12-month supervised exercise program[J]. Transplant Proc, 2019, 51(9):2952-2957. |
| [24] |
Berzigotti A, Albillos A, Villanueva C, et al. Effects of an intensive lifestyle intervention program on portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis and obesity:the sport diet study[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65:1293-1305.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Brustia R, Monsel A, Skurzak S, et al. Guidelines for perio-perative care for liver transplantation:enhanced recovery after surgery(ERAS) recommendations[J]. Transplantation, 2022, 106(3):552-561. |
| [26] |
兰美娟, 曾妃, 梁江淑渊. 双肺移植患者肺康复方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(6):659-665.
DOI |
|
Lan MJ, Zeng F, Liang JSY. Construction and application of a pulmonary rehabilitation program in patients with double lung transplantation[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(6):659-665.
DOI |
|
| [27] | Moya-Nájera D, Moya-Herraiz á, Compte-Torrero L, et al. Com-bined resistance and endurance training at a moderate-to-high intensity improves physical condition and quality of life in liver transplant patients[J]. Liver Transpl, 2017, 23(10):1273-1281. |
| [1] | 韩冬芳, 田甜, 高畅, 张婧珺, 李小妹. 肺结核患者健康促进行为与健康心理控制源关系的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1029-1036. |
| [2] | 司茜茜, 王莹, 赵福云, 马晓骁, 刘均娥. A型主动脉夹层患者Ⅰ期心肺康复护理方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1037-1042. |
| [3] | 沈支佳, 陈新宇, 钱志杰, 殷丽梅. 反复低血糖患者血糖管理行为退化特征的混合研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1043-1050. |
| [4] | 王丽梅, 李露, 李玉霞, 喻鹏, 罗倩, 张翀旎. 糖尿病周围神经病理性疼痛患者运动恐惧现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1051-1056. |
| [5] | 丁慧敏, 戴莉敏, 蔡冬青, 杨群. 糖尿病前期患者自我管理潜在剖面分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1057-1064. |
| [6] | 刘海婷, 王咏梅, 郑贝贝, 蔡丽丽, 叶林斌, 吴佳芸, 宁丽, 李益民, 陈为霞. 冠心病合并糖尿病患者药物素养自评量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1065-1071. |
| [7] | 陈丽霞, 施慧, 朱德政, 曾莹. 成人低血糖恐惧评估工具的质量评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1072-1079. |
| [8] | 中国研究型医院学会过敏医学专业委员会, 中华医学会变态反应分会过敏性疾病护理学组(筹), 中华预防医学会过敏病预防与控制专业委员会, (执笔:王青 刘君 支凡 万文锦 田丰英 霍晓鹏 周文华 杨永仕 王田田 孙劲旅). 变应原特异性免疫治疗皮下注射护理的专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1080-1083. |
| [9] | 李琪, 苏晴晴, 张瑶瑶, 王田田, 吕静, 李亚可, 李海燕. 全膝关节置换患者关节遗忘变化轨迹及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1084-1090. |
| [10] | 刘娅, 刘晓晴, 杨雪凝, 王平, 刘学奎, 罗丹. 结肠镜检查患者肠道准备失败风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1091-1098. |
| [11] | 孙晓晴, 张爱霞, 朱珠, 樊雪梅, 梅士娟, 黄欣欣, 丛胜楠, 谢红燕. 分娩心理创伤评估量表的编制及信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1099-1105. |
| [12] | 谢玉生, 黄蓉蓉, 赵雪, 马蕾, 胡雁, 杨倩, 王乾沙, 明玥. 成人重度烧伤患者肠内肠外营养的证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1106-1113. |
| [13] | 李旭琴, 冯洁惠, 黄昉芳, 俞超, 梁诗雨, 王晓, 李旭芳, 朱含. 1例行机械循环辅助桥接心脏移植患者的术前护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1114-1117. |
| [14] | 贾晓静, 陈一竹, 许志英, 和霞, 耿超. 1例尿黑酸尿症双膝关节置换术后患者并发急性心肌梗死的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1118-1121. |
| [15] | 顾培培, 曾妃, 兰美娟, 梁江淑渊, 郭璐瑶, 蔡凌云, 朱岩, 郭鸽. 肺移植患者衰弱影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(9): 1122-1129. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||